What is concussion?
Most often, shell shock in the consciousness and understanding of many people is associated with military activity. However, the opportunity to obtain it in peaceful conditions is no less.
Concussion most often occurs in persons associated with military service
Contusion is an acute injury to both individual organs and all systems, appearing under the influence of a powerful physical and mechanical factor. With this type of injury, there may be no visible violations of the physiological and anatomical integrity of the victim’s body, but serious disturbances in the functional balance occur.
Contusion grossly interferes with basic physiological processes, disrupts the functioning of motor-sensory systems and causes a disorder of higher mental functions. At the same time, suspecting this type of injury is quite problematic.
A possible synonym for the word “contusion” is “bruise.” However, in modern medicine there is no term “contusion of the whole body”, therefore these concepts are identical only when using contusion in the context of local injury (for example, contusion of the auricle). Sometimes in military medicine, to denote pathology, they resort to the concepts of “traumatic stunning” and “injury resulting from the action of a blast wave.”
Mechanisms of injury
The main destructive factor when a contusion occurs is a shock wave, which is vibrations of the airspace of various frequencies and forces that affect the human body. Under their pathogenic influence, a shift in the balance of the human body’s systems occurs, which leads to its physiological restructuring.
Due to a violation of homeostasis (constancy of the internal environment), a change in the level of produced hormones, neurotransmitters, enzymes and biologically active substances occurs. To return everything to its place, the body actively uses its restoration potential, which leads to a breakdown in adaptation mechanisms.
Eye contusion
Concussive eye injuries account for about 30% of eye injuries, which lead to partial or complete loss of vision. The clinical picture of eye contusion is quite varied. This may include minor hemorrhages under the conjunctiva of the eyelids, and crushing of the eyeball and adjacent tissues.
Kinds
There are direct and indirect contusions.
- The cause of direct contusions is the blunt impact of a damaging factor directly on the organ of vision and its appendages. The source of injury is bruises with an object or fist, falling on protruding objects (stones), blows from an air wave, or a jet of liquid.
- Indirect contusions of the eye occur after exposure to parts of the body nearby or distant from the eye. This could include blows to the head or compression of the body.
Manifestations do not always correspond to the actual severity. For example, the consequences of a relatively mild contusion can be severe changes in the eyeball. Damage to the tissues of the organ of vision depends on the direction and strength of the impact and the individual characteristics of the person’s eye. In some cases they are minor, but in others they can lead to rupture of the scleral capsule
The condition of the eye before injury is also important.
There are three degrees of severity of eye contusion.
- The first degree is lesions in which there is no decrease in vision after recovery. The victim experiences temporary reversible changes, such as erosion and swelling of the cornea, spasm of accommodation (inability to clearly see distant objects), retinal clouding and others.
- The second degree is contusions, which result in deep erosions of the cornea, narrowing of vision, local cataracts (clouding of the lens of the eye), hemorrhages, ruptures of the sphincter of the pupil and others.
- The third degree is lesions in which severe changes develop. This may be volumetric enlargement of the eye, ruptures of the sclera (the outer strong frame of the eyeball), deep hypotension or hypertension of the eye and other severe disorders.
Symptoms
After an eye contusion, its manifestations include signs of damage to the eyeball, auxiliary organs of vision, and symptoms of changes in the general condition of the victim.
Signs of a general change in the state of the body are:
- dizziness;
- headache;
- pain in the craniofacial region of the affected side;
- slight nausea;
- infection of the eyeball, which gradually decreases after 3-4 days.
Such general signs are observed in the victim in the first days after the concussion.
In the event of an eye injury, there is always the possibility of serious damage to its deep structures. Therefore, in any case, the victim should be immediately taken to a medical facility. In this case, it is necessary to limit body tremors, physical activity, pushing, and jumping.
Treatment
Treatment should be started as early as possible.
For mild cases, therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis. Immediately after the injury, it is necessary to apply cold to the injured eye and drip disinfectant drops, for example, Albucid. If the pain is severe, the victim should be given an anesthetic. After which you need to go to the emergency room.
Treatment of eye contusion can be conservative or surgical.
With conservative therapy, the patient is usually prescribed hemostatic drugs (stopping bleeding), diuretics (reducing tissue swelling), local and general antibacterial agents, anti-inflammatory hormonal and non-steroidal drugs. In addition, physical therapy methods are used - magnetic therapy, UHF.
Surgical treatment is performed for retinal and scleral tears, traumatic cataracts, and secondary glaucoma.
Possible classifications
Currently, in domestic and foreign traumatology, doctors use several different classifications, each of which reflects certain features of the occurrence of injury and its consequences.
Classification by affected area:
- spinal nerve contusion;
- bone contusion;
- contusion damage to the spinal cord;
- contusion damage to the brain;
- contusion of the organs of hearing and balance;
- contusion of the organs of vision;
- contusion damage to the spinal column;
- contusion damage to the urinary apparatus;
- contusion of the heart and adjacent vessels.
Classification by process extent:
- general contusion;
- local contusion.
General contusion is a uniform damage to all body systems. Local is characterized by the presence of traumatic pathology of one or more organs. Such a contusion is very dangerous and leads to longer treatment complications.
Classification by causes:
- shell shock during military operations;
- concussion due to injuries at work;
- household concussion.
Most often, doctors have to diagnose military personnel with “shell shock”: more than 40% of soldiers had the misfortune to suffer this injury at least once in their lives. In second place in terms of frequency of occurrence is occupational injury among workers at various enterprises. Concussion in everyday life is quite rare.
Classification according to combination with other injuries:
- isolated contusion;
- combined contusion lesion;
- combined contusion.
Classification of concussion severity:
- I degree - mild damage;
- II degree - moderate damage;
- III degree - severe damage.
In the first degree of concussion, a person loses consciousness for no more than 30–40 minutes. In some cases, the stage of absence of consciousness does not occur at all. After the victim wakes up, he is disoriented in space for some time, cannot speak, hear or move normally, and does not remember previous events. Symptoms subside within a few hours.
The second degree is characterized by absence of consciousness for more than two hours. After this, the victim complains of a severe headache, nausea or vomiting, and his pupils may be of different sizes. The duration of cognitive impairment is more than 12–24 hours. Recovery from a moderate concussion takes more than a month.
Severe damage is characterized by complete depression of consciousness up to coma, the duration of which can vary from several days to several months. The patient's reflexes are suppressed, and special life support devices are required to breathe and stimulate the heart. After emerging from a coma, the patient may completely forget some life events and lose self-care skills, speech and some motor functions. The duration of recovery after such an incident can be several years.
Classification according to the presence or absence of complications:
- complicated contusion;
- uncomplicated contusion.
Uncomplicated contusion is the mildest type of traumatic injury and occurs more often in peacetime during everyday interactions. Complicated concussion mainly affects people associated with exposure to some negative factor, as well as the military. This type of pathology is treated only by doctors with special training, and therapy lasts many months.
Degrees
- Mild degree (first) . In this case, the damage is minor and the symptoms are not too pronounced. This degree of contusion has no negative consequences and does not require special treatment.
- Average degree (second). The patient may lose consciousness for a while. He may experience diarrhea and vomiting. Often there is some lethargy, aggression, problems with heartbeat and breathing. The functioning of the brain is impaired, so all functions slow down.
- Severe degree (third). In this case, the patient may not regain consciousness for up to 3 weeks. Sometimes a patient can die if first aid is not given and taken to the hospital.
Causes and risk factors
Concussion can have several causes. The conditions for the appearance of pathology in everyday life, at work and on the battlefield differ significantly from each other, so approaches to diagnosis and treatment will differ from each other.
Explosion is one of the common causes of concussion
Table: causes of contusion in different conditions
| Military reasons | Production reasons | Household reasons |
| Use of firearms | Powerful vibrations of various equipment | Gas cylinder explosion |
| Military grenade explosion | Explosions of flammable substances in workshops | Fall from a great height |
| Prolonged stay in military equipment while it is moving | Pressure drops when diving to depth | Sudden change in atmospheric pressure |
| Violation of safety regulations during military operations | Collapse of sand or rocks | Physical and mechanical impact on the body (accident) |
| Depressurization of a submarine or aircraft | Excessive noise levels and harsh sounds in production | Strong impact on the water surface |
Table: causes of contusion damage to individual organs
| Brain | Auditory and vestibular apparatus | Visual apparatus | Spinal column |
| Traumatic brain injury | A sharp blow to the ears | Impact with force that deforms the eyeball | Traumatic damage to the bones of the spine |
| Infectious and inflammatory processes in brain tissue, leading to its enlargement | Mechanical rupture of the eardrum | Compression of the eyeballs | Infectious processes in the bones of the spine (syphilis, tuberculosis) |
| Dropsy of the brain | Accumulation of fluid in the middle ear cavity | A sharp increase in intraocular pressure | Changes in atmospheric pressure |
| Violation of the biological and chemical composition of cerebrospinal fluid | Infectious and inflammatory processes in the sinuses of the skull | Impaired blood supply to the eyeball and optic nerve | Bone compression and deformation |
Risk factors
Like any traumatic injury, concussion has certain risk factors. By reducing their number, the possibility of pathology occurring is minimized. But unfortunately, most of them cannot be completely eliminated.
Main risk factors:
- engaging in dangerous sports;
- work in physical and chemical production;
- work related to the effects of vibration on the body;
- long stay in the zone of radiation contamination;
- work with high-power radiation;
- violation of safety regulations when handling weapons;
- violation of the rules of movement in military transport;
- staying in the blast wave zone;
- close proximity to a military training ground where weapons are tested.
Signs of different degrees
First degree
With first-degree injuries, subarachnoid effusions begin to form.
Loss of consciousness lasts from 30 to 60 minutes. Clinical manifestations are very pronounced - they have a long manifestation and can increase from the second day of injury.
A distinctive feature is a symptom of amnesia. The victim may have trouble remembering why they were injured. This does not appear in all cases. But, since the symptom is transient, relief occurs within a week.
Symptoms of the neurological type after restorative procedures are very distinct - headaches, nausea and vomiting begin. Upon examination, an incomplete reaction to light may be observed. It is also important to examine reflex excitability. Changes in the vegetative-vascular system can be the same as with a concussion.
Second
The anatomical substrate that determines the second degree of contusion is the development of a planar effusion that can occupy the entire field. Loss of consciousness can last from 1 to 4 hours. Symptoms often include breathing disorders and changes in cardiac activity. But, if the treatment is correct, relief will be noticeable within a day.
After the creature is restored, the concussion will manifest itself with dizziness, headache, and lethargy. Amnesia may last a week or several months.
When examining the victim, you can notice that the nasolabial fold is smoothed, peripheral reflexes are asymmetrical, and horizontal nystagmus is observed. However, such symptoms are transient and not long-lasting. Often the process ends with degeneration of the damaged organ.
Third
The anatomical substrate that determines third-degree contusion is extensive hemorrhages around the impact, hemorrhages in the brain tissue or in the ventricles.
In fact, this degree indicates a hemorrhagic stroke.
Signs of third degree concussion: loss of consciousness occurring for more than 4 hours. You can also observe cranial disorders, Babinski and Kernig symptoms.
Diagnosis of injuries along with hematomas inside the brain is carried out in neurosurgical departments. It is important to hospitalize the victim immediately, since only qualified personnel can provide assistance.
Diagnosis of the condition
To distinguish a concussion from a regular bruise, concussion or shock, it is necessary to carry out a wide range of diagnostic measures. Since it is not possible to interview the patient at first after the injury, a brief life history is collected from his closest relatives or friends, and the circumstances of the injury and the first medical measures taken are collected from eyewitnesses of the incident.
After the patient returns to consciousness, the doctor collects complaints and checks the organs of vision, hearing, smell and the patient’s ability to move his limbs. Based on the data obtained, a preliminary diagnosis is made.
Conversation with the patient is an important stage in collecting anamnesis.
Instrumental diagnostic methods
To establish a final diagnosis, specialists resort to modern research methods. They allow us to clarify the severity of the lesion and suggest possible outcomes.
The main methods of instrumental examination are:
- X-ray examination: will determine whether the integrity of the bones (skull, limbs, spine) has been compromised;
- Ultrasound diagnostics: will show the presence or absence of hematomas and soft tissue damage;
- electroencephalography: is a recording of the bioelectric potentials of the brain, with its help you can track the decrease and increase in the activity of a particular segment, which will allow you to find out the location of the damage;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging: will allow you to differentiate a concussion from a bruise, fracture or concussion;
- visual acuity examination and intraocular pressure measurement: will help make a diagnosis of visual contusion;
- hardware diagnostics of hearing acuity using audiometry: will show the degree of damage to the hearing organs;
- static and dynamic functional tests: will allow you to determine damage to the balance organs;
- microscopic examination of the cellular composition of the cerebrospinal fluid using a puncture: will make it possible to diagnose a spinal cord contusion.
Contusion of other organs
In 5-7% of cases of chest injury, especially if the blow falls on the anterior chest and sternum, an obvious contusion of the heart is formed. Clinically and according to ECG data, they are similar to myocardial infarction. In 43-47% of cases of closed chest injury, a hidden cardiac contusion is noted, which gives a clinical picture of coronary artery disease, but its cause is revealed only through special studies.
Renal contusion is observed quite often, especially in polytraumas. The main criterion for diagnosis is the presence of obvious hematuria or microhematuria. A full range of examination should be carried out by a urologist for differential diagnosis with damage to other parts of the genitourinary tract.
The diagnosis of contusion of the liver and spleen is valid, but the diagnosis is very difficult with low severity, and more severe contusions form subcapsular ruptures. The same applies to bruises of hollow organs.
, , , ,
Treatment of pathology
Treatment for mild, severe, and moderate contusions can vary significantly. For uncomplicated pathology, the duration of treatment and recovery is about a week.
When treating a contusion injury of any severity, it is necessary to strictly adhere to bed rest, reduce the negative impact on the affected organ and the complete absence of negative stress factors.
First aid in case of concussion
Any person present at the scene of the incident should be able to provide first aid.
Specialized care is provided by emergency room or hospital doctors.
Algorithm of actions for concussion:
- Check vital signs: breathing, heartbeat.
- Determine whether a person is conscious by lightly tapping the face.
- Call emergency medical assistance.
- Place the victim in a horizontal position on his back.
- Turn your head to the side so that the patient does not choke on vomit.
- If there is vomit, it is recommended to remove it from the mouth using a handkerchief or towel.
- If there is bleeding from the nose or ears, it is necessary to make tampons from cotton wool or cotton pads to stop the bleeding.
- If there is a convulsive seizure, you need to gently fix the patient's head and make sure that he does not harm himself or others.
Absolutely forbidden:
- tilt the patient's head back: this can cause vomit to enter the respiratory tract;
- bring the patient to consciousness by hitting or pouring water on the face;
- Perform cardiac massage on a patient with chest injuries;
- try to give the patient a painkiller tablet.
Video: first aid for concussion
Inpatient treatment and medications
After providing first aid in an ambulance, the patient should be sent to a specialized traumatology, resuscitation or intensive care unit. In the first few days after the injury, you must remain in bed. Patients in critical condition are connected to a ventilator.
Medicines used for concussion:
- painkillers: Analgin, Morphine, Methylmorphine and Narcotin will reduce pain and alleviate the condition of the victim;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to reduce tissue edema: Ibuprofen, Nimesulide, Ketorolac, Diclofenac;
- glucocorticosteroids will reduce inflammation and relieve spasm: Prednisolone, Methylprednisolone;
- sedatives help restore neuropsychic balance: tincture of valerian and motherwort, camphor;
- antiemetic drugs block impulses from the center of vomiting, reducing the frequency of nausea attacks: Ondasetron, Promethazine, Cyclizine;
- diuretics relieve cerebral edema and stimulate kidney function: Furosemide, Hydrochlorothiazide, Mannitol;
- antidepressants reduce the risk of asthenovegetative syndrome in the future: Fluoxetine, Sertraline.
Photo gallery: drugs used to treat injury
Analgin relieves pain well
Diclofenac will help get rid of inflammation
Furosemide will prevent the development of cerebral edema
In cases of combined damage to the body, as well as in the formation of extensive compression or hematoma of various organs, surgical treatment is used. It is aimed at decompression and reduction of intracranial pressure.
Traditional medicine
Traditional medicine methods can only be used for mild, uncomplicated contusions. Before using any product, you should contact a specialist and consult, taking into account the possible consequences. In no case should you use only traditional methods without drug treatment, since they are aimed only at reducing symptoms and not at eliminating the cause.
Traditional medicine is good for relieving symptoms of concussion
To treat mild contusion, you can prepare the following recipes:
- 10 tbsp. l. chamomile, pour 1 liter of boiling water and let it brew for two hours. After the resulting liquid has cooled, you need to remove the flowers and drink the infusion one glass twice a day. Chamomile is believed to have a sedative effect.
- 2 tbsp. l. apple cider vinegar should be dissolved in 0.5 liters of cold water. Then you should moisten a gauze cloth in the resulting vinegar water and place it on your forehead. This method helps cope with migraines.
- 2 large burdock leaves and 10 currant leaves need to be brewed in 1 liter of hot water. After the liquid has cooled, you should soak cotton wool in it and place it on the sore spot, covering it with a towel on top. Keep it for no more than an hour. Such a compress will help relieve swelling in case of local contusion.
Treatment
Victims need rest; for moderate to severe concussions, strict bed rest for 1-3 weeks. Sedatives (bromides) and hypnotics (phenobarbital) are prescribed in the usual dosage; according to indications, drugs that stimulate respiration and cardiac activity are prescribed. In case of severe contusion, especially with the likelihood of a traumatic brain injury, a spinal puncture is indicated, always with measuring the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid and determining the content of protein and formed elements in it. For liquor hypertension, repeated punctures and dehydration therapy are needed; for hypotension, drip infusions of a 5% glucose solution are needed. At the end of the acute period, vitamins C, B1, B12, antipsychotic drugs (aminazine for 2-3 weeks), insulin (4-10 units 2 times a day) with oral glucose are prescribed. Warm baths or showers are recommended. In the future, with a long-term post-concussion psychasthenic state, a dosed workload, periodic sanatorium treatment, observation by a neuropsychiatrist, and complete abstinence from alcohol are necessary. Treatment of surdomutism and mutism should begin as early as possible, before the patient develops a consciousness of his own inferiority. Psychotherapy is of great importance - a thorough, systematically repeated examination of the ENT organs, creating the appearance of vigorous treatment. Treatment of persistent post-concussion deafness of organic origin. Persistent speech disorders require speech therapy treatment.
In case of musculoskeletal injuries accompanying contusion, treatment is carried out according to general rules. The appearance or increase of focal symptoms, changes in breathing indicate compression of the brain and require emergency craniotomy, which, if possible, should be preceded by an angiographic examination of the brain.
Signs of abdominal bleeding or peritoneal irritation prompt laparotomy.
Recovery after concussion
Recovery from injury is a very important period. Medical rehabilitation specialists treat the long-term consequences of concussion. Any patient who has suffered a concussion must be observed by a psychiatrist.
Therapeutic gymnastics and massages
A course of therapeutic exercises to restore muscle and nerve tone is especially important for patients who have been in a coma for a long time. With the help of a trainer, they gradually master the space of the gym, alternating between breathing exercises and physical activity. The duration of therapeutic exercises is several months or years.
Therapeutic gymnastics promotes rapid recovery after injury
Massage of the affected areas is carried out by a specialist. It is recommended to start with slow and smooth patting and stroking movements, gradually adding pinches and intense rubbing of the damaged areas. You can also perform massage on your own, having previously obtained information from a medical rehabilitation specialist about the method of its implementation.
Correction of cognitive impairment
Many patients, after suffering a trauma, experience problems with further socialization and return to society. To do this, after recovering from a coma, they are recommended to visit a psychiatrist. With its help, many people overcome depression and can move on with their lives calmly. The doctor shows the patient some ways to solve the problem, to which he himself did not pay any attention.
All patients who have experienced shell shock should visit a psychiatrist
Consequences of ear contusion
With an ear contusion, as already mentioned, a rupture of the eardrum occurs, as a result of which the tightness and asepticity of the tympanic cavity is disrupted. As a result, an infectious-inflammatory process develops in it and traumatic otitis media occurs, requiring the use of antibacterial therapy.
The nature of hearing damage depends on the cause of exposure and its intensity:
- With a small perforation, a defect in the eardrum of various locations and shapes is observed:
- round;
oval;
- irregular shape;
- with torn edges.
- With a fresh injury, otoscopy reveals a hyperemic medial wall of the tympanic cavity.
- For isolated membrane perforation, outpatient treatment is sufficient. As a rule, the defect quickly heals on its own, and hearing restoration occurs in full.
- With the development of inflammation, the formation of exudate occurs, and in the absence of treatment, purulent discharge occurs.
- With a fracture or dislocation of the malleus, incus, or displacement and dislocation of the stapes (auditory ossicles), often, but not always, accompanying longitudinal fractures of the pyramid of the temporal bone, blunt trauma of the skull without a fracture of the pyramid, the following are observed:
- deafness;
severe pain in the ear and dizziness;
- lack of coordination;
- feeling of stuffiness, noise on the side of the injury.
- In the absence of perforation of the membrane, which happens less frequently, the diagnosis of dislocation or rupture of the auditory ossicles is carried out using tympanometry.
- Contusion of the labyrinth (inner ear), organ of Corti, is usually combined with brain damage and requires emergency care.
It is the cause of the development of labyrinthine traumatic syndrome, which is accompanied by a violation of both auditory and vestibular function due to the resulting hemorrhage, hypoxic edema of organ structures, and violation of the integrity of moving elements, for example, separation of otoliths. - Perforation of the eardrum occurs when the pyramid of the temporal bone is fractured and a line passes through the tympanic ring.
REFERENCE: it may be accompanied by minor bleeding when the vessels in the area of the malleus handle are damaged, which is self-limiting.
During otoscopy, a defect in the eardrum is visible; in the case of an explosion at close range, traces of gunpowder are visible in the external auditory canal and on the membrane. Hearing loss due to the type of sound conduction disorder reaches 20 dB or less.
IMPORTANT: In addition to the situations described above, severe injuries to the middle and inner ear may cause damage to the cranial nerves.
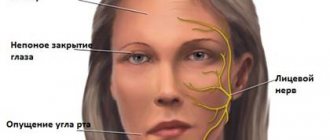
Damage to the auditory and facial cranial nerves:
- The auditory nerve innervates the cochlea; as a result of its damage, persistent sensorineural hearing loss develops, in some cases reversible.
- The facial nerve passes through the labyrinth of the temporal bone. A disruption of its blood supply, or the transfer of inflammation from the tympanic cavity leads to reversible paresis of half the face. In addition, it may affect the trigeminal and vagus nerves.
Prognosis after injury and possible consequences
People who have suffered a mild stage of concussion quite quickly return to their usual rhythm of life. In severe and moderate stages, this process can drag on for many months and even years. It is necessary that family, friends and psychologists be constantly with the victim: this will allow them to realize what happened as quickly as possible and continue to live a measured life, without withdrawing into themselves.
Complications and consequences of concussion:
- hearing loss in one or both ears;
- decreased visual acuity or complete blindness;
- paresis and paralysis of the limbs;
- disorders of urination and defecation;
- sexual dysfunction;
- insomnia and sleepwalking;
- speech and writing disorders;
- migraines, headaches and dizziness;
- asthenovegetative syndrome - weakness, lethargy, adynamia, lack of an emotional component;
- depressive and suicidal conditions;
- sudden attacks of aggression;
- change in the character and behavior of the victim.
Consequences and precautions
The consequences of such injuries can be determined by the degree of their severity , as well as the structures damaged when following the doctor’s recommendations. Often, complications can appear over time, and this is due to the fact that the brain structure gradually returns to work in a certain order.
Among the consequences the following can be observed:
- Severe headaches.
- Painful reaction to loud noises and lights.
- Sleep disturbances, increased excitability of the nervous system.
- Dizziness.
- Depressive syndrome, manifested by fatigue, apathy, lethargy.
- Stuttering.
If syndromes increase and worsen, it would be a good idea to consult a neurologist or psychotherapist. It may make sense to undergo re-treatment. Some patients are even sent to health resorts to fully recover from injury.
We wrote about the consequences of a cerebral contusion in a separate article.