Useful information about other various diseases that begin with the letter “D”: Debility, Double-wave viral meningoencephalitis, Dementia with Lewy bodies, Depressive neurosis, Dermal sinus, Cerebral palsy, Jacksonian epilepsy, Diastematomyelia (diplomyelia), Discogenic myelopathy, Dystrophic myotonia Rossolimo -Steinert-Kurshman, Diabetic encephalopathy, Dyscirculatory encephalopathy, Diffuse axonal brain damage, Benign rolandic epilepsy.
Concept - dystrophic myotonia Rossolimo-Steinert-Kurshman
Dystrophic myotonia Rossolimo-Steinert-Kurshman is a hereditary disease with a slow development, which causes the formation of myotonia in combination with deformations of the muscle zones of a dystrophic nature. The basis of the presented disease is damage to myotonin-protein kinase. The described disease causes spasms in the patient’s body, atrophic problems in the muscle tissue of the cervical region, facial area and distal areas of the extremities, as well as a reduced level of intellectual abilities, arrhythmia and endocrinological changes.
As diagnostic procedures, specialists use a variety of clinical techniques, for example: genealogical testing and DNA analysis. To treat the symptoms of the pathological process, pharmacological agents are used to combat the symptoms of deviation and further development of muscle tissue dystrophy (anabolic steroid drugs, ATP, etc. are used).
Reasons for the development of Rossolimo-Steinert-Kurshman myotonia
Rossolimo-Steinert-Kurshman myotonia is always a genetically transmitted defect. The key reason for its development is considered to be a violation in the DMPK gene, located on the nineteenth chromosome. The severity of the disease is directly proportional to the number of trinucleotide CTGs. Normally, this indicator is approximately 5-37, at 50-80 a mild form of the disease is observed, at 100-500 a late severe form is observed.
Under the influence of a violation of the DMPK gene in the body, a change occurs in myotonin protein kinase - a protein localized in skeletal and muscle tissue, in the myocardium, central nervous system, etc., which provokes the appearance of myotonic spasms, combined with atrophy of the muscles of the face, neck and limbs in the distal zones. In essence, hypertrophy of some muscle fibers occurs with simultaneous atrophy of others. As a result, some of these fibers are replaced either by other fibers or by fatty or connective tissues.
Quick Facts
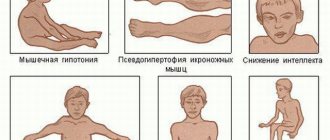
Dystrophic myotonia Rossolimo-Steinert-Kurshman is a hereditary abnormal process that can enter the child’s body from parents through an autosomal dominant pathway. Between the ages of 10 and 20, the classic type of the disease can spread. In rare situations, a congenital form of the disease may occur, since its symptoms are noticeable immediately after the birth of a newborn. According to morphological indications, the disease described is characterized by a combination of hypertrophic deformations of specific muscle areas along with atrophy of other areas. In addition, elements of muscle particles are replaced by fatty and connective tissue. When examining different samples of muscle tissue using an electromicroscope, one can see the destruction of myofibrils and disturbances in the size of mitochondria.
Differential diagnosis of Rossolimo-Steinert-Kurshman myotonia
It is necessary to differentiate Rossolimo-Steinert-Kurshman myotonia from other known types of myotonia, which in some situations may have similar signs and course. Atrophy of muscle tissue is characteristic exclusively of this disease and allows you to quickly distinguish it from Thomsen's myotonia, a sign of which is muscle hypertrophy. Early involvement of the facial muscles and dominant inheritance distinguish it from Becker myotonia. In addition to these conditions, it is necessary to differentiate Rossolimo-Steinert-Kurshman disease from ALS and Charcot-Marie-Tooth amyotrophy.
The main sources of Rossolimo-Steinert-Kurshman myotonia
According to the results of recent testing of the genes of patients with dystrophic disease, it was indicated that the main role in the pathology is played by a defective disorder formed in a specific genome, which is located on the nineteenth chromosome. It is responsible for the synthesis of myotonin-protein kinase. People suffering from this abnormality are diagnosed with a severe increase in the size of certain parts of a gene called DMPK. It should be borne in mind that the degree and type of the disease being described depends on the number of repetitions of this section.
Based on accepted standards, the number of required revolutions fluctuates around 5-37. In the case of an increase above 50-80, it indicates the presence of a weak manifestation of a harmful process; with an increase in indicators in the range of 100-500, the late stage of myotonia begins, and the congenital type develops with a deviation of 500-2000. Many analyzes show that the increase in the level of trinucleotide repeats progresses, often in female cells at the stage of meiosis. That is why during the transmission of the disease from a woman, the maximum severe type of the disease or its congenital form appears.
What is the manifestation of classic dystrophic Rossolimo-Steinert-Kurshman myotonia?
The standard abnormal process begins after the age of five and can appear before the age of 35, but most often the clinical picture of the disease appears between the ages of 10 and 20. The symptoms of the pathology are a combination of problems that arise from myotonia with myopathy factors, disorders of the cardiovascular system and central nervous system, as well as disorders of the endocrine structure and cataracts.
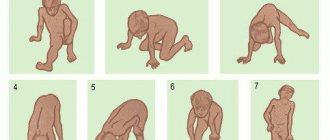
Characteristic signs of damage to the body are the formation of spasms localized in the masticatory muscles and the flexor region of the hand. In addition, doctors diagnose mechanical reflexes of the myotonic type, which are noticeable when tapping with a neurological instrument. The main feature of Rossolimo-Steinert-Kurshman myotonia is usually called the presence of atrophic disorders in different muscle groups. At the same time, with further progression, there is a gradual decrease in symptoms due to developing muscle dystrophy.
When the pathological process is located in the facial area, the patient notices a mask-like grimace of a sad type. Lesions in the muscle tissue of the mouth give rise to the spread of paresis with voice deformation and difficulty swallowing. Changes characteristic of myopathy can even appear in the respiratory zone, which causes a decrease in the level of pulmonary ventilation, the occurrence of attacks of apnea during sleep, congestive or aspiration pneumonia. Experts highlight additional patient complaints:
- Problems in the functioning of the cardiovascular system are recorded in 50% of cases.
- Central nervous system disorders that can lead the patient to a mild form of debility.
- Endocrine disorders affect the functioning of the reproductive system - men notice low libido, impotence, cryptorchidism, etc., and women notice menstruation problems, early menopause, etc.
- Deformation of the hair structure in combination with alopecia.
- In males, baldness begins in the temporal and frontal areas.
Symptoms and signs of classical myotonia Rossolimo-Steinert-Curschmann
The very first signs of myotonia can appear as early as the age of 6-7 years, but most often become clearly visible in adolescence and young adulthood from 10 to 20 years. The list of these signs includes myopathy, cataracts, damage to the central nervous system and cardiovascular system, and endocrine disorders.
The main symptom is the presence of muscle spasms, which mainly affect the masseter facial muscle and the flexor muscle of the hand. Also, experts always note atrophy of various muscles, including the distal parts of all extremities, temporal, sternocleidomastoid, and facial muscles. Myopathic laryngeal paresis is observed with difficulty breathing, voice changes, deterioration of ventilation, sleep pathologies and aspiration and congestive pneumonia. Due to changes in muscle tissue and premature loss of tendon reflexes, most patients experience a change in gait.
In approximately 50% of cases, patients complain of a symptom such as arrhythmia, along with which bundle branch block, as well as hypertrophy of the left cardiac ventricle, can be observed.
On the part of the SNS, the disease causes hypersomnia, a decrease in intellectual abilities, and there are often cases when patients have a mild form of debility. Due to pathologies of the endocrine system, sexual dysfunction occurs. In young women, the changes consist of the manifestation of hirsutism, menstrual irregularities and early menopause, in young people - a decrease or absence of desire and impotence, cryptorchidism and hypogonadism.
Representatives of both sexes have a common symptom of Rossolimo-Steinert-Kurshman myotonia - changes in the structure of the hair with subsequent loss. In men, baldness occurs in the area of the temples and forehead; in women, a local focal or diffuse disorder occurs.
Symptoms of the congenital form of Rossolimo-Steinert-Kurshman myotonia
In situations where neurologists diagnose a chronic variant of the disease, the first signs of the presence of an anomaly are pathological processes that arose in the prenatal period. Often, symptoms manifest themselves in a serious decrease in the motor activity of the developing fetus, which is noticed during an ultrasound examination by a doctor in the field of gynecology and obstetrics (during the third trimester of pregnancy). After birth, the child has the following problems:
- Diffuse disorders of muscle tissue - localized at points in the facial, chewing and oculomotor muscle tissues, as well as in the muscles of the distal parts of the limbs.
- Problems with feeding.
- Malfunctions of the breathing apparatus.
- Slow progression of motor skills.
- The appearance of oligophrenia.
Increased child mortality is recorded with increasing symptoms of the disease.
Symptoms of congenital Rossolimo-Steinert-Kurshman myotonia
The congenital type of myotonia can be noticed by a specialist even during the period of stay in the mother’s womb. This fetus does not show increased motor activity. Therefore, if a pregnant woman notices such behavior of the baby in the stomach, she should definitely undergo an ultrasound scan in the last three months before giving birth.
Signs of myotonia are also present in newborns. This is hypotonia of facial, masticatory muscles, distal areas of the limbs, and eyeballs. In addition, breathing disorders are also common. A little later, symptoms such as mental retardation and delayed motor development appear. The progression of these pathologies can occur at different rates. With the rapid pace of their development, the patient’s death from the disease can befall him at a very early age.
Diagnostic options
If you have the above complaints, you should urgently visit a qualified specialist in the field of neurology. To confirm the conclusion, the doctor will prescribe certain clinical procedures, for example:
- Genealogical examination, which will show the presence of an autosomal dominant form of inheritance of the pathology.
- DNA test.
- Electromyographic diagnostics.
- Electroneurographic examination.
- Checking sex hormones.
- Electrocardiographic assessment.
In addition, consultations are held with doctors specializing in problems of hereditary, cardiological, endocrinological, gynecological and other types.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
As a rule, Leiden-Thomsen disease manifests itself and can be identified diagnostically in prepubertal or early puberty. A specific symptom is residual tension (spastic tone) of any muscle groups that were tense voluntarily and adequately to the situation, after which they should relax - and do not relax. Most often, such tonic muscle spasms are observed in the fingers, hands, legs, orbicularis oculi muscles, and masticatory (masticatory) muscles. Accordingly, the patient for a long time, for tens of seconds, cannot, for example, open his eyes or mouth, turn his head, move his limbs, open his palm, change his facial expression, etc.
A characteristic feature is the often observed contradiction between athletic hypertrophy, rigidity, relief of spasmodic muscle groups and actually reduced muscle strength.
Reflexological examination using a neurological hammer easily reveals tonic-spastic reactions of the fingers, tongue, etc. Of the instrumental diagnostic methods, the most informative is electromyography. A consultation with a medical geneticist is required, and a detailed family history is collected and compared with the clinical picture.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Methods for treating dystrophic myotonia Rossolimo-Steinert-Kurshman
Currently, scientists have not yet been able to draw up a radial plan for getting rid of the symptoms of the described disease. Patients suffering from dystrophic myotonia are prescribed a special diet, which includes a low potassium content in foods. In addition, doctors prescribe the following procedures:
- Do not stay in the cold for a long time.
- Use of quinine, phenytoin and other medications.
- Taking steroid pharmacological drugs with anabolic properties.
- Small dosages of ATP and vitamin complexes are prescribed, in particular B vitamins.