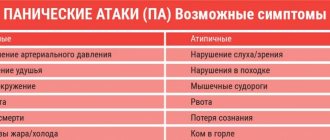
Causes of phobia: fear of doctors
Fears do not appear just like that, without a reason; any fear arises from some factor, a situation that is negatively deposited in a person’s memory. This can be any medical procedure, each of which is associated with pain and discomfort. Many patients, at the mere word of surgery or the need for surgical intervention, begin to panic and find excuses to go to the hospital. They develop fear for their own lives and mistrust of the attending physician.
According to sociological surveys, 60% of the population of our country do not trust people who took the Hippocratic oath, and 15% go to private clinics, where the quality of service is slightly better than in ordinary public clinics. And the state of hospitals, clinics and other medical institutions leaves much to be desired. And if you add the boorish attitude, incorrect diagnoses, unqualified assistance, and sometimes complete indifference of the staff, it becomes clear that even a person with a healthy psyche will not have the desire to seek any help.
Suspiciousness and self-doubt, an inferiority complex plays an important role in the fact that some adults do not go to the dentist for years. As a result of this, they end up with a sad state of their oral cavity.
Women, and especially young girls, due to their inexperience and lack of knowledge, do not undergo an ordinary routine medical examination by a gynecologist. They are sure that if nothing bothers you, then visiting a female doctor is not advisable. This is a huge stupidity, since many dangerous diseases are asymptomatic and you will still need to go to the hospital later. It’s just that the disease will no longer be in its initial stages.
How to overcome the fear of visiting a gynecologist?
15.09.2020
Every woman should visit a gynecologist once every six months. Even if it is a routine check, the reception is usually a cause for concern. It's not just young girls who are nervous about a gynecologist Even women who have been seeing their doctor for many years can still feel anxious and afraid.
There are several tips that will help you overcome your fear of gynecologists and not neglect regular examinations.
Knowing your body.
In fact, much of the anxiety associated with visits to the gynecologist is that the doctor appears to have some power. Doctors know a lot about how the human body works, but every woman can also try to get to know herself better. In addition, getting to know your own body will help you quickly detect irregularities in its functioning.
Accompaniment to the appointment.
Before going to the appointment, it is worth talking with a loved one about your fears and asking them to act as an accompanying person. Even if the accompanying person waits outside the office, awareness of his proximity will help to calm down. Having someone nearby is always a source of comfort. In addition, loved ones can also talk about their own worries, which can help find new ways to cope.
Honesty with the doctor.
Most women are afraid to see a gynecologist because they are embarrassed to ask the questions they want, usually related to their sexual health or sexual behavior. But you need to understand that these are important health issues, so you should talk about your sexual problems as honestly as possible. There is no need to be scared - doctors have already heard all this, and they will treat everything professionally. No one will judge - the doctor is here to help improve the patient’s health and sexual comfort. Up to 40% of women have trouble admitting to their gynecologist that they sometimes have unprotected sex. This is one of the most important things to tell a specialist; he must know what tests to perform, and this information is crucial for correct treatment.
Receiving the information.
Most women don't know how to choose between the different Pap tests. For example, the new ones are liquid-based, which help filter blood and other fluids; thus, cervical cell samples are much easier to read. It is also possible to provide a more accurate Pap smear reading during or immediately after your period .
You should read something about Pap smears before your appointment and don't be afraid to ask your gynecologist about things you don't understand. Don't stop reading about the Pap test. Why not get information about the entire consultation ? Every doctor has certain routines, and if you understand why he does certain things, it will be easier to accept them as natural, and the anxiety will begin to gradually disappear.
But in no case should you think that a diagnosis that matches the symptoms from the Internet will be correct. Often the same symptoms fit a dozen diseases and it is only possible to determine by reading medical sites which of them actually occurs. A doctor is still needed to look at problems from a professional point of view , order tests and choose the right treatment. Seeing a doctor instead of self-medicating can save your life.
Choosing a doctor.
Some women feel more comfortable with a female gynecologist, while others, on the contrary, feel more comfortable with a male gynecologist. Regardless of your preference, it is important to make sure that the appointment is carried out by a professional. Then the woman will be able to feel comfortable and trust her doctor with all her problems without shame or fear.
When dealing with problems with the reproductive system, it is extremely important to feel that the doctor anything you want, without any restrictions. This is the only way to ensure that all necessary medical care will be provided.
Published in Gynecology Premium Clinic
What happens to a person with iatrophobia?
A process starts in the body when the brain gives a signal for the release of adrenaline. The body cannot cope with its amount. This causes a sharp deterioration in health (tachycardia, high blood pressure, diarrhea and trembling of the limbs, dry mouth, shortness of breath, complete lack of understanding of the current situation, inappropriate behavior).
Phobia of fear of doctors requires treatment, but the patient needs to go directly to the person he is already afraid of! It turns out to be a complete vicious circle! But this is not a hopeless situation.
How to overcome this phobia
Any case of fear of doctors is individual and requires specific treatment. It is possible to get rid of jatrophobia only by finding the cause. If you analyze your inner sensations, thoughts, feelings, then this can be done by the person himself. But if, when remembering the doctor, panic and hysteria begin, it is very difficult to calm down, then the help of a psychologist is needed. To avoid visiting the hospital, it is better to go to a private clinic or call a doctor at home.
If you decide to seek help from any medical institution, then take with you a person with whom you will feel at ease and calm. He will support and understand in difficult times for you.
How not to confuse the phobia of fear of doctors with ordinary fear
A striking example and portrait of a jatrophobe - he is very actively interested in treatment with folk remedies and methods of alternative medicine. All this is explained by the fact that he believes more in some grandmother’s healer, who can cure him using a photograph or simply by preparing some special decoction. This is simple self-deception.
There are cases in the practice of doctors when jatrophobia was passed on from generation to generation.
The reason why children are afraid of doctors
Or as it is also called by professionals, iatrophobia lies largely in the behavior of the parents, since the child copies this fear from adults.
He remembers their every word and expression. When they talk about how they hurt in the hospital, how dangerous and scary it is.
It is also worth taking into account the individual characteristics of the baby; some children do not like tactile communication; any touch from strangers is at least unpleasant for them. Perhaps the child has a low pain threshold and no matter what is done in any medical institution during various procedures, it causes pain for him. With such children, even after one unsuccessful visit to the clinic, it is difficult to persuade them to just go there.
In most cases, the adults with whom the child lives are to blame for jatrophobia in children. If a mother and her child behave insecurely and too emotionally when visiting the hospital, then the child feels the same way. This is where his panic and hysteria arise.
HOW TO OVERCOME Iatrophobia
The main thing to remember when it comes to reducing your fear of the figure in the white coat is that you are working with a person. This means that relationships arise and are built between you. Dealing with anyone from the position of victim is by definition not a very inspiring endeavor and often sets an unsuccessful scenario in advance. Therefore, your main task is to put your relationship within the framework of a partnership.
If you have found the right specialist and found the strength to seek help, then:
1. Trust your doctor! To do this, be sure to obtain information about the professional competence of the specialist you personally like in advance. Trusting his actions will greatly ease your anxiety and increase your sense of control over the situation. 2. Trust yourself! Concern about the actions of medical personnel often arises against a background of general self-doubt and personal anxiety. Try to listen to your body's signals. Study the necessary information, ask disturbing questions to the doctor, and it would also be a good idea to tell him about your fears - this will help establish partnership contact between you. 3. Take any measures to prevent feelings of personal helplessness. Follow the therapeutic recommendations, and at the same time do not forget about what brings you joy: feasible physical activity, communication, social activity, creativity. You always have the opportunity to make decisions regarding vital issues, and this makes you a true master of your life, your body and soul. Remind yourself of this often and do not lose your sense of self-worth. 4. Study medical topics related to your illness, not from amateur forums on the Internet, but from more serious sources. Seek explanatory advice from several specialists, including generalists, to have a complete picture. Information about stories of successful therapy is especially important psychologically - learn something useful from them for yourself. Don't focus on failure stories; they more often end up in the general information field only because it is not customary to talk about successes loudly. 5. Organize your stay within the walls of a medical institution with maximum attention to your own comfort. Take with you your favorite household items (a warm blanket, a pillow), a good book and music player, and some little things that calm you down. If this is a short visit to the doctor at a medical center or clinic, take care of something to do while you wait in line. Let it be the least passive, that is, instead of reading a book, it is better to start writing notes on work, drawing up a personal plan, thinking about organizing some kind of family event, etc. 6. If yatrophobia manifests itself so strongly that it forces you to postpone important decisions in terms of your health and prevents you from seeing a specialist for a critically long time, you should seek psychological help. It is quite possible that one meeting with a good specialist will be enough to resolve this issue.
First of all, fear limits your freedom to make decisions, and freedom is a real privilege of an adult. Remember that the coordinated actions of the doctor and the patient, between whom a trusting partnership has developed, will most likely lead to the result you want - health. Dictionary of medical phobias: Nosocomephobia – fear of hospitals, clinics. Dentophobia - fear of dentists Tomophobia - fear of surgery or surgical operations Pharmacophobia - fear of taking medications
Causes of phobia: fear of doctors
- In adults, the reasons for this fear arise from the fact that they have encountered a medical error in the past. The situation gets worse when a relative or friend died because of it.
- Particularly suspicious and impressionable people, having watched enough films about hospital workers who are not entirely competent in their work, read terrible cases on the Internet about incorrect diagnoses, involuntarily become jatrophobes.
- When visiting a doctor, the patient is forced to entrust his health, and sometimes even his life, to some stranger. It turns out that the patient directly depends on the mood and knowledge of this stranger in a white coat! It happens that a doctor is an expert in his field, and he has been working for a long time, but there is no line outside his office. It’s just that some specialists can be professionals, but at the same time be callous, ill-mannered people.
- An insecure person is embarrassed about his body. Therefore, it is difficult for him to go to the doctor and show his body, which he himself does not like, he is ashamed of it.
- Fear of pain during treatment. Many procedures are naturally unpleasant, but the development of medicine has stepped forward significantly. To avoid pain, there are modern drugs that successfully combat this.
- People with various addictions, be it alcohol, food, tobacco, drugs, are all ardent opponents of visiting hospitals. They often avoid doctors, assuming that they will tell them about their unhealthy lifestyle and force them to undergo treatment.
- Some people are simply afraid that the doctor will find some kind of disease and this is what prevents them from going to the hospital.
- Difficult financial situation of a person. In such cases, this is a good reason for refusing to go to the hospital.
REASONS FOR FEAR OF DOCTORS
1. Most cases of iatrophobia are based on negative childhood experiences of interacting with doctors and staying in medical institutions. If we don’t talk about unpleasant procedures in clinics, people go to the doctor because of misfortunes: injuries, illnesses. Such situations in themselves cause fears in a little person; in addition, incomprehensible manipulations associated with physical invasion of the body are frightening. Both parents and doctors cannot always properly support the child and relieve emotional stress. Cases of deception leave a particularly strong imprint (“a mosquito will bite”, “the doctor will pat you and give you a sweet pill”, etc.) Sometimes one such vivid incident in childhood is enough to create an “anchor” of fear for life.
2. A visit to a doctor is never like going to a spa: as a rule, treatment is preceded and accompanied by diagnostic procedures that are not the most pleasant. Manipulation with needles and other metal objects, a feeling of embarrassment about exposing particularly sensitive and vulnerable places on the body - and all this is followed by taking medications and continuing procedures. A person’s feeling of himself as an object of manipulation is inevitable, and this is one of the most terrible “adult” experiences, which is psychologically linked to violence.
3. Like most fears such as aerophobia, fear of getting into a car accident, fear of elevators, etc., iatrophobia is always associated with a feeling of lack of control. A person is forced to entrust the most valuable thing he has - his body, health and life - to a stranger, a stranger. This is how the health care system is culturally structured and how the health care system works, that this powerful manager is assigned to us at random (they are taken to the hospital according to registration, area of the incident, according to the occupancy of the nearest hospitals, etc. There is the work schedule of doctors, the operating hours of the medical institution..) Even if the situation is not an emergency and the doctor was recommended to you by grateful people, he continues to remain the figure of a stranger to whom you transfer the authority to manage your physicality.
4. The doctor's white coat is a uniform: it denotes service, while at the same time being a sign of authority. The temple of health, the hospital, has its own clergy, who know and are more capable than those who end up there in an a priori more vulnerable position. For many, power-subordinate relationships can indeed cause severe discomfort, even to the point of developing fear, especially if there is negative experience of interaction with representatives of any power structures.
5. A case of medical error (failed surgery, incorrect diagnosis and painful useless treatment), due to which someone close to you suffered, can greatly affect the psyche of any person. Iatrophobia develops especially strongly in those who, due to medical error or negligence, have tragically lost a particularly significant relative. Moreover, there are cases where jatrophobia of a similar genesis is transmitted through generations. Particularly impressionable people can “catch” the fear of white coats after watching films or programs about how the wrong actions of doctors led to tragic consequences for the hero. Scenes of torment and scenes when doctors show uncertainty or even their own fears have a particularly strong psychological impact.
6. People with addictions (alcohol, tobacco, drugs, food) may be afraid and avoid doctors for obvious reasons. There are practically no diseases that are not aggravated by chemical or food addiction. Moreover, any responsible doctor in such a situation will begin a serious conversation about treatment by discussing what is already a “sore spot” for a person.
7. Subconscious fear that treatment will not help can play a role in refusing to go to a doctor’s consultation. The fear of hearing a sentence dooming us to an inferior life makes us afraid of a figure who brings bad news. The fear of surgery, which the doctor may condemn you to, can make you put off seeking help, even if you are in severe pain.
8. A deeper layer of jatrophobia is associated with the fear of death. “My body is betraying me,” “I am not perfect, which means I am not eternal,” “I have no control over what is happening,” these are all difficult topics related to mortality, and the figure in the white coat will persistently remind you of the need to resolve these issues yourself. with myself.
It is worth noting that the sterile, seemingly lifeless, environment of a medical institution, where there is always the smell of medicine, where you can hear the clanking of metal instruments, where you simultaneously see a large number of suffering people, causes echoes of iatrophobia in almost any, even psychologically stable, person.
Symptoms of phobia: fear of doctors
The manifestation of such fear in children consists of hysteria and panic. In adults, symptoms are much more severe and severe. These are headache, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, shortness of breath, a sharp increase in blood pressure, trembling limbs, rapid heartbeat, inadequate perception of what is happening, sleep disturbance, dry mouth, excessive sweating, blurred vision (darkening in the eyes).
People suffering from this fear postpone visiting the hospital until a critical moment. Therefore, this can end sadly, even fatally.
What is the name of fear of doctors and its symptoms?
The fear of hospitals, the phobia, manifests itself in the fact that a person requires a titanic effort of will to enter the clinic and undergo even a standard medical examination. He waits until the last minute even if he is seriously ill. Friends and relatives in hospital are not visited, as even the thought of approaching the entrance to a medical facility causes a panic attack. A forced visit to the hospital is accompanied by anxiety, weakness, attacks of nausea and dizziness, and loss of orientation in space.
Fear of doctors, phobia has approximately the same symptoms as fear of medical institutions, only it is not the hospital building that causes anxiety, but the medical staff. Doctors' fear is associated with the so-called white coat syndrome - an increase in blood pressure while it is being measured by a health worker. With daily monitoring or self-measurements, the blood pressure level is significantly lower.
What is the name for fear of doctors in psychiatry? An abnormal fear of doctors and other medical personnel is called iatrophobia. Fear of hospitals and any other medical institutions, including first aid stations at enterprises, is called nosocomephobia. The formation of both disorders is influenced by similar factors.
How to deal with phobia of fear of doctors
There are several options.
Sometimes a psychologist uses a method such as hypnosis treatment, group therapy, or psychoanalysis sessions.
If a person’s psyche is upset to a critical state, then drug treatment is carried out. The treating specialist prescribes sedatives (motherwort, valerian, phytosed, glycesed, sedistress, glycine).
In the complex, you can add treatment with folk remedies (decoction of mint, lemon balm, linden inflorescence, lavender, hops, chamomile).
Here are some recipes for soothing decoctions and tinctures:
- The tincture consists of equal parts of valerian root, fennel fruit, mint, lemon balm and caraway. Brew one tablespoon of the prepared raw material per glass of boiling water.
- This tea has a very fast effect: one part St. John's wort, horsetail, two parts black and green tea. Brew two tablespoons of this mixture in half a liter of water and leave. Add honey to taste.
- This tincture is also very calming: Two bay leaves, two cloves, a small piece of ginger and one teaspoon of cumin. Pour boiling water over and boil for ten minutes, and then infuse. All these soothing tinctures must be taken morning and evening, half a glass*
- Valerian roots, oats and lemon balm, peony rhizomes, motherwort, common hop cones - all this is mixed in equal parts and poured with vodka or alcohol. Infuse for half a month and then filter. Take one teaspoon before bedtime.
Important: never self-medicate. Consult your doctor even if you decide to drink soothing teas and tinctures, as they may have an adverse effect if taken uncontrolled. All of them have contraindications.
Advice for parents with a phobia of fear of doctors
Tell and explain to your child the significance and importance of visiting the hospital.
Talk to your child before visiting a pediatrician or other doctor; the dialogue should be open in order to clarify all the children's fears and anxieties. The child will tell the honest truth if he sees openness, love, respect and care on your part.
In many cases, parents themselves create comfort and tranquility in the hospital. For example, take your baby's favorite toy with you. Buy juice or candy, lollipops, vitamins, whatever your baby loves to eat. Let this be a little incentive for the child.
How to stop being afraid of injections? It is strictly forbidden for parents to scare their child with injections or a scary doctor who hurts. In no case should you threaten your child with phrases that they will leave him to live in the hospital if he does not obey. Maybe these methods will work, but only the first time. And as time passes, you may find out that such phrases remain in your memory for a long time. They can repeatedly affect the child’s behavior. After all, the child’s psyche is completely different from the adult psyche. Be careful with such expressions!
What is a nosophobe afraid of?
Like any phobia, the fear of getting sick can take a wide variety of forms. We will list only some subtypes of nosophobia (the more diseases are discovered, the wider the scope for the imagination of nosophobes - after all, there are more and more diseases known to science).
- Cancerophobia - fear of cancer;
- speedophobia - fear of getting AIDS;
- dementophobia - fear of going crazy;
- Cardiophobia - fear of heart attack;
- cynophobia - fear of rabies from a dog bite;
- Mysophobia - fear of pollution.
There are also “original” objects of this phobia: fear of constipation, hemorrhoids, or even a simple runny nose.
All these fears may seem completely unbelievable and ridiculous to most of us. And yet it is worth remembering that any phobia is a mental disorder. A person does not invent fear for himself - he lives in this reality and truly suffers.
Mysophobe is, in fact, so afraid of getting dirty that when he finds himself in an environment that is dirty, from his point of view, he experiences real panic. He starts soaping his hands endlessly, and getting him, for example, to simply touch the water tap in a public restroom is an impossible task. And a patient with cancerophobia cannot get rid of the obsessive thought that he has a cancerous tumor, does not believe doctors and believes that he is being deceived by hiding the real diagnosis.
Those nosophobes who are “sick” with something that is generally unknown to modern science experience special torment. After all, besides the fact that they are “seriously ill”, no one can help them - after all, there is simply no cure for their illness.