Hospitalization and treatment under the compulsory medical insurance quota. More details after viewing the pictures.
Brain astrocytoma is a primary malignant neoplasm that arises in astrocytes, stellate cells responsible for the functionality of nervous tissue and protecting neurons from destruction. The specific causes of the tumor are unknown. There is an assumption that astrocytoma appears as a result of several negative factors, including radiation exposure to the body. Experts also believe that the pathological process can be caused by genetic abnormalities.
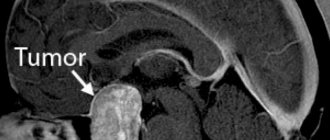
Pilloid astrocytoma of the cerebellar vermis and fourth ventricle before surgery
Classification of astrocytomas
The main types of brain astrocytomas:
- fibrillar;
- subependymal (glomerular);
- protoplasmic;
- pyelocytic (piloid);
- glioblastoma;
- gemistocytic;
- anaplastic;
- microcystic cerebellar.
The most dangerous form of the tumor is considered to be the pyelocetaceous one. It is classified as the first degree of malignancy. Fibrillar, gemistocytic, protoplasmic astrocytomas are tumors of the second degree of malignancy. They are less life-threatening. But without effective surgical treatment, grade 2 astrocyotoma leads to the death of the patient.
The third degree includes anaplastic tumors and glioblastomas. They account for more than 50% of all malignant brain tumors. Surgery is also used to treat grade 3 astrocytoma. The sooner the tumor is removed, the better the prognosis for life.
General information
This type of neoplasm accounts for at least 10% of all cases of brain tumors. Astrocytoma is a type of glioma that arises from astrocyte cells located between neurons. These cells support the metabolic process and conduct nerve impulses. Unfortunately, they are the ones who are susceptible to the negative effects of the environment. When a mutation occurs within the nucleus, the cell begins to divide uncontrollably, which leads to tumor growth. Diffuse astrocytoma grows into healthy layers of the brain, has no clear boundaries and is “scattered” over a large area. Even with an integrated approach and the use of advanced treatment methods, it is rarely possible to remove it completely, so after a while the disease usually begins to relapse.
Causes
The exact causes of brain tumors such as astrocytoma cannot be determined. Experts believe that the neoplasm is multifactorial and appears as a result of the action of several unfavorable factors. The tendency for the growth of astrocytomas is especially pronounced in economically developed countries, whose residents have to breathe exhaust fumes and are daily exposed to waste released into the environment by thousands of industrial enterprises.
The quality of human nutrition also contributes to the development of cancer: food rich in dyes, carcinogens, and animal fats is somehow involved in triggering pathological reactions in the body, including the growth of malignant cells.
Previously, oncological pathologies were diagnosed mainly in older people. Today, brain tumors are increasingly common in young and middle-aged people. The wide capabilities of modern diagnostics and neurosurgery make it possible to detect pathological changes in organs and tissues as early as possible and organize effective therapeutic measures.
Forms of the disease
Depending on the cellular composition, astrocytomas are divided into several types:
| Anaplastic astrocytoma. | A malignant tumor (III degree of malignancy), characterized by the absence of clear boundaries and rapid infiltrative growth. It most often affects men over 30 years of age. |
| Piloid astrocytoma | The tumor is benign and has distinct and clear boundaries. It is formed mainly in the area of the brain stem or cerebellum. Children are at risk. The prognosis for treatment of this form of tumor is always favorable, since it responds well to treatment and without complications. But late seeking help increases the likelihood of its degeneration into malignancy in 70% of cases. |
| Glioblastoma | The malignant and most dangerous type of astrocytomas (IV degree of malignancy). It has no boundaries, quickly grows into surrounding tissues and gives metastases. Typically observed in men between 40 and 70 years of age. |
| Fibrillar form | This is a benign type of neoplasm, but the possibility of its transformation into a malignant form increases. The tumor has no definition and grows much faster than pilocytic astrocytoma. Therapy, including surgery, does not give a 100% good result. Most often, this form is detected in young people under 30 years of age. |
Well-differentiated (benign) astrocytomas account for 10% of the total number of brain tumors, 60% are anaplastic astrocytomas and gliomas.
Symptoms of astrocytoma
Astrocytoma of the brain is accompanied by an increase in intracranial pressure, an irritating effect on brain structures and the formation of toxins as a result of the metabolic processes of malignant cells. Therefore, the main symptoms of the growth of such formations are the following:
- headache;
- nausea and vomiting;
- decreased appetite;
- fatigue and irritability;
- decreased cognitive function, deterioration of memory and attention.
The severity of clinical manifestations depends on the degree of malignancy of the tumor, its size and location. The neoplasm compresses and destroys cerebral structures, which is why focal symptoms occur. Hemispheric astrocytomas cause weakening of muscle strength in the limbs and physical weakness.
Some people have problems coordinating movement. Most often, this symptom appears when the tumor is located in the cerebellum. Mental disorders and even aggression are also possible. When the temporal lobe is damaged, speech apparatus disorders appear, memory is noticeably reduced, and hallucinations, taste, and hearing disorders may appear. Astrocytoma, localized between the occipital and temporal lobes, impairs vision. Visual hallucinations may occur. Impairment of fine motor skills and written speech is typical for neoplasms that are located in the parietal zone.
General symptoms of the disease
The clinical picture consists of many factors, which include the patient’s age, the size and location of the tumor, the stage of neglect of the tumor, the presence of chronic diseases, metastasis and secondary tumor foci. Unfortunately, the diffuse type of astrocytoma shows its symptoms only in the later stages of development. These include:
- seizures;
- regular headaches that are not relieved by any painkillers and get worse at night;
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness and fainting;
- insomnia.
Gradually, these symptoms are mixed with a picture of pronounced disorders of the nervous system and psyche:
- frequent mood changes;
- causeless aggression;
- memory loss;
- depression or, on the contrary, a feeling of euphoria;
- increased excitability;
- decreased performance.
In addition, other signs of brain tumors, including absent-mindedness and the occurrence of hallucinations, are characteristic of the overall picture.
Diagnostics
To select the correct treatment tactics and type of operation, a comprehensive diagnosis is performed. The patient is consulted for neurosurgery by neurologists. Additionally, you can contact other relevant specialists.
The examination includes the following methods:
- CT, MRI of the brain;
- electroencephalography;
- study of the vestibular apparatus;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- angiography;
- histological examination of tumor tissue.
Angiography can detect cerebral astrocytoma, plan further treatment tactics and prescribe surgery. The degree of malignancy of the neoplasm is determined by the results of histological analysis. The biomaterial is obtained during a stereotactic biopsy, and then a histological examination is performed.
Diagnosis of the disease
When visiting a neurologist, the first step will be to collect an anamnesis and a series of neurological tests. To clarify the size and location of the tumor, as well as its nature, it will be necessary to undergo several tests and examinations:
- angiography;
- MRI (in case of contraindications, CT is used);
- PAT;
- During the operation, biomaterial may be taken to study its histology, clarify the nature of the tumor and adjust the course of the surgical intervention.
In addition, if necessary, the doctor may prescribe additional tests: general and biochemical blood composition, the presence of tumor markers. All these techniques help the doctor make an accurate diagnosis and determine further treatment regimens. If a diffuse astrocytoma has not yet begun to spread over a large area of the brain and degenerate into oncology, there is a chance to reduce the size of the tumor and prevent its further growth. In some cases, treatment can give a positive result with complete elimination of the tumor.
Principles of treatment
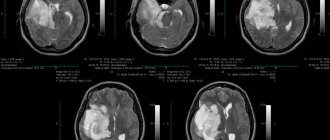
Removal of a large GRADE II WHO astrocytoma of the right temporal lobe (after surgery)
Surgery is the main treatment for astrocytoma. Additionally, specialists use chemotherapy, radiation and radiosurgery techniques. An integrated approach gives the most expected results.
When the tumor size is up to 3 centimeters, stereotactic radiosurgical removal is used. The operation is performed under tomography control. Resection can be partial, allowing to remove the accessible part of the tumor, which reduces intracranial pressure and significantly improves the patient’s well-being.
Surgical treatment of astrocytoma in Russia is carried out in large medical centers. Long preparation for surgery is usually not required. It is recommended to begin preparing for tumor removal immediately after the diagnosis is confirmed.
Indications for surgery
The presence of astrocytoma is an indication for surgery. Only complete removal of the tumor can give a favorable prognosis for life and prevent the occurrence of dangerous complications. Typically, surgery is performed when the tumor is actively growing and is in an accessible area of the brain. The operation is performed by neurosurgeons in the absence of contraindications, which include the patient’s serious condition, a difficult-to-reach location of the tumor, and the patient’s advanced age.
Features of the operation
The operation to remove the tumor is performed under general anesthesia. Many patients go to Burdenko for treatment of astrocytoma. The Institute of Neurosurgery has everything you need to receive quality care for such diseases. In some cases, the patient may be conscious during removal of the formation. Surgical treatment of astrocytoma at the Burdenko Institute is carried out by trained and experienced neurosurgeons who are fluent in modern methods of surgical treatment of astrocytoma and other malignant tumors.
Surgical treatment involves endoscopic craniotomy or open surgery. The specific technique is chosen by specialists, taking into account the diagnostic results, the patient’s age and possible health risks.
The capabilities of modern neurosurgery make it possible to perform operations on astrocytomas with minimal damage and preservation of important body functions. Endoscopic technology makes it possible to remove tumors through small incisions. The operation lasts 2-6 hours. Professional treatment of astrocytoma in Moscow at the Institute of Neurology is available to patients and often saves lives. The experience of a neurosurgeon combined with the use of innovative methods prevents life-threatening complications and relapses of the disease.
Treatment of pathological brain tumors is carried out using modern techniques, in accordance with international medical standards. With the help of modern technical equipment, it is possible to carry out informative diagnostic measures and effective removal of astrocytomas.
It is important to turn to a professional who has been helping patients with tumor processes, including malignant brain tumors, for many years. All surgical operations for astrocytomas are carried out under strict quality control and in compliance with infection safety rules.
Treatment of fibrillary astrocytoma
The choice of treatment method depends on the stage, size and growth of the tumor into neighboring tissues. Fibrillary astrocytomas in the early stages can be successfully removed surgically, while maintaining favorable prognoses. Also, the possibility of surgery may be affected by age, the presence of other medical diseases, or how close the neoplasia is located to important parts of the brain.
The most acceptable choice is radical removal of all or most of the tumor. For small sizes, minimally invasive techniques are used, and for others, open brain surgery (resection or craniotomy). In the latter case, the operation is highly traumatic, so there may be certain complications.
Rehabilitation period
After removal of a brain astrocytoma, rehabilitation takes place in a medical center. After the surgery is completed, the patient will remain in the intensive care unit for a week or more. He is under 24-hour surveillance. A few days after surgical treatment, specialists prescribe magnetic resonance imaging or x-ray diagnostics.
If there are no complications after surgery, recovery continues in the rehabilitation center. The program includes physical therapy, massage, speech therapy correction and other techniques that allow the patient to restore impaired functions and normal quality of life.
Rehabilitation after surgery for astrocytoma and surgical removal of the tumor lasts 2-3 months. At this time, the patient must follow the recommendations of the attending physician and rehabilitation specialist, and undergo diagnostics to monitor the characteristics of recovery.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy for the treatment of astrocytoma most often begins after surgery and removal of the formation. But it is possible to use the technique before surgery in order to reduce the tumor. Radiation therapy also destroys remaining abnormal cancer cells after surgery.
If the formation is inoperable, surgery is not performed, but the patient requires palliative care. Radiation exposure can reduce the pathological focus and increase the patient's life expectancy. The specific method is selected by specialists based on the diagnostic results and the general health of the patient.
A type of radiation treatment is brachytherapy. The method involves the introduction of radioactive substances directly into the malignant tissues themselves. In this case, healthy cells are preserved in full and there is no need to remove functional areas of the brain.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is an addition to surgical removal of astrocytoma. Cytostatic drugs destroy malignant cells when they enter the bloodstream and are distributed throughout the body. Chemotherapy is carried out in short courses and under the supervision of specialists.
Brain astrocytoma: diagnosis
In order to suspect and identify such a pathology, it is necessary to carefully examine the patient. The first step is collecting anamnesis (when the first symptoms appeared, how quickly they progressed, etc.). Next, a detailed examination by a neurologist is required. The specialist will check your reflexes and conduct tests to evaluate your brain function.
Well, the next stage is instrumental diagnostics. It will help to definitively establish a diagnosis and begin treatment immediately. The most popular examination methods for this pathology are CT and magnetic resonance imaging.
What does an MRI show?
This study is the gold standard for diagnosing cerebral astrocytoma. The procedure is very informative thanks to the ability of modern tomographs to perform layer-by-layer scanning of the brain in various planes. As a result of such a study, it is possible to examine in detail the changes in the selected area in 3D mode, as well as to bring a certain area closer or further, if there is such a need.
MRI of the brain for astrocytoma
During MRI of the brain, the skin remains intact and the patient does not experience any discomfort. All that is required of the person is to remove metal objects and remain motionless for the duration of the examination. The magnetic waves generated by the tomograph are absolutely safe for the human body, unlike the X-ray radiation used in CT. Thanks to this, the procedure can be repeated many times, for example, to determine the degree of tumor progression or to evaluate the results of treatment for astrocytoma.
The study does not last long (on average 15-30 minutes). After this, patients are given the results and a specialist’s report, which describes all the changes recorded during the tomography.
Preventive actions
Prevention of the growth of astrocytomas includes protecting the body from radiation exposure, excess ultraviolet radiation and other negative factors, including the consumption of foods and drinks with potentially dangerous chemical components. It is also important to pay attention to working conditions. It is recommended to limit contact with chemicals, objects and equipment that provide a high radiation dose to the body.
Regular preventive examinations and screening studies will allow timely diagnosis of brain cancer processes. The best methods of prevention are timely seeking medical help and regular diagnosis. Today, every person can undergo all the necessary studies and receive detailed information about the state of their health. If an astrocytoma is detected, it is better to remove it immediately. This will prevent the spread of the cancer process to healthy tissue and increase the patient’s life expectancy.
Local symptoms of diffuse astrocytoma
In addition to the general symptoms associated with the presence of a tumor in the skull, doctors identify focal neurological disorders. Their nature directly depends on the location of the tumor:
- A neoplasm in the frontal lobe leads to severe central nervous system disorders. The patient loses the ability to normally coordinate movements, the sense of smell decreases, and epileptic seizures begin.
- A tumor in the temporal lobe provokes the occurrence of visual and auditory hallucinations, in addition, a decrease in visual acuity, a change in the sense of smell, and loss of the ability to read and write normally.
- Damage to the occipital lobe also causes hallucinations, which a person not only sees and hears, but can also touch and smell.
- A tumor in the cerebellum area disables normal coordination, and if it affects the optic nerve, it causes temporary blindness or partial loss of vision.
If any of the listed symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Only timely seeking qualified help increases the chances of successful recovery.
Chemotherapy for astrocytoma
This course is often prescribed for children in the treatment of a diffuse type of tumor. This exposure is considered less dangerous than radiation. Of course, chemistry has side effects, but a young body is able to recover after therapy within 1–2 months. At the same time, radiation exposure can provoke the growth of tumors. In addition, chemotherapy may be prescribed to those whose tumor is not amenable to radiosurgery or traditional surgical removal. It can also be used as palliative therapy if the tumor has developed into cancer. The number of chemotherapy courses is determined by the doctor individually and depends on the patient’s age, weight, height, presence of chronic diseases, and general condition of the body. For example, chemotherapeutic intervention is contraindicated in pregnant women: the drugs can cause miscarriage, fetal hypoxia and other disorders. In this case, the woman will be offered to either wait for childbirth or have an abortion if the period is short enough.