Causes
The main reason for the development of encephalopathy is chronic hypoxia of the brain as a result of exposure to various pathological factors.
Hypoxia or oxygen deficiency leads to disruption of the normal metabolism of brain tissue, deterioration of its nutrition, death of nerve cells, and shutdown of certain areas of the brain. The most common causes of encephalopathy are arterial hypertension, cerebral atherosclerosis and diabetes mellitus.
Epilepsy should be highlighted as a separate cause. During attacks, the brain suffers from hypoxia, so patients who do not take adequate therapy develop ischemic changes in the brain.
Causes of encephalopathy
It is worth noting that the disease is unclassifiable. It is almost impossible to determine either “by eye” or with the help of the latest medical equipment.
Encephalopathy is explained as the result of brain damage due to various factors, the action of which continues or has ended, but the brain structures have not been able to recover.
Defeat does not divide people by gender or age. It manifests itself in both men and women, young and old, children are born with the characteristic features of the disease.
The main reasons contributing to the development of cerebral encephalopathy are hypoxia and toxic effects.
The first condition occurs, for example, due to respiratory arrest or prolonged oxygen deprivation. It is not necessary to have deep asphyxia - shallow breathing and a prolonged cough are enough.
The toxic effect is caused by dangerous microelements from the outside. When faced with certain diseases, the body does not remove these substances, which also serves as a source of encephalopathy.
Toxic encephalopathy is most clearly expressed. The patient begins to behave strangely: involuntary eye movements, numbness of the face, trembling of the limbs, sometimes nervous tics (twitching of the lip, nostrils). Hallucinations, migraine headaches, sleep disturbances are also observed, apathy, irritability, fatigue and even suicidal tendencies are noted. Attempts to reason with a person and refer him to a psychologist do not bring positive effects.
There are a number of chemical elements that can have a detrimental effect on brain performance: mercury, lead, manganese and others. For example, due to mercury poisoning, the patient experiences trembling limbs, bloody stools, tachycardia and other symptoms. Lead poisoning causes a sharp metallic taste in the mouth, as well as vomiting and weakness.
Kinds
All encephalopathies can be divided into two large groups -
- congenital
- acquired.
Congenital forms can arise as a result of genetic metabolic failures, due to malformations of the brain or exposure to negative factors during pregnancy (hypoxia, infections) or childbirth (birth injuries, hematomas, hemorrhages).
Acquired encephalopathies occur throughout life from the first months to old age and can be caused by various factors, which are divided into groups:
- traumatic – consequences of traumatic brain injuries, open and closed skull fractures;
- toxic encephalopathies arising as a result of brain damage by neurotropic toxins (alcohol, methyl alcohol, chloroform, lead);
- drug encephalopathies, as a toxic option, in case of overdose or poisoning with medications;
- toxic-infectious – brain damage from bacterial toxins (tetanus, botulism);
- radiation - as a result of exposure of brain tissue to ionizing radiation;
- metabolic - develop with liver or kidney failure, diabetes mellitus due to fluctuations in glucose levels;
- encephalopathy due to water-salt imbalance (swelling or dehydration of the brain), acute blood loss;
- vascular - due to chronic or acute circulatory disorders (the causes may be atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension, venous stagnation, stroke);
- metabolic - arising against the background of metabolic disorders, lack of micro or macro compounds, vitamins, for example, Wernicke encephalopathy, the cause of which is a deficiency of vitamin B12.
Causes of the disease
Dyscirculatory encephalopathy in old age most often develops against the background of other pathologies that arise as a consequence of natural physiological aging.
The main causes of the disease, which are usually identified today, are:
- the development of atherosclerosis, due to which blood flow slows down and blood vessels become clogged;
- hypertension, when vascular damage occurs due to increased arterial and intracranial pressure;
- osteochondrosis, since displacement of the spinal column provokes compression of the arteries and slows down the flow of nutrients to brain cells;
- the presence of traumatic brain injuries, which may impair blood flow;
- VSD, during which pressure surges occur;
- smoking and alcohol, which disrupt the normal functioning of blood vessels;
- obesity in the neck area.
It is noteworthy that these diseases can cause the development of encephalopathy in both young and elderly patients. Naturally, in old age the process develops faster.
Symptoms of encephalopathy
Manifestations of encephalopathy can be extremely varied depending on the cause that caused it. The severity of symptoms depends on the depth and extent of brain damage, the duration of the disease and concomitant health problems.
The earliest signs of encephalopathy may be:
- decreased mental abilities, IQ;
- difficulty in performing intellectual tasks;
- difficulties in solving problems that the patient could previously easily cope with;
- deterioration of memory, both short-term (forgot where he was going) and long-term (does not remember events of past years);
- multitasking mode causes significant difficulty;
- problems with making decisions, taking responsibility, because the person realizes that he may not be able to cope;
- difficulties in any activity where you need to think and act quickly;
- sleep disturbances and its depth, insomnia, daytime sleepiness, nightmares, sleep talking;
- daytime fatigue even with usual activities;
- exhaustion under stress;
- general fatigue under any load.
Often with encephalopathy there are complaints of frequent or episodic headaches of various localization and intensity, attacks of tinnitus, general malaise, irritability for no reason, and constantly depressed mood.
Patients often note at a doctor’s appointment that they see double, their vision and hearing decrease, especially in the evening or during periods of exercise, and episodes of increased tone of the muscles of the body and limbs may be detected. On examination, an increase in tendon reflexes, especially the knee reflexes, is revealed.
With encephalopathies, disturbances in the functioning of the limbs, disorders of the cerebellum in the form of gait disturbances, instability, especially with eyes closed, may be detected; some patients experience problems with speech - slurred speech (“porridge in the mouth”), a feeling of tongue twisting.
Autonomic disorders may occur - pressure fluctuations, sudden sweating, pallor, fainting and marbling of the skin, thermoregulation disorders, attacks of palpitations with shortness of breath and a feeling of lack of air.
Manifestations of encephalopathy can be progressive or non-progressive; in the later stages, parkinsonism or lesions of the brain nuclei may develop with a sharp disruption of basic life support functions (respiratory disorders, paralysis).
In some patients, encephalopathy is accompanied by mental disorders in the form of hallucinations, delusional disorders, and depression.
Symptoms of acute encephalopathy
Acute encephalopathies are distinguished separately - they arise as a result of severe, massive and significant damage to nervous tissue, circulatory disorders and cerebral edema.
Acute encephalopathy manifests itself as a severe headache in the back of the head and general anxiety, nausea with vomiting, blurred vision, dizziness, numbness of the fingers and toes, face, and tongue. As it progresses, there is depression of consciousness, lethargy, and there may be convulsions and paresis.
Diagnostics
The basis of diagnosis for suspected encephalopathy is data on existing chronic diseases - diabetes, intoxication, arterial hypertension, cerebral atherosclerosis, etc. It is important to take into account the initial state of health - this helps to assess the rate of progression of pathological changes.
The information obtained is supplemented by examination data from a neurologist with identification of neurological symptoms, disturbances in the motor sphere, sensitivity and higher nervous activity.
If encephalopathy is suspected, the following is necessary:
- examination by an ophthalmologist to determine the condition of the fundus;
- general clinical examinations - general blood tests, urine tests, blood biochemistry according to indications, identifying the inflammatory, toxic, allergic and other nature of the lesion;
- carrying out instrumental diagnostics.
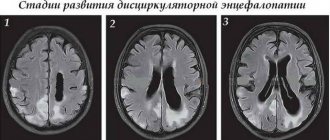
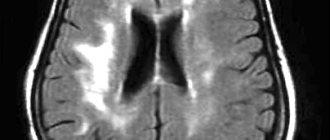
Electroencephalography may reveal pathological waves, epileptic activity and rhythm disorganization. But all this only indirectly indicates encephalopathy, since the changes in the brain substance themselves are not visible with EEG. When performing computed tomography and magnetic resonance scanning, signs of brain atrophy, reduction in size, and hydrocephalus are revealed.
Photo: brain with atrophic changes (left) and healthy brain (right)
In case of secondary encephalopathy that occurs as a symptom of other diseases, a specific examination of the underlying pathology is necessary.
Treatment of encephalopathies
The treatment of encephalopathy is carried out by neurologists together with specialists in diseases that are the cause of cerebral hypoxia (endocrinologists, toxicologists, infectious disease specialists, etc.).
There are two directions in treatment:
- eliminating the cause of encephalopathy
- fight against manifestations.
In case of acute encephalopathies, hospitalization in intensive care with hemodialysis, artificial ventilation, and detoxification is necessary. The fight against cerebral edema, seizures and vascular disorders is carried out.
As the condition improves, they are prescribed
- drugs that improve brain function - nootropics (Actovegin, Cavinton, piracetam),
- amino acids (glutamic acid, glycine),
- lecithin,
- vitamins and metabolites.
Recently, products based on Ginkgo biloba are often prescribed - “Gingko Mind”, “Gingko Biloba”. If necessary, medications are prescribed that improve vascular function - Picamilon, cinnarizine.
If there is a tendency to thrombus formation, antiplatelet agents (clopidogrel, aspirin) are used.
Courses of treatment are long, up to three months in a row.
Encephalopathy
As in cases with other diseases, the diagnosis of encephalopathy is initially based on collecting an extremely detailed anamnesis. Before prescribing therapy, the doctor collects information about the patient’s current condition, the presence of chronic diseases, problems with the patient’s vascular system, viral diseases, and mental disorders. It is also initially clarified whether the patient has diabetes or suffered from intoxication. Information is also collected on neurology - neuropathy and other health problems of this kind.
Also, if the development of encephalopathy is suspected, the following types of examinations are carried out:
- examination by an ophthalmologist to determine the current condition of the eye sockets;
- tests - general and biochemical blood, urine, to look for lesions of an allergic, inflammatory, toxic or other nature;
- complex instrumental diagnostics.
The purpose of the examination is to search for symptoms of damage to blood vessels and brain cells, allowing one to determine the causes of encephalopathy, make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
These are just the most common groups of cerebral encephalopathy. In fact, there are many more reasons for its occurrence. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, as well as the degree of progression, after appropriate examinations.
Please note: encephalopathy is a serious and dangerous disease. The same signs may indicate different diseases. Therefore, independent therapy and treatment are highly not recommended. In order not to put your life at risk, if certain symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor and be treated according to his indications.
Therapy and treatment of encephalopathy is the prerogative of a neurologist, who conducts it together with a specialist in the disease that provoked this disease. This could be a urologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist or other doctor.
The treatment itself occurs in two main directions:
- Elimination of the reasons why encephalopathy developed.
- Fighting the manifestations, signs and consequences of the disease.
Acute encephalopathy requires mandatory hospitalization in intensive care. It is necessary to connect to a ventilator, carry out complete detoxification, counteract cerebral edema, convulsions, hemorrhagic syndrome and other life-threatening manifestations.
As a rule, the full course of treatment lasts at least three months. During the treatment of encephalopathy, complications are possible, including stroke, the development of coronary disease and encephalitis, seizures of the arms and legs, coma and even death.
The prognosis for recovery from encephalopathy depends on the causes of the disease and the initial condition of the patient. In some cases, it can only be stabilized, but not completely restored.
Encephalopathy, especially in its acute form, is an extremely serious disease. His treatment should be carried out by very good doctors, armed with modern medical equipment. All the necessary conditions for defeating this disease are available in the clinics of the MedicalClub network. Contact us - our specialists are able to put even the most seriously ill patient back on their feet!
Complications and prognosis
Encephalopathy can be complicated by decreased intelligence, loss of self-care ability, and the development of stroke. Some patients continue to have manifestations of organic brain damage with disturbances in movement, muscle tone and speech.
The prognosis largely depends on the causes of encephalopathy and the degree of brain damage. In most cases, you can only stabilize the condition, but not completely eliminate the consequences.
Sources:
- Eli S Neiman. EEG in Dementia and Encephalopathy. — English-language database of current medical data Medscape, 2019.
- Sandeep Kumar Singh. Neuroprotective and Antioxidant Effect of Ginkgo biloba Extract Against AD and Other Neurological Disorders. — Neurotherapeutics: the journal of the American Society for Experimental Neuro Therapeutics, 2021.