Cerebral edema occurs against the background of blood circulation disorders caused by various diseases or functional abnormalities.
- Cerebral edema: prediction and symptoms
- Symptoms of swelling from hemorrhagic stroke
- Symptoms of swelling from ischemic stroke
- Cerebral edema from stroke and its features
- Reasons for development
- Care and rehabilitation
- Boarding houses for post-stroke patients "Olympia House"
The pathological condition has its consequences and can even lead to death; depending on the symptoms, it helps to determine the type of stroke suffered.
If even minor signs are detected and there is a suspicion of the formation of edema, it is necessary to arrange a visit to the doctor. An emergency call will help diagnose the condition of an elderly patient and promptly provide the necessary assistance, provide decent care and concern.
Cerebral edema: prediction and symptoms
Stroke is defined by medicine as a circulatory disorder and this condition leads to oxygen starvation of a certain area of the brain. Cortical cells die, and the patient's condition worsens due to the accumulation of watery secretions that put pressure on certain brain centers.
Watery accumulations are not capable of causing physical harm to soft tissues, but they accumulate in areas of nerve cells. This effect provokes an increase in intracranial pressure, which affects intracranial hypertension, the consequences of which (without providing the necessary assistance) become fatal.
With cerebral edema, a high degree of severity of the consequences of a stroke is determined, because this can cause unstable brain activity. The irreversibility of the impact is determined by real indicators of the extent of the spread and localization of edematous activity.
Without certain knowledge and understanding of the clinical picture, it is impossible to identify the symptoms of a pathological condition. The most difficult cases are considered to be attacks of hemorrhagic stroke, in which cerebral edema develops rapidly, putting the life of an elderly person in serious danger.
Causes of cerebral infarction:
A cerebral infarction (stroke) is mainly caused by a blocked artery (ischemic stroke) or a ruptured blood vessel (hemorrhagic stroke). Our specialists see categories of patients who may experience only a temporary disruption of blood flow to the brain (transient ischemic attack or TIA), which does not cause permanent damage to the brain.
Types of ischemic stroke include:
Approximately 70% of strokes are ischemic strokes. Ischemic strokes occur when arteries to a patient's brain become narrowed or blocked, causing severely reduced blood flow (ischemia). The most well-known ischemic strokes include:
- Thrombotic stroke. A thrombotic stroke occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one of the arteries that supplies blood to the brain. The clot may be caused by fatty deposits (plaques) that accumulate in the arteries and cause decreased blood flow (atherosclerosis) or other artery diseases.
- Embolic stroke. An embolic stroke occurs when a blood clot forms from your brain - usually in the heart - and travels through the bloodstream to form in narrower arteries in the brain. This type of blood clot is called an embolus.
- Hemorrhagic stroke. A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain leaks or ruptures. Brain hemorrhage can be the result of many conditions that affect the blood vessels.
These include:
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure – arterial hypertension;
- Weak blood vessel walls (aneurysms);
- A less common cause of hemorrhage is the rupture of an abnormal tangle of thin-walled blood vessels (arteriovenous malformation).
Types of hemorrhagic stroke include:
- Intracerebral hemorrhage. In intracerebral hemorrhage, a blood vessel in the brain bursts and spills into the surrounding brain tissue, damaging brain cells. The brain cells outside the leak are deprived of blood and are also damaged.
- High blood pressure, trauma, vascular malformations, high dose use of blood thinning medications, and other patient factors can cause intracerebral hemorrhage in the brain.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage. In a subarachnoid hemorrhage, an artery on or near the surface of the brain bursts and enters the space between the surface of the brain and the skull. This bleeding is often signaled by a sudden, severe headache. Subarachnoid hemorrhage is usually caused by the rupture of a small sac- or berry-shaped aneurysm. After a hemorrhage, the blood vessels in your brain may widen and narrow randomly (vasospasm), causing damage to brain cells by further restricting blood flow.
- Transient ischemic attack (TIA). A transient ischemic attack (TIA)—sometimes known as a mini-stroke—is a temporary period of symptoms. A temporary reduction in blood supply to part of the brain causes Thias, which can last only three to five minutes.
Risk factor for cerebral infarction:
- The patient has an unhealthy lifestyle and constant emotional stress (work, relationships with family, financial losses, etc.);
- Overweight or obesity (often our patients are obese due to constant stress);
- Insufficient physical activity;
- Smoking, exposure to secondhand smoke and alcohol;
- Drug use;
- Blood pressure readings above 120/80 millimeters of mercury (mmHg);
- High cholesterol level in the blood (regular laboratory diagnostics of CBC, BAC, OAM);
- Diabetes;
- Cardiovascular diseases;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Age—people aged 55 years and older have a higher risk of stroke than younger people;
- Floor. Men have a higher risk of stroke than women;
- Hormones—use of birth control pills or hormone therapy that includes estrogen.
Symptoms of swelling from hemorrhagic stroke
There are many risk factors on the basis of which one or another type of pathological condition develops.
Hemorrhagic stroke is often characterized by the release of internal fluid with characteristic hemorrhage and health complications, with pronounced symptoms:
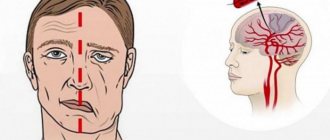
- disturbance of speech functions and functioning of muscle tissue;
- decreased limb control and facial paralysis;
- temporary loss or weakening of vision and hearing, extraneous noise;
- manifestations of swelling of the limbs and fainting, memory loss.
With a hemorrhagic stroke, there is a rapid impact on the brain and its tissues, nerve cells. The consequences of such exposure may be irreversible, therefore, if these symptoms are recorded, it is necessary to seek help as quickly as possible, providing the person with professional care and rehabilitation.
Rehabilitation
Subsequent rehabilitation is aimed at minimizing the consequences of cerebrovascular accidents and concomitant diseases, preventing the development of complications, increasing motivation for recovery, providing emotional support to the family, teaching the patient self-care techniques, and preparing for discharge to the next stage of rehabilitation, says Olga Kozlova.
It is better to start rehabilitation as early as possible; it must also be comprehensive, adequate to the patient’s condition, and also imply the active participation of the patient in his own rehabilitation. It is better if rehabilitation is carried out by a team of specialists who work as a single team and use clearly coordinated actions.
The vessel makes a verdict. How to understand how high your risk of stroke is Read more
“The team includes: a neurologist, a resuscitator (in the intensive care unit or in the intensive care unit), a cardiologist, a physical therapy doctor, a physiotherapist, an instructor-methodologist in physical therapy, a neuropsychologist-speech therapist, a medical psychologist, nurses, a social worker, and caregivers. or those caring for the patient and the patient himself, a psychiatrist. It is desirable to include a nutritionist (nutrition support specialist) in the team,” says Olga Kozlova.
Symptoms of swelling from ischemic stroke
An acute ischemic condition leads to a functional disruption of the normal reproduction of metabolic processes in neuronal cells.
Their intermediate area is filled with intracellular fluid, which leads to an increase in pressure and the formation of swelling, which has its own symptoms:
- acute headache that cannot be relieved even with strong medications;
- the appearance of vomiting and increased feeling of nausea with frequent convulsions;
- temporary disturbance of spatial orientation and feeling of loss;
- severe shortness of breath without any exertion or physical activity in patients;
- fainting and fainting, a visually determined disturbance of blood circulation.
In ischemic stroke, cerebral edema develops gradually and there is a high probability of prompt provision of the necessary assistance. At a certain level of diagnostic complications, it is important to organize constant monitoring of older people at risk.
Coma after stroke
Coma is seen as a borderline state between life and death. This complication often develops with a major stroke. Even after recovering from a coma after a stroke, the likelihood of a full recovery is, unfortunately, very low.
Signs of coma:
- general lethargy;
- quiet and incoherent speech;
- confusion or loss of consciousness;
- rave;
- lethargy;
- rapid breathing;
- weak pulse.
With relatively mild damage to brain tissue, the victim recovers within a few hours. In such cases, the prognosis is quite good.
Deep coma is characterized by a complete lack of response to external stimuli, a drop in blood pressure and hypothermia. Artificial maintenance of respiratory function is necessary; otherwise, the chances of survival are close to zero.
A person can be in a stable and serious condition from 2-3 days to several months. Coma in elderly patients is most dangerous; Their life prognosis is very unfavorable.
Cerebral edema from stroke and its features
The edematous condition is associated with quite serious consequences that may not appear immediately after a stroke. Depending on the location of the lesion, the degree of consequences and dysfunction of internal organs, the central nervous system, and the brain is determined.
Without rapid remission, which occurs thanks to good health and comprehensive rehabilitation, this condition can provoke irreversible consequences.
A severe intracranial complication associated with disruption of the central nervous system provokes the following consequences:
- distorted facial expressions;
- chronic headaches;
- limited movement;
- weakening of the sensory organs;
- deterioration of mental abilities.
After a stroke and cerebral edema, older people need to be re-taught to live and perform the usual activities for each person. To do this, it is necessary to provide him with complete rehabilitation, surround him with attention and care, and guarantee targeted medical care.
Reasons for development
Disruption of blood microcirculation in brain tissue stimulates the formation of a state of oxygen starvation.
This leads to cell necrosis, and intracellular fluid enters the cavity of the free space of the skull; brain edema can be caused by a number of reasons:
- stroke and fluid accumulation in the localization of nerve tissue;
- surgery with edema provoking coma;
- alcohol dependence and accumulation of toxic substances in tissues;
- a specific reaction of the body to a specific allergen.
Cerebral edema occurs in people of different ages, but those at risk are those whose age has exceeded 60-65 years. That is why it is important to organize constant supervision for an elderly relative with poor health, conduct regular medical examinations and strictly monitor his well-being.
Care and rehabilitation
To create optimal conditions for recovery after a stroke, it is better to choose a private boarding house for the elderly in the Moscow region. Specialized institutions provide recovery after timely identified cerebral edema, which helps minimize health consequences. Targeted and specific care ensures that negative impacts are reduced and conditions are created to restore the elderly person’s well-being.
Boarding houses for post-stroke patients "Olympia House"
Providing professional and qualified care for the elderly in Moscow, our network of boarding houses offers excellent living conditions.
Thanks to an integrated approach, each ward receives maximum attention to their health, medical care and constant supervision:
- conducting regular inspections;
- medical service;
- good nutrition and walks;
- development of a rehabilitation plan;
- psychological support.
The expanded network of private boarding houses for the elderly Olympia House includes a complex of nursing homes located in different regions. Using the services offered, you can choose the best conditions for elderly relatives and select a complex for rehabilitation and recovery.