During the period of night rest, people rarely sleep in one position. They move their legs and arms, roll over from side to side, jerk their limbs, or generally shudder. Often they don't even notice it.
What causes muscle spasms? Is this a physiological need or the cause of a possible disease? This feature is called by scientists as hypnagogic twitching or nocturnal myoclonus.
In 70% of the population this is a physiological feature. Most often occurs at the initial stage of sleep. It has no symptoms, goes away on its own and, only in isolated cases, is pathological.
Norms of twitching in a person's sleep
Most of humanity has encountered myoclonus, calling it twitching. This is a feature of the physiological state.
Occurs when frightened or during the first stage of sleep. Usually one-time and goes away immediately.
Muscle contractions also occur after physical training. In children - during intensive growth. Even hiccups are classified as physiological myoclonus.
You should not worry if these contractions are isolated, pass quickly and do not cause physical discomfort.
But, if symptoms tend to become more frequent and intensified, interfere with rest and are observed while awake, you should be wary and seek help from a specialist.
Who is most likely to experience myoclonus?
A baby twitches in his sleep as much as an adult or elderly person. Moreover, twitching occurs more often in the initial stages of falling asleep. This leads to the conclusion that the problem is equally diffusion for all age categories.
Cause of involuntary twitching
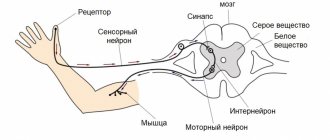
A awake man is able to control his consciousness; while falling asleep, unconscious processes come into force. In order for a person to sleep peacefully, there must be a transfer of power from the conscious to the unconscious. This process resembles the alternation of differently directed impulses. There is no switch from wakefulness to sleep in the brain.
The transition from conscious to unconscious is controlled by the middle. brain, namely the reticular activating system (RAS) and the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus (VLPO). These systems are located in the frontal lobe of the brain. Right behind the eyes, in close proximity to each other. The RAS coordinates awakening and the transition to sleep. During this period, the person is under the control of VLPO .
RAS and VLPO replace each other in a certain way. The process is controlled by serotonin, which ceases to be produced in the brain during the transition to sleep. This amazing chemical is called the “happy hormone.” Entering the body during waking hours, it helps people feel happy.
Low serotonin levels can trigger depression. Sufficiently high levels of serotonin are necessary to control the large muscles located in the limbs. Small muscles located on the wrists, eyes, lips are not controlled by serotonin.
In the first 90 minutes of sleep, the neurotransmitters GABA and glycine, which act together, immobilize the muscles of the limbs; a person cannot move as actively as during wakefulness. But during the transition phase, these neurotransmitters are still inactive, and the level of serotonin has already decreased. Therefore, muscle control is weakened. At this time, involuntary twitching occurs.
Scientific hypotheses
Some scientists see the cause of twitching in incomplete immobilization of the muscles. RAS tries to counteract VLPO , the amount of serotonin decreases, the signal goes to all parts of the body. The hypnagogic impulse indicates the passage of a signal to the muscles.
Proponents of the evolutionary hypothesis argue that twitching was inherited by modern man from his distant ancestors. The twitching was supposed to wake up the primates and prevent them from falling out of the tree. The jerk that occurs at the beginning of sleep contributes to the rapid response of the muscles.
A Current Biology study found that twitching in children is a form of brain training. They help the child's brain learn to quickly and accurately control limb movements. It was found that brain activity in anesthetized rats during sleep movement was more intense than during wakefulness. The falling asleep brain trains and learns to move its limbs correctly.
When to be wary
Scientists consider minor short-term twitches to be completely natural. At the same time, severe cramps can be a sign of serious pathology. Prolonged cramps when falling asleep are one of the manifestations of Parkinson's or Alzheimer's . They can also result from brain injury, fibromyalgia, or serious damage to the nervous system.
Photo: https://ewe.ru/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/GettyImages-608506130.jpg
Science does not stand still. It is likely that scientists will soon be able to unambiguously answer whether twitching while falling asleep is a relic of the past, or whether they still perform some important function today.
Factors influencing twitching when falling asleep
There are several main factors that can affect the intensity of nighttime shuddering:
- psycho-emotional situation at work, scandals at home, increased suspiciousness, depression lead to mental disorders. They are one of the main factors of a restless stay. They can cause neuralgic syndrome and lead to pathology;
- physical overstrain of the body during the working day. Excessive intake of lactic acid into the muscles causes tone and involuntarily contracts them;
- The process can also be influenced by external stimuli, such as the light of street lamps, noisy neighbors, extraneous noise from the street. These factors negatively affect the sensory systems, disrupting not only sleep, but also mood;
- Experts say that the position at the time of rest is very important. Blood flow should not be disturbed, muscles should be in a relaxed state, internal organs should not be pinched;
- An important factor is the excessive intensity of the brain during the daytime. This problem is associated with people whose work involves brain activity. And also creative people;
- excessive consumption of alcohol, energy drinks and caffeine will contribute to restless rest;
- The computer and computer games excite the brain, which can provoke nighttime impulses.
Causes
Most doctors do not consider nocturnal myoclonus a pathology. They attribute it to a natural function of the nervous system.
- Before going to bed, the muscles relax sharply, and the body perceives this situation as a dying process. A signal is sent to the hypothalamus. The muscles begin to contract rapidly to awaken the body and renew vitality;
- in a state of sleep, vital processes are dulled, but the brain continues to work intensively and control the situation. It sends pulses to make sure everything is working properly. These minor tremors are unnoticeable. They do not bother you and are purely physiological;
- trembling may also indicate a lack of minerals and trace elements in the body - glucose, sodium, potassium;
- rapid growth in children can cause the syndrome. But there is no reason to worry. This goes away naturally as the baby grows up;
- for people who suffer from severe snoring, a sharp start may indicate that breathing has stopped;
- taking medications or abruptly stopping them can cause limb spasms and convulsions;
- The syndrome can appear in people who have suffered traumatic brain injuries or concussions.
Sometimes a similar phenomenon can occur as a consequence of viral diseases.
In what cases is specialist help needed?
In 70% of the population, myoclonus is a physiological feature. But there are also pathological features that require the help of a specialist.
For example, when a person twitches even while awake and an increase and worsening of seizures occurs.
Trembling and twitching can cause a number of diseases:
- epilepsy;
- diabetes;
- pinched nerves;
- gout;
- muscle dystrophy;
- metabolic disorder;
- avitaminosis.
If myoclonus does not disappear for a long time, interferes with healthy sleep and contractions intensify, it is better to see a specialist and identify the cause.
Timely diagnosis will help prevent a number of hidden diseases.
Reasons why an adult twitches when falling asleep
Most often, when falling asleep, people experiencing chronic fatigue or stress startle. It has long been known that sleep consists of several phases. The transition from one of them to another takes about 2 hours, and the immersion in sleep itself occurs gradually. That is why, after a day full of emotional and physical stress, when it seems to us that we fall asleep only by placing our head on the pillow, we have not yet completely switched to sleep mode. Being in the phase of superficial sleep, a person continues to react to all many external factors: sounds, light and others that become irritants. When you fall asleep, the body relaxes, but the brain continues to work. Losing control over the body, it begins to send a signal to the nervous system, which causes a sharp short-term muscle contraction. This phenomenon is called myoclonus in medicine.
Treatment
It is worth noting that all medications must be taken after diagnosis and identification of the origin of involuntary muscle contractions.
Drug treatment is prescribed only by the attending physician, since there can be many causes of the syndrome.
Anticonvulsants from the Anticonvulsants group occupy the main place in the fight against spasms.
Among the medicines, antiepileptic drugs have proven themselves:
- Barbiturate;
- Clonazepam;
- Volproate;
- Benzodiazapine;
- bioactive supplement L-tryptophan;
- Tryptophan.
Treatment with traditional methods
The use of medicinal herbs reduces the occurrence of night tremors. They soothe muscles and improve the overall condition of the person:
- To prepare the infusion, use lavender, peppermint, valerian and primrose root. The ingredients must be mixed, take 0.5 teaspoon and pour a glass of boiling water. Infuse the resulting drink for at least an hour. When it is ready for use, you need to strain it and take 100 grams before bed.
- An infusion of young motherwort leaves has proven itself well. To prepare 0.5 liters of drink you will need 40-70 grams of fresh herbs. Filled with boiling water, it is infused for 4 hours. Strain the drink through cheesecloth or a sieve. Drink half a glass of herbal tea before meals 3 times a day.
- A water decoction cannot be stored for a long time, so in the folk treatment of shudders before bedtime, an alcohol tincture is used. Dry mistletoe leaves are mixed with alcohol in a 1:1 ratio. Leave in a dark place for 2 weeks. The alcoholic drink is filtered and used 10 drops for 10 days. Repeat course after 2 weeks. Store the tincture in the refrigerator.
- To prevent night twitching in a child, you should use an herbal infusion. Oregano, St. John's wort and blue cyanosis are taken in small quantities so that the entire collection fits into a tablespoon. Pour 1/4 liter of boiling water over the grass and leave for 24 hours. Drink 2 tablespoons of strained tea an hour before meals.
- Wormwood is actively used in folk medicine. Its calming properties help in treating the nervous system and muscle cramps. It is well suited for herbal tea, but has its downside - a bitter taste. It can be compensated by adding honey. Pour a teaspoon of wormwood into a glass of boiling water and leave for 25-30 minutes. Drink the infusion 3 times throughout the day.
In the treatment of night twitching, you can use relaxing oils for foot massage: lavender, mint, citrus. Warming your feet with mustard powder works well.
Any folk remedy has its contraindications, so do not neglect an in-person consultation with a doctor.
How to help a person get rid of myoclonus
If night trembling often bothers you and prevents you from getting quality rest, you need to follow a few simple rules:
- create and follow a daily routine. Determine the hours at which you need to go to bed and what time you need to wake up;
- You should not exercise intensely in the evening. If you wish, you can do a series of light relaxation exercises. But move exercises in the gym or fitness to the morning or afternoon;
- improve the microclimate in the bedroom and prepare a sleeping place, nothing should bother you, the bed should be comfortable and spacious;
- It is advisable to sleep in complete darkness without extraneous stimuli and noise. If this is not possible, there is an option to purchase a sleep mask and earplugs;
- Don't overeat at night. Eating fatty, high-calorie foods has a negative impact on your well-being. Fast carbohydrates are also not suitable, they immediately saturate the body with energy and provoke action;
- You should avoid drinking coffee drinks before your evening rest;
- Do not take energy drinks or alcohol at night;
- try to avoid stressful situations in the evening. If you have been too stressed during the day and cannot calm down even at night, try breathing exercises or meditation;
- give up computer entertainment before bed. They excite the nervous system and prevent sound, restful sleep.
Martial arts in the depths of the brain
The most common movement we make in our sleep is rapid eye twitching. When we dream, our eyes move according to what we are dreaming. For example, we see a tennis match in a dream, our eyes move, following it in flight. If you see that the sleeper's eyes are moving, this is the surest sign that he is dreaming.
- 630
More details - 171
More details
- 198
More details
- 234
More details
Hypnogogic seizures seem to be a sign that the motor portion of the nervous system retains some control over the body when sleep paralysis begins to take hold. Instead of one sleep-wake switch in the brain that controls our sleep, we have two opposing systems. They balance one against the other during the daily cycle.