The nature of amnesia in old age
In older years, a person’s brain functionality decreases, the process of cellular renewal slows down, and biochemical processes deteriorate. The body is aging.
Although memory loss in older people is a common problem, it is not a necessary consequence of aging. In a healthy elderly person, memory functions worse, but is generally normal, with minor defects. He analyzes and assimilates new information more slowly, remembers large amounts of data worse, and may forget the name of someone he knows.
Serious memory impairment is associated with the influence of external causes: head injuries, circulatory disorders, mental disorders, long-term use of drugs and others.
Memory deteriorates gradually. First, a person forgets the events of the present, then - details and details. Then the memory of the events of youth returns. Then the person forgets personal information and stops recognizing people.
Poor memory: causes, treatment
If relatives note that memory deterioration occurs in older people, treatment in this case must begin immediately by identifying the causes. Neurologists identify several causes of memory impairment:
- bruises, injuries, hemorrhages, concussions lead to problems with remembering information;
- with Alzheimer's disease, partial memory loss is observed in older people; treatment of this pathology is carried out by a neurologist;
- epilepsy;
- atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
- brain tumors;
- chemotherapy;
- long-term depression combined with insomnia;
- imbalance of substances in the body due to diet and nutritional disorders (for example, iodine);
- psychological factors, such as passion for something, the desire to forget about an unpleasant, traumatic event;
- in a state of passion, memory loss may occur, for this reason treatment is most effective;
When determining the causes of memory impairment, the doctor talks with the patient, conducts an examination to identify the suspected causes, after which he may prescribe a number of diagnostic methods. The neurology clinic performs various studies to determine the presence of pathologies in the circulatory system and other factors that cause memory problems. After diagnosis, the doctor selects a therapy program.
Causes
Age-related changes are the background for the development of memory problems. They cause disruptions in brain function. If a person does not train his mind, his memory will weaken over the years.
The causes of memory loss are varied. The main ones include the following:
• Lack of oxygen (hypoxia), due to which the brain suffers and remembers new information worse • Hypertension - high blood pressure • Cardiovascular diseases, which lead to impaired cerebral blood flow • Traumatic brain injuries • Severe chronic illnesses: varicose veins, diabetes diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, central nervous system problems • Intoxication of the body
The causes of memory impairment are also classified into groups. Thus, there are physiological and psychological causes of amnesia.
Physiological reasons are associated with disturbances in the functioning of the hippocampus and cerebral circulation, a decrease in the amount of proteins and hormones. These reasons include hypertension, ischemia, cerebral hypoxia, vascular aneurysm, oncology, varicose veins, intoxication of the body, taking medications and others.
Psychological ones include stress, frequent conflicts, psychotrauma, increased emotional and mental stress, loneliness, monotonous lifestyle, depression, chronic fatigue and others.
Diseases that cause memory impairment
The most common cause is traumatic brain injury. The second main reason is associated with poor blood circulation in the brain, which occurs with vascular atherosclerosis.
Having a stroke interferes with healthy blood flow to the affected area, leading to memory problems.
Vascular lesions in diabetes mellitus lead to various abnormalities, including in the functioning of the brain.
Encephalitis and meningitis affect all brain activity. If a person is diagnosed with these viral diseases, timely therapy must be started.
Thyroid disease can impair the memory of an older person. Such a patient experiences depression, irritability, weight gain, and muscle swelling. To solve the problem, normalize the level of iodine in the body with the help of medications and food.
Alzheimer's disease causes memory loss and decreased intellectual abilities. Most often it occurs in people aged 65-80 years. Unfortunately, modern medicine is not able to cure this disease, but it is possible to prolong the patient’s life and improve its quality with the help of palliative therapy. Therapy must be started as early as possible, otherwise amnesia will lead to serious consequences.
Memory impairment in older people: treatment at the Yusupov Hospital
The Yusupov Hospital is a unique medical institution that employs only experienced specialists who improve their skills and apply innovative techniques in their work. Many neurologists find it difficult to treat short-term memory disorders at the stage of selecting treatment methods. However, specialists from the neurology clinic successfully solve this problem.
The neurology clinic at the Yusupov Hospital accepts patients with memory disorders, including those who have been rejected by other medical institutions. The clinic staff ensures a comfortable stay for the patient and promptly informs him about the treatment plan. If there is a serious impairment of memory and attention, treatment is carried out in a hospital setting. Psychological assistance is also provided to patients' relatives.
If you or loved ones experience memory loss, the causes and treatment will be determined by the clinic’s neurologist during consultation and diagnostic procedures. You can make an appointment and receive detailed information about the clinic’s services by phone.
Memory impairment in the elderly: what to look out for
If a person periodically forgets some things, calls people by other people’s names, there is nothing wrong with that. Such rare forgetfulness and temporary memory lapses are typical for older people and do not harm his life.
You need to be wary when memory lapses in an elderly person occur frequently, progress and are accompanied by a deterioration in mental abilities: the ability to think logically, speak well, etc. This is how senile dementia can develop.
The person may have difficulty with everyday activities. If he pronounces words incorrectly, gets lost in space, behaves inappropriately in society, you need to take the person to a doctor.
Causes of memory loss
There are many reasons that cause short-term memory loss. Usually this is stress, overwork or strong emotional shocks of a negative connotation. With age, the above reasons are joined by others:
- diseases of the nervous system, for example, Alzheimer's disease, atherosclerotic changes in cerebral vessels, multiple sclerosis with memory loss;
- diabetes and its complications (neuropathy and vascular disorders);
- pathologies and diseases that disrupt normal blood supply to the brain;
- some mental disorders;
- serious brain diseases: inflammatory, oncological, etc.;
- long-term use of sleeping pills, anti-anxiety medications (tranquilizers and antidepressants), etc.
Types of memory disorders
Amnesia is divided into types depending on the nature of the loss of information. There are the following types of memory loss:
• Partial or complete. With partial, a person cannot remember some events of his life; with complete, memories disappear entirely. • Short term or long term. In short-term, a person does not remember new information that he received in the last hours or days; in long-term, he forgets events from the long past - from several months to several years ago. • Temporary or permanent. Temporary is associated with temporary forgetfulness, then the memory is restored (for example, a person forgets the name of a friend, and after a while remembers). Permanent amnesia is the loss of information that a person can no longer remember. • Anterograde (a person forgets the past, but remembers the present well) or retrograde (on the contrary: a person remembers the present poorly, but remembers the past well). • Gradual or sudden. Gradual memory loss occurs over time; memory weakens slowly. It is difficult to diagnose and predict. In case of sudden memory loss, a person immediately forgets important data: first and last names, address, loved ones. A lost pensioner with sudden amnesia cannot remember where his house is or clearly explain its location. • Sharp. Happens suddenly and has a strong impact. With it, a person cannot normally do even simple everyday activities; he forgets what he was going to do today. This amnesia is caused by brain pathologies or emotional problems. If you do not pay proper attention to the disease, it will begin to progress. • Visual - affects visual perception, a person does not recognize loved ones, familiar places. • Reversible (can be cured) and irreversible (cannot be cured). • Global - a person does not remember the past and does not remember new events.
There are also other types of memory loss:
• Korsakovskaya. Develops due to alcohol abuse. People forget events during periods of severe intoxication or hangover. • Senile. Develops over the years. People with this disorder increasingly remember events from past years. • Post-stroke. An attack that has been suffered impairs the functioning of a person’s senses and thinking. • Semantic. A common senile amnesia, in which memories of the outside world are lost. In a mild form a person forgets the names of objects, in a moderate form he does not remember what different objects are for, in a severe form both disorders are combined. • Procedural. A person loses everyday skills. Forgets how to brush teeth, wear clothes, and use cutlery. He needs constant help. • Professional. Associated with a person's work. He forgets how to properly perform his professional duties.
Amnesia in old age, together with disorders of thinking and attention, leads to senile dementia. The disease is progressing. It all starts with forgetfulness of individual moments and events. For example, a person forgets whether he closed the door or took his medicine. Then the events of the past are forgotten, and then the person stops recognizing his acquaintances.
How does dementia progress in older people?
“Usually, dementia develops gradually, it can be divided into stages, each of them has its own symptoms and manifestations,” says Yulia Telysheva.
Experts call three degrees of dementia:
- light;
- average;
- heavy.
Signs of early dementia at the behavioral level - a person cannot remember what happened a couple of days ago, cannot remember names and titles, absent-mindedness appears and criticism of current events weakens. Such mild cognitive impairment makes social contacts difficult, but does not yet lead to complete dementia. Things are worse for those close to the dementia patient, because one of the important symptoms of the early period of the disease is low mood. A person becomes indifferent to loved ones, their experiences and problems, and may begin to suspect them of some unseemly actions directed against him.
A timely survey of the patient shows the presence of depressive moods several years before the initial stage.
What happens at the level of behavior in a patient at the second stage? All of the above cognitive impairments are getting worse. Plus, a person may no longer be able to navigate a familiar area or the time of day.
“The patient may stop feeling hungry and forget to eat. Has difficulty coping with simple arithmetic problems and confuses days of the week and dates. The patient may be haunted by auditory and visual hallucinations that are built into his daily life. He can start communicating with them and attract the attention of those nearby,” continues Yulia Telysheva.
The last degree of dementia varies in duration from several months to several years, it all depends on the immune system and the state of the cardiovascular system. At this stage, neurons are no longer able to exercise control over various body functions. The patient may fall into states of unmotivated aggression, causing harm to himself and those close to him.
Symptoms
Amnesia is accompanied by the following symptoms:
• Confusion. Restless thoughts cause short-term memory loss. • Speech problems – associated with brain disorders. May occur due to dementia or head injuries. The person speaks indistinctly, changes words, does not pronounce the ending, and loses the logic of the conversation. • Headaches that provoke infections and traumatic brain injuries. • Trouble concentrating – caused by an infection or brain tumor. Inattention interferes with a person's ability to perform daily activities. • Impaired coordination and orientation in space. These symptoms may indicate the onset of Alzheimer's disease. • Tremor – develops along with memory loss. With sudden forgetfulness and panic, a person experiences trembling in the body. • Feeling tired. It can develop due to exercise, thyroid problems, brain tumors, or a virus. • Dizziness – indicates a lack of coordination. • Bad mood, lack of interest in everyday activities and events.
Symptoms occur in different combinations. If a person has already developed senile dementia, then additional disturbances in movement and orientation in space occur.
Also, amnesia in the elderly is characterized by additional signs that manifest themselves in psychology, behavior, and human health:
• Changes in handwriting • Violation of given promises, forgetfulness about upcoming events • Absent-mindedness in terms of daily affairs. A person may forget about simple actions: close the door, turn off the iron, etc. • Negligent hygiene: a person stops taking care of himself, forgets about the rules of cleanliness, does not maintain order at home. • The person becomes slow and cannot perform normal activities well. • Irritability, aggressiveness, demandingness, capriciousness, vulnerability, and touchiness arise. • The patient calls relatives by other people's names.
Memory loss is itself a symptom of other illnesses, often mental or neurological disorders.
Symptoms of memory loss
Memory disorder is a gradual and long-term process, so it is quite difficult to notice any changes at the initial stage. The following symptoms are typical for this condition:
- frequent headaches caused by brain injuries;
- dizziness associated with dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus;
- tremor that worsens even with a minor stressful situation;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- absent-minded attention, inability to evaluate events or situations;
- chronic fatigue caused by past diseases (infectious, viral);
- apathy, depression;
- confusion - decreased concentration;
- speech disorders – inability to express thoughts, find the right words, speech dysfunction.
If memory loss is accompanied by these symptoms, the elderly person needs care, as the risk of getting lost on the street increases.
Diagnostics
A neurologist diagnoses and treats the problem. The person may also be sent to a neurosurgeon, psychotherapist and other specialists.
Diagnosis begins with a detailed interview with the patient. Experts find out the symptoms and nature of amnesia and its cause. They use information about a person’s health and illnesses to find the root cause. This information will help restore healthy brain activity.
During the interview, the specialist finds out the following points: • When memory impairment began • What is the nature of the problem: memory is lost abruptly or gradually • What is difficult to remember • Are there any problems with everyday activities • What is the patient’s illness and what medications is he taking?
The patient undergoes laboratory tests to determine nervous system disorders that affect memory. For research we use:
• Biochemical blood test • Cerebrospinal fluid analysis • Electroencephalogram • Toxicological tests • Brain examination • Blood vessel analysis • DSM – duplex scanning of cerebral vessels • CT – computed tomography of the brain • Doppler ultrasound of cerebral vessels
It is necessary to carefully study the patient's situation and observe him for some time in order to correctly identify the problem and prescribe the correct treatment.
Reasons for the deterioration of the ability to remember in adulthood
Memory loss in adulthood sometimes takes a pathological course. This condition is called hypomnesia. The disorder manifests itself in difficulties with remembering events, dates, terms, numbers, new names, and faces. There are lapses in memory for certain events. At the same time, some people restore memories using clues. As a rule, memory impairment progresses over time. For most people, information is lost in the reverse order - from the present to the past.
Memory disorders manifest themselves in varying degrees of severity, having signs that meet the criteria:
- mild cognitive impairment;
- dementia (severe intellectual impairment).
Deterioration in the ability to remember is observed in various pathological conditions, including:
- neurological diseases;
- taking psychoactive substances, both drugs and certain medications;
- acute or chronic intoxication with ethanol and its breakdown products;
- benign or malignant brain tumors;
- severe infectious brain lesions;
- changes in the structure of cerebral vessels;
- atherosclerosis;
- persistent increase in blood pressure;
- intracranial hypertension;
- neurodegenerative processes;
- traumatic brain damage.
Among the painful conditions accompanied by severe memory impairment:
- Alzheimer's type dementia;
- vascular dementia (a common variant is cerebral atherosclerosis);
- Parkinson's disease with memory impairment;
- Hakim-Adams syndrome;
- encephalopathies (for example, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease).
Important! Memory impairment often occurs in healthy people due to overwork, lack of proper rest, and sleep disturbances.
Mnestic dysfunction is sometimes caused by treatable, reversible conditions such as:
- Clinical depression. Depressive status results in a state that mimics a memory disorder. The person indicates difficulty concentrating, difficulty remembering information, and the inability to organize thoughts in a logical order. Depression is a common mood disorder in older adults, often occurring as social activity levels change after retirement.
- Vitamin deficiency. Vitamin deficiency in old age is often associated with poor nutrition and age-related changes in metabolism. A common cause of vitamin deficiency is taking medications for chronic diseases. A lack of vitamins prevents the restoration of damaged brain structures and accelerates aging.
- Endocrine diseases. Thyroid dysfunction, for example, hypothyroidism, is accompanied by lethargy, decreased memory, attention, and intelligence.
- Dehydration. The reasons for the lack of water in the body are kidney failure, taking diuretics, chronic diseases (for example, diabetes). Dehydration is common among older adults because the brain's thirst center is less active than in younger adults. Lack of water in the body is manifested by confusion, drowsiness, and inability to concentrate and remember.
- Side effects of drugs. Some over-the-counter pharmacological products have undesirable side effects - cognitive impairment, memory impairment.
Memory tests
These memory exercises can be done independently at home to test your memory.
Test No. 1
The “Shopping List” test is suitable for testing short-term memory. Write down any 10-item shopping list on a piece of paper. Let the elderly person study it for 40 seconds and remember it. Then check how many items from the list the person remembers: you can ask orally, or write down on paper. Missing an item or incorrectly named word from the list is counted as an error. If there are no errors, then everything is fine with the memory. If a person has up to 4 errors, then he has normal memory for old age. If there are 5 or more errors, the brain needs help.
Test No. 2
Ask the subject to draw a clock face with a specific time. This test not only tests the memory of an elderly person, but also the soundness of his thinking. If the dial is depicted evenly, the numbers are located correctly and do not stand out from the general row, the hands are also even and correctly indicate the given time - the person is healthy, his memory is in order. When dementia begins, the drawing will be crooked, the numbers will be of different sizes, in the wrong order, the arrows will be uneven, and show the wrong time. Severe deviations from the normal pattern may indicate the onset of dementia. This simple test can be done regularly to check on an older person. If severe defects are detected in the drawing, the person should be taken to a doctor for diagnosis.
Test No. 3
This test tests long-term memory. You need to write down several contacts of your loved ones on a separate sheet - up to 5-10 numbers. Try to learn this list, and then check the quality of memorization after 1-3 days. If a person can correctly recall most of his contact list, he is doing well with long-term memory. If not, there is something to work on.
Treatment
A specialist will study the situation and draw up a treatment course. The sooner the diagnosis is made, the sooner therapy can begin. With reversible memory loss, this is especially necessary: it is easier to restore memory and prevent dementia.
Therapy uses medications, physiotherapy, psychological methods, dietary changes, and folk remedies.
Treat the root cause of amnesia. This can be acute or chronic circulatory failure in the brain, which occurs due to cardiovascular diseases. If a person has atherosclerosis of the head arteries, arterial hypertension, or heart disease, they need to be treated.
Medicines
For atherosclerosis of the main arteries, antiplatelet agents are prescribed, and for high cholesterol, statins are prescribed. If the cause is head injury, the person is prescribed medications to improve metabolism: absorbable, nootropic, diuretic. If memory loss occurs due to dementia, neurotropics are used. It is necessary to combat harmful factors: physical inactivity, smoking, obesity, diabetes mellitus - they can lead to cerebral ischemia.
• Antiplatelet agents and vasodilators improve cerebral blood flow and tissue blood supply. • Neuroprotectors and antioxidants harmonize metabolism in neurons, making a person more resistant to hypoxia and adverse effects. Combined neuroprotectors are drugs with multiple effects to solve several problems at once. • Memantines help with Alzheimer's disease. • Nootropic drugs stimulate cognitive abilities, improve metabolism in cerebral tissues. They help fight aging, mental disorders, and improve memory. • Anticholinesterase drugs inhibit the development of dementia in old age. • Antioxidants. They block the action of free radicals, heal and renew tissues, and make cells resistant to hypoxia. • Adaptogens - herbal remedies and multivitamin complexes. Help the body fight age-related changes.
ethnoscience
Useful herbs for general strengthening will have a good effect on the health of the entire body and improve memory. They are recommended to be used as additional means to primary drug therapy.
Several recipes:
• Pour eleutherococcus roots (40 g) with water (0.5 l), heat and boil for 10 minutes. The decoction is taken 150 ml four times a day. • Pour 1 liter of hot water over walnut leaves (50 g), cover with a towel and leave for several hours. Take 150 ml three times a day. • Pour thyme (1 tbsp) into a jar and add boiling water, leave for 15 minutes. Take one cup 3 times a day. This remedy improves memory and slows down the development of amnesia. • If memory loss is due to a head injury, you can use a walnut-based remedy. Chop the peeled walnuts into small pieces and add honey. Take one tablespoon three times a day for a month. • For atherosclerosis, which also affects memory, it is useful to take a thinning agent based on dill seeds. Place one tablespoon of seeds in a saucepan, add 0.5 liters of hot water, leave for half an hour. Take half a glass before meals 3 times a day.
The following folk remedies are useful:
• Drink pumpkin juice regularly, the daily norm is 100 ml • Drink a decoction of dried rowan bark • Eat 4 pieces of young pine buds • Drink clover tincture for 2 months
Nutrition for amnesia
It is important to change your diet. If a person is addicted to junk food, he needs to switch to a healthy diet. It is useful to include foods that strengthen memory: apple, banana, carrots, cottage cheese, sour cream, nuts, chocolate, potatoes, horseradish. Food should be rich in vitamins; you can take vitamin complexes.
Dietary recommendations:
• The basis of the diet should be plant foods and dairy products • You need to eat in small portions and regularly, follow a meal plan by the hour. • Food must be fresh and prepared from quality ingredients. • You need to avoid fatty, fried, smoked and spicy foods. Eliminate processed foods, fast food, and high-calorie foods.
Examples of healthy dishes that can be included in the menu: whole grain porridge with milk, buckwheat/rice as a side dish, light broth soup, lean meat, cottage cheese casserole, vegetable stew, fruit salad.
Additional treatment
Electrophoresis and massage are popular physiotherapy procedures. In psychological treatment, exercises are used to train the brain. Psychotherapy helps the patient to recall forgotten events. Hypnotic practices may be used.
Exercise therapy improves motor and brain activity, blood circulation, and endurance.
If the cause of memory loss is a hematoma or brain tumor, the person is prescribed neurosurgery.
The course of treatment is drawn up by the doctor after a thorough diagnosis. You can’t choose your own remedies and self-medicate. If you notice obvious symptoms of amnesia, you should immediately consult a doctor. Treatment is necessary: if the problem is neglected, it can reduce a person’s quality of life and worsen his social ties with society. In old age, amnesia progresses without treatment.
Causes of poor memory in the elderly
The formation of new brain cells - neurons - occurs continuously throughout life. Intellectual-mnestic disorders are not an inevitable consequence of biological aging. To preserve nerve tissue, it is necessary to regularly train the brain. Lifestyle, good and bad habits influence higher nervous activity.
Causes of age-related decline in cognitive functions and memory:
- As the brain ages, morphological changes occur in the hippocampus. This part of the limbic system is responsible for memory consolidation (the transition of information from short-term memory to long-term storage). The hippocampus is also responsible for spatial memory necessary for navigation.
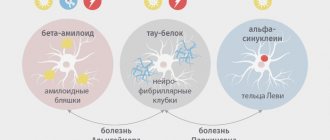
- As the body ages, a protein compound called beta-amyloid may accumulate in the nerve tissue. Disturbance in the rhythm of sleep and wakefulness, characteristic of older people, leads to an increase in beta-amyloid levels. The resulting amyloid plaques provoke irreversible changes in the brain, which are manifested by memory disorders.
- Hormonal changes in old age negatively affect mnestic function. For example, it is believed that the multifunctional steroid hormone dehydroepiandrosterone plays a role in ensuring the memorization, storage, and reproduction of information from memory. The production of this compound decreases by 80% by age 70.
- Older people are characterized by deterioration of blood supply to the brain. Reduction or blockage of cerebral vessels leads to oxygen starvation and necrosis of brain tissue. Vascular diseases are directly related to excess weight and a sedentary lifestyle, which is typical for some retirees.
- Men who systematically drink alcohol for a long period of time experience irreversible changes in the structures of the brain. A common symptom among older people who drink is the loss of acquired experience, skills, and knowledge.
For information! In old age, a slight decline in memory naturally occurs. However, short-term, episodic forgetfulness does not always act as a warning about the onset of senile dementia. The main difference between age-related memory decline and dementia is that the natural decline in cognitive potential does not lead to disability or affect daily activities. Senile (senile) dementia is characterized by persistent, pronounced deterioration of several intellectual functions, leading to the inability to self-care, perform household chores, and interact with society.
Home treatment and prevention
If a person does not have a serious condition, they can be treated at home in the comfort and peace of mind. The therapeutic course includes taking medications, performing useful exercises and medical recommendations.
To improve your health, you must comply with the following conditions:
• Sleep at least 8-9 hours a day. An additional 1-2 hour nap during the day is also recommended. • Maintain good communication with loved ones: relatives, friends, neighbors. • Avoid conflicts and stressful situations, create a calm, friendly atmosphere at home. • Stop smoking and drinking alcohol. • Eat harmoniously and nutritiously. • Walk outdoors every day. • Involve the elderly relative in family and household affairs.
Recommendations for people with memory loss
• Twice a year you need to undergo a medical examination to monitor the person’s condition. • Every year it is useful to go to a sanatorium or resort to improve the general condition and health of the nervous system. • Maintain a logical connection between the past, present and future. To avoid memory lapses, you need to talk to a person about his biography in order to maintain a healthy memory. • Keep a diary in which to record the events of the day. This will help to record facts and restore memories if they are lost. • Discuss different topics: a movie watched, a book read, events experienced. • Do drawing or music. • Walk outdoors every day. • Maintain mental work, learn new things.
Thanks to the active work of the brain, the connection between cells is strengthened, thanks to which a person maintains sanity and good thinking for a long time.
To maintain healthy memory, you need to lead an active lifestyle. Proper nutrition, walks in the fresh air, and suitable physical activity are necessary. Bad habits need to be abandoned.
To maintain strong memory for many years, older people need to monitor their overall health. Diseases affect the quality of memory. It is necessary to control sugar and cholesterol levels, and treat chronic diseases.
It is necessary to maintain brain health through intellectual activities: reading, learning new things, solving puzzles, being creative, developing in any area.
Tips from medical experts for preserving memory:
• Maintain healthy cholesterol levels. If left unchecked, memory problems may develop in old age. • Take a course of ginkgo biloba extract (40 mg) - this will improve memory. • Include foods with natural antioxidants in your diet - they will prevent the weakening of brain activity. • Contact a psychologist when you discover the first problems with memory.
Memory training in old age
To train your memory, it is important to be aware of the memory characteristics of older people. Pensioners have better developed logical, rather than figurative, memory, so information that a person actively thinks to remember, he assimilates and remembers better. Repeating new information many times will also help you remember something new. It is easier for a person to remember what makes sense to him.
To improve memory in an elderly person, it is useful to follow these recommendations:
• Be physically active. Suitable physical activity will support healthy memory. • Drawing with both hands. On a sheet of paper, try to simultaneously draw the same objects with both hands, for example, two squares, circles, triangles. Next, you can choose more complex shapes: flowers, trees, clouds. The hardest thing is to depict different objects at the same time. This exercise will train both hemispheres of the brain. • Write a summary of the text, as in your school years. You can use a short read text, radio or television news. Express the main meaning, retain more facts and precise details, maintain the style of the narrative. • Remember the last person you saw, his appearance in great detail. • Learn poetry by heart. • Perform usual actions differently. Brush your teeth with the other hand, go to the store a different way, etc. • Memorize lists. Lists can be anything: thematic and consisting of different words, everyday ones (for example, shopping in a store or a to-do list for the week). You can learn a foreign language by making lists to memorize. • Learn to play a musical instrument. • Activities to develop fine motor skills of the fingers: rotating small objects between the fingers, knitting, modeling and others. • Solve puzzles, crosswords and riddles. You can work with any information, learn foreign languages. • Take regular breaks from work for rest, for example, changing activities from mental to physical (walking, exercising, cleaning). • Keep a diary. Such an organizer will not only make the work of the brain easier, but will also help train your memory by recording notes. • Read more. This will train motor and visual memory and develop thinking. It is useful to retell what you read and analyze the work. • Train attention to detail. Remember down to the smallest detail what this or that object, person, place looks like. • Develop a positive outlook on life.
Each memory problem in old age is an individual case that requires professional study. Relatives of an elderly person need to remember the signs of amnesia in order to be able to recognize the onset of the disease in time. If you suspect a disease, you need to take the person to a specialist. Treatment is necessary in any case; self-medication is not allowed.
To strengthen and improve memory in old age, you need to follow useful recommendations, lead a healthy lifestyle, and maintain mental and physical activity. In this way, you can preserve a strong and good memory for many years.