What is vasovagal syncope
A short-term loss of consciousness with vasovagal syncope occurs when a person takes an upright position. Such phenomena occur due to stimulation of the vagus nerve, which innervates the chest, neck and intestines.
Vasovagal syncope occurs when a person is in an upright position at a time when, due to stimulation of the vagus nerve, the lumen of the blood vessels dilates and the pulse rate decreases.
The cause is usually stress, severe emotional shock, hunger, and external influences.
For differential diagnosis of serious diseases, a comprehensive examination is carried out, including 24-hour monitoring of heart function.
Treatment is aimed at combating the cause of fainting.
Like other types of fainting, vasovagal fainting develops against the background of a sharp decrease in blood flow to the brain due to the influence of a number of provoking factors: stress, nervous tension, fear, and others.
Loss of consciousness occurs due to the fact that the described processes contribute to the dilation of blood vessels, which leads to a decrease in blood pressure and heart rate (bradycardia). As a result, the brain experiences oxygen starvation.
If you notice symptoms of impending vasovagal syncope, you should lie down and loosen tight clothes, a tie, or a belt.
In most cases, the person immediately feels better. To speed up recovery, you can raise your legs above your head.
Neurologist, reflexologist, hirudotherapist
Kislitsyna Ekaterina Nikolaevna
10 years of experience
Treatment for vasovagal syncope
If it were not for the danger of injury, then treating the problem would not make sense. But given these conditions, treatment is necessary.
There are three types of treatment, namely:
- Medication. The drug of choice is midodrine. Therapy lasts a lifetime, although it may be stopped for short periods of time.
- Behavioral. It involves the use of some physical maneuvers, which should be resorted to when the first symptoms appear. These are isometric compression exercises that can cause an increase in blood pressure in the initial phase of fainting.
Three types of exercises are used, namely:
- Squeezing the ball. Strong clenching of a fist, for example, a ball. Promotes the outflow of venous blood from the brain.
- Leg compression. The legs are placed crosswise, as shown in the figure, and tensed.
Arm tension. Hands are clasped and pulled in different directions.
Kinds
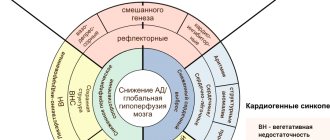
In medicine, it is customary to divide vasovagal syncope into two types.
Classical
Loss of consciousness is accompanied by phenomena characteristic of other types of fainting states. Most often, the classic type occurs against the background of emotional disturbances (fear, strong emotions, etc.), or prolonged stay in an upright position. It is detected mainly in young people under 30 years of age.
Non-classical
This type of vasovagal syncope is diagnosed in cases where it is impossible to determine the provoking factor. Loss of consciousness in this scenario occurs mainly in older people.
Mechanism of vasovagal syncope
There are three main mechanisms of vasovagal syncope. The first mechanism involves a decrease in heart rate followed by a decrease in blood pressure. The second mechanism is closely related to the work of the heart. The pulse drops below 40 beats per minute or stops completely for 3 seconds . The last mechanism is a drop in pressure, but without a drop in heart rate.
Before it comes to vasovagal syncope, symptoms may appear in the form of: hearing loss, spots before the eyes, nausea, visual disturbances, dizziness, feeling hot, cold sweat, pale skin, feeling of a strong heartbeat, shortness of breath, weakness.
Causes
The main cause of vasovagal syncope is an abnormal reaction of the body to the influence of the external environment, which has a stimulating effect on the receptors of the autonomic nervous system. The latter is responsible for the functioning of internal organs.
Modern medicine has not fully elucidated the question of what changes in the body lead to loss of consciousness. Vasovagal syncope is thought to develop due to stimulation of the vagus nerve. This theory is supported by the fact that when such conditions occur, the heart rate decreases.
There is also an opinion that instantaneous inhibition of the sympathetic part of the nervous system, which regulates the autonomic system, can lead to loss of consciousness. This explains why blood vessels dilate during fainting.
Moreover, each of the processes described above is activated under the influence of one or more provoking factors:
- strong emotional stress arising from the sight of blood, due to fear, and so on;
- pain ;
- staying upright for a long period of time;
- abrupt cessation of physical exercise;
- wearing tight ties or collars;
- binge eating;
- long stay in a stuffy room, in a hot bath;
- dieting , fasting;
- abuse of bad habits;
- chronic state of fatigue;
- depression;
- heart pathologies;
- tumor formations.
People suffering from cardiovascular diseases are strongly advised not to stay in hot rooms or in direct sunlight for long periods of time. This situation contributes to impaired blood flow, resulting in changes in blood pressure.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Fainting due to prolonged fasting is caused by a lack of vitamins and microelements. The latter leads to a decrease in hemoglobin and blood sugar levels, resulting in a malfunction of internal systems.
Under the influence of stress of a different nature (physical and psycho-emotional), the body, trying to compensate for the lack of important elements, temporarily inhibits some of its functions.
Any bad habits negatively affect the condition of blood vessels, which increases the risk of malfunctions in the cardiovascular system. The result of such processes is vasovagal syncope. Similar phenomena occur with chronic lack of sleep and fatigue. In this case, fainting performs a compensatory function of the body, whose blood flow is disrupted.
Vasovagal syncope is only dangerous when there is a risk of injury to the head and limbs from a fall. In this case, sudden memory loss signals a malfunction in the functioning of the entire organism or its individual parts.
Symptoms
The development of vasovagal syncope occurs in two stages. Initially, several symptoms appear at once, indicating an imminent loss of consciousness:
- sudden pallor of the skin;
- intense cold sweat;
- loss of strength, which is initially observed in the limbs and then spreads to the whole body;
- dizziness;
- noise in ears;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- pain appearing in the chest area;
- feeling of rapid heartbeat;
- the occurrence of tunnel vision, in which a person sees only those objects that are located in front;
- increase or decrease in heart rate.
The second stage is characterized by a short-term loss of consciousness. For some people, the symptoms described above do not ultimately lead to fainting.
Symptoms associated with loss of consciousness
Vasovagal syncope develops in two stages. The initial one is characterized by complex symptoms with a gradual loss of sensitivity.
Symptoms of fainting...
First stage:
- Intense pallor.
- Profuse cold sweating.
- Fatigue and loss of strength, which begins in the hands, then spreads to the whole body.
- Dizziness.
- Noise in ears.
- Gastrointestinal disorders.
- Pain in the chest, in the sternum area.
- Feeling of rapid heartbeat.
- Changes in field of view. Tunnel vision - only objects in front are visible.
- Abnormal perception of hot and/or cold.
This complex symptomatology is usually accompanied by loss of consciousness . However, in some cases, the described clinical picture occurs without fainting. Currently, this condition is commonly called presyncope.
Diagnostic methods
After vasovagal syncope occurs, it is recommended to seek medical help, as sudden loss of consciousness may indicate serious problems in the functioning of the internal systems. In particular, these can be cardiovascular pathologies and malignant neoplasms.
Causes of loss of consciousness with convulsions
Convulsive fainting is one of the most common pathological conditions.
In order to establish the true cause that led to loss of consciousness, the doctor carries out the following measures:
- Gathering information about the patient’s current condition and main symptoms. In terms of establishing the causes of fainting, it is important to identify the initial phenomena that preceded the loss of consciousness.
- Analysis of the patient's life. The doctor asks about the patient’s professional responsibilities, concomitant pathologies and medications he is taking.
- Collection of information about family pathologies. This stage is important, since it has been established that vasovagal syncope in approximately 30% of cases is due to a hereditary predisposition.
- External examination of the patient, during which the condition of the skin and breathing rate are assessed. Additionally, the doctor listens to the lungs and heart.
- General analysis .
- chemistry . It allows you to determine the level of cholesterol, sugar, potassium and other elements.
If the latest tests did not show any abnormalities, then other diagnostic measures are additionally carried out aimed at identifying concomitant pathologies or excluding them.
Electrocardiography
It is prescribed to assess the performance of the heart muscle.
24-hour Holter electrocardiogram monitoring (HMECG)
The procedure lasts from 24 to 72 hours, during which ECG readings are regularly analyzed. Particular attention is paid to the changes that occur in the electrocardiogram during fainting.
Echocardiography
Vasovagal syncope does not affect echocardiography readings. This procedure is performed to exclude cardiac pathologies.
Orthostatic test (title test)
It is this examination method that allows us to detect vasovagal syncope. During the procedure, which lasts no more than half an hour, the patient is placed on a special bed set at an angle of 60 degrees. The patient is connected to a device through which the work of the heart muscle is assessed.
Additionally, blood pressure indicators are measured. After loss of consciousness, there is a sharp decrease in blood pressure and a short-term stop of heart contractions (a pause occurs).
If necessary, an examination by a neurologist is carried out. Electroencephalography and MRI, respectively, can exclude the presence of epilepsy and tumor, which can also provoke loss of consciousness.
Diagnostics
You should consult a doctor immediately after the first attack occurs. Usually the causes of such fainting are not terrible, but sometimes it can indicate serious problems with the functioning of the body. For example, about tumors and cardiovascular diseases that can lead to death.
First, the doctor asks the patient when the fainting began, whether they occur in the same way, what precedes the loss of consciousness, and what the patient can attribute their occurrence to. After this, the doctor begins to be interested in the following questions:
- the patient’s profession and whether it is associated with a risk to life (driver, pilot, diver, roofer);
- whether the patient’s relatives suffer from cardiovascular diseases, whether they have experienced loss of consciousness, since vasovagal fainting can be hereditary.
Then the doctor examines the patient, notes his skin color, appearance of nails, hair, breathing rate, presence of heart murmurs and wheezing in the lungs. Prescribes general and biochemical blood tests.
In addition, diagnostics includes the following procedures:
- Electrocardiography (ECG), which determines the performance of the heart.
- 24-hour Holter electrocardiogram monitoring (HMECG). An electrocardiogram is recorded within 24-72 hours, and if fainting is detected, certain changes are displayed on it. Outside of fainting, normal values are noted.
- Echocardiography (EchoCG). It is carried out only to exclude vascular and heart diseases.
- Orthostatic test. Using this method, a diagnosis of “vasovagal syncope” is made. The essence of this procedure is that the patient lies down on a special bed at an angle of 60 degrees for 30 minutes. During this time, electrocardiogram readings are taken and blood pressure is measured automatically or manually. During fainting, there is a sharp drop in pressure and interruptions in the functioning of the heart.
Vasovagal fainting can also be isolated. They are not necessarily provoked by any disease; loss of consciousness often occurs in completely healthy people.
Therapeutic measures
The treatment regimen for vasovagal syncope is determined based on the severity of the underlying disease. Therapeutic intervention is mainly used for patients who often experience short-term loss of consciousness.
In cases where the problem under consideration arises due to mental pathologies, the treatment regimen is determined depending on the status of the underlying disease.
Therapy for vasovagal syncope consists of several approaches.
Drug treatment
The patient is prescribed the following medications:
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
- Alpha adrenergic agonists. They contribute to the narrowing of blood vessels.
- Beta blockers. Such drugs block specific receptors in the body that are activated under the influence of stress hormones (adrenaline and norepinephrine).
- M-anticholinergics. Prescribed for the treatment of bradycardia.
Surgical intervention
Used in the presence of heart diseases and tumors. Surgical intervention, during which, if appropriate indications are available, a pacemaker is introduced, is carried out subject to the following conditions:
- age exceeds 40 years;
- vasovagal syncope occurs with regular frequency;
- absence of initial symptoms indicating imminent loss of consciousness;
- arrest was recorded .
Lifestyle change
You can prevent another loss of consciousness by following these recommendations:
- drink at least two liters of liquid per day;
- exclude heavy physical activity;
- avoid emotional stress;
- sleep at least eight hours a day;
- stop wearing tight underwear, replacing them with compression ones;
- regularly perform exercises aimed at strengthening your mental state.
Special isometric exercises are also used, through which you can increase blood pressure for a short period of time:
- Holding the ball in your hand, you need to squeeze your palm. The action promotes the outflow of venous blood.
- Hands clasp together and then forcefully pull in opposite directions.
- In a standing position, the legs are crossed, after which they must be tensed.
In case of sudden loss of consciousness, the person must be placed on his back with his legs raised above his head. This pose increases blood flow to the brain.
Vasovagal syncope is not dangerous to humans. It causes only two types of complications:
- injuries resulting from a fall;
- deterioration in quality of life in cases where fainting occurs frequently.
Preventive measures can help prevent another loss of consciousness.
Treatment of vasovagal syncope
People who have had a single episode of vasovagal syncope do not need any medical treatment at all.
But if there have been recurring episodes, there will likely be more episodes if the person is not treated. And, as anyone with vasovagal syncope knows, these episodes of fainting often come at the most inconvenient or impractical times and can be very life-disrupting. Fortunately, treatment is usually quite helpful.
There are several main types of treatment for vasovagal syncope: medications, exercise, and a pacemaker.
Medications
In some people, vasovagal syncope occurs with alarming frequency, even when all appropriate precautions are taken. For these people, drug therapy is often helpful.
In the past, the drugs most commonly used for vasovagal syncope were beta blockers, but some studies have not shown any benefit and these drugs are not currently recommended.
Drugs that have been shown to have some effectiveness include:
- Midodrine, a vasoconstrictor that dilates blood vessels;
- Disopyramide, an antiarrhythmic drug;
- Serotonin reuptake inhibitors;
- Theophylline, commonly used to treat asthma.
Although one or more of these medications often helps reduce fainting, finding the “right” combination of medications is usually a matter of trial and error. Patience is required on the part of both the physician and the patient to find the best therapy.
Physical exercise
Many people with dysautonomia also tend to experience vasovagal syncope; indeed, it seems likely that many people with new-onset vasovagal syncope may indeed have dysautonomia. Because some dysautonomies respond favorably to exercise, exercise may likely have similar benefits for people with vasovagal syncope.
If you experience a recurrence of fainting, be sure to talk to your doctor before starting to exercise. Depending on the underlying cause, you may need to undergo stress testing and other tests to determine how much exercise you can tolerate.
Interestingly, some people have been able to interrupt episodes of vasovagal syncope by starting to do muscle tension exercises. These exercises apparently reduce the dilation of blood vessels and increase the amount of blood returned to the heart. Examples of exercises include:
- Cross your legs and simultaneously tense your legs, stomach and buttocks.
- Tighten your arms with clenched fists.
- Tighten your leg muscles.
- Squeeze the rubber ball.
Use of pacemakers
Several years ago, there was great enthusiasm for the use of pacemakers to treat vasovagal syncope, as the condition is usually accompanied by a sudden decrease in heart rate. However, enthusiasm for pacemaker therapy quickly waned when it was finally noted that many patients with vasovagal syncope who were given pacemakers continued to lose consciousness—they simply did so without a change in heart rhythm.
As it turns out, it is the pooling of blood in the legs, not a slow heartbeat, that causes most people to faint. However, in some cases, a decrease in heart rate may be the underlying cause.
A pacemaker should only be considered if syncope is severe or recurrent and conservative measures have failed and there is significant cardiac slowing as demonstrated by ECG testing.
Prevention measures
In order to prevent vasovagal fainting, first of all, it is necessary to avoid psycho-emotional stress. In particular, these include both conflict situations that can cause stress and prolonged stay in an upright position. At the same time, active outdoor activities are used as preventive measures to prevent loss of consciousness: walking, running, and so on.
You can also prevent the onset of another fainting spell:
- hardening or contrast shower (strengthens blood vessels);
- adherence to daily routine;
- duration is at least 8 hours;
- Regular consumption of herbal tea, red wine or coffee to restore blood pressure;
- drinking chamomile, lemon balm or St. John's wort tea, which has a positive effect on the nervous system.
Vasovagal syncope is not a dangerous phenomenon, which, however, may indicate serious pathologies: cardiovascular diseases, tumors. You can cope with such phenomena if you change your lifestyle.