Determination of tonic muscle spasms
Tonic cramps are unconscious muscle contractions that appear due to severe and sharp pain. There are three types of seizures: clonic, tonic, and tonic-clonic. To accurately determine the type of seizure in a person, timely diagnosis is necessary. Seizures are not always dangerous, but prompt treatment is necessary. An incorrectly functioning body signals that disturbances are occurring within it. In acute forms of the disease, convulsions are considered a factor in blocking the airways and stopping the heart.
Local tonic convulsions
Muscle spasm in response to excessive physical activity or prolonged uncomfortable position is a common phenomenon. Professional athletes know this more than others, but even for ordinary fitness enthusiasts, sudden muscle pain causes many unpleasant emotions.
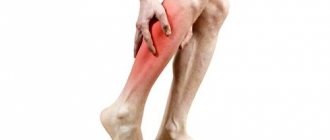
A cramped muscle is tense and hard to the touch, and the spasm is accompanied by severe pain. In addition to the calf muscles, convulsive spasms affect the muscles of the neck, and sometimes the muscles of the thigh and forearm can be affected. Usually, local tonic convulsions go away on their own within 5-10 minutes, but it’s still better not to endure the pain.
There is a simple scheme of actions that will help return the muscle to its normal state.
What to do? The most basic cause of spasm is a lack of microelements (primarily magnesium), excessive stress on an insufficiently warmed muscle, or prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position (this is what causes muscle spasms during sleep).
Therefore, people involved in physical exercise are recommended to take additional vitamin and mineral complexes, eat dried apricots before training, avoid dehydration, and most importantly, devote enough time and effort to warming up to “warm up” the muscles.
If a spasm does occur, there are techniques for local impact on the muscle. For example, if you have a spasm in the calf muscles, you need to stretch your leg forward as much as possible and strongly pull your foot towards you.
Seizures
When the body undergoes a tonic spasm, an increase in the frequency of spasmodic contractions is noticed.
The difference between tonic convulsions and other types is that parts of the body change their position, blood pressure increases, the reaction to light stimuli decreases, and breathing quickens. Severe forms of the disease can occur with loss of consciousness.
A characteristic feature of a tonic attack is rigidity of the limbs and torso. This process occurs in a short time, so it does not enter the clonic phase. The duration of convulsions is no more than 3 minutes.
The reason for the appearance of tension in the muscles is the improper functioning of the nervous system. It is influenced by improper development of the fetus during pregnancy and the formation of the body in early childhood, genetics and heredity.
Convulsions can occur with a large loss of fluid from the body, an increase in temperature, a lack of oxygen supplied to the brain, or caffeine poisoning.
Medical educational portal kbmk.info
Convulsive syndrome
- This is one of the body’s universal reactions to various harmful influences.
Cramps
are involuntary muscle contractions.
Convulsive movements can be widespread and involve many muscle groups (so-called generalized spasms) or localized in any part of the body or limb - localized or partial spasms. Generalized convulsive contractions can be slow, lasting a relatively long period of time - tonic convulsions; or may be rapid, frequently alternating states of contraction and relaxation—clonic convulsions.
There may be mixed clonic-tonic convulsions.
Generalized tonic seizures
They involve the muscles of the arms, legs, torso, neck, face, and sometimes the respiratory tract. The arms are most often in a state of flexion, the legs are extended, the muscles are tense, the torso is extended, the head is thrown back, turned to the side, the teeth are clenched, consciousness can be lost or retained.
Generalized clonic seizures
They often represent relatively rhythmic contractions of the muscles of the trunk and limbs following each other.
Clonic convulsions may not be general, but local (partial convulsions), which, for example, cause hiccups. Spasms of the muscles involved in speech and respiratory muscles lead to stuttering.
Etiology of seizures
Convulsive contractions develop as a result of dysfunction of the central nervous system caused by: 1. Neurological diseases: - epilepsy, including a genetic predisposition - volumetric processes in the brain - stroke - hypertensive crisis (hypertensive encephalopathy) - acute and chronic neuroinfections - TBI and their consequences 2. Infectious diseases: - rabies - tetanus - childhood infections with a sharp increase in body temperature 3. Toxic processes - uremia and end-stage renal failure - poisoning: alcohol (alcoholic encephalopathy), strychnine, FOS, household chemicals, carbon monoxide, sleeping pills, barbiturates - acute adrenal insufficiency - hypoglycemic coma: overdose of sugar-lowering drugs (insulin or pills with skipping meals) or due to insulinoma - a tumor of the pancreas in which a large amount of insulin is produced, therefore, blood glucose sharply decreases. - acute thyroid insufficiency 4. Disorders of water-salt metabolism - eclampsia - heat stroke 5. Hysteria 6. IHD with the development of complete atrioventricular block, severe bradycardia, therefore, cerebral ischemia occurs, can also be observed due to a Morgagni-Adams-Stokes attack
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a chronic, genetically determined brain disease characterized by recurrent seizures.
The most striking manifestations of the disease are grand mal seizures
Epilepsy Clinic
1. Often an attack is preceded by an aura (a harbinger of the disease): visual, auditory, olfactory hallucinations, parasthesia, mood disorders, sometimes there may be no aura.
2. Beginning. Suddenly consciousness turns off, the patient falls, often gets injured, sometimes an inarticulate cry is heard - the result of a tonic contraction of the respiratory muscles and vocal cords. Breathing stops, the face turns pale, then becomes cyanotic. 3. Expanded tonic phase of the seizure. The arms are tense, bent, the head is thrown back or to the side, the torso is extended, the legs are extended, tense, the jaw is tightly clenched, the eyes are open, and do not react to light. Involuntary urination and sometimes defecation may occur. Duration from 30 to 60 seconds. 4. Clonic stage. Tonic tension ends abruptly and a short-term relaxation of the muscles occurs, and after that the muscles of the torso tense again. This alternation of relaxation and tension characterizes the clonic stage of a seizure. Breathing is restored, becomes noisy, wheezing, cyanosis disappears, foam is released from the mouth, part of the eT is stained with blood. 5. Convulsions develop less and less often and stop. The patient remains in a stuporous state for some time, then falls asleep. 6. Upon waking up, the patient vaguely or does not remember what happened at all. Only general weakness, malaise, pain in the bitten tongue remind of a seizure. 7. In some cases, a major seizure follows one after another so often that the patient does not have time to recover, this is called status epilepticus, which can lead to death due to cerebral edema or exhaustion of the heart muscle, paralysis of the respiratory muscles. 8. Frequent attacks of epilepsy cause the death of brain cells during each attack, the level of intelligence decreases, and changes in personality occur. Seizures similar to epilepsy can develop with other diseases, for example, with chronic alcohol intoxication with brain damage, or as a consequence of head injury. But in 1 case it is an independent nosological disease. And when it occurs in other diseases, it is called symptomatic epilepsy or an epileptomorphic seizure.
Treatment of epilepsy
1. Protect the patient from bruises 2. Prevent tongue bite, but do not insert metal objects, as a tooth may break, get into the larynx (mechanical asphyxia) ... unshakable confidence that a person who has had an epileptic attack needs to unclench his teeth and put something between them.
Beauty! And they put it in - at least they try. And epileptics later, having come to their senses, are surprised to realize that their mouth is filled with plastic from a chewed-up fountain pen (at best) or fragments of their own teeth (at worst). So: don’t! Don’t shove anything into a person’s mouth, he’s already having a hard time. You will only make things worse... © First Aid.
10 misconceptions 3. Intravenous bolus diazepam (Seduxen, Sibazon, Relanium, Valium). Dosage: 2-4 ml or 10-20 mg. It can be repeated after 10-15 minutes; it is administered slowly, as breathing may stop. Administration of diazepam more than 2 times is not advisable. 4. To combat seizures you can: magnesium sulfate 25%, sodium thiopental, hexinal 5. To combat cerebral edema, diuretics: furosemide, mannitol, mannitol 6. Hospitalization is carried out either with a first-time seizure for examination and clarification of the diagnosis, as well as with status epilepticus
Status epilepticus can develop as a result of - the patient’s refusal to take medications - a sharp reduction in the dose of the drug - the addition of an acute infection. Diazepam tablets can be used as maintenance therapy to prevent the occurrence of a seizure.
Tetanus
The causative agent is the anaerobic bacterium Clostridium Tetani, which produces an exotoxin that affects the spinal cord and medulla oblongata and develops when the pathogen enters the wound. Incubation period: 6-14 days.
Tetanus clinic
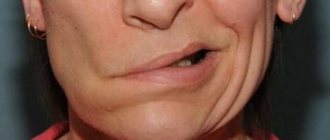
1. Beginning. Characterized by convulsions, convulsive contractions of the masticatory muscles, closing of the jaws, convulsive contraction of the facial muscles, a peculiar grimace appears (LSardonic smile |) This type of convulsions is called trismus. 2. After the appearance of trismus, cramps within several hours involve all muscle groups, in descending order. (Muscles of the head, neck, torso, lower limbs) 3. Breath holding, cyanosis 4. Due to a sharp contraction of the long extensor muscles of the back, the patient bends in an arch, leaning on the bed with the back of his head and heels (opisthotonus) 5. Convulsions can occur under the influence of noise, bright light etc.
A brain tumor
It can be primary or secondary (metastatic). Sometimes it is asymptomatic for a long time. The clinic is characterized by a predominance of partial seizures over generalized ones. Manifestation of a convulsive seizure in the early stages of the disease. 70% of patients have signs of focal brain lesions. With tumors of the frontal zone, mental and behavioral disorders occur.
Rabies
The causative agent is the RhabdoviridaeLyssavirus virus, which is secreted by sick animals in the saliva, usually infected through bites by a sick animal, rarely when saliva gets on the skin and mucous membranes that have damage, most often the saliva of birds. Incubation period 15 days v 2 months
Rabies Clinic
1. Increase in temperature to subfebrile levels 2. Hydrophobia - convulsive contraction of the respiratory muscles at the sight of water or at the sound of pouring water 3. Further, general tonic convulsions and spasm of the swallowing muscles develop. 4. Next comes pronounced excitement - the patient screams, jumps out of bed, incoherent speech, auditory and visual hallucinations. 5. Copious secretion of sticky saliva that runs down the chin.
Tetany
This condition is caused by a decrease in calcium levels in the blood.
Calcium levels are normally regulated by parathyroid hormones. They are located near the thyroid gland. Occurs when operations on the thyroid gland are unsuccessful, damage occurs and hormone deficiency occurs, therefore, a violation of calcium metabolism. A decrease in calcium levels in the blood causes an increase in nervous and muscle excitability. Partial convulsions are characteristic, consciousness is preserved during the seizure.
Chronic alcoholism
Seizures are characterized by: 1. Occurrence during the period of abstinence 2. Development of a seizure on an adrenergic background, that is, in a state of increased excitability of the parasympathetic nervous system: increased blood pressure, tachycardia, sweating, tremor. Generalized convulsions predominate.
Eclampsia
The highest stage of late toxicosis of pregnant women, occurs against the background of nephropathy (edema, hypertension, proteinonuria). Usually, a convulsive seizure is preceded by preeclampsia (headache, flashing spots before the eyes, pain in the epigastric region).
First, small fibrillar contractions of the facial muscles occur, then tonic convulsions at 10- 20 seconds, the patient loses consciousness, then clonic convulsions develop.
Hysteria
Most often, this is a hysterical attack that develops in response to mental trauma or emotional shock.
The seizure occurs without an aura and is not accompanied by loss of consciousness. The patient falls, but does not hurt himself; tonic convulsions develop, which are pretentious in nature (theatrical) and are characterized by great diversity, both in manifestation and in duration. They differ significantly from the relatively stereotypical seizures of epilepsy. A typical so-called hysterical arc, when the patient leans on his heels and head, as a result of which the torso is bent in an arc. Patients can bite the fingertips of the tongue, lips, eyes are tightly closed during a seizure, the patient actively resists attempts to open them. When the eyes can be opened, it is noted that the pupils react well to light, unlike epilepsy. Occasionally there is urinary incontinence, but never defecation. Following tonic convulsions, clonic convulsions may develop, but unlike epilepsy they are chaotic and resemble purposeful movements. Patients tear their clothes and hit their heads on the floor. After the attack ends, sleep does not occur.
Treatment of hysteria
1. Remove viewers. 2. Tranquilizers.
Seizures in children
You can read about seizures in children in a separate article.
Convulsions due to metabolic disorders
The basis of seizures is a reduced threshold of excitability of the neuromuscular system, as a result of which seizures occur even in normal conditions. Observed in various diseases accompanied by disorders of calcium, phosphorus, lipid, and amino acid metabolism.
Methods for examining patients with seizure syndrome
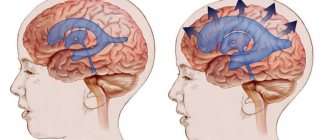
1. EEG - there is a focus of paroxysmal activity, characteristic of epilepsy 2. X-ray of the skull (Better than MRI), a tumor appears, defects in the development of the skull bones. 3. Angiography of cerebral vessels: aneurysms, blood clots are detected 4. Spinal puncture - disturbances in liquorodynamics, high cerebrospinal fluid pressure is observed in cases of volumetric processes in the brain. Blood in the cerebrospinal fluid indicates a cerebral hemorrhage. 5. EchoEg - displacement of brain structures in any direction due to volumetric processes that take up space and displace the brain to the opposite side. 6. Radioisotope brain scan - look for an area of increased isotope capture or decreased capture. 7. CT scan - look for a tumor or enlargement of the ventricles 8. Electromyography - study the level of muscle excitability
Signs
Medical experts call epilepsy the main disease leading to convulsive syndrome. The approach of a tonic attack can be predicted in advance by several signs: hearing and smell become more acute, and an unpleasant taste appears in the mouth. Epileptics fall into unconsciousness and scream or howl loudly. The muscles experience extreme tension: the jaws tighten, breathing becomes difficult, the face turns blue. The duration of the attack does not exceed 3-5 minutes. After the muscles relax, a sleepy state sets in, and the person is unable to remember what happened.
Localized and generalized tonic seizures
Generalized convulsions : convulsions of the torso, limbs and lungs are added to muscle arrhythmia. The arms twist unnaturally, but the lower limbs remain in a relaxed state. The entire body is under extreme tension. The jaw closes tightly due to the tension on the face, and the head tilts towards the back. A person under such tension is rarely conscious. Generalized tonic convulsions are combined with epileptic seizures. A similar effect can occur due to the penetration of a toxic substance into the body.
Localized seizures are characterized by a paralytic effect on only one part of the body. Contractions do not occur constantly, but in portions, with short intervals. During localized convulsions, the person remains conscious. It is necessary to eliminate the source of irritation and provide rest for the body. No special medical skills are required to eliminate such seizures.
Features of tonic seizures
Tonic cramps are severe tension in one or more muscles. It grows slowly and then goes away on its own. During an attack, the muscle becomes hard to the touch and stands out prominently through the skin. Most often, such spasms are localized in the legs or arms. They are also possible on the face, neck, back, and stomach. Spasm can occur both as a result of pathologies of the brain or internal organs, and under the influence of external factors.
We recommend reading: How to tell if your child is having seizures
Tonic seizures can be local or generalized. The most common are local spasms of one muscle, mainly the calf or foot. This type of cramp is also called crampy. It is very painful and most often occurs at night. There are also tonic spasms in the hands. They develop as a result of overexertion of the hand during prolonged writing or working at the computer. Tonic spasms can also affect the muscles of the neck or face. In this case, blepharospasm, trismus, torticollis, hemispasm and other pathological conditions appear.
Generalized tonic convulsions occur with epilepsy or serious damage to the nervous system. At the same time, all the muscles of the limbs, torso, neck, and face tense. Most often, the body is stretched, sometimes arched, the head is thrown back. Spasm of the respiratory muscles, slowing of the pulse, involuntary urination and defecation may occur. The jaws are clenched tightly, so biting the tongue is possible. In severe cases, the patient loses consciousness.
Along with spasms of the striated muscles of the skeleton, there are spasms of smooth muscles. They are observed in angina pectoris and bronchial asthma. There may be spasms of the esophagus, intestinal or renal colic. If skeletal muscle cramps, apart from pain, cause almost no inconvenience, then contractions of smooth muscles disrupt the functions of internal organs. They can lead to heart failure and respiratory arrest.
A tonic spasm can affect just one muscle
Differences between clonic and tonic seizures
A specific feature of tonic spasms is the sudden tension of all muscles. The body is held in a tense state for a long time. The cause of tonic seizures lies in the cerebral cortex. Convulsions can overtake the patient in his sleep if he was very active the day before. Spasms usually do not affect the facial muscles, respiratory system and arms.
Clonic seizures vary in frequency. Severe spasms are replaced by temporary relaxation. Irregular spasms occur on the face and hands. The torso is involved in a convulsion if the patient has developed attacks of epilepsy. Tonic and clinical convulsions occur alternately in acute epilepsy.
Diagnostics
Early diagnosis is necessary to determine the cause of tonic and clonic seizures. The results obtained will determine the risk of recurrence of attacks, the nature and scope of therapeutic measures, and the outcome of the disease. The examination begins with a history and medical examination, after which the neurologist prescribes additional procedures:
- Laboratory tests.
In a biochemical blood test, attention is paid to pH, nitrogen content, and protein levels. Diagnosis of neuroinfections is carried out by identifying specific antibodies and changes in the cerebrospinal fluid. Hereditary diseases are confirmed by molecular genetic analysis. - Tomography.
Neuroimaging methods provide insight into structural disorders in the central nervous system. Brain CT data are highly informative for traumatic brain injuries, hemorrhages, and tumors. MRI is better at detecting foci of neurodegeneration, demyelination, and ischemia. - Electroencephalography.
The leading method for diagnosing paroxysmal conditions is EEG. The study determines epileptiform activity, clarifies its localization and the functional state of the brain.
Changes in blood vessels are detected by neurosonography, which helps verify ischemic damage. The displacement of the midline structures of the brain is visible on Echo-EG; ultrasound is used to examine the condition of parenchymal organs (kidneys, liver). Mixed seizures must be differentiated from other paroxysmal conditions encountered in neurology and the clinic of internal diseases.
Causes of tonic seizures
Causes of seizures include:
- Disturbed neurology
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system, swelling.
- Infectious diseases
- Poisoning of the body
- Hysterics
- Sprains and microtraumas
- Overheating and lack of water in the body
- Depletion of the body in vitamins and minerals
- Diabetes, kidney disorders, impaired thyroid function.