Parkinson's disease is a severe degenerative disease. It is diagnosed in 60–140 people out of 100 thousand patients. Mostly elderly people are affected. The onset of the disease is diagnosed at the age of 55–58 years. Refers to incurable pathologies. Men are more often affected. The juvenile form also occurs in twenty-year-old patients.
The pathology is chronic, accompanied by motor disorders. But drugs have been developed that can slow the progression of Parkinson’s disease, relieve symptoms, and improve the patient’s quality of life and care.
The symptoms of Parkinson's disease have been known for more than a millennium, but J. Parkinson described and systematized them at the beginning of the 19th century. Pathology was named after him. The biochemistry of destructive processes in the extrapyramidal system began to be studied in detail in the 50s. last century.
Treatment of Parkinson's disease was carried out using belladonna alkaloids, surgical therapy was developed - destruction of the basal ganglia was carried out. Currently, the gold standard of treatment is the use of Levodopa.
Definition of disease, cause of disease
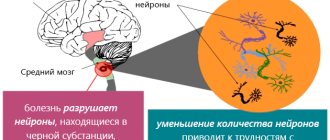
Parkinson's disease is a chronic neurodegenerative disease of the extrapyramidal motor system. Develops slowly. The main cause of the pathology is the destruction of neurons that produce dopamine in the substantia nigra and other parts of the brain.
The causes of Parkinson's disease have not been determined. Factors contributing to the development of the pathological process:
- Aging is accompanied by a decrease in the number of neurons and an increase in Lewy bodies.
- Heredity - 15% of patients have a family history of Parkinson's disease. But the gene responsible for its development has not been identified.
- Intoxication, living in disadvantaged areas - the influence of pesticides, herbicides, insecticides, FOS, heavy metal salts has been proven.
- The use of medications that have extrapyramidal disorders as a side effect.
Smoking is not a provoking factor. Parkinson's disease is diagnosed less often in patients with bad habits than in non-smokers. This is associated with the dopamine-stimulating effect of nicotine.
What to do to reduce the risk of disease
There is no specific prevention for Parkinson's disease. But there are recommendations for the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases in general.
These recommendations boil down to maintaining a healthy lifestyle. A normal work schedule and physical activity are needed: it has been proven that running significantly reduces the progression of such diseases. All fine motor skills and playing musical instruments are demonstrated. Also, eat healthy. Some drugs can be toxic to dopaminergic neurons, so it's a good idea to avoid bad habits.
Symptoms of Parkinson's disease
There are true Parkinson's disease and parkinsonism syndrome - a complex of symptoms that develop after head injuries and severe intoxication.
Characteristic signs of the disease:
- Tremors in the arms and legs - in Parkinson's disease, they occur at rest. Frequency of up to 6 involuntary movements per second. Occurs at an early stage of the disease. Starts with one arm, then spreads to the other side of the body. A “yes-no” symptom may be observed. During sleep and at rest, the tremor stops, but intensifies during emotional shocks.
- Hypokinesia – decrease in motor activity. This symptom manifests itself as a change in handwriting, speech, and the disappearance of characteristic facial expressions.
- Muscle rigidity – increased muscle tone. The limb freezes in a bent or straightened state. A typical symptom is the “supplicant pose.”
- Postural instability - this symptom occurs in the later stages of the pathological process. Patients have difficulty starting and finishing movement. The body may begin to move faster than the legs. In this case, the center of gravity shifts and the patient falls.
In addition to the main diagnostic signs, Parkinson's disease is accompanied by autonomic and mental symptoms. They are individual. Both obesity and exhaustion, sweating, drooling, psychosis, and hallucinations are observed.
Early signs
1. Problems with the sense of smell . It often happens that it is the inability to smell for no apparent reason (runny nose, burn of the mucous membranes by chemicals, etc.) that indicates parkinsonism. You can test the capabilities of your sense of smell on foods that have a pronounced smell: bananas, cucumbers, etc.
2. Decreased sense of taste . Along with the loss of smell, loss of taste may also develop. Since Parkinson's disease affects the brain structures responsible for the production of happiness hormones, the level of dopamine (the pleasure hormone) begins to decrease. Food is often that same pleasure. And if suddenly the pleasure from it begins to decrease due to lack of taste, then it is worth visiting a doctor.
3. Trembling of the limbs . Tremor is one of the most striking symptoms of a terrible disease; even an ordinary person can use it to determine the presence of pathology. Naturally, it does not immediately become so noticeable. It all starts with a shiver. It is worth straining if there is twitching of the fingers, chin or trembling of the hands. Moreover, it is important to understand that in Parkinson’s disease, tremors at rest may disappear or decrease. At the initial stages of the disease, the frequency of trembling is 3-7 Hz, but then as the pathology progresses, it increases. “It is necessary to identify the symptoms of the disease in a timely manner, which means taking a close look at yourself or loved ones, looking for such signs as a characteristic tremor of the hands and head at rest, a change in gait - the patient begins to walk in small steps - is there a tendency to causeless and frequent falls,” says Olga Pylaeva.
4. Decreased voice power . It is believed that in Parkinson's patients the “power of the voice” fades away quite quickly. And this happens faster than with standard age-related changes. If the voice becomes quieter and more hoarse, speech loses emotion, trembling notes appear, you need to visit an ENT specialist. You should do the same if those around you can no longer hear you.
“Tango will help!” A doctor talks about new treatments for Parkinson's disease Read more
5. Muscle stiffness . The appearance of a feeling of stiffness and tension in the limbs that does not disappear during movement (that is, does not disappear if a person begins to walk after, for example, prolonged sitting) should alert you. If it's not Parkinson's, it could be arthritis. It is worth considering that this symptom is one of the three main ones indicating the development of a severe neurological disorder. Problems with the nervous system can also be signaled by painful sensations that appear in the hip or shoulder. Against the background of such a problem, slowness of movements may also develop.
6. There is a mask on the face . The name “Parkinson's mask” hides the complete absence of facial expressions. The person will look upset and even apathetic, while being in a cheerful and cheerful mood. Many people do not notice such a symptom until others begin to point out their unsociability. Facial muscles, as experts say, due to a lack of the same dopamine, harden and lose reaction speed. At the earliest stages, the mask does not yet appear, but some slowness of facial expressions is noted.
7. Excessive sweating . A nervous disorder such as Parkinson's widely affects the functioning of the nervous system. And the body can easily lose control of its basic functions. This also applies to the regulation of sweating. And this happens for no apparent reason.
Article on the topic
"There's something wrong with my memory." How are Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases different?
Pathogenesis
The target organ for Parkinson's disease is the brain, the structures of the extrapyramidal system. With the development of the pathological process, the death of nerve cells in the substantia nigra occurs. Overt symptoms occur when 60% of neurons are lost.
In parallel, an increase in Lewy bodies is detected. The latter are also formed during natural aging, but in Parkinson's disease their number is several times higher.
The death of glial cells and an increase in phages are observed. Although Lewy bodies are not considered a characteristic symptom of the disease, as the disease progresses they are found in all structures of the brain. In later stages - and in the cerebral cortex.
The components of the extrapyramidal system are responsible for the automation of movements - walking, running, emotional reactions. Normally, this part of the brain sends impulses to peripheral motor nerve cells and ensures that the muscles are ready for movement. The ability to take the intended posture depends on the coordinated work of the extrapyramidal system.
The identification of dopamine helped explain the functions of this part of the brain and explain the symptoms of Parkinson's disease. A characteristic sign of the disease is a sharp decrease in neurotransmitter in all parts of the brain. Symptoms of Parkinson's disease depend on which part of the extrapyramidal system is affected.
Diagnostics
Comprehensive diagnosis of the disease is based on the study of the neurological status, patient complaints and a combination of a number of criteria.
Among the instrumental research methods, the most reliable is positron emission tomography (PET), in which radioactive fluorodopa is injected intravenously and the degree of its accumulation in specific areas of the brain is assessed. The disadvantage of the method is its high cost and low prevalence. Other laboratory and instrumental methods do not reliably identify the causes of the disease and prescribe its treatment, therefore they are used to exclude other diseases with similar symptoms.
To make a diagnosis, a combination of hypokinesia with one or more signs (rest tremor (frequency 4-6 Hz), muscle rigidity, postural disturbances) is necessary.
Classification and stages of disease development
Doctors distinguish 5 stages of Parkinson's disease. The basis is the progression of symptoms.
Classification according to Hoehn and Yahr:
- Stage zero – there are no signs of the disease.
- The first is that motor symptoms appear. One side of the body is affected.
- The second is a bilateral defeat. Symptoms intensify and new areas of the body are affected.
- Third, postural instability is diagnosed, but the patient can care for himself.
- Fourth, the symptoms of the movement disorder progress, the patient can only move short distances.
- The fifth stage of the pathological process - the patient is completely incapacitated. Symptoms of mental disorders and autonomic disorders intensify.
There are 3 main forms of the disease. The classification is based on the severity of one or another group of characteristics:
- Rigid-bradykinetic – increased muscle tone, contractures. The patient freezes in one position for a long time. For example, "petitioner" or "mannequin".
- Trembling-rigid form - the main symptom is trembling of the limbs, general stiffness of movements.
- Trembling - tremor of the limbs, tongue, jaw, tongue. Muscle tone is normal, the patient can control motor activity.
Diagnosis of Parkinson's disease
It is almost impossible to recognize Parkinson's disease at an early stage. Initial symptoms - trembling fingers, fatigue - are attributed to stress and fatigue. But early diagnosis improves the patient’s prognosis, increases the duration of socially active life, and reduces the rate of destruction of brain cells. As symptoms progress, one can even assume Parkinson's disease in absentia.
The initial diagnosis is established based on an analysis of the patient’s complaints and the results of a neurological examination. It is also recommended to obtain an opinion from 2 doctors, since in a quarter of cases the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease is made incorrectly.
Differential diagnosis
If there are 4 characteristic symptoms, an error in the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease is unlikely. But in any case, other similar diseases should be excluded. The following are not typical for the pathology:
- early postural instability, dementia, impotence, urinary incontinence, difficulty swallowing and speaking;
- lack of any response to Levodopa;
- rapid progression of brain disorders;
- cerebellar damage;
- visual disturbances not caused by drugs.
Treatment of Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease is an incurable destructive disease. Therapy is aimed at eliminating symptoms, reducing the rate of patient degradation, improving quality and increasing the active period of life.
In the conservative treatment of Parkinson's disease, the following drugs are used:
- Drugs that increase the amount of dopamine in the brain - Levodopa. To stabilize the active substance in tissues, Tasmar (Tolcapone) is prescribed.
Tasmar is prescribed as part of combination therapy for Alzheimer's disease - in parallel with the main therapeutic agents. The drug reduces the activity of the enzyme that converts levodopa into one of the phenylalanine derivatives. Levodopa is an effective drug used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
- Dopamine receptor agonists - to stimulate this area, mimic the action of the neurotransmitter.
- MAO inhibitors – inhibit enzymes that break down dopamine. For example, such as Segan (Yumex, Selegiline, analog Deprenil, Eldepril).
One of the effective anti-Parkinsonian medications is the drug Segan (Yumex). Its main active substance, Seleginine, reduces the destruction of dopamine in the brain, and also enhances the effect of another substance - levodopa, which, when it enters neurons, is converted into dopamine. The use of selegiline improves brain function and also has a positive effect on mood and overall well-being.
- Dopamine reuptake inhibitors - increase the sensitivity of receptors to the neurotransmitter.
- Anticholinergics - to relieve symptoms of the disease such as hypersalivation, hyperhidrosis and excessive activity of the sebaceous glands.
If conservative treatment of Parkinson's disease is ineffective, surgical intervention is indicated. Destructive operations and stimulation of brain areas are used.
Methods of surgical treatment of Parkinson's disease:
- Thalamotomy - indicated when the main symptom is tremor and only one side of the body is affected.
- Pallidotomy - such an intervention for Parkinson's disease is performed when the main symptom is movement disorders.
- Neurostimulation – if conservative treatment of Parkinson’s disease is ineffective or if there is intolerance to medications. This procedure involves implanting electrodes into brain structures. The patient can independently regulate the intensity of stimulation.
The intervention is permitted for Parkinson's disease with bilateral involvement. This operation is reversible and easily tolerated. The downside is its high cost.
When might there be an effective cure for Parkinson's disease?
— Now there is great interest in cell replacement therapy, that is, the creation of a certain type of cells that will help replace lost functions. Parkinson's disease has become one of the first areas where such treatment has already reached clinical trials, testing the effectiveness and safety of the drug in humans.
Several clinical trials for treatments for Parkinson's disease have already begun. Several more should begin at the end of 2019 - beginning of 2020. Each case uses a different source of dopaminergic neurons. It should be noted that researchers in different parts of the world do not work separately, trying to get ahead of each other, but have united into a community that meets once a year and shares their results. Together they identify any difficulties, features, or new approaches. This is exactly what is needed to solve the problem as quickly as possible.
The first trials began last year in Japan, and the first patient was transplanted with [the necessary cells] in November 2021. Clinical trials have also started in China, but I don’t know what stage they are at. Also, clinical trials should begin in Sweden and the USA in the near future. I hope that Russia will join in over time.
The results of Japanese tests should be known by 2023.
Prognosis, prevention of Parkinson's disease
The prognosis is unfavorable. Without treatment, after 8 years the patient becomes completely dependent on relatives and cannot care for himself. When using Levodopa, the active life expectancy for Parkinson's disease is 15 years. But the speed of its development is individual.
Prevention is as follows:
- high-quality treatment of brain pathologies and head injuries;
- avoid stress;
- take vitamins and supplements such as phenylalanine (L-Phenylalanine);
- Observe safety precautions when working with pesticides and chemicals.
Parkinson's disease is an incurable pathology. But scientists are conducting research and developing new therapy methods. At the first signs of Parkinson's disease, you should consult a doctor and begin drug treatment.
Bibliography
- Vasiliev Yu.N. Parkinson's disease: pathogenetic significance of stress. Irkutsk, 2009, “Imprint”. – 128 p.
- Samii A., Nutt JG, Ransom BR Parkinson's disease (English) // The Lancet. – Elsevier, 2004. – Vol. 363. – P. 1783 – 1793. – PMID 15172778.
- Levin O.S., Fedorova N.V. Parkinson's disease. – M.: 2006. – 256 p.
- Sayutina S.B., Shprakh V.V. Parkinson's disease (in questions and answers). Irkutsk: RIO IGIUVA, 2010. – 124 p.
- Yakhno N.N.. General neurology: textbook. allowance / N. N. Yakhno, V. A. Parfenov. – 2nd ed., rev. and additional – M.: MIA, 2009. – 208 p.
- Zhukova N.G., Zhukova I.A., Gashilova F.F. Diagnostic criteria and treatment algorithms for Parkinson's disease: Textbook. – Tomsk: Publishing House “Printed Manufactory”, 2007. – 122 p.
- Fahn S. The medical treatment of Parkinson disease from James Parkinson to George Cotzias. Mov Disord. 2015; 30(1):4–18.
- Mak MK, Wong-Yu IS, Shen X, Chung CL.Long-term effects of exercise and physical therapy in people with Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2021 Nov;13(11):689–703.
- https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parkinson's_Disease#Pathogenesis