For some, constant changes in emotional state are the norm. But from a scientific point of view, an unnatural change in physical and mental state means so-called lability. Under the influence of external or internal factors, the nervous system may react too aggressively to circumstances. In its advanced form, this is fraught with irritability and disruptions of the mental system.
In everyday life, such reactions are often classified as natural processes. But even attacks of aggression, for example, when touching hot objects or when pain occurs, are considered emotional lability. Lability is a negative quality of a person if it occurs too aggressively and uncontrollably.
What characterizes intellectual instability?
Unlike emotional lability, its intellectual subtype can be very useful in a person’s everyday life. For example, intellectual lability is characterized by the ability to quickly switch attention and instantly respond to surrounding circumstances. Also, a person with similar phenomena has the ability to quickly learn new skills and abilities. It is easier for them to learn and be in conditions that are not natural for them.
The higher a person’s intellectual lability, the more successful he is in life. His reaction is heightened, he can be trained, explores new opportunities, and is able to succumb to feelings of envy, motivating himself with this. And those who do not have the described type of lability are more susceptible to anger, a feeling of fatigue, irritability, and nervous disorders.
Therefore, passivity and stability of the intellect are a negative quality for a person.
Wide range of manifestations
Manifestations of autonomic lability are associated with all areas that are controlled by the autonomic nervous system; symptoms of the condition can be varied:
- fainting and dizziness;
- increased fatigue (due to lack of adequate adjustment of heart rate relative to stress);
- increased or decreased sweating;
- headache;
- disturbances in the digestive tract, which lead to constipation, diarrhea, bloating, loss of appetite;
- difficulty urinating;
- problems in the sexual sphere (lack of erection, vaginal dryness, nonorgasmia);
- visual impairment (increased sensitivity to light, blurred vision);
- poor tolerance to cold and heat;
- sleep disorders;
- tremor;
- rapid heartbeat, lability of blood pressure;
- apathy, lethargy, weakness, constant mild malaise;
- increased irritability;
- decreased concentration;
- sudden mood swings;
- speech disorders;
- unreasonable fears, anxiety and neurotic phobias;
- pain in joints and muscles;
- dry skin;
- numbness in various parts of the body.
Individuals with vegetative lability have an increased sensitivity to mental trauma, stress, meteorological changes, and a tendency to seasickness and air sickness.
Emotional instability
But emotional lability is a negative manifestation of any pathology or abnormality.
In particular, a state of emotional instability can be caused by:
— Age-related dementia;
— Schizophrenia;
— Consequences of traumatic brain injuries;
— Neoplasm of the brain;
— Strokes, heart attacks;
- Atherosclerosis.
According to numerous expert opinions, this type of lability is a consequence of a depleted nervous system. And if aggression or emotional instability occurs, you should consult a doctor.
Reasons for failure
Lability of the autonomic nervous system can develop gradually and occur suddenly. This condition often remains undiagnosed, since patients do not attach importance to the manifestations, considering them the result of stressful situations and fatigue. Patients may also be considered hypochondriacs.
The causes of autonomic lability can be varied:
- stress factors;
- adverse effects of the external environment;
- infectious diseases;
- intoxication;
- surgical intervention;
- traumatic brain and other injuries;
- change of climate and time zones;
- pregnancy;
- menopause;
- psychological trauma, including childhood trauma;
- lack of vitamins (especially vitamins B1, B3, B6 and B12 and vitamin E).
There is also the possibility of autonomic lability due to dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, which can be caused by various diseases.
Such diseases include ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, diabetes, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, paraneoplastic syndrome, sarcoidosis, Sjögren's syndrome.
Autonomic instability
There is another type of negative lability. This is a disturbed vegetative system. This includes the factor of control over body movements, stability of the musculoskeletal system and all key organs. If you feel dizzy, lose control of yourself, notice tremors in your limbs or numbness, then you are likely to develop autonomic lability. The disorder is also manifested by erectile dysfunction, vaginal dryness, tachycardia and impaired sleep stability.
With all these manifestations, you should also consult a specialist.
Anatomical and physiological implications
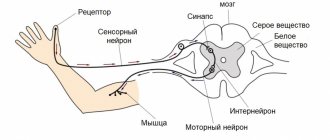
The autonomic nervous system is part of the body's nervous system.
Its functions include control and regulation of the work of internal organs (intestines, stomach, heart, etc.), lymphatic, circulatory systems, and glands of the body. This system also regulates the process of sweating, heart rate, thermoregulation, and blood pressure. It is also responsible for a person’s reaction in stressful situations, for the ability to fully relax physically during rest, for the digestion and assimilation of food consumed. The functioning of the autonomic nervous system is beyond human control.
The autonomic nervous system consists of two divisions - sympathetic and parasympathetic. The parasympathetic nervous system regulates the functioning of the endocrine system, the digestive tract, is responsible for metabolism and lowering blood pressure.
The sympathetic nervous system is active in stressful situations. It is responsible for supplying muscles with oxygen, rapid heartbeat, and breathing.
In a normal state, there is an adequate response of the autonomic system to external stimuli (stress, temperature, sounds). With the syndrome of increased lability of the autonomic nervous system, an individual may experience inadequate reactions to common stress factors: increased sweating at low temperatures, increased blood pressure with minor stress.
Reflexes of the autonomic system ensure an adequate response of the body to stress, and a person’s understanding of the presence of anomalies in his condition or sensations.
Autonomic lability is not an idiopathic disease. Often it is a sign of vegetative-vascular dystonia. This disorder is present in approximately 80% of the population, in adults and children.
Mental instability
Mental lability is manifested by an unstable emotional state. Such people can suddenly change their mood, become overly impressed, and try to shift responsibility to others. In advanced stages, depression, split personality, and aggression can develop. Therefore, this type of mental instability should be treated by psychiatrists, not psychotherapists.
In the modern world, the described types of unstable human condition appear in young, middle, and adulthood. The cause of deviations can be both hereditary factors and the person’s lifestyle.
We also recommend reading the article about disgust.
Examination and diagnosis
To make a diagnosis, a comprehensive examination is necessary, since the symptoms of autonomic lability are similar to those of other diseases. It is necessary to exclude mental illnesses, neuropsychiatric disorders, and also in the case of physiological manifestations, to exclude organic pathologies.
After excluding other diseases, the likelihood of disorders in the autonomic nervous system is considered. Often, collecting an anamnesis, interviewing the patient, and a superficial examination is sufficient.
A neurologist should pay attention to constriction or dilation of the pupils, increased sweating, or excessive dryness of the skin, pallor, or hyperemia of the skin. To assess the work of the autonomic system, the work of skin, somatovegetative, and sweat reflexes is analyzed.
Also, to assess the degree of violations, tests are prescribed for the biochemical composition of urine and blood.
What is vegetative lability
The disease has diverse manifestations.
If there are disturbances in the functioning of the autonomic system, then it is no longer able to provide an adequate response to stress.
More often, her reaction to an external stimulus may be too violent.
For example, with a minor conflict, a person may experience palpitations, a sharp rise in blood pressure, and an attack of suffocation. These reactions in the form of dysfunction can be observed in the gastrointestinal, genitourinary, and respiratory systems.
A person loses his appetite, suffers from incomprehensible pain in the stomach or heart, sleeps poorly, and becomes irritable.
Problems arise in the family and at work, which further provokes the disease; a “vicious circle” arises from which the patient can no longer escape on his own.
When visiting a doctor, no pathology in the organs is detected; such patients are often considered hypochondriacs or malingerers.
Symptoms
Signs of autonomic lability are associated with those systems and organs that are controlled by the ANS:
- hyperventilation syndrome;
- difficulties with bowel movements, flatulence, loss of appetite, irritable bowel syndrome;
- erectile dysfunction and ejaculation, vaginal dryness, anorgasmia, decreased libido;
- hypersensitivity to bright light, blurred vision;
- bad feeling;
- problematic sweating, intolerance to high and low temperatures, excessive dryness of the skin;
- severe migraines, dizziness and even fainting;
- joint pain, muscle spasms;
- tachycardia, pressure surges;
- tremor of the limbs, numbness of body parts;
- cystalgia.
From the side of mental activity the following are observed:
- insomnia, interrupted sleep;
- hysterical fits;
- speech disorders;
- panic attacks, increased levels of anxiety, neurotic phobias;
- tearfulness, moodiness;
- increased fatigue, weakness, apathy, inability to concentrate;
- severe irritability, aggression, anger, inexplicable and frequent changes in mood.
Experts note that the lability of the autonomic nervous system is also manifested by hypersensitivity to stressful situations, experiences, the opinions of others, weather changes and a predisposition to kinetosis.
What it is
Autonomic lability is a malfunction in the activity of the autonomic nervous system (hereinafter abbreviated as ANS). Its main purpose is to adapt the functioning of the body to environmental changes, ensuring homeostasis. An example is sweating as a natural way to cool the body through evaporation. However, the ANS determines not only the physiological state of a person, but also takes part in his behavioral aspects, and therefore in his mental activity.
If the ANS is functioning normally, the person feels good in all respects. But as soon as it malfunctions, inexplicable things begin to happen: my head hurts, my hands tremble, sweat appears on my forehead. And in parallel with this, irritation increases for no apparent reason, you want to cry, lie down and do nothing. It is this borderline state, when both the body and the psyche fail, that is vegetative lability.
Many experts insist that it is not an independent disease, since it includes symptoms of various abnormalities in the functioning of the ANS:
- somatoform-vegetative dysfunction of the nervous system (vegetative-vascular dystonia);
- autonomic disorder;
- vegetative neurosis;
- autonomic-vascular type of hypothalamic crisis;
- psychovegetative syndrome, etc.
In this regard, sometimes autonomic lability is spoken of not as a separate disease, but as a complex syndrome.