Trembling inside the body can occur for various reasons. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital conduct a comprehensive examination of patients using the latest equipment from leading manufacturers in Europe, Japan, and the USA. After receiving the results of instrumental and laboratory studies, at a meeting of the expert council with the participation of candidates and doctors of medical sciences, doctors of the highest category, a collegial decision is made on further tactics for treating patients.
Body tremors can be a natural reaction to stress. With strong anxiety, the body increases the production of stress hormones - adrenaline and cortisol. They become the source of energy necessary to eliminate the situation that has arisen. An excess of completely unused internal energy causes tension and trembling within the body. Trembling in the body is observed in people who are trying to hide their emotions. In this case, unrealized hormones remain inside the body and cause overstrain, manifested by trembling of individual muscle fibers or muscle groups.
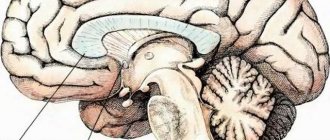
The cause of internal body tremors may be autonomic dysfunction. An imbalance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the autonomic nervous system can occur during chronic stress, depression, after suffering a severe infectious disease, or as a result of chronic somatic pathology. The cause of trembling inside the body can be pathological processes in the cerebellum, thalamus, hypothalamus, subcortex or cerebral cortex. Trembling in the body is one of the signs of complications of diabetes mellitus.
Under stress
Acute stress occurs due to a one-time exposure to a strong traumatic factor. It is accompanied by trembling in the body, psycho-emotional agitation or a depressive state. Chronic stress develops with prolonged exposure to unfavorable factors:
- interpersonal conflicts;
- tense family relationships;
- monotonous and unloved work;
- lack of vital interests;
- lack of personal communication;
- long absence of vacation.
Patients in a state of chronic stress are unsure of themselves and others. They experience nervous disorders and panic attacks, during which trembling occurs inside the body, increased sweating, and increased body temperature. Emotional lability, vulnerability, and touchiness develop.
To eliminate the symptoms of stress and tremors within the body, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe tonics and sedatives, herbal remedies, and vitamin and mineral complexes to patients. In the rehabilitation clinic, physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out to balance the processes of excitation and inhibition in the cerebral cortex. Psychotherapists use innovative psychological techniques.
For autonomic dysfunction
Autonomic dysfunction is a complex of clinical manifestations of a functional disorder of the autonomic nervous system, which entails disruption of the functioning of internal organs. This is a specific syndrome that can accompany any somatic pathology.
Violation of nervous regulation on the part of the autonomic nervous system can be provoked by one of the following factors:
- burdened heredity;
- hormonal dysfunction;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- organic brain lesions;
- unfavorable external factors leading to constant psycho-emotional stress.
Patients with autonomic dysfunction complain of rapid heartbeat, periodic feeling of a sinking heart, pain in the heart area. They are worried about rapid breathing, difficulty or inability to take a deep breath or exhale, a feeling of lack of air, and causeless attacks of shortness of breath. There are fluctuations in blood pressure, a feeling of coldness in the extremities, and periodic fluctuations in body temperature. The functioning of the digestive organs is disrupted - abdominal pain, constipation alternating with diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and belching occur.
Patients note general weakness, decreased performance, and lethargy. They experience excessive irritability, impaired sleep quality, frequent dizziness, a constant feeling of anxiety, and periodic trembling within the body. Diagnosis of autonomic nervous system dysfunction is often difficult.
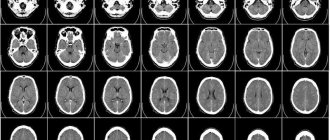
At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors conduct a comprehensive examination, including registration of an electrocardiogram, rheovasography, rheoencephalography, computer and magnetic resonance imaging. Patients in the neurology clinic are advised by cardiologists, endocrinologists, and gastroenterologists.
To treat autonomic dysfunction, neurologists use medication to relieve acute attacks. Patients are prescribed herbal medicines, physiotherapeutic procedures that improve sleep quality, diet therapy and physical therapy. Psychologists use innovative psychotherapeutic techniques.
Pulsation in the abdomen
Colitis
Gastritis
Atherosclerosis
17439 March 10
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Pulsation in the abdomen: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Normally, pulsation in the abdomen can be felt after a long stay in an uncomfortable position, playing sports, or when exposed to factors that irritate the nervous system. There is no cause for concern if the pulsation goes away on its own after a short rest on your back.
However, the sensation of a pulse in the abdomen can be a symptom of various diseases of the organs and systems of the abdominal cavity. The abdominal cavity is a container for many organs, such as the stomach, liver, gall bladder, and intestines; Important blood vessels (abdominal aorta) and lymphatic vessels and nerve bundles are located here.
Failure in the functioning of at least one of the organs that make up the abdominal cavity leads to functional disorders of varying degrees of severity.
Most often, it is impossible to independently identify the cause of pulsation in the abdomen; to do this, you need to consult a doctor, since in addition to “harmless” indigestion, the cause can also be more serious life-threatening conditions. Types of pulsation in the abdomen
Pulsation in the abdomen can vary in location: above the navel, in the solar plexus, to the right or left of the center of the abdomen.
Possible causes of pulsation in the abdomen
- Digestive disorders.
- Pregnancy.
- Features of the menstrual cycle.
- Pathology of the abdominal aorta.
- Tumors of the abdominal organs.
By indigestion
we mean pathologies of the stomach, intestines, pancreas of various natures and diseases of the biliary tract. Most often, gallbladder diseases do not manifest themselves as pulsations in the abdomen; the symptoms of these conditions are characterized by aching pain in the right hypochondrium, which in some cases becomes acute and unbearable (for example, with biliary colic), yellowing of the sclera and skin, etc.
The clinical picture of gastritis
include heaviness in the abdomen, pulsation in the epigastric region (the space located directly under the xiphoid process and which is a projection of the stomach onto the anterior abdominal wall), heartburn, nausea, in some cases vomiting, and loss of appetite.
When overeating due to overstretching of the stomach walls, pulsating sensations in the abdomen may also appear.
Colitis
is manifested by inflammation, constipation, diarrhea (or their alternation), the appearance of blood or mucus in the stool, discomfort and unpleasant sensations in the abdomen, weakness, and lack of appetite.
Provoking factors for colitis can be poor-quality food and water, as well as wearing tight, uncomfortable clothing that puts pressure on the intestines. Pulsation in the abdomen can appear in diseases such as Crohn's disease
(a chronic inflammatory disease of the gastrointestinal tract, characterized by damage to the epithelium of the intestinal tube and impaired digestion and absorption of nutrients) and
intestinal tumors
. With intestinal tumors, the following nonspecific symptoms are possible: upset stool, weight loss, decreased appetite up to aversion to food, a significant increase in abdominal volume.
The clinical picture of intestinal obstruction is as follows: impaired passage of feces and gases, pain and pulsation in the abdomen, in some cases there is a feeling of increased peristalsis, nausea, vomiting. The appearance of these symptoms in combination or separately requires immediate medical attention. Lack of proper treatment for the development of intestinal obstruction can cause severe complications and even death.
During
pregnancy
, as the baby develops and grows, the uterus enlarges. This process is accompanied by pressure on surrounding organs - the intestines, the bladder, which is manifested by frequent urination, pulsation in the abdomen, heartburn (in late pregnancy, which is associated with increasing intra-abdominal pressure).
Sometimes a woman mistakes the movement of the fetus for a pulsation in the abdomen. In the prenatal period, in the later stages, pulsating sensations in the abdomen may appear due to fetal hiccups. This condition is not pathological unless it is permanent.
During
menstruation,
the endometrium, the cells lining the inside of the uterine cavity, is renewed. During this period, the uterus contracts in waves, which in some women is accompanied by pain, and in others by a feeling of pulsation in the abdomen. This condition is physiological and does not require specific treatment. In cases where a woman acutely experiences the above symptoms during menstruation, which disrupts the usual rhythm of her life, it is advisable to consult a doctor to select optimal therapy.
Aorta
is the largest unpaired vessel in the human body. It is part of the systemic circulation, the main function of which is to provide all organs and tissues with oxygen-rich blood. The aorta is usually divided into three sections: the ascending aorta, the aortic arch and the descending aorta (divided into thoracic and abdominal).
The abdominal aorta supplies blood to the stomach, intestines, kidneys, spleen, as well as the testes in men and ovaries in women.
An aneurysm is a pathology of the vessel wall in which a peculiar protrusion, similar to a sac, is formed on it. The presence of an abdominal aortic aneurysm may be manifested by pulsating sensations in the abdomen. Abdominal pain is often absent or tolerable, but attacks similar to radiculitis or exacerbation of inflammation of the pancreas are also possible. Men over 60 years of age are more often affected, and most of them are long-time smokers. When the diagnosis is made late, the aortic wall becomes thinner, which can lead to rupture of the aneurysm during physical stress or even at rest.
Doctors include congenital pathology of connective tissue, diseases of an inflammatory nature (for example, aortitis), non-infectious (specific) inflammation (for example, Takayasu's disease), penetrating wound or blunt trauma of the abdomen, hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis (characterized by the deposition of cholesterol plaques in the vessels) as the causes of the development of aortic aneurysms. , which makes their walls less resistant to the effects of blood pressure).
Which doctors should I contact if I have pulsation in my abdomen?
If indigestion occurs, you should contact or. In cases where the disorder is infectious in nature, an infectious disease specialist will provide assistance.
In case of digestive disorders, accompanied by profuse vomiting, repeated loose stools, severe dehydration develops - this condition may require hospitalization.
Treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysm is usually performed by a surgeon.
During pregnancy, women are observed.
Diagnostics and examinations for pulsation in the abdomen
To diagnose gastritis or colitis, gastro- or colonoscopy (in some cases, studies are carried out with sedation) and ultrasound of the abdominal organs to detect tumors in the abdomen are widely used. When conducting endoscopic examinations, it is possible to take material to determine the cellular characteristics of the formation, which determines the tactics of further treatment.
For Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease is a chronic, steadily progressive degenerative disease of the central nervous system. Neurologists suggest that the pathological process develops under the influence of age-related, genetic and environmental factors. In Parkinson's disease, there is a deficiency in the production of dopamine, an excess of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine and the excitatory amino acid glutamate, as well as insufficient production of serotonin and norepinephrine.
Patients experience the following symptoms of the disease:
- hypokinesia (decreased motor activity);
- rest tremor (shaking inside the body);
- rigidity (plastic increase in muscle tone, increasing during the study);
- postural instability (characterized by staggering when walking, frequent falls).
Tremor is a regular, rhythmic, involuntary trembling of the limbs, head, facial muscles, tongue, and lower jaw. It is more pronounced at rest and decreases with active movements. In patients suffering from Parkinsonism, tremors begin in the distal part of one arm. As the disease progresses, it spreads to the opposite arm and lower extremities. The movements of the first, second and other fingers of the hand are multidirectional. They look like rolling pills or counting coins. Sometimes with Parkinson's disease there is a shaking of the head like “yes-yes” or “no-no”; patients’ eyelids, tongue, and lower jaw tremble. The tremor increases with excitement and practically disappears during sleep.
With Parkinson's disease, patients develop depressive states, cognitive and psychotic disorders. The disease is also characterized by autonomic disorders: decreased blood pressure with changes in body position, constipation, seborrhea, urination disorders, drooling, pain syndromes.
Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital take a differentiated approach to the treatment of each patient. If Parkinson's disease manifests itself in middle age or is at the initial stage of development, conservative drug treatment is prescribed:
- drugs with an antioxidant effect (monoamine oxidase (MAO) type B inhibitors, tocopherol, glutathione, thioctic acid, deferoxamine);
- DA receptor agonists (ADAR);
- dopamine transport inhibitors.
In severe forms and late stages of Parkinson's disease, neurosurgical treatment is carried out in partner clinics.
Essential tremor
Essential tremor is a serious disease of the nervous system that manifests itself as trembling inside the body. Minor nodding movements of the head are present both in a state of complete relaxation and under light loads. During the initial examination, neurologists also detect tongue tremor. Patients may experience increased muscle tone and a change in voice timbre. They feel a vibration that is not associated with excitement.
Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital perform computer or magnetic resonance imaging for patients with essential tremor. Depending on the results of the examination, drug therapy or surgical interventions are performed. Patients are prescribed beta-adrenergic blockers, sodium channel blockers, benzodiazepines and mediators of inhibitory processes in the central nervous system. As the symptoms of the disease progress, neurosurgeons at partner clinics perform surgical interventions: destruction of the ventrointermediate nuclei of the thalamus or hardware stimulation of the deep areas of the brain through the introduction of electrodes controlled by an implanted device.
If there is trembling inside the body, call the Yusupov Hospital. The clinic’s doctors will use modern diagnostic methods to determine the cause of your condition and provide comprehensive treatment.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis begins with a history and general examination of the patient. The range of other laboratory and instrumental methods is wide:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Biochemistry of blood.
- Ultrasound of the heart and blood vessels, abdominal organs, thyroid gland.
- Bicycle ergometry.
- Holter monitoring.
- X-ray of the chest organs.
- Spirography.
- Electrocardiogram.
- Study of the hormonal status of the body.
To clarify the diagnosis, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging may be required. If an oncological disease is suspected (with paraneoplastic syndrome), patients are prescribed a wide range of studies - ultrasound of the pelvic organs, invasive methods of examining the intestines, fibrogastroscopy with tissue biopsy.