The vessels of the brain form a complex circulatory system, which must ensure constant delivery of nutrients and oxygen to nerve cells.
The circle of Willis is a closed complex of arteries that provides blood supply to the structures of the central nervous system due to the redistribution of blood.
Pathologies in its structure and function lead to various neurological disorders. We will talk further about what the Circle of Willis is and what it means if it is open.
About the Circle of Willis of the brain
The circle of Willis protects the brain from hypoxia when blood flow through the arteries is impaired. Redistribution of blood helps prevent the death of neurons due to thrombosis, compression or rupture of blood vessels.
A closed circle system with anastomoses ensures normal blood flow due to the blood that flows through the vessels of the opposite side. An anastomosis is a small artery that connects two areas of the nervous system with separate blood supplies.
Anatomical structure
The vessels of the circle are located under the arachnoid membrane in the area of the optic chiasm at the base of the brain. In most people, several vessels are involved in the formation of the arterial circle:
- anterior communicating artery;
- posterior communicating arteries;
- left and right anterior cerebral arteries;
- left and right posterior cerebral arteries;
- supracuneiform part of the internal carotid artery.
All arteries connect with each other, forming a vascular heptagon. Due to this, anastomoses are formed between the carotid and basilar arteries. This makes it possible to prevent ischemic brain damage due to unilateral disturbances of blood flow through the vessels.
Functions
The main function of the arterial circle is to ensure normal blood supply to the brain in case of pathology of individual vessels. This is achieved due to its closed structure and constant blood flow through several arteries.
VC development options
Completely closed VC, in which there are no missing or underdeveloped (hypoplastic) components, occurs in only 20–25% of people.
There are a huge number of possible variants of the anatomical structure and development of the VC. The most common ones are:
- hypoplasia of one or two PCAs;
- hypoplasia or absence of the ACA segment;
- PSA hypoplasia;
- absence of one of the SSAs.
A - normal Circle of Willis B - hypolasia of the right posterior communicating artery C - hypolasia of the left posterior communicating artery D - bilateral hypoplasia of the posterior communicating arteries E - absent or undeveloped right posterior cerebral artery F - absent or undeveloped left posterior cerebral artery G - hypoplasia of the left communicating artery and the right posterior cerebral artery is absent or not developed H - hypoplasia of the right communicating artery and the left posterior cerebral artery is absent or not developed I - hypoplasia of the anterior communicating artery J - anterior communicating artery and hypoplasia of the left posterior communicating artery K - hypoplasia of the right anterior cerebral artery and hypoplasia of the right posterior communicating artery
What pathologies are possible
The circle of Willis has a complex structure and consists of 10-12 arteries. Therefore, some people may have diseases associated with vascular damage. They are divided into two groups: congenital, which arose during intrauterine development of the fetus, and acquired, developing after birth. The most common pathologies are:
- Aneurysm is a local protrusion of the arterial wall outward. A person can go for a long time without any symptoms, which makes timely diagnosis difficult. If blood pressure increases, the aneurysm may rupture. In this case, an intracranial hematoma develops. The patient complains of headache, nausea, vomiting and dizziness. He experiences neurological disorders, including severe paralysis or death. Aneurysms can be located on any vessel;
- hypoplasia is characterized by underdevelopment of the artery with a decrease in its diameter and lumen. This leads to insufficient blood flow. If the circle is closed, then the disease is asymptomatic, since blood flows to the brain through other vessels;
- aplasia is complete underdevelopment of the artery. Can be observed in any vessel. Aplasia of the anterior or posterior communicating artery leads to the fact that the circle of Willis becomes open. This is fraught with the development of cerebral ischemia against the background of concomitant pathologies: atherosclerosis, aneurysms, thrombosis, etc.;
- trifurcation of the carotid artery with its splitting into three vessels. The condition is not manifested by any diseases, however, if the patency of the artery is impaired, cerebral ischemia is possible.
What is the Circle of Willis?
The brain has a complex structure of the vascular system.
The main component of the arterial network is the Circle of Willis (abbreviated as VC), thanks to which there is a reliable blood supply to this organ.
Essentially, the circle of Willis (or arterial) is an anastomosis (connection) of oval-shaped blood vessels located at the base of the brain.
Arterial blood enters the VC through the following main vessels:
- The right and left internal carotid arteries form the anterior cerebral vessels in both hemispheres, connected by a vascular bridge.
- Vertebral arteries - after fusion they create an unpaired basilar vessel, from which two posterior cerebral arteries arise. The posterior cerebral arteries are connected, in turn, to the internal carotid arteries - a closed system is obtained.
Features of the anatomy of the VC are usually called variants.
The classic version of the arterial circle is closed, has a symmetrical shape, which is formed by the following arteries:
- PMA - forebrain.
- PCA - posterior brain.
- ACA - anterior connective.
- ZSA - rear connecting.
- ICA - internal carotid (suprasphenoid part).
Is an open circle of Willis good or bad?
The structure of the arterial circle has many variations. Normally, it is closed, which helps protect nervous tissue from ischemia and damage.
In some people, the circle of Willis is not closed on the side of the anterior or posterior communicating artery. This condition is not always regarded by doctors as a pathology.
An open arterial circle is bad. In the absence of all anastomoses, a person has an increased risk of developing ischemia of nervous tissue against the background of atherosclerosis, thrombosis and arterial embolism.
However, the condition itself does not require treatment, since pathologies arise only against the background of concomitant diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Diseases of the circle of Willis: treatment
Many people, having learned that they have a variant of the development of the circle of Willis that does not correspond to the norm, fall into despair, believing that they have a serious disease that requires certain therapy. But in reality, treatment for the circle of Willis is not carried out.
As we said above, there are different options for the development of the Circle of Willis, and those that are considered the norm are not found in every person. The vessels of this arterial basin are designed not so much to supply blood to brain cells, but to compensate for the disturbances in cerebral blood flow that arise as a result of thrombosis due to the transfer of blood from one arterial basin to another. Therefore, in most cases, the developmental pathology of the circle of Willis does not require treatment.
If there is an aneurysm of one of the arteries of the circle of Willis, the treatment is surgical and consists of ligating the aneurysm. In cases where the aneurysm is opened, conservative treatment is carried out, the same as for subarachnoid hemorrhage caused by any other cause.
Clinical manifestations
Violations of the structure of the circle and its openness lead to disruption of the blood supply to the brain. Depending on where ischemia develops, a person may develop different symptoms. The first symptoms are often:
- dizziness that occurs during severe physical or emotional stress;
- severe headache that does not disappear when taking painkillers;
- migraine attacks with nausea, vomiting, and fear of loud sounds and lights.
As anemia progresses, neurological disorders occur. The patient may complain of impaired sensitivity on the skin, decreased muscle strength or complete absence of movements in the arm or leg, frequent dizziness, etc. Cognitive functions are also impaired: the ability to remember information decreases, the patient takes a long time to make decisions, forgets the way home, etc. With ischemia frontal cortex, speech is impaired. The patient cannot speak clearly or does not perceive the speech of other people.
Diagnostic measures
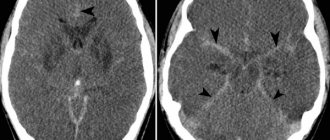
Detection of an open arterial circle requires instrumental studies: angiography, Dopplerography, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
These methods allow you to visually assess the condition of the arterial vessels and identify their pathological changes. Only the attending physician should interpret the examination results.
Angiography
“Gold standard” for examination of cerebral vessels. Angiography allows you to assess the condition of blood vessels, detect aneurysms, narrowings and complete blockage of the lumen. The principle of the method is similar to radiographic studies. Radiocontrast agents are used only to identify blood vessels on images.
They are inserted through a small catheter into the artery. Contrast agents circulate along with the blood and are clearly visible on the resulting images. They are excreted from the body in the urine, without having a negative effect on internal organs. Modern angiography allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of the arteries of the circle of Willis.
Dopplerography
The method is carried out simultaneously with ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels. Dopplerography allows you to evaluate the structure of the vessels of the circle of Willis and identify their anomalies. In this case, the doctor can examine the speed of blood flow.
Treatment approaches
If the arterial circle is not closed, special treatment is not required. Without accompanying changes in the blood vessels, people do not experience any symptoms of disease. Therapy should be aimed at preventing arterial pathologies and eliminating them.
For this, patients are prescribed a number of medications, and are also advised to adhere to a diet and change their lifestyle.
Non-drug approaches
All patients should adhere to medical recommendations regarding lifestyle:
- exercise regularly. To prevent vascular diseases, aerobic exercise is recommended: walking, jogging, cycling and swimming. Classes should be ongoing and suitable for the person’s level of physical fitness;
- eliminate bad habits: smoking and drinking alcohol;
- Avoid fatty, salty, fried and spicy foods in your diet. They contribute to the development of atherosclerosis and hypertension. Both conditions are often complicated by thrombosis, aneurysms and their rupture;
- It is recommended to eat more vegetables, fruits, berries, nuts and lean meats. They are rich in beneficial amino acids, vitamins, microelements and biologically active substances that have a positive effect on the condition of the cardiovascular system;
- Limiting salt intake to 5 g per day. If the patient has severe arterial hypertension, then the volume of consumption is reduced to 1 g;
- avoid stressful situations at work and in your personal life.
These recommendations reduce the risk of developing heart and vascular diseases by preventing pathological changes in the arterial circle of the brain.
Medicines
Medications are recommended for people with vascular pathology of the circle of Willis and accompanying changes in the arteries. Medicines of the following pharmacological groups can be used:
- drugs that improve cerebral circulation (Cerebrolysin, Cavinton, etc.). They normalize vascular tone and increase the intensity of blood flow in the arteries of the brain. This avoids ischemia and neurological disorders;
- nootropics – Phenotropil, Glycine, Nootropil, etc. They enhance metabolic processes in neurons and reduce their sensitivity to damaging factors. Requires long-term use over several months to obtain a therapeutic effect;
- antioxidants (Dihydroquercetin, Mexidol) protect nerve cells from damage, including toxic substances. The effect is achieved by blocking free forms of oxygen, which negatively affect the structures of neurons;
- antispasmodics (Drotaverine, Papaverine and their analogues) are prescribed for spastic changes in blood vessels. Allows you to dilate arteries and restore normal blood supply to the brain. They have only a symptomatic effect and do not affect the underlying disease;
- B vitamins, which stimulate the restoration of nerve tissue and neuron membranes. Used in courses in the form of intramuscular injections;
- To eliminate pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Nise, etc.) are prescribed. They are highly effective for any form of headache, except migraine.
All medications are prescribed only by a doctor. Medicines have contraindications, failure to comply with which may cause progression of the underlying disease or lead to the development of side effects.
Surgical treatment
In case of multiple blood flow disorders, the patient is prescribed surgical interventions. They may be associated with the creation of a shunt or mechanical expansion of the lumen of the arteries. A shunt is a bypass for blood flow, which is placed around a narrowed area, an area of hypo- or aplasia. Mechanical expansion of the vessel is carried out using a stent or ballooning.