The list of such pathologies includes health disorders associated with disorders occurring in the psyche. They can be triggered by social, biological or psychological factors. People who have difficulty coping with accepting the realities of real life are most often susceptible to illness. They are often unable to recover from failures that have occurred. There is some inadequacy in actions, behavior and thinking.
Psychological developmental disorders
These pathologies in ICD-10 are included in the heading F80-F89. The diseases included in it always begin in childhood, including infancy. Their development requires a delay in the development of the nervous system or its damage associated with pathological maturation. They are characterized by a constant course, there are no relapses.
The lesions affect motor functions, speech, and visual-spatial skills. In most cases, environmental factors in this pathology are important, but not decisive. At the same time, the etiology of the lesion is not precisely defined, due to which an exact determination of the causes of developmental disorders cannot be established at the moment. Today it is also common to include autistic disorders among such pathologies.
Classifications of mental disorders.
Table of contents
- 1 Principles of classifications.
- 2 International classification of mental and behavioral disorders in accordance with the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10)
Principles of classifications.
Classification of mental disorders is one of the most important and complex problems in psychiatry. There are three main principles for classifying mental disorders.
1.Syndromological principle.
The theoretical basis of the syndromological approach is the concept of “single psychosis”. The concept is based on the idea of the unified nature of various mental disorders. The difference in the clinical picture is explained by observing patients at different stages of the disease.
The establishment of the etiological factors of individual mental illnesses has called into question the concept of a single psychosis. However, since the second half of the twentieth century, the syndromic approach has again begun to be widely used in creating classifications. The renaissance of the syndromic approach is largely associated with the achievements of experimental and clinical psychopharmacology. When prescribing drug therapy, which at the present stage of development of psychiatry is still of a so-called “syndromic” nature, doctors focus not on the cause of mental disorders, but on the identified psychopathological symptoms and syndromes.
2. Nosological principle.
The classification of mental disorders based on the nosological principle became possible as a result of discoveries of the relationship between the cause, clinical manifestations, course and outcome of the disease.
The nosological principle consists in the division of diseases based on the common etiology
,
pathogenesis
and uniformity
of the clinical picture
.
According to etiological
In principle, mental illnesses are divided into
endogenous
,
exogenous
and
psychogenic
.
In the development of endogenous
Heredity plays a big role in diseases. Typically, an endogenous disease is indicated by the spontaneous nature of the onset of the disease and the course of the disease, which is little dependent on external conditions.
Exogenous
mental disorders include diseases caused by external factors - traumatic brain injuries, infections and intoxications
A special type of exogenous diseases - psychogenics
. The occurrence of psychogenic diseases is associated with emotional stress, family and social problems.
The traditional division of mental disorders into organic
and
functional
. The presence of distinct changes in the structure of the brain leads to the appearance of persistent negative symptoms - memory impairment and intellect.
3.
The pragmatic (statistical, eclectic) principle
acquires particular importance in connection with the creation of national and international organizations regulating economic, social and legal issues of psychiatric care.
Planning medical and social measures is impossible without reliable data on the prevalence of mental disorders. The resolution of legal issues depends on the accuracy and reliability of the diagnosis. In Russia, the international classification of mental and behavioral disorders (ICD-10)
, developed by WHO. The ICD was developed with the aim of unifying the diagnostic approach when conducting statistical, scientific and social research.
International classification of mental and behavioral disorders in accordance with the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10)
In Russia,
the international classification of mental and behavioral disorders (ICD-10)
, developed by WHO, is used. The ICD was developed with the aim of unifying the diagnostic approach when conducting statistical, scientific and social research.
The tenth revision of the classification is currently in effect, with mental disorders and behavioral disorders included in the fifth section. Each diagnosis included in the classification can be presented as a code consisting of a letter (“F” for mental disorders) and several numbers.
In ICD-10, the concept of “disease” is replaced by the broader term “disorder”; the concepts of “neurosis” and “psychosis”, “endogenous” and “psychogenic” are not used. The classification does not deny the etiological approach. In particular, such generally accepted nosological units as schizophrenia, organic disorder, and stress response are used. The etiological principle is used provided there is no significant disagreement in assessing the nature of the disorder. However, more often the diagnosis in ICD-10 is based on the identification
of the leading psychopathological syndrome.
Full text
International Classification of Mental and Behavioral Disorders in accordance with ICD-10
Psychological disorders treatment
Treatment of psychological disorders in patients of any age can only be prescribed by an experienced specialist. Previously, the patient undergoes a thorough health examination. It is carried out in order to exclude the possibility of the presence of a physiological disease. Passing symptoms can be provoked, for example, by endocrine or neurological disorders.
After eliminating physiological causes, the patient's psychological state is examined. An important part is collecting a family history. The fact of hereditary damage to psychological diseases has not been confirmed at the moment, but there are cases of familial predisposition. Doctors suggest that they may be associated with family habits and hereditary character traits.
The following are used in therapy:
- medications: antipsychotics, antidepressants, mood stabilizers;
- psychological classes, both individual and in groups;
- Physical therapy classes are shown.
Often patients may be advised to find an additional hobby. It can distract the patient from unpleasant thoughts.
Psychological personality disorders
After confirmation of the diagnosis, pathology refers to severe psychological deviations in the psychological sphere of a person’s consciousness. They are found in human popularity and are diagnosed in about 12% of the population. Disorders are more often diagnosed in males.
They are characterized by obvious violations of destructive behavior patterns. This list does not include personality disorders caused by pathologies or brain injuries.
According to ICD10, psychological disorders are divided into:
- Schizoid, characterized primarily by disturbances of contact in society, a tendency to recluse and complete isolation. Patients lack a proper sense of reality. A schizoid can be continuously busy with endless and meaningless mental work.
- Paranoid disorders accompanied by an increased level of suspicion. Patients are characterized by increased sensitivity, high ambition, and inability to accept personal failures. Over time, the severity of the reaction does not dull, but appears regularly with increasing force.
- Dissocial, characterized by a disdainful attitude towards social, personal, and everyday responsibilities.
- Emotionally unstable, in which instincts and feelings become the determining reasons for actions.
- Hysterical, in which patients are characterized by dramatization of what is happening, excessive pretense in the manifestation of feelings.
- Anankastnye, a striking feature of which is pedantry at the level of pathology. Petty scrupulousness contradicts a real love of order.
- Anxious, which is accompanied by a constant feeling of fear and personal tension. A person constantly assumes that something tragic might happen to him. Accompanied in most cases by an inferiority complex.
- Dependents, characterized by a personality’s tendency to completely subordinate to others, pathological passivity, and the inability to make adequate decisions independently.
According to ICD 10, “other disorders” include narcissism, eccentricity, infantilism, psychoneurotic and passive-aggressive disorders. Doctors also separately identify pathologies of an unspecified type.
Types of mental disorders
According to the ICD-10 classification of mental disorders, the following types of diseases are distinguished:
- Organic disorders. These are diseases that arise due to brain damage (for example, due to trauma, stroke, degenerative changes). With organic lesions, dementia often develops.
- Alcohol, drug and other substance use disorders. At some stage, these substances become the most valuable for humans. This is how addiction syndrome develops.
- Schizophrenia and delusional disorders. Schizophrenia is characterized by a breakdown in the processes of thinking and perception. The perception of colors, sounds, and shapes is impaired.
- Mood disorders. They are also called affective disorders. These are different degrees of mania, bipolar disorder (manic-depressive psychosis), depression.
- Neurotic disorders. These are various types of phobias, panic attacks and anxiety. This also includes obsessive-compulsive disorders, which are characterized by obsessive thoughts and actions. For example, performing certain rituals, such as washing hands several times, fear of stepping on the line between the tiles of the sidewalk, etc.
- Behavioral syndromes. These are disorders associated with physiological and physical factors. For example, changes in eating behavior (anorexia, bulimia) and sleep disorders.
- Mental personality disorders. These include disorders that lead to serious deviations in lifestyle. The most striking example is paranoid disorder, in which a person distorts facts, seeing in them malicious intent towards himself.
- Mental retardation. This is a disorder or delay in the development of the psyche of varying degrees.
- Mental development disorders. A type of congenital disorder associated with improper maturation of the nervous system. This includes autistic disorders and autism.
- Emotional disorders that develop in childhood. These include conditions associated with disturbances of attention, activity and behavior.
The most common mental disorders include:
- Depression is depression, loss of the ability to enjoy life.
- Bipolar disorder – sudden mood swings from euphoria to severe depression.
- Panic attacks are attacks of inexplicable fear and anxiety.
- Schizophrenia is a disease accompanied by impaired thinking, hallucinations and delusions.
- Dementia is the degradation of thinking abilities.
- Neurosis is an obsessive hysterical state.
- Psychosis is a disorder of perception of a real situation. Unlike neurosis, with psychosis the patient is not aware of his condition.
- Phobias are an inexplicable fear of something (for example, claustrophobia is the fear of closed spaces).
Mental disorders manifest themselves in the form of phobias. Photo: shalunx13 / Depositphotos
Signs of mental disorders
Signs of a mental disorder should be considered only as a whole, since the same symptoms can indicate completely different diseases. However, some manifestations can be considered indicative. Let's talk about them in more detail.
Mood changes
The mood changes for every healthy person depending on the situation. It is normal for a person to feel sad when losing a loved one or after leaving a job. If your mood changes for no apparent reason and lasts for more than 2 weeks, then you should be wary. Such changes include:
- feeling of depression, melancholy, feeling of worthlessness;
- foolishness not characteristic of age;
- unnatural frivolity;
- optimism that has no basis;
- lack of emotions, apathy;
- aggression, anger and irritability;
- tearfulness or loudness, inability to cope with emotions;
- inability to restrain sexual desires or, conversely, decreased libido.
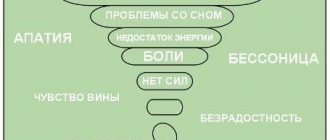
Asthenic syndrome
Modern psychiatry defines asthenic syndrome as a feeling of weakness, increased sensitivity and/or low performance. The person is unable to cope with everyday tasks. Often with asthenia, sleep and daily routine are disturbed.
Obsessive thoughts and actions
This is a wide range of manifestations - fears, suspicions, suspiciousness, passion for excessive purity, and the like. With such violations, people may return home several times to check whether the stove or iron is turned off, or whether the door is closed.
The desire for perfect cleanliness can be a symptom of a mental disorder. Photo: AndreyPopov / Depositphotos
Hypochondria
A person develops an obsessive fear of discovering various diseases (usually life-threatening) in his body. He may also constantly look for signs of these diseases and regularly consult a doctor for no apparent reason.
Important! Hypochondria should be distinguished from well-founded fears for one’s health. A doctor can make a diagnosis of hypochondriacal syndrome only if this condition continues in the patient for more than 6 months after diagnostic tests have been completed that exclude the suspected disease.
Internal alarm
A person experiences a constant feeling of anxiety, the origin of which he himself cannot clearly explain. He, without apparent reason, fears for the well-being of his loved ones or is afraid of becoming a victim of an accident. This disorder is characterized by symptoms such as muscle tension, sweating, and discomfort that periodically occurs in the solar plexus area. As a rule, this condition develops in people exposed to regular stress.
A person with mental disorders has difficulty controlling their emotions. Photo by Anna Tarazevich: Pexels
Thinking disorder
This includes both acceleration and inhibition of the thought process. If a person’s speech is intermittent, it means that the speech apparatus does not keep up with the train of thoughts. Long pauses between words indicate inhibition. Such signs may indicate dementia, depression, or manic-depressive psychosis.
Illusions and hallucinations
Many people confuse these concepts. An illusion is a distorted representation of real objects and phenomena. For example, patterns on a wall may appear to a person to be a tangle of snakes.
Hallucination is the perception of something that is not really there. Hallucinations are visual, auditory, tactile, olfactory and gustatory.
Delusional thoughts
It manifests itself in the form of incorrect judgments that the patient tries to impose on others. For example, talking about their great mission or about the secret conspiracy of family members. There are several types of delusional thoughts. Delusions of attitude - thoughts that everything around you is against you; delusions of jealousy - an obsessive suspicion of your partner of treason; delusions of damage - thoughts that you are constantly being robbed.
Important! Delusional disorder differs from ordinary delusions in that the patient does not perceive even the most irrefutable evidence that he is wrong.
Other symptoms of mental disorders
Other common signs of mental illness include:
- groundless fears;
- emotional inhibition, apathy;
- inappropriate emotions (for example, joy at the loss of a loved one);
- violation of the volitional sphere;
- absent-mindedness.
Causes of psychological disorders
The list of provoking factors may include:
- severe pregnancy in the patient’s mother;
- birth injuries;
- presence of genetic predisposition;
- severe stressful situations;
- experiences, including in childhood, of psychological or physical violence.
The presence of one or even several provoking factors at once does not guarantee the onset of a psychological disorder.
In such patients, disturbances are caused by the characterological constitution, the habitual model of behavior used, and a certain personal structure.
Symptoms and signs of psychological disorder
At the moment, doctors are not ready to strictly define the specific symptoms and signs of a psychological personality disorder. Manifestations in each patient are strictly individual. But there are general points that suggest the need to seek advice.
According to ICD10, the main symptoms and signs include disturbances in behavioral reactions, mental activity, and actions that go beyond the recognized framework of current cultural and moral beliefs and norms. Physical, cognitive and neurological symptoms are observed. They are prone to increased levels of fatigue. They often feel excessively happy or excessively unhappy without a specific reason. Logical relationships are broken.
ICD10 calls the signs:
- spatiotemporal disorientation;
- quick and groundless changes in mood;
- inadequate attitude towards one’s own physical and emotional state;
- the appearance of hallucinations;
- cases of confusion;
- confusion;
- fright;
- lack of reaction to what is happening.
Sleep is often disturbed. This can equally manifest itself as increased levels of drowsiness and insomnia. A common trigger is depression associated with serious stress, for example, the loss of a close relative. There may be a violation of the order of self-identification. The patient creates an alternative personality that has nothing to do with what happened. The weakening of memory to the level of its complete absence is diagnosed. Mental interest is disturbed, often accompanied by delirium. In some cases, the patient suffers from bouts of unreasonable laughter or a tendency to unreasonably increased tearfulness. Doctors include alcohol and drug abuse among psychological disorders.
Signs characteristic only of men are highlighted separately. They may be associated with untidiness in appearance and violation of hygiene standards. Men experience failures especially painfully and tend to blame the entire world around them for what happened. They become irritable and tend to offend and humiliate their interlocutors.
Diagnosis of psychological disorders
When diagnosing psychological disorders, doctors must first prescribe an examination of all body systems. This is necessary to exclude physiological causes of pathology.
Patients are prescribed ECHO, MRI, CT, and examination by an endocrinologist and neurologist is recommended. A study of the medical history is carried out. Psychological manifestations often become side effects of taking certain medications. For example, prescribed in the treatment of neurological diagnoses.
An important part of the diagnosis is a personal conversation with the patient. It is recommended to involve close relatives and those people with whom the patient is in constant contact.
Types of psychological disorders
In modern medicine, there are several main types of psychological disorders, which differ in symptoms and types of manifestation. Often, to eliminate the disease or enter a state of stable remission, depending on the type, different treatment options are required.
Neuropsychological disorder
Differs in manifestations of destructive behavior. In most cases, it is caused by improper functioning of the brain. Stand out:
- Exogenous or external causes associated with head injuries, illnesses, chemical poisoning, psychological trauma. May be associated with disorders of the cardiovascular system, leading to impaired blood supply to the brain.
- Endogenous or internal causes, which are mostly genetic, caused by a violation in the set of chromosomes.
Due to the commonality of psychotypes, they can often be transmitted from parents to children. Among the provoking factors are some diseases, including cerebral vascular sclerosis, diabetes mellitus, cerebrovascular accidents, and infectious diagnoses. Can be triggered by taking drugs and alcohol.
Mixed developmental disorders
In ICD13 they are classified as F83. The first manifestation is most often noted in childhood or infancy. Typically associated with chromosomal or genetic disorders. Accompanied by speech and school skills impairments. Motor functions may be impaired. They are diagnosed only in the case of a complete combination of several psychological disorders aggravated by life circumstances.
Specific psychological development disorder
Today, this category of pathological disorders has been poorly studied. An accurate diagnosis is complicated by the unreasonable combination of violations of the proper and timely acquisition of language skills, accompanied by motor disorders. But it is not recognized as intellectual retardation as such.
Mixed specific psychological development disorders
They are also established in the case of a combination of several factors recognized in the ICD10. Verbal intelligence suffers, and there are disturbances in the development of speech functions. There may be cases of disorientation and problems with logic are identified. Memory suffers.
Causes of mental illness
The most common diseases have long been scientifically explained. But in practice, it happens that it is difficult for a person to establish the cause of a particular disease. Generally speaking, there are several mandatory factors and causes of mental illness due to which the disease can develop:
- unfavorable environment;
- hereditary factor;
- unwanted or unsuccessful pregnancy;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- the reason lies in childhood;
- neuro poisoning.
- injuries associated with psychological and emotional factors.
A huge number of mental illnesses are inherited. In this case, a person becomes predisposed to developing diseases. This applies in particular to those people whose both parents had mental disorders. Mental disorders that are inherited are:
- schizophrenia;
- bipolar disorder;
- depression;
- epilepsy;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- schizotypal disorder.
Psychological development disorder in a child
They are diagnosed when a child has a combination of impairments in school skills, poor speech development, and problems with motor functions. In this case, it is impossible to establish an accurate diagnosis due to the lack of predominance of one of these disorders.
Additionally, a certain level of cognitive impairment is detected. The disadvantage of diagnosis is the frequent use of diagnosis in the absence of a real opportunity to establish the exact cause and the leading predominant factor. Often such children are diagnosed with mental retardation. An important condition is the identification of the first signs of pathology at a very early, often infancy, age.
The leading causes are called biological factors. Including minor tissue damage to brain structures, which provoked a disruption in the formation of interanalyzer connections.
An additional provocateur is the lack of information associated with the low family level. Manifestations include:
- speech disorder dyslexia;
- dysgraphia, which manifests itself in the occurrence of problems with the development of written speech skills;
- dyscalculation disorders.
Such children should be under constant supervision of a psychiatrist. The course of treatment includes psychotherapy sessions and drug therapy. It is difficult for children to master the curriculum of a secondary school. They successfully master the rules of acquiring school skills in Type VIII schools. Although such a translation is recommended only in situations where the level of pathology is on the same level as mental retardation.
There is a clear trend towards a decrease in the level of impairments in adolescence; often the pathology can eventually be smoothed out completely, but problems with cognitive efficiency can remain in adulthood.
Causes of mental disorders
There is no single cause of mental disorders. As a rule, they arise under the influence of many factors, including:
- hereditary;
- biological (state of internal organs and tissues);
- psychological;
- social;
- cultural.
A growing body of research points to a genetic component to mental health. For example, with a hereditary tendency, even small life problems for a person turn into a real tragedy. This vulnerability, combined with stress, can lead to mental illness.
All causes of mental disorders can also be divided into internal and external.
Internal reasons:
- Brain diseases and traumatic brain injuries. For example, brain tumors can greatly change a person's state of mind.
- Infectious diseases that negatively affect the nervous system. The main danger of most infections is toxins that poison nerve tissue.
- Diabetes. High blood sugar levels are toxic to tissue. First of all, blood vessels and nerve tissues suffer from this.
- Diseases of internal organs affecting the blood supply to the brain. These are pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, disorders of the liver, kidneys and endocrine system.
- Congenital malformations and hereditary diseases.
Psychobiome: the role of gut bacteria
Another cause of mental disorders may be changes in the intestinal microflora. There have been many studies showing the relationship between the microbiome and the nervous system4. Not long ago, the term psychobiome arose. It characterizes the impact of microflora on the state of the human psyche. For example, some microorganisms secrete signal substances that travel through the bloodstream to the brain. Other bacteria stimulate the secretion of hormones. In addition, the intestines contain neuron-like cells that are connected to the vagus nerve.
External reasons:
- Mistakes in raising a child, family conflicts and domestic violence.
- Frequent stress, overwork.
- Features of the social environment, working conditions.
- Exposure to certain chemicals (alcohol, drugs, medications and others).
- Radiation exposure.
Major psychological disorders
Currently, experts suggest that by 2021, psychological disorders may take fifth place in the list of diseases leading to disability. According to Russian doctors, pathologies can be diagnosed in at least every resident of modern Russia. Approximately similar levels of indicators are observed in all developed countries of the world.
All the reasons for the occurrence of such pathologies are not known to modern doctors today. Conducted research shows that the list of provocateurs may equally include genetic predisposition and external life events. Diseases of the nervous system, leading to psychological pathologies, are caused by all factors that disrupt the activity of the central nervous system.
Despite the inability to identify the exact cause of the onset of psychological disorders, these pathologies can now be successfully treated. Depending on the degree of damage, treatment uses only courses of psychotherapy or medications, including antipsychotics and antidepressants.
Currently, psychiatrists are highlighting an increase in the number of confirmations of diagnoses of depressive disorders and phobias. They can often be accompanied by bipolar disorder.
The danger of each of these diagnoses is a violation of the patient’s socialization. Even a violation at the mildest level leads to a decrease in the level of performance. Patients become socially isolated. They often prefer loneliness and family ties are disrupted. Pathology leads to the appearance of suicidal thoughts.
Another large group is fears. They are established whenever a level of panic is detected in the perception of objects, natural phenomena, or events. Modern man often becomes pathologically afraid of spiders, the dark, water, and some animals. The reason can actually be any factor. Moreover, in such a situation, fear is not caused by a natural sense of self-preservation. It is inexplicable and appears unreasonably. The concern is that in reality there is no threat to health, much less life.
The number of diseases associated with unreasonable feelings of fear is incredibly large. Many of us also encounter their manifestations during rush hour in a subway car or in a large chain store. The crowds of people that surround us here are unpleasant even for healthy people. But it is not rejection that speaks of pathology, but rather fear at the level of a panic attack, in which the patient may begin to choke and may faint.
The list of major pathological disorders includes alcohol and drug addiction, bulimia, anorexia, and obesity. Doctors often encounter pathological sleep disorders.
Depression
Depression is a common mental disorder and one of the leading causes of disability worldwide. About 264 million people worldwide suffer from depression1. Women are more susceptible to this disorder than men.
Patients with depression are characterized by feeling depressed, loss of interest and the ability to have fun, feelings of guilt, low self-esteem, sleep and appetite disturbances, fatigue and poor concentration. There may even be symptoms that cannot be explained by objective physical causes. Depression, either long-term or episodic, can significantly interfere with daily life, work and school. In the most severe cases, depression can lead to suicide.
Prevention programs exist to help reduce the incidence of depression in both children (for example, by providing protection and psychological support after physical or sexual abuse) and adults (for example, by providing psychological support after natural disasters and conflicts).
There are effective treatments. Mild to moderate depression can be treated with narrative therapy, particularly cognitive behavioral therapy and psychotherapy. Antidepressants have been used successfully to treat moderate to severe depression, but are not the first choice for mild depression. They are not used to treat depression in children and are used with caution and not primarily in the treatment of depression in adolescents.
Management of patients with depression should include psychosocial elements, particularly identifying stressors such as financial problems, work difficulties or psychological abuse, and sources of support such as family and friends. It is important to ensure that social interaction and participation in society are maintained and renewed.
Psychological disorders list
This list is currently incredibly wide, but experts identify the largest groups:
- Alcohol addiction, caused by a pathological passion for drinking alcoholic beverages, often caused by a violation of social adaptation. This also includes drug addiction. Admission leads to persistent mental disorders.
- Schizophrenia, in which the patient most often experiences perceptual disturbances. Often accompanied by fantastic delusions and hallucinations.
- Pathologies of the brain, most often first manifested in childhood, sometimes in adolescents, the pathology intensifies as they grow older.
- Disorders that occur in the emotional sphere, often called affective disorders. This section includes bipolar disorder, which is increasingly being diagnosed today.
- Neuroses and numerous variants of phobias that arise from a combination of internal and external conflicts.
- Physiological disorders associated with pathologies of eating, sexual, labor, and sleep dysfunction.
- Disorders that occur in adults are associated with pathological conditions in the field of social adaptation, and there is a lack of development in the emotional sphere. Patients often deny the presence of problems and refuse any medical care options.
- Cases of mental retardation. In such a situation, all areas of life suffer, the patient needs constant monitoring, and is almost always unable to care for himself.
In the modern world, everyone can sometimes suspect one or another type of psychological illness. But an accurate diagnosis can only be established in a medical institution by a qualified doctor. If you suspect the presence of a pathology, it is recommended to immediately contact a specialist.
When to seek professional help
Perhaps you or your loved ones have developed suspicious signs of one or another type of psychological disorder. This may include insomnia, fear, depression, short-term memory loss, loss of spatial orientation, and even hallucinations. In such cases, it is recommended to immediately contact a specialist!
Modern medicine has long used special diagnostic tests that make it possible to determine a real mental disorder in the early stages. So often the problem of simple emotional exhaustion and fatigue can be mistaken for a full-fledged mental disorder and vice versa. Therefore, you should never self-diagnose and try to recover by taking antidepressants or sedatives.
The Korsakov clinic uses a modern recovery method, approved not only by the Russian healthcare system, but also by a number of Western experts. The complex of mental health treatment measures also includes establishing a lifestyle, reducing stressful situations, establishing a healthy diet, fortifying the body, and protecting oneself from social and everyday problems. In the process of in-depth psychological assistance, a person’s social activity is restored and negative factors are neutralized. As a result of such actions, the nervous system usually returns to normal.
We also recommend reading the article about gambling addiction.