What is lumbodynia
Pain with lumbodynia can be chronic or acute/subacute, but in any case it is caused by spinal pathology. Lumbodynia syndrome is considered a sign of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, although often with this diagnosis there may be no pain at all. The severity of pain can vary and depends on the individual and a combination of a number of factors. It occurs mainly in people of working age (25-45 years).
Lumbar pain can be localized only on one side or on both (right-sided, left-sided, symmetrical). It most often worries in the lower lumbar region and can radiate to the gluteal region (one or both buttocks).
Treatment of lumbodynia
In the conservative treatment of lumbodynia, first of all, the underlying disease is treated, against which the pain syndrome occurred in the lower back. The doctor prescribes an individual course for the patient, depending on the cause of the disease, age, gender, characteristics of the body and varying from the intensity of pain and the duration of clinical manifestations.
Rest is one of the components of treatment, without which therapeutic methods may not have the desired effect.
The course of treatment for lumbodynia can last three to six weeks. The course of treatment may include the following procedures:
- drug treatment is used to relieve pain using spinal joint blocks, intravenous and intramuscular injections: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs help reduce inflammation and reduce lower back pain, muscle relaxants, with drug treatment, relax spasmodic muscles, diuretics are used for tissue swelling, group vitamins Prescribed to nourish nervous tissue and improve the transmission of nerve impulses, chondroprotectors activate metabolic processes in articular cartilage.
- massotherapy;
- gentle manual therapy, increasing the mobility of motion segments, helping to reduce low back pain and improve the biomechanics of movements;
- autogravitational traction of the spine;
- acupuncture – to relieve pain, get rid of swelling and inflammation;
- hirudotherapy - to normalize blood circulation and metabolism;
- laser therapy and barolaserotherapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- electroanalgesia;
- kinesiotherapy;
- physical therapy is one of the most effective methods in the treatment of chronic lumbodynia associated with degenerative diseases of the spinal column. With the help of exercises, the abdominal and back muscles are strengthened, gradually relieving the patient of pain.
Surgical treatment of the disease is resorted to in some cases when conservative, drug treatment is not effective for six months.
Kinds
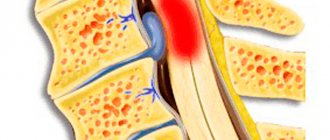
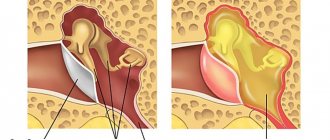
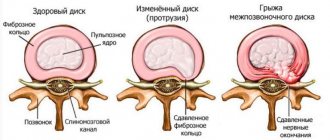
Vertebrogenic lumbodynia is the main manifestation of the chronic form of osteochondrosis (lumbar zone) and is more often characteristic of men. Can have any duration (last from several weeks/months to several years). If the cause of pain is diseases of the intervertebral disc (herniation, protrusion), then lumbodynia is called discogenic.
In addition to the above, “classic” one, there are other types. It can be combined with nagging pain in one or both legs (sciatica), in which case it is called lumboischialgia. (left-handed or right-handed). Depending on the distribution (on one or both limbs). Accompanies the non-radicular phase of lumbar osteochondrosis.
When the pain is intensified not only by movements, but even by the slightest activity, such as talking, sneezing, bending over, then this type is called lumbodynia with muscular-tonic syndrome. Often, there is a moderate curvature of the spine, causing pronounced reflex tension in the lower back muscles (bilateral or unilateral), which provokes pain.
Why is lumbodynia dangerous?
In the chronic form of lumbodynia, which the disease develops in the absence of timely treatment of the joints and spine, attacks of lower back pain become more frequent, with an increase in their duration and intensity.
Lumbar ischalgia is one of the severe complications of lumbodynia, accompanied by symptoms such as pain, fever or coldness in the lumbar area. Sudden, often unilateral pain in the lower back, radiating to the buttocks and spreading along the back of the thigh and to the knee. After some time, the pain drops even lower, and the patient has difficulty straightening his leg and limps heavily when walking.
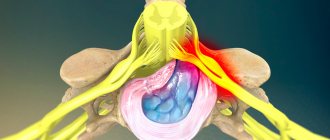
Sciatica is another complication of lumbodynia. An attack of sciatica is caused by damage to the spinal roots of the lumbosacral region and leads to weakness and numbness in the leg. Compression of the spinal cord roots is especially dangerous because in difficult cases it leads to paralysis of the legs.
Causes of lumbodynia
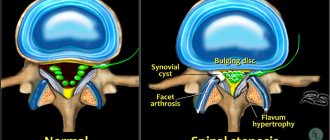
Low back pain (lumbodynia), both chronic and acute, is most often caused by pathological processes (degenerative-dystrophic) in the spine, especially in the lumbar region. In addition to osteochondrosis, lumbodynia is caused by its complications, such as protrusion, spondylolisthesis, intervertebral hernia, spondyloarthrosis, spondylosis.
The mechanism of lumbodynia is based on irritation of the nerves (especially sinuvertebral). Pain is especially pronounced with cracks in the fibrous ring. Also the cause is abnormalities in the development of the lumbar spine.
Pain can occur after a single physical overload, lower back injuries, hypothermia, stress, sudden turns of the body, hypothermia, exposure to drafts, prolonged exposure to an uncomfortable or monotonous position. Moreover, lumbodynia can manifest itself not only after a few days or weeks, but even several months after the provoking factor.
The risk group also includes those who are overweight, have certain chronic diseases, have infectious diseases, workers in hazardous industries, those who experience increased stress, lead an adynamic lifestyle, or are in an uncomfortable or the same body position for a long time.
Types of lumbodynia
There are two types of lumbodynia: acute and chronic.
Acute lumbodynia occurs suddenly after heavy lifting or sudden awkward movement. Most often, a person's metabolic processes in the spine are disrupted. Lower back pain decreases when lying down and increases with any movement. This form of the disease may resolve abruptly.
Chronic lumbodynia can be a continuation of the acute form or appear independently of it. The chronic form of the disease occurs due to arthrosis of the facet joints, myofascial syndrome, spondylolisthesis or spondylolysis, and vertebral instability. With chronic lumbodynia of the spine, treatment will be more difficult, due to the greater “neglect” of the situation.
Symptoms
With vertebral osteochondrosis, lumbodynia is aching in nature and is more pronounced in the morning. May have different durations, decrease or increase during the day. There are provoking factors that increase or decrease the intensity of lumbodynia. For some it is caused by activity, while for others it is its absence; accordingly, opposite actions ease the pain. A combination of these manifestations may occur in the same person.
Pressure on the vertebrae and paravertebral areas in the lumbar area is usually painful. In addition, bending and many other movements are difficult and most often accompanied by pain. Patients have difficulty bending, especially forward, and the angle of inclination of the torso becomes limited. There may be sharp pain in response to palpation of the exit point of the sciatic nerve on the thigh.
Doctors explain the subsidence of pain in the lying position by reducing the load on the lumbar intervertebral discs. Patients intuitively or consciously find the most comfortable position (in which the pain is least pronounced). Most often, this is a position lying on your side with your legs bent.
At first, there is moderate lumbodynia, gradually the pain intensifies, but does not reach the same degree of severity as with lumbar pain (lumbago), also called acute lumbodynia. Patients can move around and do work, but the quality of life is significantly reduced.
Diagnosis of lumbodynia
Lumbodynia can be diagnosed in different ways. A neurologist diagnoses this disease. The most common is a clinical examination and questioning of the patient, combined with static and dynamic examination of the spine, as well as manual diagnostics. Additionally, the organs of the pelvic and abdominal cavities are examined to exclude diseases that are a source of referred pain. In addition, MRI, radiography, and ultrasound diagnostics will not be superfluous. During the examination, lumbodynia is differentiated from myositis of the spinal muscles and pathologies of the hip joint.
IMPORTANT! Lumbodynia is a serious symptom that can tell a person about significant problems in the lumbar spine, ranging from inflammatory phenomena to destructive diseases. That is why, if you have lumbodynia, you cannot self-medicate, but you should definitely consult a specialist!
Experienced doctors at the Kuntsevo Medical and Rehabilitation Center will conduct a thorough diagnosis and understand the causes of the symptom. A treatment plan for the patient will then be drawn up. Make an appointment with our doctor and take a step towards getting rid of lumbodynia!
Sign up
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of lumbodynia is not difficult, since its clinical manifestations are such that they can easily distinguish it from other diseases. It is much more difficult to determine the cause that caused this syndrome. In order to obtain the desired data, you must:
- conduct a somatic examination to exclude non-vertebral causes;
- take laboratory tests;
- undergo an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- undergo an examination by a gynecologist and urologist;
- undergo an x-ray of the spine in two projections: straight and lateral;
- undergo or MRI, which are the most highly informative diagnostic methods for lumbodynia.
Treatment with manual therapy
You can get rid of lumbodynia only by eliminating the causes that caused it. This type of treatment can be considered complete. In other cases, the help will have a temporary effect and after some time, lumbodynia will appear again, and if the treatment was inadequate, it will intensify or recur. It is important to find a good chiropractor, otherwise you may not only not be cured, but even make things worse.
Since the main cause of lumbodynia is considered to be vertebral osteochondrosis, the cause of which, in turn, is improper functioning of the spine, it is not lumbodynia that should be treated, but osteochondrosis. In addition, by getting rid of osteochondrosis, you will protect yourself from the occurrence of its complications, such as hernias and disc protrusions.
Manual therapy is considered one of the most effective ways to eliminate problems in the spine. It is especially effective in combination with the subsequent implementation of a complex of physical therapy (physical therapy). All this not only improves the condition, but also stimulates recovery processes, thanks to which the course of the disease can sometimes not only be stopped, but also reversed.
The number of procedures is prescribed individually, based on the patient’s health characteristics, stage of the process, complications, and concomitant diseases. It is also necessary to perform exercise therapy to consolidate the achieved result and maintain it after treatment.
Diagnosis and treatment
Lumbodynia is difficult not to notice, as it makes itself felt immediately. It is important to accurately establish the cause of its occurrence, since therapy depends on this. The patient may be prescribed the following diagnostic procedures:
- laboratory blood test
- x-ray of the lumbosacral spine;
- MRI or CT scan of the lumbar region;
- Ultrasound of the genital organs, abdominal cavity.
If the cause of lumbodynia is an infection or gynecological diseases, then you will need to consult a specialized doctor, as he will take part in drawing up a treatment plan. Treatment involves eliminating the pain syndrome and the causes of its occurrence. Discomfort is relieved with:
- blockades using anesthetics;
- manual techniques (massage);
- taking (orally and locally) painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs (in the form of tablets, ointments, injections);
- therapeutic exercises;
- osteopathic technicians.
If lumbodynia is chronic, its treatment will take longer. During therapy, a strict restriction on physical activity is introduced, the patient needs the most gentle regime of work and rest; wearing a corset may be prescribed. However, it should be remembered that without treatment of the underlying disease that provoked attacks of lumbodynia, pain can return at any time, so complex therapy is required.
Branch:
Manual therapy
The reception is being conducted
Make an appointment with a chiropractor (video consultation available)
Your message has been sent
Thank you for contacting Multidisciplinary Medical!
Your message will be processed shortly and we will contact you to clarify the details.
Be healthy!
Join us on social networks!
Current news, promotions, useful information.
How to find us
OUR ADDRESS
Moscow, st. Shchukinskaya, 2
Shchukinskaya, Streshnevo, Sokol
TELEPHONE
+7