Article:
In early childhood, neuropsychiatric disorders such as tics are quite common.
The scientific name is tic hyperkinesis. Parents immediately notice changes in the baby’s behavior. Uncontrolled movements of certain parts of the body or certain muscles in a child cannot but become a cause for concern and questions arise:
- Where did the disease come from?
- Could it have been prevented?
- What to do?
- How to treat?
This list can go on for a long time. One thing is clear - there is certainly cause for concern. And the first thing you need to do is find out as much information as possible about this neurological disorder.
So what are nervous tics in children and what is their danger?
GENERAL CONCEPT OF TIKS
This is the most popular pathology of the children's nervous system at an early age. It is simply impossible not to visually notice the manifestation of a tic, although some parents manage to go for weeks or even months without seeing any oddities in their child’s behavior.
Tics are involuntary, stereotypically repetitive, sudden or jerky movements that are the result of spontaneous contraction of individual muscles or groups of muscles.
At the initial stage of development of the disorder, attacks occur quite rarely, and repetitive movements do not cause much concern or problems. The child can even restrain or control them. However, attempts to control the tic cause him:
- internal discomfort;
- feeling of anxiety;
- mental stress.
When control over oneself weakens, tic manifestations occur, and the baby immediately receives obvious relief.
Nervous tics in children are usually detected between the ages of two and fifteen years. In the period of 6–8 years, tic hyperkinesis most often develops, while at 14–15, in approximately half of the cases it disappears spontaneously.
Fun fact: Boys are five times more likely to have the disorder than girls. From a scientific point of view, this is explained by the more stable psyche of female representatives.
Symptoms of tics in a child
Primary tics are more common in male children. Chaotic actions are usually expressed locally, affecting the muscles of the face or shoulders and do not spread to other muscle structures. Such movements are most often observed during stress. Sometimes tics last for years and persist into adulthood.
The most common manifestations are blinking, teeth grinding, grimacing, shrugging, limb twitching, hair manipulation, various vocalizations, screams, loud breathing, and walking in circles.
Primary tics are accompanied by disorders such as anxiety, inattention, depression, disinhibition, uncoordinated movements, inability to absorb information, rapid fatigue, inhibited actions, sleep problems, motion sickness, etc.
Children often encounter difficulties in educational institutions. The teacher may think that the child does not care about studying and imitates peers and adults. Severe suggestions and punishments only increase stress, which only makes the situation worse.
Secondary tics usually begin in parallel with the leading disease and disappear after restoration of health. Their course and characteristics will depend on which particular area of the cerebral cortex was affected by the disease.
If involuntary movements are hereditary in nature, they often appear in preschool age. Children are diagnosed with motor and sensory tics, vocal tics (swear words and expressions). The baby wants with all his might to perform an action that resembles a yawn or sneeze. In this case, the tic is semi-voluntary: the child is convinced that he is doing something to alleviate the unpleasant sensations.
In Tourette's disease, the symptoms of this disorder are determined by the age of the child. As a rule, the disease debuts in the preschool period. First, facial tics and shoulder twitching appear, then they move to the limbs. There is a tilting and turning of the head, clenching and unclenching of fists, jumping, squats, contractile movements of the muscles of the back and abdomen. Later, vocal tics are added, sometimes ahead of motor actions.
The culmination of symptoms occurs between the ages of eight and eleven years. In severe cases, children need help and household services and cannot attend classes. By about 12–15 years of age, the disease enters the residual phase, where local and widespread tics are noted.
With this disease, infrequent types of tics are observed:
- palilalia – regular repetition of certain phrases;
- echolalia - repetition of phrases that were uttered by others;
- Copropraxia is not the most decent movement.
Nervous tics appear when children are awake. The child does not exhibit negative symptoms during sleep.
VARIETIES OF NERVOUS TICS IN CHILDREN
Each child has his own individuality, and therefore nervous tics that arise for one reason or another are different.
Tic manifestations generally have two types:
- Motor (motor). They are detected by spasms of individual muscles, their groups or movement of limbs and other parts of the body.
- Voice (vocal). They can be recognized in the form of frequently repeated individual sounds, syllables, exclamations, words and even phrases.
Both groups are divided into simple and complex tics. Everything is clear here. A simple form - one short movement or sound, a complex one - several muscle groups are involved, if there are vocal disorders, progress is also observed in them.
MAIN MANIFESTATIONS
Localization of tic movements most often occurs in the facial or neck muscles. Over time, they can spread from top to bottom. The most common examples of simple childhood motor tics are:
- frowning;
- blinking;
- squinting;
- moving the wings of the nose;
- drawing in air through the nose;
- twitching of the corner of the mouth;
- turning or tilting the head;
- shrug;
- flinching;
- twitching of limbs;
- flexion or extension of fingers;
- snapping fingers.
Vocal tics are manifested by coughing, throat sounds, sniffling, spoken syllables or exclamations. This is a meaningless sound that interferes with speech and gives the impression of stuttering or stuttering. If no measures are taken to eliminate them, the situation will only get worse. Tic movements also progress and reach a new level in the form of:
- grimace;
- head tossing;
- touching various parts of the body with hands;
- contractions of the abdominal muscles or diaphragm;
- squats;
- bouncing.
All of the above nervous tics in children are not all manifestations of the disease. They can be individual and atypical. It all depends on the child’s level of development, his character and temperament, sensitivity to environmental stimuli and a number of other reasons.
FEATURES OF THE DISEASE
Initially, the child exhibits motor tics, and if the situation worsens, then vocal tics join them. However, there are cases when hyperkinesis begins with sound tics, which significantly complicates diagnosis and delays treatment.
In severe cases, several types of spontaneous movements are observed simultaneously. Sometimes they are accompanied by vocal tics.
Nervous tics in children have their own characteristic features, which make it possible to distinguish them from other pathologies of motor functions. They can be divided into several points:
- Self-control. It should be noted that it works only in the early stages of the disease. This means that the child can control his seizures, but over time it becomes more and more difficult to do so.
- Increased symptoms due to stressful situations. The same tendency is observed at the end of the day due to overwork of the nervous system. The autumn-winter period is the peak of the disease.
- The child's consciousness is not affected in any way. This fact allows us to exclude the development of epilepsy.
- Hyperkinesis does not occur during sleep. This feature is relevant in the presence of vocal tics and confirms the absence of pathologies of the upper respiratory tract.
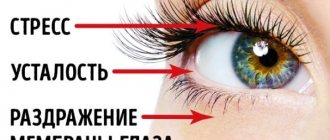
- A nervous eye tic in a child can at first be mistaken for developing conjunctivitis, but soon everything becomes clear.
The following pattern has been noticed: the earlier the disease appears in a child, the more severe it will be. If appropriate measures are not taken, hyperkinesis develops into a chronic form. In this case, treatment is complicated by the fact that several muscle groups may gradually be involved. Pathological movements move from the head to the lower organs and become more complex, vocal tics are added. Doctors assess them as generalized.
Tic manifestations that arise after the age of ten are almost always classified as transient. This means that they disappear spontaneously and unnoticed, just as they appeared. They are also called transient. They do not require special participation from the medical side.
REASONS FOR THE APPEARANCE
Despite countless years of research into nervous tics in children, doctors have not been able to come to a common point of view regarding the provoking factors. But among many theories, it was found that the most likely are the consequences of traumatic influences. These include:
- Fright.
- Fear.
- Divorce of parents or forced separation from one of them.
- Change of environment.
- First of September. The first days of school are extremely stressful for a child.
- The birth of a second child in the family.
Heredity also plays an important role in the occurrence of tics. Children whose parents experienced hyperkinesis in childhood are much more likely to develop it too.
An unstable situation in the family or immediate environment that a child encounters in kindergarten, school, or in the yard is, of course, the main provoking factor. Children's relationships, communication with peers and adults, can be of a very diverse nature. They often contain conflict situations, and they serve as the starting point of nervous disorders.
Organic brain damage can also cause nervous tics in children. Sometimes they are a consequence of the following events:
- severe maternal pregnancy and difficult childbirth;
- traumatic brain injury;
- a previous neuroinfectious disease.
Separately, it should be mentioned that the reasons for the development of tics may be hidden in a lack of any vitamins, minerals or trace elements. Since the child’s body is just being formed and is very unstable to external influences, hypovitaminosis can cause disturbances or malfunctions of the nervous system.
It has been noticed that the disease progresses in waves. If the child is in a calm, balanced mental state, then tic movements may decrease to minimal manifestations or not be observed at all. At the same time, any stressful situation, fear or anxiety, serves as an impetus for exacerbation of the condition and intensification of tics.
Causes
Vocal tics can be primary or secondary. Primary, or idiopathic, tics are a single dysfunction of the nervous system when no other signs are observed. Secondary disorders serve only as a manifestation of the underlying disease of the central nervous system. Both types have almost the same symptoms.
Primary vocal tics can develop due to:
- nervous stress, which most often causes tics. Patients are mainly children 7-12 years old who have problems in the family, school or communication with peers, and who have also experienced severe fear or shock. Involuntary sound pronunciation can provoke a lack or, on the contrary, excess of attention, demands on the child, as well as strictness of upbringing;
- overwork and lack of sleep;
- genetic predisposition. Scientists have found that tics are inherited in an autosomal recessive manner: if one of the parents has a defective gene, the risk of passing it on to a daughter or son is 50%. However, even with the presence of a vicious gene, there is no guarantee that a child will necessarily develop a tic;
- Excitement about starting school leads to the appearance of a tic in 10% of cases, which is associated with a new situation and environment, a radical change in the daily routine, unusual rules and restrictions;
- Excessive consumption of stimulants - tea, coffee, energy drinks - activates the nervous system and makes it work harder. The result is irritability, mood swings and uncontrollable sound pronunciation.
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES
Before starting any treatment, you need to have your child examined by a specialist. After the initial examination, the neurologist refers the patient to undergo electroencephalography. It makes it possible to identify the following indicators:
- local cerebral disorders;
- foci of pathological activity;
- analysis of the state of brain activity.
Repeated studies allow you to monitor the effectiveness of the therapy. A biochemical blood test is mandatory. If the doctor deems it necessary, the child may be sent for an MRI.
Identifying nervous tics in young children, establishing their causes and prescribing adequate treatment is the task of a neurologist. But the direct responsibility of parents is to ensure a comfortable stay for the child at home, in an educational institution or on the street. It is necessary to find out the factors that pose a threat to the baby’s psyche and eliminate them in any way.
TREATMENT
Very often, children who are diagnosed with tic hyperkinesis do not need special therapy. It is absolutely meaningless, and only correction of the patient’s lifestyle helps. However, if the tics become generalized, then treatment cannot be avoided. But which method the doctor chooses depends on the severity of the disease, age and physical characteristics of the child.
An integrated approach to treating tics in children is possible. It includes:
- Activities aimed at properly organizing the child’s daily routine. Protecting him from stress, anxiety and other troubles.
- Drug-free therapy. This complex includes a visit to a psychotherapist, physiotherapeutic procedures, and reflexology.
- Treatment with medications.
At the initial stages of the development of tics in young children, only routine measures are sufficient for visible positive dynamics. Rationally organized time for activities and rest, timely going to bed, proper nutrition, and exercise are the key to a positive outcome from a nervous disorder.
Family psychotherapy is of no small importance. If the situation in the family has given impetus to the development of tics, then you need to try to correct it. Under no circumstances should the child witness quarrels or scandals. It is necessary to create a calm, trusting environment so that the child feels loved and protected. You should not pull back or remind him of his nervous disorder, as this will only aggravate the situation.
Good results in the prevention and treatment of tics are provided by educational games using fine motor skills, art therapy, and relaxation. The most commonly used physiotherapeutic methods to combat this disorder are:
- biofeedback method;
- audiovisual stimulation method;
- acupuncture;
- laser therapy;
- ozokerite applications;
- massage of the cervical-collar area;
- electrosleep.
In cases where drug treatment cannot be avoided, sedatives are first prescribed. They have a general calming effect, remove nervousness and irritability. If the expected effect is not observed, the doctor prescribes tranquilizers. Their scope of action is the relief of emotional stress, anxiety and fears.
With progressive tic hyperkinesis, which is not amenable to gentle treatment, more severe drugs are used. These include antipsychotics and antidepressants. Unfortunately, these medications have a lot of side effects and are used only as a last resort, only as prescribed by a doctor and strictly following the dosage. The main indicator for use is the safety of the child, taking into account the special sensitivity of the not yet formed organism, including the nervous system.
Treatment of tics in children is usually carried out on an outpatient basis, since hospitalization can be an additional source of anxiety. For the same reason, drug therapy is avoided by injection.
Tics, nervous tics, treatment of tics in Saratov, Russia
Sarklinik provides treatment for tics and tic-like hyperkinesis in children, adolescents and adults. As a result of treatment of tics and hyperkinesis, signs of organic cerebral dysfunction and disorders in the serotonin-monoamine oxidase system are eliminated, the work of the extrapyramidal system and deep structures of the brain, cholinergic regulation, histamine synthesis in the blood, excretion of catecholamines, processes of excitation and inhibition in the central nervous system are normalized. correction of neurotic disorders that occur during the course of the disease (tics, hyperkinesis). Sarklinik provides treatment for tics in children in Russia , treatment of tics in Saratov for children, adolescents, and adults.
POSSIBLE CONSEQUENCES
Nervous tics in children of different ages, regardless of the cause, are signals that not everything is all right with the child, his mental state is at the limit of his capabilities, and he needs immediate help. If the irritant is removed in time, the tic manifestations go away spontaneously.
What happens if you leave everything as is? There are several possible scenarios here:
- Epilepsy. Tics may be symptoms of the early stages of this severe neurological disease.
- Severe neuroses, psycho-emotional disorders. Untreated hyperkinesis progresses in the child’s body, causing new manifestations of the tic condition. Lack of qualified help leads to the development of depression and other critical conditions.
- Tourette's syndrome. Although this mental disorder is not a consequence of parental inactivity, its clinical picture necessarily includes both motor and vocal tics.
Even if hyperkinesis disappears on its own after a week without any consequences, it is necessary to go to the doctor and undergo diagnostic procedures. This is a guarantee of the child’s health, and is done with the aim of eliminating the above diseases.
Treatment of motor and vocal tics in Saratov
Treatment of tics should be comprehensive. It is necessary to take into account the types of tics, the stage of the disease, the individual characteristics of the patient’s nervous system, and the social situation in the family. Optimization of the daily routine, psychological correction and training, and drug therapy are mandatory. Doctor Sarklinik has been successfully using hardware and non-hardware methods of treating tics for many years. Treatment is being carried out for vocal tics in Saratov; — sound ticks in Saratov; - motor tics; - motor tics; - tic disorders; - clonic tics; - tonic tics; - dystonic, tonic-clonic tics; - turretism; - Tourette's syndrome. As a result of therapy, there is an improvement in the motor and emotional spheres, motor and sound tic-like movements disappear. The effectiveness of treatment depends on the individual characteristics of the child, adolescent or adult, the severity of symptoms at the time of treatment, the age of the patient, and the intensity of treatment. Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis, in courses. Under no circumstances should you scold children; if you notice any of the symptoms we mentioned above, it is better to consult a doctor. And remember that treating tics is a very complex process that requires persistence, persistence and time. Your child needs care, attention, understanding and help from you! Don't blame your child or yourself. Complex treatment will give positive results. On the sarclinics website you can ask a doctor a question about your problem online for free.
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Text: ® SARCLINIC | Sarclinic.com \ Sarсlinic.ru Photo 1: © zurijeta / Photobank Photogenica / photogenica.ru Photo 2: © altanaka / Photobank Photogenica / photogenica.ru The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all coincidences excluded. When using materials from the site sarclinic.ru, an active hyperlink is required!
Related posts:
Speech echolalia in children: correction, treatment, symptoms
Parasomnia, illnesses during sleep and upon awakening
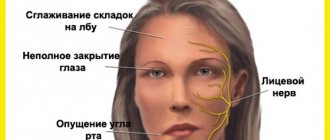
Paresis of the facial nerve in newborns, neuritis of the facial nerve in children, damage during childbirth
Akatagraphy, treatment of akatagraphy
Yactation, rocking, nodding movements of the head, torso, body
Comments ()
ADAPTATION IN SOCIETY
Children, as we know, are cruel by nature, so it will be very problematic for a child with obvious manifestations of hyperkinesis to adapt to a new team. But it’s not his fault that the nervous tic happened to him. When communicating with adults, it is very important for him to feel a tolerant attitude. And if at home they constantly focus attention on this topic and reprimand the child, believing that he is doing this on purpose, the situation only gets worse.
Parents should be completely on the side of the child, and he should feel this not only in words. This is what it should look like:
- all conversations about nervous disorders, including tics, should be prohibited, especially in the presence of a baby.
- do not focus on the problem, behave freely and naturally.
- conduct an explanatory conversation with teachers or educators of the team that the child attends, and call on them for assistance.
- choose a suitable leisure activity for your child. Single active sports, such as skiing or swimming, are encouraged.
- provide nutritious and varied nutrition.
During adolescence, a teenager’s body is unpredictable, and also undergoes hormonal changes. If at this stage nervous tics are also detected, then this can generally turn into a personal tragedy. First of all, self-esteem suffers; the child withdraws into himself, does not want to communicate with anyone, and is fixated only on his illness.
The parents’ task is to consider the threat in time and take all measures to eliminate it. Even if the tics do not go away on their own, there is every chance that properly selected therapy or medication will help get rid of them. In any case, you can and should strive to live a full life.
Types of hyperkinesis
There are many types of involuntary movements, which are classified according to the location of the lesion, clinical manifestations, duration of attacks, their frequency, and emotional accompaniment.
There are several large groups of hyperkinesis, which, in turn, can be divided into subtypes: 1. Tics. They are characterized by involuntary and stereotyped movements that are not unnatural. The tic intensifies due to emotional excitement. After diverting attention from the stimulus, the attack disappears. 2. Tremor. Characterized by trembling of the whole body or parts of it. Most often, the disease manifests itself in small movements of the head, hands and fingers. 3. Choreic hyperkinesis. It manifests itself in the fact that a person’s legs and arms twitch simultaneously, and the movements are very impetuous and chaotic. The poses are not natural. This situation can be provoked by rheumatism, as well as hereditary degenerative pathologies. 4. Facial blepharospasms, paraspasms and hemispasms. This type of pathology is represented by smooth or sharp twitching of facial muscles. 5. Torsion spasm. Movements with it are arrhythmic, tonic, unnatural. In this case, the person has limitations in movement and self-care.
These types of hyperkinesis are the main ones and can be divided into many subtypes.
PREVENTION TIPS
To prevent a child’s nervous tics from developing into more serious mental disorders over time, all possible measures must be taken to prevent them. You don't need anything supernatural to do this. It will be enough not to forget that the baby sees the behavior of the parents and people around him, draws his own conclusions and evaluates the events taking place due to his level of development.
The psyche of a child at an early age is unstable and vulnerable, so any clarification of the relationship between parents in a raised voice is a stressful situation that can lead to tic manifestations. It is in the family that the child should feel support and understanding. This is his fortress, in which, if necessary, he can hide from all his fears. If there is no such relationship, then the risk of developing tics is quite high.
Children living in a calm, friendly environment are very rarely susceptible to nervous tics. To avoid having to treat the consequences of mental imbalance in a child, it is enough to create comfortable conditions for him. They are as follows:
- avoidance of anxiety and stressful situations;
- healthy, full sleep;
- high-quality and healthy food, a ban on fast food and overly sweet and fried foods;
- compliance with the daily routine, proper organization of rest;
- dosed computer use and TV viewing;
- maximum exposure to fresh air;
- classes in sports sections that match the interests and temperament of the child;
- inadmissibility of overwork.
In rare cases, raising the younger generation does not involve punishment. They are certainly necessary, but within reason. Physical impact is immediately excluded. Only moral methods of influence are acceptable. The child must clearly know what offense he is being punished for and how he should have done the right thing. At the same time, you should assure the child that punishment does not affect his love for him. Only in such a situation will he draw the right conclusions and receive minimal nervous shock.
Even if the appearance of nervous tics in a child could not be avoided, it should be remembered that this is not the worst thing that could happen to him. Modern medicine, combined with parental care and attention, can work wonders.
Features of the development of pathology in children
Hyperkinesis in children
are involuntary movements that are observed in both younger and older children. According to G. G. Shanko, the prevalence of hyperkinesis among schoolchildren is 1.38%, and more than 1/3 of them have hyperkinesis in the form of tics. Naturally, its manifestations can be different. It should be noted that the movements of body parts during an attack are not characterized by any unnaturalness, but their feature is involuntary. The most common form of pathology is facial muscle tics, which manifests itself in frequent blinking of the eyelids, sniffing, smacking and grinning.
No less often, hyperkinesis in children is manifested by tics of the arms and legs. Sometimes the pathology can manifest itself complexly in uncontrolled involuntary muscle movement throughout the body.
The cause of the disease in children can also be brain damage. However, infectious processes in the body, fear, nervous tension, emotional, psychological or physical trauma are also not excluded. It should be noted that those movements that a child repeats too often, even if they are involuntary, soon become a habit and can appear in adulthood. Naturally, pathology requires serious intervention from pediatricians, neurologists, and psychologists.
Hyperkinesis in children should be treated after the first symptoms appear. For this, doctors may prescribe sedatives. In addition, the child should be protected from stress and nervous situations. Try to walk with him in the fresh air as much as possible, follow a daily routine. Provide your baby with adequate nutrition. You should not scold, punish or shame your child because of his problem. Try to be patient and surround him with love, care and your support.