For everyone familiar with traditional and scientific medicine, our brain, both in an adult and in a newborn child, is, unfortunately, very little studied. But, nevertheless, it is a multifunctional guide not only in the conscious perception of the current reality, in making any decisions, in performing elementary unconscious actions, but is also undoubtedly considered the main coordinating center of the work of our entire body and neurological system as a single whole.
The work of the brain center is carried out continuously not only in a state of active wakefulness, but also in a passive state of deep sleep.
What is the expansion of the subarachnoid space
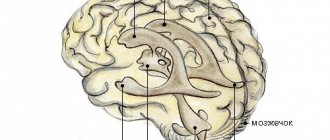
The human brain is surrounded by three protective membranes - hard, arachnoid and soft. The latter is directly adjacent to the medulla and provides its nutrition. The arachnoid membrane is connected to other membranes of the brain using connective tissue membranes. In areas where there are no membranes, there are cisterns.
With concomitant expansion of the subarachnoid space, arachnoiditis should be taken immediately.
The inflammatory process rapidly spreads to the brain tissue.The disease can lead to disability, serious visual impairment, hydrocephalus, and seizures.
Neurologist, reflexologist, hirudotherapist
Kislitsyna Ekaterina Nikolaevna
10 years of experience
Cerebrospinal fluid circulates in the 4 ventricles of the brain (third, fourth and two lateral) and the subarachnoid space. Liquor performs the functions of feeding neurons, removing metabolic products, and mechanically protecting the brain.
The normal amount of cerebrospinal fluid in children is 80-120 ml, in adults 120-160 ml. It is updated 3-5 times per day. The rate of circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid is affected by the position of the body, the intensity of the heartbeat and breathing.
The expansion of the subarachnoid space occurs due to difficulty in the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. Fluid accumulates in the subarachnoid spaces, dilating the ventricles of the brain.
The mechanisms of development of the disorder are different: the tumor mechanically blocks the paths for the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, inflammation provokes increased production of cerebrospinal fluid. Intracranial pressure may increase.
The effectiveness of drug treatment
If the baby has signs of neurological disorders, the doctor may prescribe vascular drugs, the effect of which is aimed at improving cerebral circulation, as well as sedatives for a good night's sleep for the child. But before you start treating a child’s troubled sleep with drugs, you first need to analyze the general atmosphere in which he lives and the causes of the problems. The problem can be solved without the help of medications, by normalizing the child’s daily routine and eliminating irritants.
If the increase in the interhemispheric fissure of the infant occurs as a result of infection, then in this case the doctor prescribes a course of treatment with antibiotics. Thus, the conclusion about the expansion of the interhemispheric fissure in a child after undergoing an ultrasound is simply a statement of fact if the indicator is only slightly higher than the norm.
The consequences of widening the interhemispheric fissure in infants are quite different. In most cases, it leads to developmental delays. This is why it is so important to start treatment as soon as possible, if necessary. It is prescribed on the basis of a specific diagnosis made not only based on the results of neurosonography, but also on the basis of certain complaints and changes in the child’s behavior.
Symptoms of the disease
The expansion of the subarachnoid space in an adult has characteristic signs:
- paralysis of the laryngeal muscles responsible for articulation and, as a result, speech impairment;
- loss of sonority ;
- difficulty swallowing;
- disturbances of visual and auditory perception;
- severe pain in the head, especially in the morning;
- nausea and vomiting accompanying headache;
- dizziness;
- drowsiness or sleep disturbances;
- dementia;
- impairment ;
- hallucinations;
- walking disorders - the patient is able to imitate walking movements in a lying position, but when standing up, walking is difficult, the gait is uncertain, shuffling;
- increased fatigue.
In young children, there is an abnormal enlargement of the skull as a result of developed hydrocephalus. Earlier symptoms are:
- increased sensitivity to sound and light stimuli;
- excessive regurgitation;
- unequal pupil size;
- strabismus;
- problems ;
- slowly overgrowing fontanel;
- swelling of the fontanel;
- restless behavior due to changing weather;
- tremor of the chin and limbs.
The intensity of symptoms depends on the causes of the disease and the severity. In the absence of adequate and timely treatment, expansion of the subarachnoid space in infants is dangerous due to the possible development of hydrocephalus.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
This disease leads to a lag in motor development, seizures, paralysis, and intellectual impairment. The effects of hydrocephalus can last a lifetime.
Clinical symptoms of increased liquor spaces
Signs of dilation of the ventricles and subarachnoid cavities in newborns:
- Constant irritability;
- Negative reaction to strong noises, flashes of light;
- Restless sleep;
- Frequent regurgitation;
- Strabismus;
- Different pupil sizes;
- Moodiness when weather changes;
- Slow overgrowth of the fontanel;
- Twitching of the chin.
Deviations must be detected immediately after their occurrence. Correction of changes should be carried out immediately after detection.
Clinical symptoms of subarachnoid enlargement in adults:
- Dyspeptic disorders (vomiting and nausea);
- Headache;
- Drowsiness;
- Constant dizziness;
- Increased intracranial pressure;
- Dementia;
- Memory problems;
- Disorders of spatial orientation;
- Unsteady gait.
Determining clinical signs in a child and an adult requires contacting a neurologist. The specialist will detect the pathology and give a referral for an MRI of the convexital cerebrospinal fluid cavities.
At the initial stages there are no manifestations of pathology. Symptoms depend mainly on the severity of the deformity and the causes of the pathology. In small children, the disease is provoked by arachnoiditis, birth trauma, and meningitis. Tumors are a common etiological factor in the occurrence of pathology in adults. Compression of the cerebral parenchyma causes defects in the destruction of white and gray matter. The formed cavities are filled with liquor.
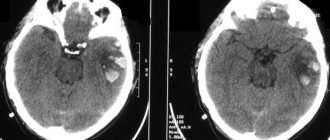
Analysis of brain tomograms in people with enlarged cerebrospinal fluid cavities: atrophic changes in the cortex of the frontal, occipital, and temporal regions. The number of convolutions is smoothed out, and blood accumulations are visible.
The presence of concomitant complications in a child is dangerous, so invasive diagnostic measures are postponed to the second year of life. A reliable diagnosis can be made after taking a biopsy of the enlarged cavities. Microscopic assessment of the properties of cerebrospinal fluid makes it possible to differentiate inflammatory, tumor, and ischemic changes.
Magnetic resonance imaging reveals accompanying pathological changes:
- Leukomalacia is a pathology of impulse signal transmission due to softening of the meninges;
- Inflammatory foci;
- Collections of blood.
An MRI picture of a moderate expansion of the external cerebrospinal fluid spaces shows morphological changes, but a whole range of diagnostic methods is required to make a correct diagnosis.
Tomograms of hypertensive hydrocephalus
Reasons for expansion
In infants, the disorder occurs due to congenital malformations, birth injuries, brain tumors, and infectious diseases. In some cases, the subarachnoid space and ventricles return to normal by the age of two years. However, pathology requires constant monitoring by specialists who can determine the further prognosis of the disease and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
In adults, expansion of the subarachnoid space occurs as a consequence of a stroke, vascular pathologies, head or spinal injuries, infectious and colds, and tumor cell degeneration. Meningitis, encephalitis, ventriculitis, tuberculosis, inflammation of the sinuses are diseases that affect the brain and can cause disruption of the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
The disease may indicate concomitant leptomeningitis or arachnoiditis - inflammatory processes in the tissues of the soft and arachnoid membranes of the brain. Long-term exposure to toxic substances, such as alcohol, arsenic, and lead, can cause inflammation.
Therapeutic measures in the fight against disease
The treatment of such pathologies in the brain is carried out by a neurologist, and it is he who should be consulted if you have reason to suspect hydrocephalus or arachnoiditis. Consultation with a doctor is necessary if there has been a head injury due to childbirth or mechanical impact. Even if the doctor does not diagnose anything, it is much better to play it safe and not worry in vain than to suffer from a serious illness and not even know it.
Treatment of an enlarged subarachnoid space in most cases involves eliminating the very cause that provoked this condition in the child. As a rule, the provoking factors of enlarged subarachnoid convexital spaces are sinusitis, otitis and increased intracranial pressure or infectious diseases. As a treatment for this deviation, a complex of antibacterial drugs and vitamins (especially group B) is prescribed. Treatment takes quite a long time and is prescribed individually, taking into account the patient’s age and the nature of the expansion of the subarachnoid spaces. Among the drugs that are used in the treatment of this disorder in children, the following can be noted:
- products that expel excess fluid (Diacarb, Veroshpiron, Asparkam);
- medications to improve brain trophism (Cavinton, Pantogam).
If we are talking about an adult or a child over 3 years old, then the treatment tactics will be slightly different. Treatment will include:
- diuretics;
- barbiturates;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- saluretics;
- vasoactive drugs;
- plasma expander solutions;
- painkillers.
In addition to drug therapy, the doctor can prescribe a number of physioneurological procedures that will eliminate the symptoms of the disease and restore normal metabolism of brain cells and tissues.
Speaking about treatment prognoses, they are favorable; the main thing is to start drug therapy in a timely manner.
If drug therapy does not provide the desired result, then surgical intervention is indicated.
Such diseases cannot be ignored and left to chance; at the first symptoms, qualified medical diagnosis is immediately required. If the disease is neglected, the person will experience dementia, gait disturbances, speech defects, problems with urination, developmental delays and a number of other unpleasant phenomena. Now you know what expansion of the subarachnoid space means. Being theoretically savvy in such medical issues, you will be able to cope with the disease and recognize its symptoms in a timely manner.
The subarachnoid space (SAS) exists in all people. It is located between the soft and arachnoid (arachnoid) membranes of the brain. Its purpose is the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, that is, cerebrospinal fluid.
Expansion of SAP occurs when a lot of cerebrospinal fluid is formed, or its outflow is obstructed. Since the brain is placed in a limited cavity of the cranium, as the volume of fluid increases, its structures are subject to compression. There is a general (uniform) expansion and a local one .
Subarachnoid fissure - the layers of the meninges diverge above the recess of the gyrus and connect above its surface; these spaces are called fissures. The concept of SAP expansion is only a conclusion obtained from X-ray, ultrasound or tomographic diagnostics. Additional examinations are needed to determine.
Causes of pathology in uniform and local: increased formation of cerebrospinal fluid; malabsorption due to inflammation, swelling; obstructions to outflow - tumor, cyst, hemorrhage. They may occur during the period of intrauterine development . In this case, the baby is born with hydrocephalus (water on the brain). Provoking factors: developmental defects; anomalies in the structure of the skull, its connection with the spine; trauma during childbirth; maternal infectious diseases.
Diagnostics
An accurate diagnosis can be made after a comprehensive examination. To study the state of brain structures, the following methods are used:
- Computed tomography is a method for diagnosing pathologies of the brain and central nervous system using x-rays. It is highly informative and accurate. The disadvantages of the method are high cost and health risks from irradiation. Although the x-ray dose is much lower than permissible, the method is contraindicated for pregnant women.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is one of the most effective diagnostic methods; it allows you to obtain a layer-by-layer picture of each part of the brain. MRI with contrast is used to examine the condition of the vessels of the head and determine disturbances in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. Before the procedure begins, the patient is given a contrast agent intravenously. The disadvantages of the method are the high cost and the presence of contraindications: MRI is not performed if the patient has metal implants or a pacemaker.
- Cisternography is a type of X-ray diagnostic examination used in combination with CT to study the flow of cerebrospinal fluid. Requires injection of air or contrast agent.
The patient is prescribed a general and biochemical blood test, urine and cerebrospinal fluid tests. To collect cerebrospinal fluid and measure intracranial pressure, a lumbar puncture is performed - a puncture of the spinal cord membranes at the lumbar level.
When examining cerebrospinal fluid, the concentration of protein and glucose, the number and structure of cells are determined, and a bacterioscopy of a Gram-stained fixed drop is performed. Additionally, an examination of the fundus is performed. If tumor cell degeneration is suspected, a biopsy is performed.
The neurologist also studies the patient’s medical history, conducts an examination and makes a conclusion based on all the data.
Features of brain examination in children
CT and MRI are considered the most effective modern diagnostic methods, however, their use is undesirable for young children. It is difficult for a child under one year of age to lie still for a long time. Therefore, in cases where there is still a need to resort to CT or MRI, children are given anesthesia.
To detect expansion of the subarachnoid space in children, the following is used:
- Neurosonography is an ultrasound examination of brain structures. To conduct the examination, the child must have a non-ossified fontanel. The procedure is safe, takes no more than 15 minutes, can be performed repeatedly, and does not require special preparation. A sonologist interprets the results.
- Echoencephalography is a method of examining the brain using ultrasound, used in children with already overgrown fontanelles and in adults. Can be carried out in one- and two-dimensional modes. Allows you to determine the damage to the brain and its displacement relative to the bones of the skull under the pressure of cerebrospinal fluid. Does not require preliminary preparation and is not harmful to health. The disadvantage of the method is its low accuracy.
To prevent brain damage due to birth injuries, hypoxia, and infectious diseases, neurosonography is performed in maternity hospitals. Pediatricians also monitor the growth of the skull in children - this simple procedure allows them to detect hydrocephalus.
Clinical signs
Manifestations of SAP expansion differ in adulthood and in infants.
In adults
A large amount of fluid in the space limited by the bones causes an increase in cerebrospinal fluid pressure. The symptoms of this pathology consist of the following disorders:
- headache that does not respond to painkillers;
- nausea, vomiting;
- feeling of pressure on the eyes.
These signs appear suddenly or gradually intensify, with periodic subsidence and exacerbation possible. With brain atrophy, the pressure inside the skull may not increase, so the detection of SAP expansion is an incidental finding during instrumental examination.
If hydrocephalus is not recognized in time and treatment is not started, then complications arise from compression and progression of the underlying disease.
These include:
- unsteadiness when walking;
- dizziness;
- instability when changing position;
- difficulty coordinating movements;
- sensation of tinnitus.
Visual disturbances are manifested by decreased acuity, loss of fields, and congestive changes in the fundus. Long-term hydrocephalus leads to blindness due to atrophy of the optic nerves.
The neurological consequences of expansion of the subarachnoid space include:
- decreased motor function of the limbs - paresis (partial immobility) and paralysis;
- increased tendon reflexes and muscle tone;
- muscle spasm, which leads to contractures (limited mobility) of the limbs;
- in severe forms – loss of consciousness, convulsions.
Increased intracranial pressure is accompanied by mental disorders:
- mood swings - causeless euphoria with a sharp transition to indifference, isolation;
- aggression;
- nervousness, anxiety, restlessness;
- psychosis with hallucinations and delusions.
Watch the video about intracranial pressure:
Signs in infants
A feature of the structure of a newborn’s skull is the pliability of the bones. As the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid increases, the size of the head increases compensatoryly . At the same time they discover:
- swollen veins on the surface of thin skin;
- spherical head;
- the large fontanel is tense, motionless (no pulsation);
- seam divergence;
- when tapped, a sound appears, like hitting a cracked pot;
- upward gaze is limited, there is swelling of the optic discs in the fundus.
The consequences of hydrocephalus include:
- delay in psychomotor development;
- late acquisition of skills (the child later sits down, rolls over, holds his head up, begins to walk);
- increased tone of leg muscles;
- low physical activity, obesity;
- mental disorders - apathy, no attachment to parents, reduced intelligence.
Symptoms
Exercises to dilate blood vessels in the brain
– this is a pathology that is manifested by an increase in the volume of the skull, oculomotor disorders, and impaired motor coordination, which is the reason for an instrumental examination. Newborns often undergo neurosonography, ultrasound, and MRI. Expansion of the cerebrospinal fluid spaces of the brain in infants is accompanied by symptoms:
- Unreasonable crying.
- Psychomotor agitation.
- Sleep disorder.
- Frequent regurgitation.
- Increased muscle tone.
- Throwing the head back.
A newborn baby rises on his toes when trying to support himself on a horizontal surface. His arms are clenched into fists, indicating increased muscle tone. Typical manifestations: loss of appetite, refusal to eat, slow weight gain, retarded physical development, Graefe's symptom (a white stripe of sclera between the pupil and the upper eyelid). The baby's fontanelle often protrudes, and cranial sutures may diverge.
At the same time, signs are revealed: weak support on the lower extremities, suppressed step reflex (congenital motor automatism - if you hold the child in an upright position, with support on his legs, slightly tilting forward, he involuntarily makes movements with his lower extremities that imitate gait), delayed mental and physical development . Signs of impaired cerebrospinal fluid dynamics in preschool children:
- Restlessness, excessive mobility.
- Aggression towards others.
- Hysterical manifestations.
- Impaired speech and psycho-speech functions (stuttering, poor vocabulary, incorrect diction, difficulties in constructing complex, detailed sentences).
- Violation of excretory functions (enuresis).
- Visual dysfunction (squint).
Manifestations in older children include pain in the head area, frequent bleeding from the nasal passages, memory impairment, inability to concentrate, neurotic symptoms (anxiety, touchiness, tearfulness), and disinhibited behavior. In severe cases, symptoms of mental development disorders appear, including debility
Such children have difficulty mastering new educational material, get tired quickly, and write and read slowly. Signs of a disorder in the autonomic system are often observed - increased sweating, paresthesia (sensitivity disorder in the form of goosebumps, burning, itching in the skin area). Symptoms of impaired cerebrospinal fluid dynamics in adults:
- Inability to maintain balance.
- Impaired motor coordination and motor functions.
- Auditory and visual dysfunction.
The expansion of the occipital cistern is accompanied by atrophic changes in the structures of the nervous tissue. With mild local uneven expansion in the area of the subarachnoid convexital (convex) space, symptoms are usually not observed or are mild (moderate pain in the head area, mild nausea in the morning, transient visual disturbances).
Expansion of the zone of cerebrospinal fluid spaces located in the brain, moderate to severe in adults, is manifested by pain in the head area, worsening in the morning, nausea, often accompanied by vomiting, dizziness, increased fatigue, irritability, and daytime sleepiness.
The main symptoms are often supplemented by a feeling of pressure on the eye area, increased sensitivity to external stimuli - bright light, loud sounds. The development of pseudobulbar syndrome is possible, for which the typical symptoms are: speech dysfunction associated with impaired innervation of the muscles of the speech apparatus, dysphagia (impaired swallowing), changes in the strength and tone of the voice.
Types of pathology
Let's take a closer look at each of them and find out what this disease is, what the consequences of lack of therapy are, and what clinical manifestations it is accompanied by.
The expansion of the subarachnoid convexital spaces indicates that there is an uneven distribution of fluid. This leads to cerebrospinal fluid pouring into the cavity and causing dropsy or hydrocephalus. Unevenly distributed cerebrospinal fluid can provoke intracranial pressure and dilate the ventricles of the brain.
If during the course of this disease the ventricles are within normal limits, then there is a possibility that by the age of 2 the baby will be able to outgrow hydrocephalus, but in any case the doctor is obliged to prescribe treatment. Parents should not wait for the child’s skull to strengthen by the age of 2 and the disease to recede on its own; this may not happen, but you will still lose time.
In order for SAP to expand, an excess amount of cerebrospinal fluid is needed. This occurs for one of the following reasons or a combination of them:
- increased education (uniform expansion);
- malabsorption due to inflammation, swelling (there are usually local and uneven changes);
- obstructions to outflow - tumor, cyst, hemorrhage (both local and general disturbances occur depending on the level of blockage of the cerebrospinal fluid circulation);
These pathological mechanisms can arise during the period of intrauterine development. In this case, the baby is born with hydrocephalus (water on the brain).
The factors of this pathology are:
- malformations (closure of outflow holes, narrowing of the Sylvian aqueduct, defect in the structure of the SAP);
- anomalies in the structure of the skull, its connection with the spine;
- trauma during childbirth;
- infectious diseases of the mother - syphilitic, toxoplasma, cytomegalovirus, rubella.
Older children and adults suffer from hydrocephalus for the following reasons:
- inflammation of the brain tissue (encephalitis) or membranes (meningitis, arachnoiditis);
- skull injuries, concussions;
- hemorrhage – ventricular, intracerebral with transition to the ventricles;
- cyst or tumor of the brain.
A special form of the disease is atrophy (reduced volume) of the brain and filling of the formed spaces with fluid. Such changes are typical for elderly patients against the background of complications of diabetes with widespread arterial damage (macroangiopathy).