One of the symptoms of tumors in the brain is headaches, accompanied by visual disturbances, clouding of consciousness, causeless vomiting and other symptoms. Only a doctor can reliably assess the clinical picture, therefore, if characteristic sensations appear, it is necessary to contact a medical institution and conduct a series of studies. In the vast majority of cases, the causes of pain are non-oncological in nature, but you can only reliably find out during a medical examination.
What can headaches mean?
Cephalgia itself is not a typical sign of cancer and is considered exclusively in conjunction with other symptoms. Headaches can also be caused by other reasons, the most common of which are:
- migraines, which are characterized by attacks of throbbing pain that last for several days;
- hypertension, in which pain is localized in the back of the head and parietal area, occurring with sudden jumps in blood pressure;
- VSD and other vascular diseases;
- neurological diseases - pinched nerve roots, vertebrogenic neuralgia, etc.;
- viral or colds, characterized by a sharp increase in temperature;
- inflammation of ENT organs;
- cranial injuries and post-traumatic pathologies;
- stress, overwork, overheating, etc.
It is important to distinguish symptoms characteristic of tumor development from other types of headaches.
Symptoms
Signs of brain cancer are divided into general cerebral, i.e. manifested in all types of disease without exception, and focal ones, from the totality of which one can form a primary idea of the localization of the neoplasm.
Common symptoms of a brain tumor that appear as a result of increased intracranial pressure include:
- the appearance of constant headaches, which intensify with sudden movements of the head and are not relieved by medications;
- sudden dizziness, nausea and vomiting, fainting;
- feeling of constant fatigue, drowsiness;
- the appearance of problems with visual perception – blurred pictures, “sights”, hallucinations;
- violation of spatial orientation and coordination.
In turn, focal symptoms of brain cancer depend on the location of the tumor and allow localization of the pathology:
- in the forehead area - due to weakening of one half of the body, loss of smell, change in the patient’s character;
- in the temple area - for convulsions, speech disorders, developing forgetfulness;
- in the crown area - for speech impairment, loss of sensitivity of half the body;
- in the occipital lobe - due to loss of vision in one of the eyes;
- in the cerebellum - by vibration of the eyeball, lack of coordination of movements, spasm of the neck muscles;
- in the brain stem - due to unsteadiness of gait, disturbances in swallowing and difficulty speaking, weakness of the facial muscles.
In order not to miss the onset of the disease, if even one or two of the first signs of brain cancer appear, you must consult a neurologist and undergo an examination.
What kind of headache is it like with a brain tumor?
Pathological neoplasm cells, growing inside the skull, compress the walls of blood vessels, deform and compress the meninges. This leads to increased intracranial pressure, which causes severe headaches. For primary tumors of brain tissue, cephalgia is often the only sign of the development of pathology. It is necessary to undergo examination if:
- the head begins to hurt during sleep or in the morning, from the moment you wake up;
- the pain intensifies when you lie down, as well as when coughing and sneezing, during physical activity;
- pain sensations are bursting, pulsating or squeezing in nature;
- pain is accompanied by double vision, confusion, irritability to the point of aggression, dizziness;
- seizures similar to epileptic ones appear;
- From time to time, causeless nausea occurs, after painful bouts of vomiting, some relief is felt.
Attacks of cephalalgia intensify as the tumor grows. If at first they can be stopped by taking corticosteroids and diuretics, then over time the effectiveness of these drugs weakens.
Common symptoms of a brain tumor
Any brain tumor manifests itself with signs that can be divided into three groups:
- Discomfort associated with increased pressure inside the skull due to neoplasm and swelling. The patient complains of headache, periodic dizziness, problems with attention and memory, nausea and vomiting, disturbances in thinking and consciousness.
- Symptoms associated with dysfunction of certain nerve centers that are destroyed due to compression of the adjacent areas of the brain by the tumor. Noticeable disturbances depend on the location of the formation, so seizures with convulsions, disturbances in the movement of certain muscle groups, disturbances in sensitivity, speech function or vision may occur.
- A group of symptoms caused by brain misalignment. This means deterioration of the condition and the risk of a threat to life. Signs include poor eye coordination, neck pain and tension, vomiting, breathing problems, and fainting.
Not every tumor is benign. At the slightest suspicion of the presence of a tumor in the brain, it is important to visit a doctor and undergo an examination.
How are cerebral tumors diagnosed?
If you experience headaches that resemble the symptoms described above, you should visit a doctor as soon as possible. In a public clinic, you should first contact a general practitioner, who will perform an initial examination and refer you to a neurologist to rule out other causes of cephalgia. Often, a neurologist can determine the presence of a brain tumor after an initial examination and studying your reflexes, reactions to auditory and tactile stimuli, checking coordination and motor activity. In doubtful cases, the doctor issues a referral for research:
- echo-encephalography to assess intracranial pressure;
- electroencephalography to measure the functional activity of the brain using its bioelectric signals;
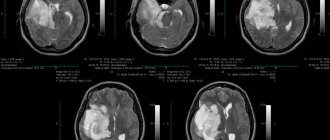
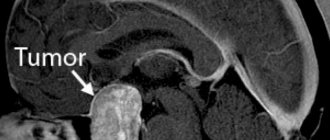
- computed tomography to visualize the tumor and identify concomitant pathological processes in brain tissue;
- magnetic resonance imaging for a more accurate assessment of the spread of the oncological process.
At the same time, ophthalmological examinations are carried out, during which your visual acuity is checked, visual fields are determined, and ophthalmoscopy is performed. In addition to standard tomography, MRI of cerebral vessels and other specialized magnetic resonance studies may be prescribed. In some cases, diagnosis requires a stereotactic biopsy and histological examination of brain tissue. After the final diagnosis is made, treatment is already completed by an oncologist.
Persistent headaches are a reason to go to the clinic
Constant headache is a serious symptom that should never be ignored. A specialist – a neurologist – must determine its source. A competent doctor in this specialty knows well how headaches occur with a brain tumor, so he is able to draw certain conclusions already during the initial consultation and prescribe an adequate examination.
However, when visiting a doctor, a person often gets worried, gets lost, does not clearly formulate his complaints, and forgets important details. To prevent this from happening, it is useful and proper to prepare in advance. Make a list of questions you want to ask your doctor, including:
- describe your feelings as fully as possible;
- indicate what leads to increased pain and its decrease;
- list the medications that do not help and those that help (if any);
- mention what is accompanied by a headache - nausea and vomiting, dizziness, tingling, numbness, impaired balance, speech, vision, etc.
If you need a second opinion to clarify your diagnosis or treatment plan, send us an application and documents for consultation, or schedule an in-person consultation by phone.
+7 499 490-24-13
Expert opinion
Why early diagnosis is so important
A feature of tumor processes localized in brain tissue is their location in the space limited by the walls of the skull (intracranial). Because of this, even a benign tumor after a certain time becomes life-threatening for the patient, since its growth leads to compression of cerebral tissues and an increase in intracranial pressure.
According to medical statistics, brain tumors account for about 6% of all tumor pathologies detected by oncologists. Out of every 100 thousand people, 10-15 patients are diagnosed with a cerebral tumor. However, existing methods of treating cerebral oncological diseases can guarantee a patient's life extension by more than 10 years only in the first stage of the disease. An operation performed at the second stage of tumor development prolongs the patient’s life by 5-10 years. When a tumor is detected in the third and fourth stages of the disease, the prognosis is almost always disappointing.
To exclude an unfavorable outcome, it is necessary to undergo an annual check-up of your health status. Modern diagnostic equipment allows you to detect pathological neoplasms even before you develop warning symptoms. The examination will help identify a health problem at a stage when it can be successfully eliminated. Don’t give the disease the slightest chance to defeat you, do a check-up right tomorrow.
What is a brain tumor
A brain tumor refers to all neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature that develop in the brain organ itself (primary) or as a result of metastasis of cancer that has affected another organ (secondary). Secondary pathology is always malignant, while primary pathology can be benign or cancerous.
Making an accurate diagnosis and determining the type of tumor is difficult due to the variety of symptoms, difficult access to the affected organ, anatomical features and the functioning of an important element of the central nervous system.
It is important to know that oncological tumors grow rapidly and are difficult to treat. While non-cancerous ones grow more slowly, and early detection allows for complete recovery. Over time, a benign neoplasm can develop into a malignant one.
The danger of any cancer lies in its long-term latent course. Symptoms appear as the pathology develops, and, unfortunately, when all the signs are present, the survival prognosis is disappointing. This is why it is important to pay attention to changes in your health and know the symptoms of a brain tumor.
Diagnostics
Due to the fact that the tumor is located inside the skull, it is difficult to diagnose this disease in a timely manner. Sometimes large tumors give sparse symptoms, while small ones are accompanied by vivid symptoms. While the symptoms are mild, patients rarely see doctors; a person seeks help from a specialist only when their health begins to rapidly deteriorate.
Typical cerebral symptoms are:
— Headache is the most common and early symptom of a brain tumor. The pain can be dull, intermittent, or bursting. The appearance or intensification of pain in the second half of the night or in the morning is typical.
Typically, headaches arise or intensify during stress and physical exertion.
- Vomiting is also a typical symptom, most often occurring in the morning, on an empty stomach and against the background of a headache. Vomiting is not associated with food intake and occurs without nausea. Sometimes vomiting occurs due to a change in head position. Vomiting is observed as an isolated symptom in children.
Article on the topic
Early diagnosis of cancer.
What tests should be taken regularly? - Dizziness , a feeling of spinning objects or your body, as if the ground is moving away from under your feet.
Occurs in the form of attacks, with a certain position of the head. This symptom usually appears in the later stages of the disease.
- Mental disorders - against the background of clear consciousness, there are disturbances in memory, thinking, perception, and the ability to concentrate. Patients cannot remember the names of loved ones, their address, have poor orientation in space and time, become irritable, frivolous, aggressive, prone to unmotivated actions, manifestations of negativism, or apathetic, lethargic. Delusions and hallucinations are sometimes observed.
- Convulsive (epileptic) seizures - may be the first symptom of the disease, especially if they occur without an apparent reason for the first time after the age of 20. The frequency of seizures usually increases.
- Problems with vision - a feeling of fog before the eyes, flashing spots. Usually the symptom is observed in the morning. There may be a decrease in visual acuity, which without intervention can lead to optic nerve atrophy and blindness.
The patient may also complain of a lack of pain or tactile sensitivity, hearing or speech impairment, and hormonal disorders. It may be difficult for the patient to maintain balance, especially with their eyes closed.
Article on the topic
Cancer detected at an early stage is curable. How to examine a child? The speed and intensity of the development of symptoms depend on the location of the tumor and the characteristics of its growth, and it is on the basis of these symptoms that the location of the tumor is determined. In fact, neoplasms can put pressure on some parts of the brain, which leads to obvious symptoms.
If you have at least a few of the listed symptoms, you should contact a therapist, who will assess the patient’s condition and refer for tests necessary to identify oncological pathology.
Mandatory examination methods include determining the activity of tendon reflexes, testing tactile and pain sensitivity. If a brain tumor is suspected, the patient is referred for computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Based on the results of these studies, a decision is made to hospitalize the patient in a specialized hospital. The oncology clinic conducts examinations, the purpose of which is to confirm the diagnosis and decide on the patient’s treatment tactics.