After a person has at least once been in a state of severe alcoholic intoxication, due to the consumption of large quantities of alcoholic beverages, he begins to be interested in the question: will the organs and their functions be restored? It is especially important whether brain cells are able to recover after quitting alcohol. The same question is asked by a person undergoing rehabilitation after treatment for chronic alcohol addiction.
There are times, especially on holidays, when a person, without meaning to, drinks a very large dose of alcohol in a short time. It is clear that you should not expect pleasant sensations after this. People who suffer the most are those who are not used to drinking alcoholic beverages, or who do so rarely and in small portions. They will have headaches from drinking alcohol for a long time.
Research shows that only five percent of ethanol leaves the body naturally, that is, through sweating and urination.
The rest of it is broken down in the body, and it will take some time to remove all the breakdown products of ethanol from the body. It also depends on the physical condition of the person, what age he is, and his gender. And of course, what drinks did he drink and in what quantities.
Destructive effects of ethanol on brain cells
There is no doubt that ethanol destroys brain cells. This is evidenced by gait disturbances, inhibition of reactions, and memory disorders. As soon as ethanol stops entering the body, functions are gradually restored.
Everyone knows that alcohol is harmful to health. It all starts with a violation of consciousness, and can lead to the fact that a person becomes disabled forever. There are some factors that help determine how much damage is done to brain cells and what effect ethanol has on them.
These include:
- how often a person drinks alcohol and in what quantities;
- at what age did he start drinking alcohol, and when did he become dependent on alcohol?
- what gender is the person, how old is he, is he educated, is there a genetic predisposition to alcohol addiction, and have there been any cases of chronic alcoholism among relatives;
- what physical condition the person is in;
- whether fetal alcohol syndrome has been observed in humans.
Disorder of consciousness for a short time, which occurs after drinking alcohol, occurs much more often than doctors previously claimed. Such a result can be defined as a possible consequence of alcohol intoxication, which does not depend on whether the person has symptoms of chronic alcohol dependence or how old he is.
Scientists conducted an experiment trying to identify the negative effects of ethanol on brain cells associated with short-term consciousness disorders. More than seven hundred students participated in the experiment. They all answered the same question: has it ever happened to you when, waking up in the morning, after a night of alcoholic outpourings, you were unable to remember what you did in the evening and where you were?
More than half of the youth already had experience of drinking alcoholic beverages, and answered in the affirmative: yes, after drinking a large amount of alcohol they experienced memory disorders. Forty percent of them said this had happened in the past year, and nine percent of respondents had consumed alcoholic beverages in the past two weeks and experienced brain fog.
Is it true that alcohol kills brain cells?
Return to all news
Where did the idea that alcohol kills brain cells come from? One potential source for this claim is a 1990 study by British scientists Harper and Krill. They found that drinkers had fewer brain cells overall than nondrinkers. Consequently, some people began to think that alcohol causes brain cell death.
However, according to a recent article in the American journal Scientific American Mind, alcohol does not directly cause the death of brain cells, but it can seriously damage them. In particular, it can be dangerous for neuron dendrites. Dendrites are specialized branched processes of neurons (nerve cells) that perceive information and transmit it to the cell itself. Thus, damage to dendrites causes a disruption in the exchange of information between brain cells.
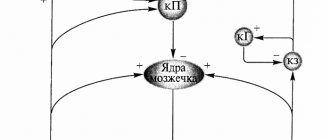
These disorders, in particular, occur in the cerebellum, which is the part of the brain responsible for the position of the body in space and coordination of movements. According to Dr. Petney, these injuries may not always result in permanent impairment of brain function, but they can cause changes in neural structure. So perhaps the main question is not whether alcohol kills brain cells, but what harm it does to the brain.
Alcohol use and mental health problems:
Anxiety and depression are fairly common consequences of drinking alcohol. A more serious disorder, alcohol psychosis, can be caused by drinking more than 300 ml of alcohol every day for several weeks. In addition, stopping alcohol consumption can become a real problem for drinkers and provoke nervousness, tremors, palpitations, as well as alcoholic psychosis when the binge is interrupted.
Alcohol and brain dysfunction:
Alcohol causes severe dehydration. In extreme cases, dehydration can reach the point where permanent brain damage occurs. This is one of the conditions that can be accompanied by alcohol intoxication (poisoning). In addition, alcohol-related brain disorders include alcohol-related dementia and Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome.
Alcohol and the risk of dementia:
A recent study found that those with a specific form of the gene, apolipoprotein E4, have a higher risk of developing dementia if they drink alcohol regularly. Those who do not have apolipoprotein E4 are also at risk of developing dementia, and this increases in proportion to the amount of alcohol consumed regularly.
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome:
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome is caused by a deficiency of thiamine, or vitamin B1 as it is otherwise known. A deficiency of this vitamin is observed in 93% of alcoholism patients. Drinking alcohol for a long time leads to disruption of the supply and storage of thiamine in the body. First, Gaye-Wernicke encephalopathy occurs, which is manifested by lack of appetite, general weakness, memory disorders, pathological eye movements, and unsteady gait. If this condition is not treated, it leads to Korsakoff's syndrome, accompanied by dementia and psychosis.
Can drinking alcohol improve brain function?
Despite all the negative effects of alcohol, some studies have shown that alcohol can have a positive effect on brain function. For example, a study published in the American Journal of Epidemiology demonstrated that the ability to perceive and learn about the world around us is higher in those who drink alcohol in their daily lives, compared to those who did not drink it at all. However, researchers are concerned that the study's findings will be used to encourage increased drinking.
| Hangover relief at home Special offer - hangover relief at home from RUB 4,000. 20/08/2021 Read more |
| They got rid of the binge, what next?.. After a person is brought out of the binge, the patient and relatives have this question: “What to do next?” 18/07/2021 Read more |
| Detoxification from binge drinking in St. Petersburg around the clock The state of binge drinking is one of the manifestations of alcohol addiction 21/06/2021 Read more |
| Anonymous treatment of alcohol addiction This treatment must be carried out in accordance with approved protocols and standards for the treatment of drug addiction patients. 14/05/2021 Read more |
| Immunological rehabilitation of drug addict patients A reissued and expanded monograph has been published 30/03/2021 Read more |
| Safety measures during a pandemic Our employees follow all safety measures to ensure the full protection of patients and clinic staff. 20/11/2020 Read more |
| International conference An international conference dedicated to means and methods of combating the use of psychoactive substances was held in St. Petersburg 14/10/2019 Read more |
| Cheaper at night PROMOTION! Detoxification program “Cheaper at night” 31/07/2019 Read more |
| Administrator vacancy Administrator of a medical drug treatment center 30/04/2019 Read more |
| Programs for express withdrawal from binge drinking Programs for express withdrawal from binge drinking: Standard, Comfort and VIP 22/03/2019 Read more |
The effect of alcohol on the female brain?
Complications caused by drinking alcoholic beverages are more serious in the fairer sex than in men.
It has been experimentally proven that ethanol behaves much more aggressively towards the cells of a woman’s body than towards the cells of a man. Organs and their functions are more susceptible to the negative effects of alcohol. The destruction of the liver, damage to the heart muscle and cells of the nervous system occurs faster.
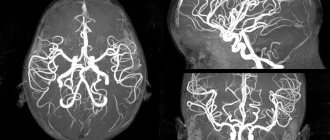
Having carried out a comparative analysis of the results of studies of the human brain using MCT, scientists have established the fact that the negative effects of ethanol manifest themselves in the fact that the brain decreases in size.
The degree of such a decrease is the main indicator that organic changes are present in the brain cells. And the longer the experience of drinking alcohol, the higher these indicators.
In addition, the results of the experiments showed that both women and men who suffer from alcohol addiction face certain problems when they have to learn something or remember any information. All this occurs due to frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Note that the male representatives who participated in such an experiment had twice as much experience of regular consumption of large amounts of alcohol than the fairer sex.
It turns out that the negative effects of ethanol on both the male and female brains manifest themselves in the same ways. But it is necessary to take into account that women took exactly half as much alcohol. From all this we conclude that ethanol has a stronger effect on the female brain.
In contrast, two articles were recently published in an American publication discussing the role of gender in the effects of ethyl alcohol on the body.
The authors came to the opposite conclusion, that is, according to them, ethanol has the same effect on everyone without exception. This means that experiments of this kind need to be continued in order to find out the specific effects of ethyl alcohol on a woman’s brain cells.
How does alcohol affect the brain? Worse than you could imagine
Sometimes you can hear people who abuse alcohol say that their brains have completely drank. Most often this happens due to their inappropriate behavior, illogical decisions, immoral and unexplainable actions, not only while intoxicated, but even sober. Alas, the crude description of a “drunk brain” is not a figure of speech. Alcohol has a destructive effect on all human organs and systems. But the effect on the brain is especially clear.
A drop to defeat
A slurred tongue, an unsteady gait, defiant behavior that is not characteristic of a person when sober - all these are external manifestations of the brain working under the influence of alcohol.
The more you drink, the more noticeable they are. A person in a state of strong alcoholic intoxication makes a repulsive impression on others. But the external manifestations of the harmful effects of alcohol cannot be compared with what happens inside the body, in particular, with the brain.
The blood supply to the brain occurs many times more actively than to other organs. Ethanol penetrates into gray matter cells within minutes of consumption. It has been proven that any exogenous (coming from outside) dose of alcohol is toxic to the brain because it damages the membranes of neurons and can lead to cell death. You must understand that even one drop of alcohol has a damaging effect. In this case, a small number of neurons die. But the higher the dose, the more “victims”.
Alexander Alishevich , chief physician of the City Clinical Narcological Dispensary in Minsk:
— In general, the brain is a target organ that immediately suffers when drinking alcohol, just like the liver. But the liver has a colossal resource for regeneration and is capable of resisting and neutralizing the toxic effects of ethanol for quite a long time. The brain is not. Relatively speaking, under certain circumstances, 1/8 of the healthy part of the liver is enough to restore the normal functions of the organ. And if neurons die, there is no chance of recovery.
To be fair, the expert notes, neurons still have some ability to resume functions. In this case, we are not talking about the appearance of new cells to replace the dead. If the neuron survives, it takes approximately 7 years to restore its damaged substances. Compare: internal epithelial cells in the intestines are renewed within a few days. The brain is the most “long-lasting” tissue in the human body in terms of self-healing, and only if the cells affected by the attack remain alive. When drinking alcohol (especially more frequently and in large quantities), there is no talk of saving brain cells.
Exhaustible resource
At birth, the human nervous system contains a fantastic reserve - an average of 100 billion neurons. Over time, neurons wear out, “age” and, having served their purpose, die. Their supply is not renewed. But this natural decline was initially taken into account by nature when forming brain potential. The quantitative composition of neurons is also influenced by external factors, for example, high body temperature during viral and bacterial diseases, stress, intoxication... In particular, alcohol intoxication, which occurs when drinking alcohol, is called the main cause of mass death of brain cells.
Microscopic studies show that in place of neurons killed by ethanol exposure, so-called foci of cellular devastation and/or connective tissue scars are formed. Healthy parts of the brain shift to fill the void. As a result of numerous atrophic and dystrophic changes, the brain of a drinking person decreases in volume and seems to shrink.
Alcohol intoxication also leads to irreversible vascular changes and impairs cerebral circulation. Venous blood stagnates in the veins of the brain, which provokes the development of thrombosis and increases the risk of micro-strokes (minor hemorrhages). There is an opinion that in people who abuse alcohol, strokes (acute cerebrovascular accident) occur almost 5 times more often.
Typically, the greatest losses from ethanol exposure are suffered by neurons in the frontal lobes of the brain. These are centers that are responsible for motivation, planning, goal-directed behavior and provide the ability to solve problems and achieve goals, overcome difficulties and develop. Alcohol abuse leads to disruption of these functions. Over time, a drinker develops so-called “alcoholic automatism” - a type of behavior based on standard, stereotypical thoughts, actions, words, which gradually become scarcer and narrower. Roughly speaking, a person stops developing as a person, and the process of degradation begins. The result of many years of alcohol consumption can be dementia (dementia), alcoholic epilepsy, encephalopathy and a number of other neuropsychiatric disorders.
Alexander Alishevich:
— Scientists believe that in the absence of external damaging factors, the number of neurons deposited at birth, taking into account their natural decline, would be enough for one thousand years of brain functioning at full capacity. Alcohol abusers often damage their brains for 40-50 years. In my practice, there was a young man who was assigned to a boarding home for the disabled due to dementia that developed as a result of alcohol abuse. He was 33 years old. So “drank your brain” is not a figure of speech, but a harsh reality with prolonged and systematic use of alcohol.
Thiamine deficiency and Korsakoff-Wernicke disease
If a person systematically drinks alcohol, without control over the amount he drinks, and this lasts for quite a long time, then he has every chance of developing brain dysfunction or damage to his cells. Moreover, this can be caused by the consumption of large amounts of alcohol, or there may be serious disturbances in the liver due to chronic alcohol dependence.
For example, most people suffering from chronic alcohol addiction have a lack of thiamine in their bodies, or as it is also called vitamin B1. It may be lacking due to poor nutrition, metabolic disorders in the body and, of course, due to the abuse of alcoholic beverages. It plays an indispensable role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. It supports the normal functioning of the cardiovascular system, digestive tract, and nervous structures.
Most people suffering from chronic alcohol addiction are deficient in vitamin B1. And this can lead to such a serious illness as Korsakoff-Wernicke syndrome, or more precisely, Wernicke syndrome and Korsakoff syndrome.
Wernicke's disease is characterized by paralysis of the eye muscles, disturbance of consciousness and impaired coordination of movements. Sometimes a patient with a similar syndrome cannot independently find the door of the room to leave, he cannot move without someone else's help. If at least one of the signs of the disease appears, you need to urgently seek medical help.
Most people suffering from alcohol dependence, along with Wernicke's syndrome, experience Korsakoff's syndrome, which is also called alcohol paralysis. With this disease, memory impairment is observed, when he forgets everything that happened to him before the disease, but can describe in great detail the events that took place several years before.
In addition, he remembers well everything that happens to him after his illness. The patient begins to invent non-existent events, or talk about those that really happened, but at the same time greatly distorts the facts. All this is accompanied by disorientation. The patient ceases to navigate the world around him and himself. Sometimes, even after seeing his reflection in the mirror, the patient does not realize that it is him.
Call us now:
+7 (812) 454-00-50
Prices for Ultramed clinic services
Is it possible to restore brain cells?
It was believed that a person is born with a specific number of brain cells, and if they are somehow damaged, then they cannot be restored. Scientists believed that neurons under the influence of ethyl alcohol were destroyed and no longer function. in order to restore their activity it is necessary to strengthen the remaining nerve cells, since there is no possibility of adding new ones. But in the second half of the last century, scientists discovered that the formation of new neurons is possible. This process is called neurogenesis. After this discovery, scientists developed a new approach to the treatment of disorders of brain cells.