What is gastric neurosis? This is a gastric disease that is now becoming more common. It can appear in absolutely each of us. But it is more often observed, nevertheless, in young people against the background of mental and physical stress, some other neurosis, alcohol and nicotine abuse, with diseases of the intestines, stomach, and other organs.
In addition, this disease can be caused by:
• stressful situations;
• emotional stress;
• malnutrition;
• mental overstrain;
• general intoxication.
It leads to disruption of the stomach and general functional disorders, often associated with exhaustion of the nervous system.
What is gastric neurosis?
All systems of the human body have nerve endings, so neurosis can occur in any organ.
There are especially many of them in the gastrointestinal tract, and therefore gastric neurosis occurs quite often. Psychosomatic causes usually do not cause severe pathologies of the stomach. But pain during the development of this pathology is felt quite strongly, which is why the quality of life of the sick person is significantly reduced. Feeling severe pain, people often do not want to believe that the cause of their occurrence is psychological. However, it is important to take into account that a prolonged depressed state causes a general decrease in immunity, and failures of the immune system can provoke the development of various infectious diseases.
Psychiatrist consultation
treatment of neuroses at home and in the clinic
rehabilitation until complete recovery
We work around the clock
Call a doctor at home Leave a request and we will call you back in 1 minute
8
Or call
Symptoms and diagnosis of gastric neurosis
In the presence of gastric neurosis, chronic and long-term symptoms occur, which lead to a significant deterioration in the patient’s quality of life. During examination using fibrogastroscopy, ultrasound, and laboratory diagnostic methods, doctors do not detect signs of serious organic pathology. In patients suffering from gastric neurosis, the following signs of digestive tract pathology occur:
- A feeling of heaviness in the stomach that occurs after eating;
- Fast saturation;
- Pressure or pain in the epigastric region of the abdomen;
- Heartburn behind the sternum;
- Nausea;
- Gagging or vomiting.
Patients experience an unpleasant feeling in the stomach, and some patients experience “tissue damage.” Patients may interpret discomfort in the upper abdomen as pain. Patients suffering from gastric neurosis may experience alarming symptoms, for which doctors at the Yusupov Hospital carry out immediate clinical diagnostics:
- Increased body temperature above 38.5°C;
- Weakness;
- Night sweats;
- Weight loss of more than three kilograms;
- Periodic vomiting;
- Blood in the stool or tarry stools;
- Severe localized abdominal pain.
The clinical picture of gastric neurosis can vary significantly from case to case. Some patients complain of mild pain, while in others the pain syndrome affects the entire abdomen or is clearly localized in the hypochondrium or epigastric region. In severe cases of the disease, symptoms of chronic gastritis or gastric ulcer occur. They do not actually indicate the presence of these diseases, but are associated with a reflex decrease in the acidity of gastric digestive juices and the accumulation of mucus in the stomach
The following signs indicate the psychogenic nature of stomach disease:
- The presence of numerous somatic manifestations;
- Absence of pathological changes in organs in the presence of pain in them;
- Prolonged course of the disease without improvement;
- Variability of the clinical picture;
- Dependence of symptoms on external factors (stressful situations);
- Presence of signs of dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system;
- Ineffectiveness of treatment with medications used in gastroenterology.
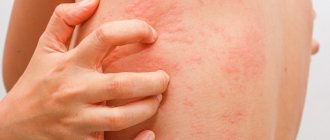
A feature of gastric neurosis is that the disease manifests itself not only in disruption of the digestive system, but also in emotional changes. Sometimes patients cannot accurately indicate the location of pain. They become anxious, gloomy, and may experience symptoms of depression.
Gastric neurosis is a diagnosis of exclusion. When a patient with a clinical picture of a gastrointestinal tract disease is admitted to the therapy clinic, gastroenterologists conduct a comprehensive diagnosis using modern research methods:
- X-ray of the stomach;
- Fibrogastroscopy;
- Echography.
Laboratory diagnostics include a study of the acid-forming function of the stomach using pH-metry, clinical and biochemical blood tests, determination of the presence and titer of cancer tumor markers, urine and stool analysis.
If during the examination no organic pathology of the stomach is revealed, the patient is consulted by a psychotherapist and receives treatment aimed at correcting the patient’s emotional state.
Diagnosis of gastroneurosis
Many signs and symptoms of gastric neurosis are identical to those that develop with gastritis.
Therefore, to correctly diagnose this disease, it is important to pay attention to the presence of psychological symptoms, such as rapid heartbeat, headaches, overexcitation, insomnia, panic attacks, phobia, hypochondria, etc. Characteristic signs of gastric neurosis in children are nervous vomiting, not accompanied by nausea. In adults, this disease often manifests itself in the form of anorexia (complete lack of appetite) or bulimia (a condition in which a person eats too much food). Both of these pathologies are dangerous and can ultimately even lead to death.
Why does the disease occur?
When we talk about the common causes of intestinal and stomach diseases, they are often caused by bacteria, hereditary predisposition, and acquired chronic pathologies.
But do not forget that the vagus nerve is involved in organizing proper gastric secretion. When it is at rest, secretion occurs normally and the person feels comfortable. But psychological shocks and past illnesses, as well as simply constant anxiety, can lead to serious problems.
Among the common causes of gastric neurosis are:
- Problems of a psychological nature. They arise when a person feels constant anxiety, is dissatisfied with himself, or experiences a tragic event. Psychologists note that neurosis can cause a break with a loved one, being in a negative environment in a team at work, or the loss of a relative.
- Wrong lifestyle. The nervous system suffers due to lack of sleep, poor work-rest balance, and constant severe stress.
- Nutrition problems. The gastrointestinal tract makes itself known when you eat a lot of fatty, heavy foods, consume a lot of sweets and starchy foods. Poor diet is another risk factor. To avoid getting sick, you should give up frequent snacking and balance your diet.
- Past illnesses. Many viral diseases, as well as problems with the stomach and intestines, quickly provoke neurosis. The problem appears against the background of gastritis, neoplasms, ulcers and other problems.
- Negative effects on the gastrointestinal tract. The disease can manifest itself after severe poisoning, as well as during intoxication, against the background of bad habits.
Treatment options
The main therapeutic method used to treat gastric neurosis, as well as all other neurotic disorders, is psychotherapy.
Therapy involves group and individual personality-oriented sessions. During these sessions, the specialist helps the patient to discover the psychological conflict that caused the development of gastric neurosis in order to rebuild the personal relationships that caused the development of the pathology. The main task in this case for the psychotherapist is to switch the patient’s attention from the symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases to resolving the internal psychological conflict. Gastroenterological drugs are also used for treatment. They are prescribed to improve metabolic processes, eliminate spasms, normalize the secretion of gastric juice, and protect the gastric mucosa. Medicines are also prescribed to the patient for psychotherapeutic purposes - to give him confidence that treatment is being carried out. In advanced cases, the treatment regimen may also include tranquilizers and antidepressants.
Burning in the abdomen due to stomach diseases
The most common condition that causes burning pain in the upper abdomen and chest is gastroesophageal reflux, when gastric juice containing hydrochloric acid flows into the esophagus.
This can occur with diseases such as gastroesophageal reflux disease, chalazia cardia (insufficient closure of the muscle sphincter, which is located in the lower part of the esophagus), hiatal hernia. Our expert in this field:
Allahverdyan Alexander Sergeevich
Surgeon-oncologist, professor, MD. Head of the ROH expert group. International expert
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
In addition to burning pain, this condition is characterized by heartburn - a burning sensation in the stomach and chest. Symptoms usually worsen after eating, bending forward, or lying down.
According to statistics, the backflow of gastric contents into the esophagus occurs at least once a week in every fifth adult.
Sometimes “heartburn” is actually a manifestation of coronary heart disease. This condition will be more serious than gastroesophageal reflux. And in some cases, “stomach pain” may even be a manifestation of an atypical form of myocardial infarction. Therefore, you should consult a doctor in any case. And if the burning sensation is severe and does not go away for a long time, or your health has deteriorated significantly, it is better to call an ambulance.
A burning sensation in the upper abdomen is also characteristic of a stomach ulcer. Sometimes burning pain begins to bother you immediately after eating, sometimes after a couple of hours, and sometimes on an empty stomach (hunger pain is also characteristic of duodenal ulcers).
Our offers
Our clinic treats mental disorders in Moscow.
If you have symptoms of stomach neurosis, contact us. We employ experienced psychiatrists. They specialize in the treatment of psychosomatic diseases of various internal organs caused by psychological reasons. Our doctor will examine you, perform the necessary tests, after which he will make an accurate diagnosis and provide appropriate treatment. If necessary, a psychiatrist can visit your home.
Call by phone
Intestinal symptoms
What abdominal pain is associated with intestinal diseases?
The intestine is the longest organ of the digestive system, which occupies most of the abdominal cavity. Therefore, with its diseases, pain of varying intensity may occur in the upper, middle and lower parts of the abdomen, on the left, on the right and around the navel. Most often, they may be associated with stool rather than food intake. But the presence of diseases, even such dangerous ones as ulcerative colitis, is not always accompanied by pronounced abdominal pain, and the initial stage of cancer does not cause abdominal pain at all, so it is necessary to pay attention to other symptoms and undergo regular preventive examinations.
Diarrhea (diarrhea)
Diarrhea is a clinical symptom of various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and especially the intestines. The main symptom of diarrhea is frequent bowel movements, more than three times a day, with the release of watery or pasty stools. According to the nature of the course, acute and chronic diarrhea are distinguished.
Acute diarrhea lasts no more than two to three weeks and is often infectious in nature. Chronic diarrhea is characterized by a long course (more than 2 weeks) and can be caused by many reasons.
Occasional loose stools can occur in healthy people, but prolonged diarrhea can be a symptom of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, intestinal dysbiosis, Clostridioides difficile infection, inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, lactase deficiency and other diseases. Chronic diarrhea leads to impaired absorption of substances necessary for the body: proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals. Therefore, this condition requires contacting a gastroenterologist, in-depth diagnosis and timely treatment. Read more about the causes and treatment of diarrhea.
Constipation (obstipation)
Constipation can be associated both with errors in diet and lifestyle, and with intestinal diseases, including the presence of polyps and neoplasms. In addition, it can be a manifestation of other diseases, for example, insufficiency of the thyroid gland. Therefore, self-medicating constipation can lead to dangerous health conditions, including bowel cancer.
Although researchers have not been able to identify a single root cause of constipation, one scientific review indicates that functional constipation and irritable bowel syndrome with constipation are associated with an imbalance of gut flora. People with constipation tend to have lower levels of certain types of bacteria, including bifidobacteria, so adjusting your diet and using probiotics as prescribed by your doctor may help improve the situation. Read more about the causes and treatment of constipation.
Changing the shape and appearance of the chair
Examination of stool samples is one of the main ways to diagnose intestinal diseases. It is also possible to pre-visit a doctor by self-diagnosis based on the appearance of the stool.
Normal stools are brown, banana-shaped, and thick as toothpaste. There may be slight deviations associated with an increase in fiber, foods and medications in the diet that color feces. The normal frequency of bowel movements according to the World Health Organization ranges from 2 times a day to 4 times a week and should occur easily and without straining.
The onset of an inflammatory process in the intestines can be signaled by increased bowel movements and the appearance of loose stools mixed with mucus. As the situation worsens, stools become loose and frequent. Also, loose stools can signal errors in nutrition or the presence of food intolerance.
The cause of dense, fragmented feces of the “sheep” or “pine cone” type may be a lack of water and fiber in the diet and a sedentary lifestyle. But if such stool is observed for more than 3 months, it is a symptom of chronic constipation.
For more information about the connection between the appearance of stool and intestinal diseases, read our article “How to determine intestinal disease from stool?”
Increased gas and bloating
Gas production in the intestines is a normal part of the digestive process, but some strains of intestinal bacteria produce more gases than others. With an increased content of such bacteria, excessive fermentation occurs, gas retention in the intestines and bloating. Also, increased fermentation of food can be caused by impaired digestion of food due to food intolerance and insufficiency of enzymes for its breakdown, for example, lactase deficiency.
Heartburn
Increased gas production in the intestines and constipation cause bloating and increase pressure on the diaphragm and lower esophageal sphincter. This can promote the reflux of stomach and duodenal contents into the esophagus and cause heartburn.
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting can be both symptoms of an intestinal infection and intestinal obstruction.