Many functions of the human body continue to function after death for several minutes, hours or even weeks. This sounds like science fiction, but it is a documented fact. Nails and hair grow for several days after death, and skin cells also function. It has been proven that the brain continues to function for some time. So how long does the brain live after a person’s death?
Controversies and theories
Numerous studies have been carried out, the results of which were the statement that the human brain continues to function for 4-6 minutes after the death of the body. Many scientists have argued about how a person sees and relates to his own death and still cannot come to a common conclusion.
Some doctors believe that the individual’s mind dies immediately, while others believe that it continues to work indefinitely. Recent testing has shown that after death, the work of the central nervous system does not stop. Therefore, in a state of clinical death, a person can be aware of what happened to him, because consciousness continues to function.
Modern medicine has reached a high level of development. New devices can keep the body in working condition (pumping blood and oxygen) for years. Therefore, a reasonable question arose: how long does the brain live after death, and what can be considered death in general? Its main symptom is the death of neurons, which leads to the loss of the individual’s personality.
Diagnostics
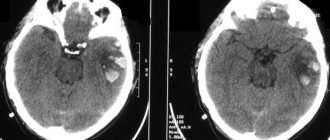
When diagnosing, the doctor must collect anamnesis. He must find out how long ago the patient fell into such a dangerous state, under what conditions he lost consciousness, whether he had speech or motor activity
It is important to know what event preceded the loss of consciousness. An examination is carried out by a neurologist, he necessarily assesses the patient’s level of consciousness and checks his reflexes. Body temperature must be measured
If the temperature is below 32.2°C, it may distort the picture and show a false death. In this case, the person may be alive, but tests will show the opposite, since physiological processes literally freeze from the cold
Body temperature must be measured. If the temperature is below 32.2°C, it may distort the picture and show a false death. In this case, the person may be alive, but tests will show the opposite, since physiological processes literally freeze from the cold.
From the editor: Prevention of migraine with the help of medications and folk remediesA blood test is prescribed that will help determine whether the metabolism is disturbed, whether there is hormonal dysfunction, and at what level the glucose levels are.
To correctly diagnose brain death, inpatients resort to instrumental research:
- encephalogram (EEG);
- contrast study of cerebral vessels;
- test with irritation of the eardrums (ice water is dripped onto them through the ear canal);
- apneic oxygenation test.
Oxygen starvation is extremely destructive for neurons, even if it is not long-term. Literally after a few minutes of complete lack of oxygen supply, tissues begin to die. The electroencephalogram in this case will show a zero line. This means that there is no brain activity at all.
Encephalography examines brain activity. In this case, the device registers biocurrents, their work is reproduced on paper in the form of curves.
The diagnostic protocol also includes the study of cerebral vessels using a contrast agent. It cannot always be accomplished, as there may be financial restrictions, and sometimes there is simply no equipment. The essence of the test is that a contrast agent is injected, which enters the brain vessels through the bloodstream and identifies possible areas of necrosis. If the brain is dead, the substance does not enter its vessels. This is one hundred percent confirmation of death.
Apneic oxygenation involves temporarily removing the patient from a ventilator. The goal is to observe whether spontaneous respiratory movements have appeared. The monitor monitors the level of carbon dioxide in the blood. It is carbon dioxide that stimulates the body to produce breathing movements. If after 8-10 minutes breathing does not appear, and the level of CO2 in the blood jumps by 20 mm Hg. Art. higher than the original, we can definitely talk about death.
Dying from a scientific point of view
A serious illness or fatal injury leads to exhaustion of the body and the development of a thermal state. As a result, the functioning of all organs and systems is disrupted.
At this stage, timely intervention by doctors with the help of intensive care can help return the body to normal.
If resuscitation does not give a positive result, a preagonal state occurs, the main characteristics of which are:
- decreased blood pressure;
- weak brain response to stimuli;
- slow heart rate;
- weak breathing.
The body uses all its strength to correct the situation. Therefore, in a state of death agony, a person may feel improvement, but this lasts only a moment. The central nervous system cannot cope with its work, so the pressure can be restored and breathing can return to normal.
The body spends its last strength on this, after which clinical death occurs. There is no breathing, the heart does not beat, all metabolic processes in the cells slow down and stop. The body lacks oxygen, the brain suffers the most. After the actual death of the body, the stored nutrients last no more than 6 minutes. This is exactly how long the brain works after cardiac arrest.
If, within 6 minutes after cardiac arrest and lack of breathing, the necessary actions for resuscitation are carried out, which will prevent necrosis of organ cells, then the person can be brought back to life.
If biological death has occurred, that is, the cerebral cortex has died, then this is irreversible. With the help of the device, you can maintain the heartbeat and ventilate the lungs for some time, but this is no longer a sign of life.
What are the different types of death?
Doctors distinguish 3 types of non-violent death:
- physiological or from old age;
- pathological or from illness;
- sudden or from sudden acute conditions.
Sudden death is one of the most tragic, when a person ceases to live in complete prosperity. Most often, sudden cardiac arrest leads to such an end, which can occur in both an adult and a child.
The heart is a very complex organ; comparing it with a simple pump is incorrect. In addition to specially organized cells—cardiocytes that form cavities—it has an autonomic nervous system. All this is controlled by the brain and spinal cord, and also responds to hormones and electrolytes contained in the blood. Failure of any of the components may result in a sudden stop.
In essence, sudden cardiac arrest is the collapse of all life support systems. The blood stops carrying oxygen and removing waste products, life simply stops.
Anyone nearby should begin manual CPR. With the efforts of those around you, you can maintain life for up to half an hour. This time is enough for doctors to arrive and provide specialized assistance.
How does lack of oxygen affect the brain?
There are two forms of oxygen deficiency:
- Anoxic damage. The brain is completely deprived of oxygen through sudden cardiac arrest, suffocation or any other injury.
- Hypoxic damage. He receives a smaller dose than is needed for full functioning.
The organ will not be harmed by a few seconds without oxygen, so people can dive or live with breathing problems.
How long does the brain live without oxygen? The onset of anoxic damage depends on many factors: the condition of the organ, the level of oxygen in the blood at the time of injury, and the general condition of the body. A minute without oxygen can cause serious injuries, and the condition only gets worse:
- 180 seconds will result in loss of consciousness;
- neurons begin to die after 1 minute without oxygen;
- 3 minutes lead to serious consequences;
- 5 minutes is inevitable death;
- 10 minutes - coma, while the brain can still function, but suffers severe damage;
How many minutes does it take for the brain to completely die? 15 minutes is enough for irreversible consequences.
If you train your body, you can hold your breath for up to 22 minutes, and the brain does not suffer any damage.
How to recognize the first signs that a person is dying
Signs that a person is dying can occur weeks, and even months before the fatal end. Scientists have been studying this issue for a long time and have determined that patients have special “reflex signs” that cannot be found in healthy people. Symptoms of imminent death persist even after seemingly successful treatment, and these bells indicate that the person is at the point of no return. These signs include:
- Shortness of breath even with minimal physical exertion. Shortness of breath has a special character that has nothing in common with the shortness of breath of a person who is out of breath.
- Excessive appetite, accompanied by slow or sudden weight loss.
- Fluid retention in the body, as a result of which there is severe swelling of the lower extremities to a bluish tint.
- A constant feeling of fatigue and drowsiness at hours that are uncharacteristic for a healthy person, for example, the morning.
- Intermittent sleep, being awake at hours when a healthy person is in the deepest sleep, such as dawn.
- Mental disorders - delirium.
- Frequent nausea, yellowness of the skin, loss of taste.
Simple everyday activities for a person who is near death are excessively tiring. People stop being interested in previously favorite things, begin to talk and communicate less with relatives, and sleep more. Scientists indicate that this is how energy imbalances, caused by deterioration of metabolic processes and brain functions, work.
Of course, not a single scientist or doctor can say exactly about the moment of death. In this whole series of factors, significant phenomena play a role: current illnesses, the course of the disease, the treatment methods used.
Why is oxygen so important?
Of the total body weight, gray matter occupies only 2%, but at the same time, for full-fledged work, it consumes 20% of all gas entering the body. Without oxygen, the brain will not be able to do its job.
Glucose is needed to perform any activity, such as the neurons that control all body functions. Without oxygen, cells will not be able to produce this substance and subsequently convert it into the necessary energy.
If you deprive the brain of oxygen, the cause of its death will be the inability to nourish the cells, because there simply will not be energy (glucose) for this.
Why is biological death inevitable?
Death creates space for new things. This statement is also true for the human body, which consists of billions of cells that divide every day and thus ensure growth. Living organisms have a very effective method of destroying unnecessary or potentially dangerous cells, such as viruses or cancer cells: programmed cell death - where old cells are replaced by new, identical cells. But over time, cell division slows down and stops. Telomeres, the ends of chromosomes, are probably responsible for this: if telomeres are shortened by cell division, then eventually the cells stop dividing, and as a result, old cells do not die. Today scientists know that the shorter the telomeres, the faster the body ages. This occurs even despite the existence of telomerase, an enzyme that can ensure cell division continues. The fact is that telomerase can also accelerate the development of cancer and for this reason the enzyme is active only in a few cells.
Editor's Note: Best Head Examination Methods
In fact, everything in our Universe does not exist forever - even stars have their own life cycle
It turns out that the process of physical aging ends with the failure of several organs: the cardiovascular system, lungs and brain do not function. From a medical point of view, there are different types of death: “clinical death”, in which the cardiovascular system fails, the pulse and breathing stop, and the organs are no longer supplied with oxygen and nutrients. In cases of clinical death, cardiopulmonary resuscitation is still possible and is often successful. However, in case of brain death, resuscitation is impossible.
What confirms brain death?
The main criteria for death may be the following:
- Lack of response to external stimuli.
- No brainstem reflex:
- emetic;
- pupil reaction to light;
- corneal reactions;
- no breathing.
But such indicators cannot always indicate the occurrence of death. It is mandatory to measure the pupils, which must be fully dilated or of average size. If the pupils are narrow, this may indicate the presence of vital processes.
In general, it is very difficult to determine this condition; any mistake will cost the patient’s life. There are basic criteria for organ death, which were formulated in 1968 at Harvard. All neurologists and resuscitators adhere to them and always use them before turning off the ventilator and declaring death.
First, each patient is diagnosed with a disease, based on which various causes are identified that led to the death of the human brain. Afterwards, all conditions that are externally similar to death, but can be reversible, are necessarily excluded:
- overdose of medications;
- poisoning of the body with toxins;
- dysfunction of the endocrine system.
After this, doctors determine the symptoms of organ stoppage:
- coma;
- no reaction to pain and irritants;
- no reaction of pupils to light;
- absence of reflexes of the pharynx, trachea and eyeball.
Also, a test is carried out for the presence of breathing - the blood is saturated with gases, controlling their quantity, after which the mechanical ventilation is stopped, and the level of carbon dioxide in the arteries is measured. The result is considered positive at 60 mmHg. Art. and lack of breathing. If breathing resumes, the lungs are ventilated again and try to restore the person’s vital functions.
Another stage is monitoring a person for 6 hours with primary brain damage. They check all parameters, the presence of a reaction, and monitor all changes that may appear in the presence of brain activity.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing, the doctor must collect anamnesis. He must find out how long ago the patient fell into such a dangerous state, under what conditions he lost consciousness, whether he had speech or motor activity
It is important to know what event preceded the loss of consciousness. An examination is carried out by a neurologist, he necessarily assesses the patient’s level of consciousness and checks his reflexes
Body temperature must be measured. If the temperature is below 32.2°C, it may distort the picture and show a false death. In this case, the person may be alive, but tests will show the opposite, since physiological processes literally freeze from the cold.
A blood test is prescribed that will help determine whether the metabolism is disturbed, whether there is hormonal dysfunction, and at what level the glucose levels are.
To correctly diagnose brain death, inpatients resort to instrumental research:
- encephalogram (EEG);
- contrast study of cerebral vessels;
- test with irritation of the eardrums (ice water is dripped onto them through the ear canal);
- apneic oxygenation test.
Oxygen starvation is extremely destructive for neurons, even if it is not long-term. Literally after a few minutes of complete lack of oxygen supply, tissues begin to die. The electroencephalogram in this case will show a zero line. This means that there is no brain activity at all.
Encephalography examines brain activity. In this case, the device registers biocurrents, their work is reproduced on paper in the form of curves.
The diagnostic protocol also includes the study of cerebral vessels using a contrast agent. It cannot always be accomplished, as there may be financial restrictions, and sometimes there is simply no equipment. The essence of the test is that a contrast agent is injected, which enters the brain vessels through the bloodstream and identifies possible areas of necrosis. If the brain is dead, the substance does not enter its vessels. This is one hundred percent confirmation of death.
Apneic oxygenation involves temporarily removing the patient from a ventilator. The goal is to observe whether spontaneous respiratory movements have appeared. The monitor monitors the level of carbon dioxide in the blood. It is carbon dioxide that stimulates the body to produce breathing movements. If after 8-10 minutes breathing does not appear, and the level of CO2 in the blood jumps by 20 mm Hg. Art. higher than the original, we can definitely talk about death.
Editorial: Sensory or sensory neuron
How long does the brain survive after cardiac arrest?
Conducted studies have shown that the activity of the central nervous system in the absence of a heartbeat lasts differently for each individual person. Therefore, it is impossible to say exactly how long the brain lives after cardiac arrest. When the oxygen supply instantly stops, it is impossible to calculate the duration of clinical death, which leads to its death.
The neurons that suffer the most are those that begin to die after 10 minutes without recharge. But in fact, these cells can continue to work. There were cases when, after resuscitation, already dead areas began to function as before again.
Organ damage due to lack of oxygen depends on many indications. After quality therapy, some damage may be compensated or disappear. If he has been without oxygen for a long time, the consequences may include:
- damage to specific areas (loss of the ability to speak, but the patient understands the language);
- change in character;
- memory problems;
- loss of coordination (some people could no longer write or walk);
- impaired perception of pain;
- behavioral changes, incontinence, aggression;
- the occurrence of chronic pain when there is no injury (occurs when the organ cannot correctly process the information received);
- mental illness.
Possible reasons
Brain death can occur for various reasons, but the pathophysiological processes are approximately the same. Brain death occurs due to persistent circulatory disorders, oxygen starvation, and stagnation of metabolic products. Diseases that lead to organ death can be varied: trauma, inflammatory diseases, heart disease, multiple organ failure and many others.
After cardiac arrest, the brain does not die immediately. This depends on many criteria: the general condition of the patient, concomitant diseases, the age of the patient, the disease that caused this condition, the ambient temperature. Irreversible tissue necrosis begins after 3 minutes, but in young healthy people this process is slower. At low air temperatures, the brain dies more slowly. If after 3 minutes or more the patient responds to resuscitation measures and returns to life, no one can predict the consequences; perhaps some neurons have died, and this will significantly affect the patient’s life in the future.
Studying gene expression in brain cells after death
For several hours after death, some brain cells remain active. Some of them even significantly increase their activity.
This discovery was presented by collaborators at the University of Illinois at Chicago. The work was published in the journal Scientific Reports.
The team analyzed gene expression in brain tissue obtained during routine neurosurgery. This was done several times to simulate different intervals after death (within 24 hours). It turned out that some genes increased their expression during this period of time.
These “zombie genes” were specific to one cell type: inflammatory glial cells. After “death”, for several hours they continued to grow and expand the network of their process structures.
This discovery fits quite logically into the functions of glial cells, since their main task is to cleanse surrounding tissues of metabolic products after various injuries. Another context of the new discovery is more important: most studies conducted on brain tissue that were obtained post-mortem aim to determine the effectiveness of various drugs for the treatment of neuropsychiatric diseases (for example, autism, schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease and others), but in these research does not take into account the fact that after death some genes and cells remain active.
According to the data obtained, about 80% of the analyzed genes remained relatively active within 24 hours - their expression did not undergo significant changes. Among them were the so-called “housekeeping genes” responsible for the most basic cellular functions. At the same time, another group of genes, responsible for processes such as memory, thinking and pathological seizure activity, sharply degraded within a few hours. It is these genes that may be extremely important for researchers studying schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease and epilepsy. The third group of genes, “zombie genes,” increased their activity, the peak of which occurred at 12 hours postmortem.
This discovery makes an important contribution to the biological context of preclinical research investigating neuropsychiatric diseases.
Source: https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-85801-6