Agitation is a condition in which the patient exhibits febrile motor agitation and demonstrates increased talkativeness.
The patient experiences anxiety, he fusses, does not find a place for himself, performs any actions automatically, and loses the ability to build logical chains. As a rule, agitation occurs against the background of a mental disorder. If the condition is not controlled, it can lead to the patient’s aggression, directed both at himself and at others.
Causes
Agitation can develop for a variety of reasons, including after severe stress. However, the most common cause is mental illness: schizophrenia, depression, neurosis, anxiety disorder. Agitation is also a frequent accompaniment of Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia.
Another group of reasons is drug intoxication, including that occurring during the treatment of mental disorders.
Agitation can occur with alcohol and drug poisoning.
Agitation in children most often manifests itself during recovery from general anesthesia.
Causes (etiology) of the disease
Agitation occurs during times of tension caused by severe stress. It can also manifest itself in many mental illnesses, for example, anxiety neurosis, agitated depression, catatonic schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease. A state of alcohol or drug intoxication can also cause agitation. In some cases, agitation is a symptom of an infectious disease.
It should be noted that in some professions associated with increased risk to life, in emergency situations, agitation is often confused with confusion.
Agitation
Symptoms
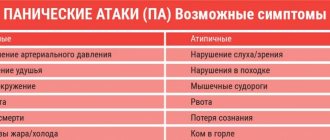
The main symptoms of agitation are increased motor and speech activity of a non-constructive nature. A person repeatedly makes the same type of movements, shouts out the same phrases, without subjecting his actions to critical analysis.
Also, most patients experience:
- hand trembling;
- sweating;
- pale skin;
- cardiopalmus;
- labored breathing;
- increased blood pressure;
- hyperthermia;
- sleep disorders.
Agitation in depression is characterized by a rolling feeling of devastation after an attack. Episodes of hallucinations are occasionally observed.
Symptoms (clinical picture) of agitation
When a person exhibits agitation, the following symptoms can be observed:
- motor or speech restlessness; very often the patient does not notice changes in his behavior;
- hand trembling;
- sweating;
- increased heart rate;
- rapid breathing;
- pallor.
In a state of agitation, a person develops a feeling of absence of thoughts and emptiness, he loses the ability to reason and establish complex causal relationships.
Agitation can be identified if a number of signs are present. For example, the patient’s behavior changes, but he himself does not notice it. There is speech anxiety, fussiness in movements, the person’s hands tremble, the face turns pale, sweating increases, and the heart rate increases. In such a state, there are no thoughts, a kind of emptiness is formed, the ability to reason is lost, and causal complex connections are not established. Doctors pay special attention to such a problem as the occurrence of agitation in Alzheimer's disease. In this case, patients also suffer from severe behavioral disorders. In particular, depression occurs, there are complaints of hallucinations of various types, and the person tends to wander.
In this case, the state is characterized as overexcited, excessive agitation is noted. A person begins to use obscene expressions that were previously unusual for him, and clouding of consciousness occurs. With such disorders, normal daily life is disrupted, and problems with sleep arise. In addition, there is a risk that a sick person in a state of agitation will harm himself or those caring for him.
Often, changes in the environment can provoke agitation; factors such as fatigue and fear have an equally pronounced effect on the development of the disease. It has been proven that in some cases, agitation is caused by somatic diseases and infections. You should know that the causes of agitation can be eliminated and cured, which is why it is so important to get help from a qualified specialist. In the event that agitation is not a medical cause, behavioral techniques are used for treatment that can influence the patient’s routine life and distract him from the stress caused by a particular problem.
Agitation in children: characteristic features
In children, agitation occurs during postoperative awakening from anesthesia. It manifests itself as uncontrollable agitation, inappropriate actions, and anxiety.
The child is aggressive towards the doctor and parents, does not give in to persuasion, is irritable, cries for a long time and inconsolably. The condition can last up to half an hour from the moment of regaining consciousness. Then the baby calms down on his own or with the help of medications.
The syndrome is observed in children aged from one to seven. Usually found in patients with prenatal and postnatal disorders, birth injuries.
Agitation - what is it?
Agitation, meaning of the word: setting in motion. Derived from the Latin agitatio. Next we give a definition and concept.
What is agitation? Agitation is an emotional state of increased agitation, speech and motor activity. A person has a need to perform the same type of actions. For example, he constantly shakes his leg, moves small objects in his hands, and runs from corner to corner. Simply put, the person becomes very agitated, fidgety and reactive. At the same time, he experiences severe anxiety and fear.
Agitation is not an independent disease. It can occur in both healthy people and people with mental disorders (as a symptom).
Symptoms
The movements are automatic and simple. As a rule, they are not realized by the person himself. However, others can see drastic changes in his behavior.
Agitation, other symptoms:
- fussiness;
- increased speech activity (swearing, swearing, using words that are unusual for this person in everyday life);
- paleness;
- tremor of the limbs;
- increased sweating;
- cardiopalmus.
There is confusion and disorientation. A person cannot establish cause-and-effect relationships; it is difficult for him to concentrate and reason. A state similar to a vacuum arises in the head. Agitation cannot be left untreated, because in this state a person becomes dangerous to himself and others. Agitated activity is often accompanied by aggression.
Causes
Agitation is a psychological reaction to shock and overexertion. Occurs at times of severe stress, exhaustion and mental disorders, for example, anxiety depression, schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease, paranoia, bipolar disorder.
Other causes of agitation:
- severe fear;
- sudden and serious changes in life;
- psychotrauma;
- dangerous work in extreme, stressful conditions;
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- coffee abuse;
- avitaminosis;
- taking medications.
Sometimes the phenomenon of agitation is noticeable during infections, drug or alcohol intoxication, and withdrawal syndrome.
Treatment
Agitation is completely treatable, but for this it is important to correctly determine the root cause. If you have suspicious symptoms, it is recommended to immediately contact a psychotherapist or psychologist. He will conduct diagnostics according to his profile, and if necessary, refer you for examination to other specialists, for example, an endocrinologist.
The main method of treatment is psychotherapy. Its goal is to increase stress resistance. In addition, it is aimed at working out the root cause. In some cases, medications (neuroleptics, anxiolytics, antipsychotics, antidepressants) or herbal preparations are used.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by a psychiatrist; to clarify it, a consultation with a neurologist and narcologist may be required.
In addition to observing the patient’s behavior, the doctor measures pulse and blood pressure and collects family history. In some cases, the results of clinical and biochemical blood tests, measurement of hormone levels in the blood, urine analysis, and MRI of the brain may be required.
Blood tests are necessary to differentiate between agitation and akatasia, which are very similar in symptoms. Akatasia can occur as a result of taking medications (antidepressants and antipsychotics) that relieve agitation. An additional dose of these drugs can worsen the condition of a patient with akatasia.
Treatment
Depending on the severity of the symptoms, either a conversation is held with the patient, or an attack of agitation is stopped with medication, often in a hospital setting.
Treatment for the condition depends on the cause that caused it. Individual or group psychotherapy is indicated for patients who have suffered severe stress.
Patients need to create favorable conditions and adjust their sleep and wakefulness patterns. Relatives and friends of patients need to build trusting and supportive relationships with the patient.
Drugs for the treatment of agitation
First and second generation antipsychotics and benzodiazepines are most often used in treatment.
Depending on the severity of the underlying disease, the drugs are taken orally or administered intramuscularly/intravenously.
To relieve an acute attack of agitation, the drug of choice is haloperidol, which is administered both in tablet form and intramuscularly. Olanzepine (Egolanza, Zolafren, Olfrex), sulpiride (Eglonil), and aripiprazole (Arilental, Frame, Zikalor) are also used.
Medicines to relieve agitation are used strictly as prescribed and under the supervision of a doctor!
List of used literature
- Gelder M., Goeth D., Mayo R. Oxford Manual of Psychiatry / Trans. from English: In 2 volumes - K.: Sfera, 1999. - T. 2
- Nitrutsa M.I., Nagnibeda A.N. Emergency psychiatric care at the prehospital stage. – St. Petersburg: Special literature, 1998–2000.
- Protsenko D.N. International recommendations for the treatment of agitation and delirium in adult patients in intensive care units // Medical alphabet. – 2014. – T. 2. – No. 9.
- Smulevich A.B. Psychopathology and clinical picture of depression developing in schizophrenia // Psychiatry and psychopharmacotherapy. – 2003. – No. 5.
Frequently asked questions about agitation
How to treat agitation?
The condition is treated with medications. Most often, the patient is hospitalized in a hospital. Subsequently, depending on what caused the agitation, the underlying disease is treated and a course of psychotherapy is prescribed, designed to stabilize the patient’s psychological state.
What can cause agitation?
The phenomenon develops against the background of mental illnesses - schizophrenia, depression, manic-depressive psychosis and anxiety disorders. The condition can also be caused by alcohol and drug intoxication, and drug poisoning. Agitation often accompanies senile dementia and Alzheimer's disease, and is observed in healthy people who have suffered severe stress.
Can agitation be cured?
This condition is not a disease. It can be described as a behavioral disorder that accompanies certain diseases. Their cure has a beneficial effect on the general condition of the patient. If agitation is caused by stress, psychotherapy, adherence to a daily routine, and a generally comfortable environment for the patient can cause an improvement in the condition without the use of medications.
Main features
It is necessary to pay attention to how agitated activity will manifest itself, since it will be somewhat different from other disorders.
We should also not forget that the patient himself may not notice these signs; it is important for relatives or close people to pay attention to this in order to seek help as early as possible. The main signs of agitation:
- Agitation begins to unfold with the manifestation of fussiness and restlessness in movements.
- Trembling appears in the hands, the skin turns pale, sweating increases, breathing and heart rate increase.
- Thinking becomes confused, speech becomes confused. It is difficult for a person to complete a sentence; he seems to rush from one thought to another or repeats the same words.
- The more serious the disease, the more pronounced the symptoms will appear - moreover, during attacks the patient can cause harm to both himself and others. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to the signs of the disorder as early as possible.
- If agitation acts as a symptom of other diseases, then it can be accompanied by visual or auditory illusions, sometimes by attacks of spontaneous shouting of curses, as well as motor tics.
Agitation is a common symptom of a disease called agitated depression. Her symptoms will be somewhat different. It must be said that with this disorder a combination of various symptoms will appear, characteristic of both ordinary depression (depressed mood, apathy, sleep disturbances, etc.) and agitation.
Firstly, such patients experience causeless anxiety. They begin to worry about their loved ones, their health and physical condition. They are captured by a certain premonition that something bad is about to happen.
Secondly, the patient’s speech changes, he repeats the same phrases, usually somehow related to his anxiety. Moreover, this can amount to a couple of words, which he will restlessly repeat and repeat.
Thirdly, there are behavioral changes. It will be difficult for the patient to literally sit still. He will constantly move, move, restlessly walk from corner to corner.
We recommend: Affect: characteristics of the phenomenon
With serious development of this disease, it can be combined with delusional states and obsessions. In some, especially severe cases, suicide attempts may occur, as well as various types of auto-aggression (aggressive behavior directed at oneself, for example, self-torture).