Types of stroke
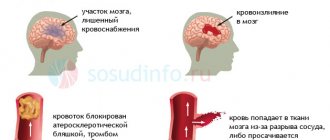
Clinicians distinguish two types of stroke: hemorrhagic and ischemic. The ischemic type accounts for more than 80% of all cases of the disease. It occurs due to narrowing or blockage of blood arteries, which impedes the flow of oxygen to the brain. Typically, this type of stroke occurs after age 60.
Hemorrhagic occurs when blood vessels rupture as a result of high blood pressure and bleeding in the brain. In this case, the prognosis for recovery is unfavorable and the survival rate is quite low.
It is also worth highlighting transient ischemic attack (ministroke). An acute transient circulatory disorder lasts from 5 to 10 minutes, but if this is not given due importance, the consequences can be quite serious.
Signs of a stroke
Most often, cerebrovascular accident occurs suddenly. Symptoms include:
- Increased blood pressure.
- Strong headache.
- Dizziness.
- Loss of balance.
- Noise in ears.
- Visual impairment (loss of fields).
- Numbness of the facial muscles and limbs.
- Articulation impairment.
In addition, older women may have atypical symptoms: hiccups, fever, attacks of fear.
A stroke can develop from several hours to days. You can understand that changes in blood circulation are occurring by the occurrence of tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), attacks of fear, decreased attention, and loss of orientation.
The appearance of such symptoms is a reason to seek emergency medical help. Taking timely measures will help stop cell death and avoid serious complications.
Care for elderly patients
Proper care of an elderly patient plays a very important role in the general treatment plan for stroke. This will help not only reduce the number of medications prescribed, but also avoid many complications due to unwanted drug interactions.
If the swallowing function is preserved and the patient is conscious, then she is fed in the usual way. Nutrition should include all the necessary proteins, carbohydrates, amino acids, fiber and vitamins. Fats are strictly limited. In case of stroke, fractional nutrition in small portions is indicated. The patient should spend at least half an hour in a sitting position after eating. Often caregivers or nurses help feed her. If the function is impaired even slightly, the patient will be fed through a special tube.
Stroke in older women
According to statistical studies, stroke occurs in 1.5-2% of the population every year, while timely medical care is provided only in 50% of cases. It is for this reason that this pathology often causes disability and death.
As a rule, women are susceptible to stroke after 60 years of age, while in men this risk occurs much earlier - after 40 years of age. This is largely due to hormonal disorders that occur in the body of women during menopause. Smoking, alcohol, long-term use of hormonal drugs, and blood clotting disorders also contribute to the development of stroke in women.
Women suffer the pathology more severely than men and only a small percentage of patients return to a normal lifestyle. The reason for this is untimely provision of medical care.
Signs
Unfortunately, older people often ignore symptoms indicating a pre-stroke condition. As a result, they turn to a medical facility for help late, which increases the risk of death.
A particularly difficult situation is blurred symptoms in people:
- with a history of dementia;
- with vision problems;
- leading a sedentary/lying lifestyle.
Therefore, they require constant supervision to recognize the first symptoms of an impending stroke in order to seek medical help in time.
Ischemic
It is characterized by a slower onset of symptoms. The first symptoms may appear several hours after a cerebrovascular accident.
Symptoms:
- weakness;
- problems with coordination of movements, visual analyzer and orientation in space;
- vomiting accompanied by headache.
Hemorrhagic
Early signs:
- rapid breathing accompanied by wheezing;
- gagging;
- hypertension, accompanied by increased blood pressure;
- Strong headache;
- intermittent heartbeat;
- lack of response to stimuli;
- paralysis of facial muscles and limbs;
- loss of consciousness.
Characterized by rapid development. Symptoms depend on the affected area, so coordination of movements, vision or hearing may be impaired, and convulsions are not excluded.
Spinal
Most often it is diagnosed already at the stage of hematoma formation. Despite the dependence of symptoms on the affected area, paralysis of the limbs is almost always observed. Also signs are:
- memory loss;
- complete or partial loss of sensitivity;
- headache;
- muscle weakness;
- difficulty keeping your head straight;
- urinary/fecal incontinence.
How to recognize a stroke
You can determine the development of a stroke by doing the following:
- Try to quickly repeat the phrase.
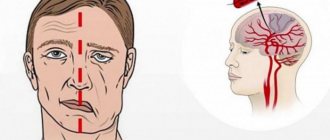
- Smile widely (if a stroke develops, the immobility of part of the face will be noticeable).
- Raise your arms up (if cerebral circulation is impaired, this will not be possible).
- Ask the person to show their tongue (in the case of a stroke, its tip will be deviated towards the brain lesion).
If the patient cannot pass this test, you must immediately call an ambulance, and during this time provide first aid:
- Lay the patient down, raising his head above body level.
- Provide air flow (open a window, balcony).
- Free yourself from tight clothing (unfasten your bra, belt, belt, tie, etc.).
- When vomiting, turn your head to the side.
- Measure blood pressure, pulse, record all readings.
When signs of a stroke appear, it is important to behave calmly and reassure the person, since excessive emotionality contributes to increased blood pressure.
Recovery of older women after stroke
The most favorable period for starting rehabilitation is the first 3-4 weeks. It is important to remember that due to age, women already have a limited reserve of recovery capabilities. This is due to the presence of other chronic diseases (osteoporosis, chronic joint diseases, pathological fractures, etc.), previously suffered and untreated micro-strokes, and a low ability to form new networks of neurons.
Recovery after a stroke takes from 6 months to 2 years. Further, all changes in the body become irreversible.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 3/5 — 5 votes
Share article on social networks
Prognosis and possible complications
Stroke in old age often has severe complications and consequences. The most favorable prognosis is partial restoration of functions affected by damage to parts of the brain.
Most often, older people who have suffered from this disease have problems with disorientation, speech and coordination of movements. However, this is only possible if medical care was provided in a timely manner.
If medical assistance is not provided within 2-3 hours after the onset of the first symptoms, then the person is susceptible to complications such as:
- Paralysis, paresis.
- Serious speech defects (up to its complete absence).
- Strabismus and other vision pathologies.
- Urinary and fecal incontinence.
- Dysphagia (impaired swallowing).
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Poor circulation of the inner ear, often hearing loss.
- Parkinson's disease.
In most cases, people who have had a stroke are unable to lead a normal life and require constant care.
Symptoms of stroke in older people
A stroke is a deadly condition that occurs during an acute sudden disruption of the blood supply to brain cells, and then the death of a section of brain tissue occurs. For older people, this disease occurs quite often than in the younger generation. If a stroke occurs, then literally minutes count. It is important that those around the patient can quickly find their bearings; his further recovery depends on this.
During a hemorrhagic attack, the symptoms are as follows:
· Severe headache that causes rapid breathing.
· The heartbeat becomes intermittent, the patient faints.
· Blood pressure rises, and the face turns red.
· Numbness of the limbs and facial muscles.
· Nausea and vomiting.
Very important to know! Signs of this type of stroke develop very quickly, which is why the patient may immediately lose consciousness. Depending on which area of the brain the blood vessels ruptured, the patient may lose hearing and vision, experience seizures, and may fall into a coma.
During an ischemic stroke:
· The patient has an acute headache, nausea and vomiting.
· The patient cannot make virtually any movement due to weakness.
· Vision deteriorates, the picture before the eyes becomes double.
· Spatial orientation is impaired.
· Speech is slurred, the patient speaks unintelligibly.
· Memory loss appears and dates become confused.
Important! This type of stroke develops gradually and becomes acute within 6 hours.
Short-term symptoms should not be taken lightly. Therefore, run the test:
· Face. During an attack it becomes asymmetrical.
· Speech. It is difficult for the victim to repeat the phrase, his speech is slurred.
· Hands. It is difficult for the patient to raise both arms up, one hangs or falls to the side.
If you have any doubts, ask the victim to stick out his tongue; during a stroke, it falls to the side.
It is necessary to call an ambulance as quickly as possible if any of the signs occur.
Sometimes seemingly insignificant signs of a stroke almost always lead to severe brain damage, which can lead to serious consequences.
In older people who have had a stroke, the prognosis is rarely positive due to a weakened immune system and the presence of existing diseases. Cerebral hemorrhage and its consequences are different and individual for all people. For some, life after a stroke was happy, while for others there were unfavorable outcomes. If medical assistance was provided in a timely manner, within the first six hours, then the prognosis is likely to be positive.
Rehabilitation
Elderly people who have suffered a stroke must undergo a long course of rehabilitation. This period is very important, since rehabilitation will help minimize the consequences of circulatory disorders and significantly improve your overall condition.
The list of actions to restore the patient includes both physical and psychological assistance. A person must feel important and supported; only in this case will he be able to overcome the psychological discomfort associated with the partial loss of cognitive functions.
Even if the patient’s motor function is normal, it is necessary to purchase an orthopedic mattress. When a disruption in activity does occur and a person has limited physical capabilities, it is necessary to regularly change his position (to avoid bedsores).
Often, a person who has suffered a stroke is prescribed medications to normalize blood circulation. They must be taken strictly according to the regimen prescribed by the attending physician. If signs of apathy or aggression appear, the help of a psychologist, and in some cases a psychiatrist, is necessary.
Prevention
The following preventive measures will help prevent a stroke:
- Annual medical examination (cholesterol control, blood glucose levels).
- Regular blood pressure monitoring.
- Quitting alcohol and smoking.
- Sleep at least 7 hours.
- Daily walking.
- Proper nutrition (the diet should include a lot of protein, vegetables, fruits).
- Active lifestyle (exercise, yoga, swimming).
Stroke is a disease that leads to disability. To avoid it, you need to be careful about your health and lead a healthy lifestyle.