Main symptoms and indications for surgery
Seeking professional help is important for any type of defect.
They are classified by size (small - up to 10 sq. cm, medium - up to 30 sq. cm, large - up to 60 sq. cm, extensive - more than 60 sq. cm) and by localization (occipital, parietal, frontal, temporal, combined ). In the Department of Neurosurgery of the City Clinical Hospital named after. Eramishantsev (Moscow) cranioplasty is prescribed only after a comprehensive diagnosis using CT, MRI, radiography, and determining the nature of the problem. The main symptoms indicating the possible need for surgical intervention include:
- headaches and local pain in the area of the defect, which arise as a result of changes in weather and even air temperature;
- protrusion of the contents of the skull during physical exertion, sneezing, coughing or sudden movements of the head;
- memory and sleep disturbances, emotional agitation, difficulty performing intellectual tasks and concentrating;
- disorders of the cardiovascular system and problems with blood vessels of the neuro-endocrine system.
Experts include the elimination of cosmetic defects and sealing of the cranial cavity as indications for cranioplasty. In the second case, at least two goals are pursued: to normalize cerebral hemodynamics and liquorodynamics, to protect the brain from the effects of external factors.
Features of the operation
Surgical intervention should not be started when inflammatory processes are detected in the cranial cavity, in the meninges or brain. Contraindications also include noticeable mental abnormalities of the patient, the presence of a piece of bone tissue or a foreign object in the cranial cavity, and bulging of the brain in the problem area. If visual examination and diagnosis do not reveal any of the listed points, surgery is prescribed.
Skull plastic surgery after trephination and other similar manipulations are called cranioplasty. It is aimed at restoring the integrity of the skull after decompression and stabilization operations, gunshot wounds, falls from a height, and mechanical damage. The choice of intervention technology depends on the timing of the plastic surgery, and it can be primary (1-2 days after injury), primary delayed (up to 2 weeks), early (up to 8 weeks), late (more than 2 months).
There are several rules that must be followed during any type of cranioplasty surgery:
- maximum possible preservation of bone tissue elements;
- use of separated fragments as an autograft;
- strict correspondence between the plate size and the size of the closure area;
- absence of sharp and too thin parts of the skull.
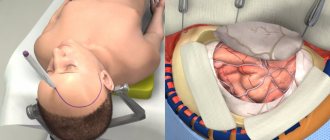
Elimination of a skull defect is a rather complex and responsible operation, the first step of which will be excision of the meningeal scar. All manipulations are performed as carefully as possible to avoid trauma to the brain tissue. For good adhesion of the skull bones and the implant, the edges of the entire problem area are exposed, and the material is necessarily installed “flush” with the skull bones. To prevent such a negative phenomenon as graft displacement, reliable fixation is carried out. Conventional soft tissue suturing is not enough.
Cranioplasty: the use of 3D printing for cranioplasty in Russia
Last year we talked about the use of industrial 3D printing in medicine to create an active prosthetic finger. And on the Internet there are more and more stories about the use of 3D printing in the medical field: developments are underway on 3D printing of biomaterials, the technology is used in dentistry, replicas of human body organs are printed, which help to carefully think through and correctly plan successful operations. It is the latest application of 3D printing in medicine, to which we have a hand, that I will talk about today. Under the cut you will find a description of the patient’s history, the process of processing DICOM files and photographs of the skull surgery itself.
Background of injury
It all started in 2010. A two-year-old boy named Lesha was running at home, fell, hit the back of his head on the baseboard, and hit his head. The emergency medical team first took Lesha to the district hospital of the Moscow region, from where, with the assistance of the territorial center for disaster medicine, he was transported by ambulance to the Research Institute of Emergency Pediatric Surgery and Traumatology (Research Institute of Emergency Pediatric Surgery and Traumatology (Research Institute of Emergency Pediatric Surgery and Traumatology).
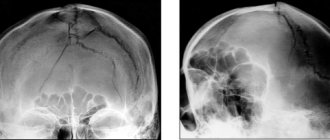
Since the condition was serious, the child was urgently sent for a CT scan of the head, which revealed spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage in the deep parts of the left temporal lobe, diffuse edema of both hemispheres, compression of the cerebrospinal fluid spaces and displacement of the median structures, descending herniation at the level of the tentorium cerebellum and foramen magnum — the injury was serious. An emergency craniotomy was performed to remove the intracerebral hematoma and plastic dura mater, which involved using a titanium plate and the child’s own bone to “patch” the hole. A sensor for measuring intracranial pressure was also installed. Then a long period of treatment followed, and on January 6, 2011, Lesha was finally discharged in satisfactory condition and went home. He was to be regularly monitored at the consultative and diagnostic center of the Scientific Research Institute of NDT.
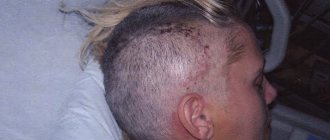
In November 2014, the boy’s mother complained that the bone flap that covered the brain had become mobile. After contacting the consultative and diagnostic department of the Research Institute of NDHiT, the child was recommended to be hospitalized for re-plasty of the skull defect.
Skull replica and 3D printing
Since the skull is an anatomically closed system, for its proper functioning, the mobility of the bone flap, which has partially resolved over time, must be eliminated. Typically, such an operation lasts more than one hour; doctors are forced to model the plate along the way, relying only on CT data, which means that the child’s skull will be trepanned for a long time, which entails certain risks.
In order to perform preoperative modeling of the plate, a replica skull was required. It will allow you to see in detail the area that will undergo repeated intervention. Thanks to 3D printing, it has become possible to create a three-dimensional model of a child’s skull in a short time.
Using KT images to create a 3D model
3D modeling from computed tomography (CT) data was the first step to create a replica of the skull. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images would also be suitable for this work.
We had a full set of CT images in DICOM format, from which we had to make a solid-state 3D model.
First, a mask was made from the CT scan, based on which a 3D model was generated.
This screenshot shows that some of the skull fragments are “suspended” in the air. If the position of the fragments mattered to doctors, then at the 3D printing stage we would have used stereolithography (DLP) technology. This technology involves the use of support material, and in order to keep the bone pieces suspended, the supporting structures would simply not be removed. But since the doctors did not require this, we removed all unnecessary things and “cleaned up” the 3D model.
Since we were going to print the skull from gypsum (full-color sandstone or gypsum polymer), the 3D model was first adapted to the characteristics of this material. In particular, it was necessary to maintain the thickness of the walls so that when removed from the printer it would not fall apart.
Preoperative plate modeling
Once the 3D model was ready, checked and re-checked, the printing phase began. We tried to print the skull as quickly as possible; the entire modeling and printing process took about a day. As soon as the technologists gave the go-ahead, the skull was promptly delivered to the clinic and handed over to the doctors. The finished skull looked like this:
The titanium plate was modeled before surgery:
Everything is ready, it's time for the operation.
Photos of the operation itself (it’s better not to look at the impressionable):
The operation was a success, and it was exciting, interesting and inspiring to have a hand in it.
Advantages of using 3D printing for cranioplasty
- Increasing diagnostic accuracy
- precise planning of the operation
- reduction of surgical time
- convenience of storing data in digital format (if necessary, you can always refer to the 3D model and print it again)
A bright 3D future
This is not the last use of 3D printing in this area, and if you are interested, I will definitely share with you new stories and not only medical ones.
In general, reading articles on the topic of additive technologies, especially on the RuNet, you can come across different views on these technologies. Both the admiring ones, who attribute impossible advantages to 3D printing, and the purely negative views of the “Luddites.” As a person who works with this technology every day, I can say that it really opens up new horizons for us, we just need to use it correctly.
ps While the post was hanging here, a couple of people have already written who are facing similar operations on the skull, and they want doctors to prepare in a similar way for their operations in order to reduce the time of the operation itself and increase the chances of success. I wonder why doctors don’t offer this preparation option to their patients, or am I mistaken and these are isolated cases? Maybe it’s just that not all doctors know that this is possible in Russia?
Types of implants for plastic surgery
If you believe historical data, a description of materials for plastic surgery of a trepanation defect first appeared in the medical literature back in 1565. At that time, the choice of specialists settled on gold plates. Modern doctors have a significantly increased choice of materials. Main types of implants:
- Autografts. This involves the use of patient tissue, which is taken during the initial operation. It is possible to produce material of the required size from the bone of the cranial vault or rib. If the problem area is small, preliminary crushing of bone fragments is performed to achieve the desired size.
- Allografts. In this case, the doctor uses materials that have been canned, frozen, or decalcified. Materials refer to bones and dura mater taken from corpses and carefully processed.
- Xenografts. This type of transplant refers to materials taken from animals. This group also includes inorganic materials, implants made on the basis of hydroxyapatite (a mineral from the apatite group, an analogue of chlorapatite and fluorapatite).
When choosing, it is important to consider the following requirements: biocompatibility, plasticity, resistance to mechanical stress, no risk of infectious complications, compatibility with modern neuroimaging methods.
Today, such a service as skull plastic surgery with a titanium plate is quite popular. It is possible to manufacture a graft from titanium alloy, stainless steel, chromium- and cobalt-based alloy. But practice shows that the most suitable option is the patient’s own bone tissue. Therefore, the task of reconstructive neurosurgery specialists is to preserve skull fragments as much as possible during the primary operation.
Depending on the situation in the neurosurgery department of the City Clinical Hospital named after. Eramishantsev's methods are used: the uatoplasty method using a pedicle graft, free autoplasty, bone-saving method, adhesive osteosynthesis, grinding of fragments with subsequent placement on the dura mater.
Indications and contraindications for plastic surgery of skull bone defects
| Indications for plastic surgery | Contraindications to plastic surgery |
|
|
Possible complications after surgery
If the patient’s own biomaterial is used during the operation, then the risk of any exacerbations will be minimal. The recovery period in this case will last less than with the installation of alternative grafts. Possible consequences of cranioplasty after trepanation:
- bleeding (reducing blood loss is achieved through infiltration of the skin);
- development of purulent-inflammatory processes (most often due to rejection of an artificial implant);
- infection of the problem area (the main reason is insufficient treatment of the operated area with disinfectants).
The capabilities of modern neurosurgery, a wide variety of surgical methods and materials make it possible to eliminate defects in the skull of any shape, size and level of complexity without consequences.
Are you interested in the price of skull surgery? Call our clinic and make an appointment with a neurosurgeon. Contact phone number. All further actions can be learned only during a face-to-face consultation.
Materials for cranioplasty and requirements for them
modern implants made by 3D printing
Regardless of the composition and method of obtaining a graft for cranioplasty, it must meet certain requirements:
- safety, low risk of infectious complications and other negative effects on the body (biocompatibility);
- absence of carcinogenic effect of artificial materials;
- high strength, low electrical and thermal conductivity;
- high survival rate;
- lack of tendency of the graft to stimulate a strong scar process;
- the possibility of using diagnostic techniques (MRI, etc.) after cranioplasty with artificial materials;
- ease of modeling and processing;
- convenience and completeness of sterilization;
- availability and reasonable price for most clinics.
Biological transplants obtained from the patient or donor are most often frozen or lyophilized (freezing under vacuum conditions). In this state, they can be preserved for a long time without losing their structure or changing their composition, which is extremely important for good engraftment in the future. In addition, lyophilized grafts are non-toxic and can be used for large cranial bone defects.
In cases where cranioplasty is performed on an emergency or urgent basis, frozen biological tissues may not be available, so surgeons use compositions based on acrylic resin (styracryl, butacryl, etc.). They are considered low-toxic, easily modeled and accessible, and provide hermetic closure of the bone defect. As the acrylic resin graft heals, it grows with connective tissue, which will firmly hold it in place after the adhesive composition has dissolved.
Experts in the field of neurosurgery are unanimous in their opinion that the best material for cranioplasty is the patient’s own tissue, so bone fragments are, if possible, completely preserved when treating a head wound. Bone fragments from the patient’s skull can be preserved in advance so that they can be used for skull surgery a little later. The disadvantages of the method are the resorption of bone grafts and a high risk of infection.
The most widely used grafts in modern neurosurgery are synthetic materials - metal plates, polymers, ceramics, etc. Among metals, preference is given to titanium, which is not only strong and lightweight, but is also well compatible with human tissue and has a minimal risk of infection. Among the polymers, polymethyl methacrylate, hydroxyapatite, and repirene are especially popular.
Today, neurosurgeons are increasingly resorting to the use of titanium grafts in the form of meshes, which are individually manufactured in accordance with the parameters of a particular patient’s defect. This approach allows you to reduce surgery time, reduce the risk of complications and provide maximum aesthetic results.
Often, with severe trauma to the skull, not only the bones of the head are damaged, but also the dura mater, which disrupts the tightness of the skull, creating the risk of infection, leakage of cerebrospinal fluid, damage to brain tissue and other dangerous complications. In this regard, it is extremely important to promptly and completely eliminate the defect of the dura mater.
One of the most effective ways to close a defect in the dura mater of the brain is the use of a donor membrane subjected to lyophilization. Such a flap can cover very large defects, is easily fixed to the edges of the wound defect, and prevents the leakage of cerebrospinal fluid. In an emergency operation, the surgeon can use polyethylene as a flap.