The phenomenon of coma has been known since ancient times and is still not fully understood. The term is translated from Greek as “deep sleep.” In reality, a coma has very little in common with sleep; it is a dangerous near-death state.
The modern medical community views coma as a defensive reaction, which manifests itself in the loss of consciousness in response to critical disruptions in the functioning of the body. When a person remains unconscious for a long time, irreversible changes begin to occur in the body: reflex activity decreases, breathing becomes difficult, blood circulation is disrupted, and failures occur in almost all vital systems.
What causes coma: the main reasons
It is believed that a person can fall into a coma due to impaired blood circulation in the cerebral cortex. Another most common cause is toxic damage to cells of the central nervous system. Various diseases or injuries can provoke the occurrence of pathologies:
- strokes;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus;
- inflammatory diseases: meningitis, encephalitis;
- poisoning resulting in pathologies in the kidneys or liver;
- a series of consecutive epileptic seizures;
- hypoxia as a result of suffocation, drowning, cardiac arrest.
In medicine, there is such a thing as a medically induced coma. In this case, the patient is deliberately rendered unconscious using special drugs. This method is used for complex neurosurgical procedures, as well as to stop epileptic seizures in especially severe cases.
Funeral arrangements
Why do people fall into comas?
Comatose states can have different durations, but on average their duration reaches 1-3 weeks. How quickly a person will recover from a coma depends on the causes of its development, the volume and timeliness of treatment, as well as the severity of the patient’s condition.
Coming out of a coma is characterized by gradualness. First, reflexes and the work of the autonomic nervous system are activated. In this case, the patient often experiences delirium, erratic movements, and sometimes convulsions. Brain functions recover slowly, so the person spends a long time in the intensive care unit. He barely remembers how the coma began, and after it he can no longer recall what happened to him during the period of loss of consciousness.
Depth of coma
There is a widespread belief that a person always falls into a coma suddenly. However, this is not the case. In some cases, it can even develop over several days.
Comatose states are divided according to the degree of their depth. It is customary to distinguish several stages:
- Prekoma. It is characterized by the patient experiencing stupor, slowness of reaction, or, conversely, increased excitability. Basic reflexes are preserved, but mental activity is deformed.
- Superficial coma. The person is in a state of stupor or falls asleep. A complete blackout of consciousness does not occur; some simple movements are preserved.
- Deep coma. The patient spends all the time unconscious, muscle movement occurs reflexively. Reactions to external stimuli are weakened.
- Atonic coma. Reflexes disappear, all systems stop functioning independently, and the patient is connected to life support machines.
The last stage of a coma can most likely lead to death. However, medical practice knows cases when even the most severe patients were able to return to consciousness with partial or almost complete restoration of cognitive functions.
Hyperglycemic coma, symptoms and emergency care
In pathology, there are several stages, each of which has its own distinctive features.
- Previous stage. The precoma state can last from a minute to 2 hours. Signs include confusion, in which periods of lethargy are abruptly replaced by nervousness and agitation. Coordination of movements may be impaired.
- Coma 1st degree. It is characterized by symptoms such as increased muscle tone, tendon reflexes, and difficulty swallowing food. In this case, the pupil begins to react weakly to light.
- Stupor 2nd degree. The person is immobilized and has no contact with the outside world. The pupils narrow, there is no reaction to light, breathing is impaired. In rare cases, tension in the limbs may be observed, quickly followed by relaxation, and chaotic movements of the patient. Involuntary urination or bowel movements may occur.
- Coma 3rd degree. The person is unconscious, there is a decrease in blood pressure and body temperature. Interruptions in the respiratory rhythm and convulsions are possible.
- Stupor 4 degrees. There is no manifestation of any reflexes. Human life is supported only by medical equipment (ventilator and parenteral nutrition). The stage is characterized by the process of dying of the body.
The classification of pathology is based on the reasons that led to its development. There are the following types of comas:
- Diabetic. Pathology can occur in people suffering from diabetes. The cause is an increase in blood glucose levels. In this condition, the patient's mouth emits a strong odor of acetone.
- Hypoglycemic. It also develops in diabetic patients, but its cause is a decrease in blood glucose. Characterized by a strong feeling of hunger.
- Traumatic stupor. Occurs against the background of brain damage due to traumatic brain injury. A distinctive feature is the appearance of vomiting at the precoma stage.
- Meningeal pathology. It is observed in cases where the cerebral cortex is affected by meningococcal infection. The state of precoma is marked by severe pain in the head. The patient cannot raise his leg in a straight position. If you tilt the head of such a patient, his knees will bend. A rash may occur on the skin and mucous membranes of external and internal organs.
- Cerebral cerebral coma. Becomes a consequence of the development of tumors in the brain. The state preceding coma is accompanied by a gradual increase in headaches, vomiting, and difficulty eating. The same symptoms are characteristic of coma, which occurs against the background of a brain abscess due to inflammatory diseases (sinusitis, tonsillitis, etc.)
- Hungry stupor. The result of grade 3 dystrophy, which occurs after prolonged fasting. Most often it develops due to a lack of protein in the body, which is responsible for the functioning of vital organs, incl. brain.
- Epileptic stupor. Occurs after a severe seizure of epilepsy. It is characterized by dilated pupils, lack of reflexes, decreased blood pressure, etc. Without timely medical intervention, it can lead to death.
There is a food coma, which has nothing to do with loss of consciousness. This is the drowsiness that some people experience after or during a heavy meal.
Only a specialist can distinguish fainting from a coma state, so at the first symptoms of pathology you should call an ambulance.
Before doctors arrive, first aid for a coma is provided as follows: the patient is placed on his side to minimize the risk of the tongue sticking into the throat, the buttons on the chest are unbuttoned, and the collar is loosened. If a person regains consciousness, you should find out what sensations he experiences, what chronic diseases he has.
Measures to maintain the functionality of vital organs can be reduced to supporting breathing, the circulatory system, therapy with anticonvulsants, antiemetics, sedatives and other drugs. Gastric lavage, administration of glucose, vitamins, etc. can be performed.
After complex treatment has been completed, the patient has emerged from a comatose state, he may suffer from memory impairment and lack of concentration. A person may not have psychological problems until a coma sets in, and after it they appear (aggression, irritability, development of depression).
Coma is an extremely serious condition of a person who has lost consciousness. Coma is accompanied not only by loss of consciousness. Depending on the degree of coma, brain functions are switched off, all body functions and metabolism slow down or almost stop, and the nervous system suffers significantly. In some cases of coma, the brain, which does not receive enough oxygen, begins to die.
Causes of coma
Brain damage due to any trauma;
Intoxication with alcohol or drugs;
Drug intoxication;
Prolonged lack of oxygen supply to the brain;
Infections that affect the brain;
Bleeding in the brain;
A person may fall into a coma if they have a stroke.
Degrees of coma and their causes
First degree coma
The patient speaks slurred. Reacts to pain. The reaction of the pupils is weak. It is quite possible to bring a person out of a first-degree coma.
Second degree coma
The patient is in a state of sleep. He hardly responds to physical stimuli. His thought processes are slow. Blood pressure decreases. All body functions are inhibited. It is possible to bring a person out of a coma, although it is extremely difficult.
Third degree coma
The person is in a deep state of sleep. He does not react to any stimuli, his mental activity does not work. Sometimes a person in a state of third degree coma reacts to pain, but very rarely. In this case, a person is not able to control his natural processes of urination and feces.
Fourth degree coma
The patient’s reflexes and reactions are absent, there is practically no breathing, or breathing is completely supported by the artificial life support system. The heartbeat is uneven and the blood pressure is very low. At this stage, the brain begins to deteriorate. This is the stage of the deepest coma. Unfortunately, it is impossible to bring a person out of this coma.
Brain function deteriorates depending on the severity of the coma. In the first degree, brain functions are slightly damaged, and in the fourth degree they cannot be corrected.
How can you bring a person out of a coma?
Today there is no answer to the question: how to bring a person out of a coma. Medical workers advise relatives to stay close to the person, talk to him as if he is conscious, read books to him, and take his hand. It is possible that any sound or action will be a stimulus for him to come out of the coma. There was a case when the daughter of a man who fell into a coma played a musical instrument for him, and thanks to this he woke up.
Usually this condition lasts no more than three weeks, although it happens that a person is in a coma for up to several months or even years. The longest coma lasted 37 years. When awakening, a person will not wake up as in the fairy tale about the sleeping beauty and will not immediately get to his feet. Don't expect him to immediately speak and start functioning as before.
Often, when a person wakes up, he does not understand where he is or how he got to the hospital. He needs the support of his family and friends to restore his mental functions. Therefore, you should not despair if your relative or loved one is in such trouble; you should not bury him in advance. Have patience and faith that he will again live a full life, as before.
On average, a coma lasts 1-3 weeks. However, there are often cases when it lasts for a longer time - people can lie unconscious for years.
The patient's return to consciousness occurs gradually. At first he comes to his senses for a couple of hours, then this time increases more and more. As a rule, the body goes through several different stages during this time. And the consequences will depend on how he copes with the load placed on him.
Since the brain is affected during a coma, one should be prepared for the fact that the patient may not recover many vital functions. For example, quite often people cannot walk, talk, move their arms, etc. Naturally, the severity of the damage directly depends on the degree of coma the patient was in.
Among the most common problems faced by a person who has been in a coma are memory impairment, decreased attention, and various changes in behavior (lethargy, aggressiveness, etc.). Sometimes relatives do not even recognize the person close to them.
Also, after a coma, many patients take a long time to restore everyday skills. For example, they cannot eat on their own, wash themselves, etc.
One of the signs of a person's recovery and recovery after a coma is the desire for some kind of activity. However, in this case, you should not be overly happy and immediately give the patient maximum loads - too abrupt a return to normal life can have a negative impact on his condition and lead to a noticeable deterioration in well-being.
The role of communication with a person in a coma
There is no consensus on the benefits of communicating with a person in a coma. However, scientists have reason to believe that, to some extent, the patients' subconscious retains the ability to perceive external signals.
The patients themselves, who were lucky enough to emerge from a comatose state, report that their sensations were close to falling asleep. None of the respondents could accurately describe what happened while they were unconscious.
Although the benefits of communicating with comatose patients have not been proven, family members and acquaintances often express a desire to maintain contact with their loved ones. In this case, the recommendations are as follows:
- Introduce yourself and share positive news. You should maintain a calm, measured tone and an average volume of your voice.
- It is better to conduct a conversation with a patient in a coma as if he were conscious and acting as a listener.
- Relatives can express their support by sitting next to, touching, or holding the patient’s hand. Sometimes relatives read books aloud.
- There is a theory about the beneficial effects of music. People who are unconscious are allowed to play their favorite songs in their headphones.
Characteristic signs of coma
- Doctors should also pay attention to the patient’s body position. Typically, the appearance of a patient with his head thrown back and increased muscle tone indicates the onset of an irritated state of the lining of the brain. The latter is typical for meningitis or cerebral hemorrhage.
- Cramps throughout the body or in individual muscles indicate that the cause of the coma was most likely an epileptic seizure or a condition of eclampsia (manifests in pregnant women).
- Mild paralysis of the upper or lower extremities clearly indicates a stroke. In the case of a complete absence of any reflexes, they speak of severe, deep-seated damage to a large type of surface of the cortex or damage to the spinal cord.
- The most important thing when carrying out a differential diagnosis of coma is to establish the patient’s ability to open his eyes or respond to sound (pain, light) stimulation. If the reaction to a painful or light stimulus manifests itself as a voluntary opening of the eyes, then the patient is not in a state of coma. And, on the contrary, if the patient, despite the efforts and efforts of the doctors, does not react and does not open his eyes, then they speak of a comatose state present.
- Studying the reaction of the pupils in case of suspected coma will be mandatory. Features of the pupils will help determine the probable location of damage in the brain, as well as determine the cause that caused this condition. It is “testing” of the pupillary reflex that is one of the most reliable diagnostic studies, which can give an almost 100% prognosis. If the pupils are narrow and do not react to light, this indicates possible poisoning of the patient with alcohol or drugs. If the patient's pupils are of different diameters, then this indicates increasing cranial pressure. Wide pupils are a sign of a diseased midbrain. If the diameter of the two pupils dilates equally, and the reaction to light is completely absent, then they speak of an extreme type of coma, which is considered a very bad sign, which most often indicates a possible imminent brain death.
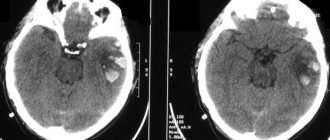
Modern medicine has made a breakthrough in instrumental diagnostics, making it possible to correctly determine the causes that contributed to the coma. It is also possible to correctly identify any other type of impairment of consciousness. With the help of CT or MRI, it is possible to most accurately determine the structural changes that have occurred in the brain, determine the presence or absence of tumors of a three-dimensional type, and also establish the characteristic signs of increased intracranial pressure. Depending on what the images show, the doctor makes a decision on further therapy, which can be conservative or surgical.
If there is no possibility and conditions to conduct CT and MRI diagnostics on the patient, then radiography of the cranial cavity is performed (or an image of the spinal column is taken). Taking a biochemical blood test will help characterize the metabolic process of coma. In some cases, a test may be performed to determine the level of glucose and urea present in the blood. A separate analysis is carried out for the presence of ammonia in the blood. In addition, it will be important to determine the percentage of gases and electrolytes in the blood.
If CT and MRI do not reveal an obvious disorder on the part of the central nervous system, then the reasons that could put the patient into a coma themselves disappear. Next, doctors test the blood for the presence of hormones such as insulin, thyroid and adrenal hormones. In addition, a separate analysis is carried out that can determine the presence of toxic substances (sleeping pills, drugs, etc.) in the blood. This is a bacterial blood culture.
EEG is considered one of the important diagnostic studies that can differentiate coma from other types of consciousness disorders. To carry it out, an electrical recording of the brain potential is made, which helps to determine coma, distinguishing it from a brain tumor, drug poisoning or hemorrhage.
How is rehabilitation after a coma?
Bringing a patient out of a coma is often not an easy task. However, doctors are making every effort to ensure that consciousness is restored and the person can return to a full life. For this purpose, various drug therapy regimens are used. In case of a favorable outcome, subsequent rehabilitation is carried out.
The main task at this stage is to create in the patient the mood for a complete recovery and return to his former life. Often, a comatose state and subsequent treatment becomes a difficult experience for a person, and he needs the help of specialists. You should seek support from specialized rehabilitation centers.
In Belarus, in 2004, a medical rehabilitation center was formed on the basis of the Republican Clinical Hospital in the village of Aksakovshchina, Minsk region. Anyone in need can get help here for free.
Treatment of coma
Treatment of a comatose state should take place in two directions: on the one hand, maintaining the vital functions of the human body in order to prevent possible brain death; on the other hand, treatment is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause that contributed to the development of the coma.
The first route, aimed at maintaining vital functions, usually begins in the ambulance. First aid is carried out to all patients without exception, long before test results are received.
This involves performing procedures aimed at maintaining normal airway patency:
- correction of a sunken tongue;
- cleansing the oral and nasal cavities from vomit present in them;
- use of an oxygen mask (if required);
- use of a breathing tube (in the most severe cases).
In addition, it is necessary to establish normal blood circulation by administering antiarrhythmic drugs that will help normalize blood pressure. The patient may also undergo cardiac massage.
In intensive care, the patient can be connected to an artificial respiration apparatus, which is done in extremely severe comatose states. If there are convulsive characteristics, it will be necessary to introduce glucose into the blood and normalize body temperature. For this, the patient is covered with a warm blanket or placed around with heating pads. If the patient is suspected of being poisoned with narcotic or sleeping pills, the stomach is washed.
The second stage of treatment involves performing a thorough examination using highly qualified tactics, which will depend on the root cause that caused the coma. If the cause is a brain tumor or a resulting hematoma, then surgery should be immediate.