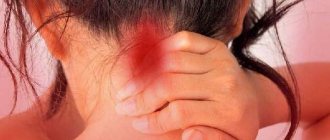
Pain in the back of the head is a fairly common problem. And she has many reasons. Therefore, it is important to find their problems in order to feel relief. Let's find out together with a specialist how to do this.
Headaches in the back of the head can have several different causes. For example, it may only be muscle damage due to a minor injury, or it may be a secondary symptom of other pathologies. The type and location of pain can play a critical role in diagnosing the cause. If the pain is severe and repeated, be sure to consult a doctor.
Causes of pain in the back of the head in an adult
“Pain in the back of the head itself does not indicate the cause of this pain,” explains neurologist Elena Gaivoronskaya.
– The doctor assesses the frequency of pain, its intensity, duration, nature (pulsating, pressing, stabbing), associated symptoms. Only on the basis of all this data can a diagnosis be made. There are a number of reasons why headaches may occur predominantly in the back of the head.
headaches .
This is the most common cause of pain in the back of the head. Such pain can last from 30 minutes to 7 days. Such pain can be caused by severe stress, overwork, lack of sleep, malnutrition, poor posture or not drinking enough water.
Patients with this problem usually feel tension in the back or front of the head. The pain can range from dull to severe.
Migraine.
Another common type of headache that often appears in childhood and gets worse with age. Migraines are most common in women. Its symptoms include severe pain on one side of the head with nausea, vomiting and blurred vision. Patients are usually sensitive to light, noise, or smell. Physical activity may increase pain. It can last from several hours to several days.
Causes of migraines include emotional or physical stress, environmental and dietary changes. Sometimes medications (such as birth control pills) can also cause migraines.
Overuse of medications or recurring headaches.
These headaches can develop if a person takes too many painkillers. They are very strong and are often accompanied by nausea, anxiety, irritability, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, memory loss and even depression.
Occipital neuralgia.
A rare but severe headache that usually begins at the base of the neck and spreads to the back of the head and then behind the ears. Often occurs when the occipital nerves, which run up the back of the neck to the base of the skull, are damaged or irritated. The pain is accompanied by a burning or shooting sensation and persists on one side of the head, but often intensifies with movement of the neck. The patient is usually sensitive to light.
Possible causes include spinal injury, tumors, nerve damage caused by diabetes, swollen blood vessels, and rarely infection.
Headaches during physical activity.
They occur as a result of stressful activities and often occur after physical exercise. This pain resembles palpitations and can last from 5 minutes to 2 days.
Often occurs after heavy weight exercise or running. But sometimes they happen after sexual intercourse or pushing in the toilet.
Headache due to arthritis.
It appears in the back of the head and intensifies with movement. May be the result of arthritis of the first, second or third vertebra. Either it is associated with changes in the bone structure of the neck or inflammation of the blood vessels in the head.
In addition, the cause of a headache in the back of the head can be:
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- high blood pressure;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- stress;
- brain tumors;
- brain aneurysm;
- subarachnoid cerebral hemorrhage;
- cervical spine injuries and traumatic brain injuries;
- meningitis.
Pain at the base of the skull
Rheumatism
Arthritis
27968 11 February
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Pain at the base of the skull: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
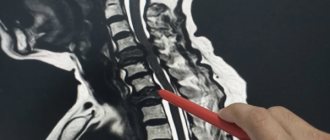
Pain at the base of the skull (vertebrogenic cervicocranialgia) is a pain syndrome localized in the cervico-occipital region, which can spread to the frontotemporal region and the eye area on the homolateral side. It has been proven that the source of pain can be the structures of the upper cervical spine. Typically, this is the level of the C1, C2 and C3 vertebrae, which includes joints, discs, ligaments and muscles. The lower cervical vertebrae, as a rule, play an indirect role in the formation of clinical symptoms of pain.
Pathological diseases of the cervical spine, which are accompanied by intense or aching pain, experts call “painful neck” syndrome.
The International Headache Society, 3rd revision (ICHD-3) recommended considering cervicogenic headache as secondary, arising due to changes in the cervical spine, including bone structures, intervertebral discs, and soft tissue structures, the pathology of which is often accompanied by pain in the cervical spine. neck. 70% of patients with pain in the cervical spine simultaneously experience headache, but only in 18% of cases is it considered a consequence of neck pain.
In the genesis of headaches in childhood and adolescence, functional disorders in the spinal motion segments of the cervical spine, in particular disorders in the structures of its upper cervical spine, play a significant role.
Types of pain at the base of the skull
Cervicogenic pain is indicated by differential features such as unilateral headache extending from the back of the head to the front, and evidence of involvement of the cervical spine. An attack of pain can be triggered by applying pressure to trigger points in the neck/occipital area or holding the neck in an awkward position. It is important that in some cases such pain has migraine-like features - a number of patients experience photo- and phonophobia, lacrimation, nausea, vomiting, which can sometimes be regarded as a manifestation of migraine.
Pain at the base of the skull is characterized by limited range of motion in the cervical spine, soreness of the neck muscles, changes in muscle tone, or a reaction to passive or active stretching. Usually the pain is combined with a functional block at the upper cervical level.
Injuries to the upper cervical spine due to tumors, fractures, infections, and rheumatoid arthritis can cause headaches that present clinically in the same way as cervicocranialgia. However, a feature of cervicogenic headache is that it is provoked by movements in the cervical spine, and after performing certain warm-up movements in the neck it can stop. Most often, such complaints are not associated with serious pathology, and the patient makes a full recovery.
Possible causes of pain at the base of the skull
Pain at the base of the skull is based on functional and organic changes in various anatomical structures of the cervical spine: joints, ligaments, fascia, muscles, nerves. The leading role is given to degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine. However, there are only isolated indications of the role of functional disorders.
One of the main causes of neck pain is staying in a fixed position for a long time. Other causes of the disease include:
- osteochondrosis, spondyloarthrosis, spondylosis, uncovertebral arthrosis and other changes in the spine;
- neck injuries, injuries;
- sprains;
- intervertebral disc herniation;
- spondyloarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis.
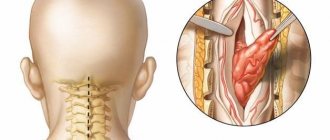
A common cause of cervicogenic pain is inferior oblique muscle syndrome.
A spasmed muscle can compress the neurovascular bundle passing under it (segment of the vertebral artery with the periarterial sympathetic plexus, occipital nerves) - for this condition, the development of paresthesia in the scalp is typical, and sometimes there is pain when combing the hair. It has been observed that stimulation of the cervical structures causes pain, and anesthesia reduces it. Lately, doctors are increasingly talking about “text neck” syndrome, which develops in people who spend a lot of time reading texts from electronic devices (gadgets).
The head of an adult weighs about 5 kg - this is the weight the neck experiences in its normal position. When reading from gadget screens, the head is usually tilted: when tilted just 15°, the load on the spine increases to 12 kg, and when tilted 60° – up to 27 kg. As a result, posture changes, the intervertebral discs of the cervical spine suffer, muscles spasm, and pain occurs at the base of the skull.
The main manifestations of pain at the base of the skull include:
- frequent contraction of the neck muscles, convulsions;
- painful sensations when turning the head;
- noise in the head, sleep disturbance;
- pain in the cervical spine, radiating to the head;
- dizziness;
- constant tension in the neck and back of the head.
The presence of three to four signs should make the patient think about seeking medical help.
Which doctors should you contact if you experience pain at the base of the skull?
To determine the cause of the headache, you should contact a general practitioner or. The doctor will prescribe the necessary examination, determine the cause of the disease and prescribe treatment.
Diagnosis and examinations for pain at the base of the skull
The following diagnostic criteria are used to make a diagnosis:
- The causal relationship of headache with pathology of the cervical region is based on at least one of the following signs:
- clinical signs confirm that the source of pain is located in the neck;
- pain stops after diagnostic blockade of neck structures or nerve formations (with an adequate comparative study with placebo).
Using clinical, laboratory and/or neuroimaging methods, signs of disorder or damage in the cervical spine or soft tissues of the neck that are a reliable or possible cause of headache are determined:
- X-ray of the cervical region in several projections;
Modern methods of treatment
Treatment methods depend on the diagnosis.
Tension headaches.
They are usually treated with painkillers, massage and sometimes meditation. However, frequent tension headaches require medical supervision.
Migraine.
Treatment for this disease includes painkillers and rest in a darkened room. Doctors often recommend lifestyle changes, hormone therapy, and anti-migraine medications such as triptans to reduce the frequency and intensity of migraines.
Returning pain.
The best treatment for this type of pain is to stop taking painkillers. Yes, at first the headaches get worse, but they go away quickly.
In severe cases, you should consult a doctor - physical or behavioral therapy may be required to break the habit of using analgesics.
Occipital neuralgia.
It can be treated with heat compresses, rest, massage, physical therapy or painkillers. Severe pain may require oral muscle relaxants, nerve blocks, steroid injections, or local anesthesia. In rare cases, surgery is necessary to relieve pressure on the nerves or block pain impulses to that part of the body.
Pain during physical activity.
Taking painkillers before exercise can solve this problem. In addition, it is important to avoid stress, eat right and get enough sleep.
Diagnostic methods
Timely diagnosis will allow you to determine the exact cause of pain in the right side of the back of the head and begin treatment. This will require an examination by a therapist, neurologist, traumatologist or other specialists as indicated. Additional examinations are also prescribed that are aimed at detecting or excluding specific diseases:
- X-ray of the cervical spine is the main method for diagnosing injuries, fusion of the vertebrae, and their deformation;
- MRI, CT of the neck and head are the most accurate, informative methods, thanks to which you can detect diseases of blood vessels and soft tissues, as well as neoplasms, cysts, aneurysms;
- blood tests will show the presence of an inflammatory process, and will also indicate diseases of the internal organs;
- Dopplerography - examination of blood vessels using ultrasound after adding a contrast agent.
A simple examination will not help determine the reasons why the right back of the head hurts. This will require various instrumental examinations and analyses, the accuracy of which depends on the quality of the equipment and the qualifications of specialists. The Clinical Brain Institute has modern equipment for diagnosing diseases of the neck and head, and also employs doctors with many years of experience. This makes it possible to identify complex diseases in the early stages and successfully treat them without complications.
Popular questions and answers
We asked neurologists to answer questions related to headaches in the back of the head.
When can a headache in the back of your head be dangerous?
“Such symptoms,” says neurologist Olga Zincheva, “can include:
- concomitant increase in body temperature;
- weakness, awkwardness;
- numbness and tingling in the limbs or one limb;
- prolonged increase in pressure, difficult to reduce;
- severe headaches;
- headaches are accompanied by nausea and vomiting;
- double vision, impaired consciousness.
When to see a doctor for a headache in the back of the head?
“There are signs,” explains Olga Zincheva, “that require medical attention:
- you have a headache for the first time for no apparent reason;
- pain lasts several days;
- there are concomitant diseases.
“You need to go to the hospital immediately,” adds colleague Elena Gaivoronskaya, “if the headache occurs suddenly, it is very intense, there was no such pain before, or if the pain is accompanied by weakness in the limbs on one side of the body, a distortion of the face, speech disorder, or lack of coordination. If you have other alarming symptoms, you should consult a doctor as planned. You should also see a neurologist if you are taking too many pain medications or if your headaches are affecting your quality of life.
Treatment of pain in the back of the head
Pain in the right occipital part of the head is not a separate disease, but one of the symptoms of a number of pathologies. The set of techniques will include techniques to relieve symptoms and to eliminate the main cause of pain in the back of the head on the right. Most of them are available at home, but are carried out only with a doctor's prescription.
- Drug treatment is the main stage. The patient is prescribed muscle relaxants, drugs to correct blood pressure, substances to improve blood supply and nutrition to the brain. Additionally, medications may be prescribed to improve lipid metabolism and remove bad cholesterol, and medications to nourish intervertebral cartilage.
- Massage and physical therapy are an important step for neck diseases, spinal curvatures, and osteochondrosis. You can do it yourself, at home, but massage is only effective if performed by a specialist.
- Diet is necessary for atherosclerosis, osteochondrosis and other diseases. The patient's diet should contain a large amount of fiber and vitamins. You should avoid spicy, fatty foods, and excess animal products.
- Physiotherapy is effective for muscle and vascular spasms, chronic diseases of the cervical spine. The procedures are carried out in a course, with an interval of several days. Exposure to heat, laser, ultrasound, electric current or magnetic radiation stimulates blood circulation and regeneration processes.
In most cases, treatment is carried out with medications that the patient must take at home. However, in case of exacerbation of diseases, suspicion of the development of complications, as well as for additional diagnostics, the Clinical Institute of the Brain has the possibility of inpatient treatment and examination. This allows you to be under the supervision of qualified doctors and staff around the clock and accurately track the dynamics of disease development.