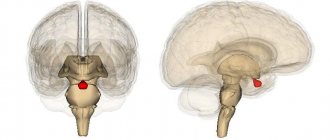
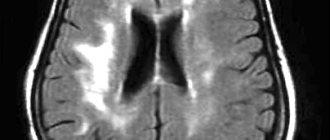
Agenesis of the corpus callosum is a congenital pathology of the brain, the cause of which in most cases is a genetic factor; a disorder develops in utero in the fetus. This anomaly is quite rare.
The corpus callosum is the plexus of nerves in the brain that connects the right and left hemispheres. The shape of the corpus callosum is flat and wide. It is located under the cerebral cortex.
With agenesis, there are no callosal adhesions connecting the hemispheres, either partially or completely. This pathology develops in one case out of two thousand conceptions and can be caused by heredity or spontaneous unexplained gene mutations.
Pathogenesis and etiology of the disorder
As mentioned above, the development of agenesis can be triggered by heredity, but most often the reasons for its occurrence cannot be determined.
This pathology has two clinical syndromes. In the first case, the patient’s intellectual abilities and motor activity are preserved, and the disease manifests itself as disturbances in the processes of transmitting impulses from the left hemisphere to the right and vice versa. For example, a patient who is right-handed cannot determine which object is in his left hand, because this requires the transfer of information from the right hemisphere to the left, where the speech zone is located.
In the second case, together with agenesis of the corpus callosum, the patient also has other malformations of the brain, including disturbances in the processes of neuron migration or hydrocephalus. In such cases, patients suffer from severe convulsive seizures and also lag behind in mental development.
Symptoms
Agenesis of the corpus callosum in the newborn initially manifests itself through epileptic seizures during the first weeks of life or during the first two years. However, not all people experience seizures; in mild cases, the disorder may go undetected for several years. Other disorders may appear at an early age.
Physical:
- low muscle tone;
- impaired vision;
- feeding difficulties;
- abnormal features of the head and face;
- sleep problems;
- epileptic seizures;
- hearing impairment;
- chronic constipation.
Cognitive impairment:
- difficulty solving problems and complex tasks;
- lack of ability to assess risk;
- difficulty understanding abstract concepts;
- decreased perception of emotions.
Developmental delays:
- difficulties in learning to sit, walk, ride a bicycle;
- delays in speech and language acquisition;
- clumsiness and poor coordination;
- delayed toilet training.
Some patients exhibit external signs:
- deep-set eyes and prominent forehead;
- an abnormally small head (microcephaly) or an unusually large head (macrocephaly);
- congenital abnormalities of the hand (camptodactyly);
- growth retardation;
- small nose with inverted nostrils;
- abnormal ears;
- short arms;
- decreased muscle tone;
- laryngeal abnormalities;
- heart defects.
In some mild cases, symptoms do not appear for many years. Older patients whose symptoms were missed in childhood are usually diagnosed with signs such as seizures, monotone or repetitive speech, and frequent headaches.
Predisposing factors
In its normal state, the corpus callosum is a dense plexus of nerve fibers designed to unite the right hemisphere of the brain with the left and ensure the exchange of information between them. This structure is formed from 10 to 20 weeks of pregnancy, the corpus callosum is formed at 6 weeks.
Agenesis can manifest itself in varying degrees of severity: absence, partial or incorrect formation, as well as underdevelopment of the corpus callosum.
In most cases, the cause of this disorder cannot be determined, but there are a number of factors that contribute to the occurrence of such a pathology. Predisposing factors include:
- process of spontaneous mutation;
- hereditary causes;
- chromosome rearrangement;
- the effect of toxins due to taking medications during pregnancy;
- insufficient provision of the fetus with nutrients during intrauterine development;
- viral infections or injuries suffered by the mother during pregnancy;
- disruption of metabolic processes in the mother's body;
- alcoholism during pregnancy.
Identifying the causes of such pathologies is difficult; it is only possible to identify the factors that can provoke their development.
General information
What to do if you have brain damage?
The corpus callosum is located in the deep part of the longitudinal fissures of the brain. In general, such an organ can be divided into three large sections - posterior, middle and anterior. Now I would like to consider in more detail what each part of the corpus callosum is.
If we talk about the anterior section, then it bends forward, then down and at the very end back. Thus, an organ is formed, which is called the knee of the corpus callosum, which smoothly passes into the lower parts of the carina or directly into the beak of the corpus callosum. Then, the latter continues to advance to the final plate, located in front of the common commissure and slightly below it.
The middle section of the corpus callosum is also called the brain stem. It has the appearance of a certain convexity, which, in turn, resembles the shape of a rectangle. It is this part that is considered the longest of all that are present in the adhesions of the human brain.
Rear end. Here is the splenium of the corpus callosum, a thickening. By the way, the roller hangs in a free style over the epiphysis of the brain, as well as over the plate of the lid, located in the middle part of the brain.
At the very top of the corpus callosum there is a very thin layer of gray fluid, the so-called gray vesture. In some individual situations, such a substance can form four small thickenings, which are located along the corpus callosum and look like thin stripes. There are two such stripes on each side of the corpus callosum.
If you cut the brain hemisphere horizontally, touching the upper part of the corpus callosum, you can clearly see the white matter that separates both hemispheres of the brain. This white matter in each hemisphere of the brain has a special oval shape and is called by scientists the semi-oval center.
Along its entire perimeter, such liquid is accompanied by small layers of gray matter. Certain white fibers extend from the corpus callosum over the entire area, which diverge radially into each individual hemisphere of the brain.
Manifestations and signs of anomaly
Agenesis of the corpus callosum of the brain manifests itself in different ways, depending on the degree of the disorder; the main symptoms in the presence of this anomaly are:
- processes of nerve atrophy in the organs of hearing and vision;
- cysts and neoplasms in the part of the brain where the hemispheres connect;
- microencephaly;
- prone to seizures;
- presence of facial dysmorphism;
- the occurrence of defects in the development of the visual organs;
- porencephaly;
- pathological changes in the fundus;
- delays in psychomotor development;
- schizencephaly;
- presence of lipomas;
- disturbances in the development of the gastrointestinal tract and the presence of formations;
- early puberty and so on.
In addition to the above, the disease can manifest itself with Aicardi syndrome. This genetic disease is extremely rare and is characterized by abnormal development of the brain and visual organs. Agenesis also causes changes in bones and skin lesions.
History of discovery
Despite the active study of brain structures in the last century, the functions of the corpus callosum have long remained in the shadow of the scientific microscope of researchers
Fiber formation received close attention from the American neuropsychologist Roger Sperry, who later received the Nobel Prize for his study
The scientist performed a series of surgical interventions on the corpus callosum: like any neuropsychologist, Sperry cut the contacts, removed the structure and observed the functioning of the brain after the operations. He noticed a pattern: when the neural network connecting both hemispheres was removed, a patient who had previously suffered from epilepsy got rid of his illness. The researcher concluded: the corpus callosum is actively involved in the epileptic process and the spread of pathological excitation throughout different parts of the brain. In 1981, Roger Sperry was awarded the most prestigious international prize in the field of physiology and medicine for the results of his work.
However, despite such studies, the full functional set of this structure is still not discovered, and many mysteries in the functioning of the brain are associated with its activity, including the development of the schizophrenic process.
Establishing diagnosis
Diagnosis of agenesis of the corpus callosum is quite difficult and in most cases is detected in the 2-3 trimester of pregnancy. The main diagnostic methods include:
- echography;
- MRI;
- Ultrasound.
However, echography does not make it possible to detect the disease in all cases, and if the agenesis of the corpus callosum is partial, then its detection is even more difficult.
Difficulties in diagnosing the disorder arise because this pathology is often associated with a number of other disorders and genetic symptoms. In order to conduct a more detailed examination of the patient, specialists resort to karyotyping, ultrasound analysis and MRI.
Using a combination of examination techniques, it is possible to obtain a complete picture of the disease.
Diagnostics
Agenesis of the corpus callosum is often diagnosed during the first two years of life. An epileptic seizure in a newborn may be the first sign indicating a disorder.
In some cases, mental retardation appears, or intelligence may be only slightly impaired or subtle psychosocial symptoms may be present. In this case, the child should be examined for brain dysfunction.
Brain scans are necessary to diagnose abnormal conditions and include:
- High-resolution prenatal ultrasound (prenatal screening for trisomy in the first trimester), cost of the study - from 2 thousand rubles.
- Prenatal magnetic resonance imaging. MRI of the fetus to confirm the diagnosis and identify the presence of brain problems. This advanced test, high-resolution images, provides the best information about the underlying cause of the syndrome. MRI is the method of choice when assessing both the corpus callosum and often associated anomalies Cost from 5 thousand rubles.
- MRI after birth for additional information about the baby. The cost of scanning is from 10 thousand rubles.
- CT scan. The cost of the procedure is from 3 thousand rubles.
Agenesis of the corpus callosum in a newborn
Agenesis of the corpus callosum in a newborn is sometimes associated with chromosomal or genetic disorders. In this case, doctors recommend genetic testing through amniocentesis during pregnancy or a blood test of the baby after birth.
Basics of therapy
Currently, there are no effective treatments for such an anomaly as agenesis of the corpus callosum. Correction methods depend on the diseases that were caused by this disorder, and therefore are selected individually.
Treatment is aimed at minimizing the manifestations of the disease. But, according to experts, it does not give the desired effect, and besides, the methods have not been fully developed. Therapy for the most part consists of the use of strong medications.
The following drugs can be used:
- benzodiazepines and phenobarbital , which allow you to adjust the frequency of attacks in the presence of infantile spasms;
- corticosteroid hormones (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone) in combination with basic anti-epileptic drugs;
- neuroleptics and diazepam drugs , the action of which is aimed at reducing behavioral disorders;
- nootropics (Semax, Piracetam) and neuropeptide drugs (Cerebrolysin);
- Children are most often prescribed Asparkam, Diacarb, Mexidol .
In addition to taking medications, if the need arises, surgical interventions are also performed, for example, stimulation of the vagus nerve is performed. But this can only be done in cases where agenesis has caused serious disruptions in the functioning of vital human organs.
This pathology can cause disorders in the musculoskeletal system and cause scoliosis, so specialists prescribe physiotherapy and exercise therapy. In some cases, surgery is also used.
Nowadays, agenesis is being carefully studied, but no tangible results have yet been achieved.
Development of interhemispheric interaction (corpus callosum) through kinesiological exercises.
Development of interhemispheric interaction (corpus callosum) through kinesiological exercises.
Batysheva E.V. (educator-psychologist)
“A well-constructed brain is worth more than a well-filled brain.”
Michel de Montaigne
The unity of the brain consists of the activity of two hemispheres, closely interconnected by a system of nerve fibers (corpus callosum). The corpus callosum is necessary for coordinating the brain and transmitting information from one hemisphere to the other. Violation of the corpus callosum distorts the cognitive activity of children.
For the successful learning and development of a child, one of the main conditions is the full development of the corpus callosum in childhood. The corpus callosum (interhemispheric interaction) can be developed through kinesiological exercises.
Kinesiology is the science of developing mental abilities and physical health through certain motor exercises. Kinesiological exercises are a set of movements that allow you to activate the interhemispheric effect, which includes: complexes of kinesiological and breathing exercises, acupressure, stretching, breathing exercises, oculomotor exercises, bodily exercises, exercises for the development of fine motor skills, relaxation exercises and massage. These exercises will help ensure a complete and harmonious development of younger schoolchildren.
Stretching normalizes hypertonicity (uncontrolled excessive muscle tension) and hypotonicity (uncontrolled muscle flaccidity).
Breathing exercises improve the rhythm of the body, develop self-control and volition.
Oculomotor exercises allow you to expand your field of vision and improve perception. Unidirectional and multidirectional movements of the eyes and tongue develop interhemispheric interaction and increase the energy level of the body.
When performing bodily movements, interhemispheric interaction develops, involuntary, unintentional movements and muscle tension are relieved. It turns out that a person needs movement to consolidate thoughts.
Relaxation exercises help you relax and relieve tension.
Kinesiological techniques are aimed at activating various parts of the cerebral cortex, which makes it possible to develop a person’s abilities or correct problems in various areas.
The kinesiology method allows us to coordinate the activity of the main centers of the brain in children. After all, by teaching the left hemisphere, we teach only the left hemisphere. By training the right hemisphere, we train the whole brain. Differentiated learning, taking into account the functional asymmetry of the child’s cerebral hemispheres, is one of the most effective ways of learning.
Practical part.
Exercises must be done daily for 6-8 weeks, 15-20 minutes a day. To gradually increase the complexity of the exercises, you can use:
- acceleration of the pace of execution,
- performing exercises with a lightly bitten tongue and closed eyes (excluding speech and visual control),
- connecting eye and tongue movements to hand movements,
— connecting breathing exercises and visualization methods.
The main part of the kinesiological complex is occupied by exercises for the arms and legs, massage of the ears.
1. "Ears."
Goal: energizing the brain.
Gently straighten and stretch the outer edge of each ear with the same hand in an upward direction - outward from the top to the earlobe 5 times. Massage the auricle.
2. "Ring"
.
Goal: development of interhemispheric interaction (corpus callosum).
Alternately and as quickly as possible, move your fingers, connecting the index finger, middle finger, etc. in a ring with the thumb. The exercise is performed in direct (from the index finger to the little finger) and in the reverse (from the little finger to the index finger) order. At the beginning, the movements are performed with each hand separately, then together.
3. "Fist-rib-palm"
.
Goal: development of interhemispheric interaction (corpus callosum), arbitrariness and self-control.
The child is shown three positions of the hand on the floor plane, successively replacing each other. Palm on a plane, palm clenched into a fist, palm with an edge on the plane of the table, straightened palm on the plane of the table. The child performs the movements together with the instructor, then from memory for 8-10 repetitions of the motor program. The exercise is performed first with the right hand, then with the left, then with both hands together. If there are difficulties in performing the task, the instructor invites the child to help himself with commands (“fist-rib-palm”), pronounced out loud or silently.
4. “Lezginka”.
Goal: development of interhemispheric interaction (corpus callosum), arbitrariness and self-control.
The child folds his left hand into a fist, puts his thumb to the side, and turns the fist toward himself with his fingers. With his right hand, with a straight palm in a horizontal position, he touches the little finger of his left. After this, simultaneously changes the position of the right and left hands for 6-8 changes of positions. It is necessary to achieve a high speed of changing positions.
5. “Frog.
Goal: development of interhemispheric interaction (corpus callosum), arbitrariness and self-control.
Place your hands on the table. One hand is clenched into a fist, the other lies on the plane of the table (palm). Change the position of your hands simultaneously and in different directions.
6. "Castle".
Goal: development of interhemispheric interaction (corpus callosum), arbitrariness and self-control.
Cross your arms with your palms facing each other, clasp your fingers, and turn your arms toward you. Move the finger that the instructor points to. The finger must move accurately and clearly. It is undesirable to allow movement of adjacent fingers. You can't touch your finger. All fingers of both hands should participate in the exercise sequentially. In the future, children can do the exercise in pairs.
7. "Ear-nose"
.
Goal: development of interhemispheric interaction (corpus callosum), arbitrariness and self-control.
The child is asked to grab the tip of his nose with his left hand, and the opposite ear with his right hand. Simultaneously release your ear and nose, clap your hands, change the position of your hands “exactly the opposite.”
8. “Mirror drawing.”
Goal: development of interhemispheric interaction (corpus callosum), volition and self-control, elimination of mirror perception.
Place a blank sheet of paper on the table. Take a pencil or felt-tip pen in both hands. It is necessary to draw mirror-symmetrical drawings and letters with both hands at the same time. When performing this exercise, you will feel how your eyes and hands relax. When the activity of both hemispheres is synchronized, the efficiency of the entire brain will noticeably increase.
9. Breathing exercises.
Goal: activation of the brain stem, rhythm of the right hemisphere, energization of the brain.
1st option.
Inhale, pause, exhale, pause. When performing breathing exercises, it is more effective to additionally use figurative representation (visualization), i.e. connect the right hemisphere. For example, there may be an image of a yellow or orange warm ball located in the stomach, respectively inflating and deflating in the rhythm of breathing. When inhaling, the lips extend into a tube and “drink” the air with a noise.
2nd option.
Breathe only through the left, and then only through the right nostril (in this case, the thumb of the right hand is used to close the right nostril, the remaining fingers look up, and the little finger of the right hand is used to close the left nostril). Breathing is slow and deep. Breathing only through the left nostril activates the right hemisphere of the brain, promotes calm and relaxation. Breathing only through the right nostril activates the left hemisphere of the brain and helps solve rational problems.
3rd option.
Take a deep breath. Pause. As you exhale, pronounce the sounds: pf-pf-pf-pf-pf. Pause. Inhale. Pause. As you exhale: r-r-r-r. Pause. Inhale. Pause. On the exhale: z-z-z-z. Pause. Inhale. Pause. On the exhale: w-w-w-w. Pause. Inhale. Pause. On the exhale: mo-me-me-mo.
10. Oculomotor exercises.
Goal: development of interhemispheric interaction (corpus callosum), formation of a space scanning vector.
1st option.
The head is fixed. The eyes look straight ahead. It is necessary to practice eye movements in four main (up, down, right, left) and four auxiliary directions (diagonals); bringing the eyes to the center. Each of the movements is done first at arm's length, then at elbow distance, and finally near the bridge of the nose. Movements are performed at a slow pace (from 3 to 7 seconds) with fixation in extreme positions; Moreover, the hold should be equal in duration to the preceding movement. When practicing oculomotor exercises, it is recommended to use any bright objects, small toys, etc. to attract the child’s attention. Those areas in the child’s field of vision where the gaze “slips” should be given additional attention, “drawing” them several times until the retention becomes stable.
2nd option.
The head is fixed. The eyes look straight ahead. Practice eye movements in four main (up, down, right, left) and four auxiliary directions (diagonals); bringing the eyes to the center. Eye movements must be combined with breathing. During the deep inhalation phase, it is necessary to make movements with the eyes, then hold the eyes in the extreme lateral position during the breath-holding phase. Return to the starting position is accompanied by passive exhalation. The exercises can be performed with the tongue lightly bitten or the jaw clenched tightly.
eleven . An important part of kinesiology exercises is self-massage . Goal: improving the function of receptors, pathways, strengthening reflex connections of the cerebral cortex with muscles and blood vessels. Massage of the fingers and ears is especially effective.
There are the following self-massage techniques: stroking, rubbing, kneading, active and passive movements.
1. Place the hand and forearm of the left hand on the table. Using the edge of the palm of the right hand, “sawing” in all directions of the back of the left palm is simulated. The same is done with the other hand.
2. Move the knuckles of the fingers of your right hand clenched into a fist up and down the palm of your left hand. Same for the other hand.
3. Self-massage of fingers. Using the index and middle fingers of the right hand, rotational and rubbing movements of the fingers of the left hand are performed. Then change hands.
4. Movements as when rubbing frozen hands.
Thus, kinesiological exercises make it possible to use those parts of the brain that were not previously involved in learning and solve the problem of failure. The use of kinesiological exercises not only contributes to the development of mental abilities and physical health, but also improves memory and increases stability of attention. Facilitate the writing process. They develop creative abilities based on visual and figurative thinking, stabilize the psyche, and develop intuition. They improve memory, increase intellectual capabilities, help overcome mathematical difficulties, and activate the work of the brain.
List of used literature:
1. Paul I. Dennison. Brain gymnastics. Guide for teachers and parents. M., 1999. “Educational Kinesiology for Children.” M., 1984.-48 p.
2. Sirotyuk A. L. Teaching children taking into account psychophysiology: A practical guide for teachers and parents. M.: shopping center. Sphere, 2001. -128 p.
How many days are available for patients?
In cases where the disorder is not associated with the occurrence of other developmental pathologies, the prognosis is favorable. About 80% of children have no developmental disorders or minor neurological problems.
However, in most cases, agenesis of the corpus callosum provokes the occurrence of various kinds of consequences and associated pathologies, and in such a situation there can be no talk of a good prognosis.
Patients experience intellectual impairment, neurological problems, developmental delays and other symptoms with which they do not live for a long time. Patients are treated according to symptoms and the therapy has little effect.
Agenesis of the corpus callosum can be classified as a disease with a large number of developmental anomalies and unfavorable prognosis.
Malformations of the corpus callosum and their consequences
Hypoplasia, or, as this disease is also called, microcephaly, is a complex pathology, during the course and development of which there is a significant decrease (the value is taken based on normal indicators) in the volume of the brain and, accordingly, the corpus callosum as well.
In most cases, along with the diagnosis of hypoplasia, other disorders are observed, including improper development of the present parts of the corpus callosum (dysplasia or dysgenesis), insufficient development of the spinal cord, underdevelopment of the limbs and a number of internal organs.
The main cause of developmental disorders and reduction in size (or complete absence) of the corpus callosum is one or another congenital pathology. Factors causing such changes:
- Presence of bad habits in a pregnant woman (smoking, taking drugs or alcohol);
- intoxication;
- exposure to radiation (ionizing);
- consequences of complex and serious diseases - rubella (acquired in adulthood or especially during pregnancy), influenza, toxoplasmosis.
Particular attention should be paid in the early stages (1-2 trimesters) of pregnancy - during the formation of brain structures.
Symptoms of the disease:
- decrease in brain volume relative to normal indicators (main symptom);
- changes in the usual structure of the brain convolutions and some structures (the convolutions are flat);
- insufficient development of the temporal and frontal lobes of the human brain for normal functioning;
- reduction in the size of the pyramids - elements of the medulla oblongata (pyramidal syndrome develops);
- disorders and malfunctions identified in the functioning of the cerebellum;
- dysfunction of the brain stem (part of the brain);
- in most cases there is an intellectual impairment;
- physical development disorders;
- neurological disorders and characteristic disorders;
- pathology of the optic thalamus.
With hypoplasia, the skull is smaller than a person should normally have.
Despite the development of modern medicine, there is no high-quality and effective treatment for such a disorder. It is possible to reduce symptoms to a minimum.
It is important to remember that this anomaly leads to a decrease in life expectancy. The main measure of influence is taking medications.
If appropriate measures are not taken at the early stage of development and formation of the anomaly, then the majority of patients in the future (already in childhood and adolescence) will experience various problems in the field of neurology.
Also, many patients with hypoplasia have moderate and severe intellectual impairment, developmental delay, both mental and physical.
Thus, according to various medical studies, in at least 68-71% of cases diagnosed with hypoplasia of the corpus callosum, there is a consequence such as mental retardation. In addition, the disorder leads to the emergence of more serious mental disorders, such as schizophrenia.
Dysgenesis of the corpus callosum can cause changes in the muscle system and in the skeleton as a whole. It is a common cause of scoliosis.
There are delays in the mental and psycho-emotional development of children and adolescents. Intellectual impairment, neurological problems, and developmental delays are also observed, so patients in most cases require constant supervision and intensive treatment.
If measures are taken to eliminate the manifestations, children can learn the necessary skills, including mastering a simple school curriculum.
The first trimester is the most important stage of pregnancy. It is during this period that all the main organs are formed, and it is at this time that they are most vulnerable. The neural tube forms towards the end of the trimester, at 12-13 weeks.
The expectant mother undergoes an ultrasound, and it shows whether the newborn has any abnormalities in the structure of the brain, including the corpus callosum, because they will lead to mental retardation.
Therefore, it is very important to monitor your health, undergo all examinations on time and take vitamin complexes during pregnancy.
The main malformations of the corpus callosum:
- Dysgenesis
- Agenesis
- Hypoplasia
All these defects entail a number of disturbances in the functioning of other organs. But most importantly, they are the cause of mental retardation.
Parents of children with these defects talk about fairly favorable prognoses if there are no concomitant diseases of the central nervous system.
Such children, of course, are doomed to take medications for life: nootropics that improve the nutrition of brain tissue, neuroleptics that correct behavior, hormonal and anticonvulsant drugs.
Such children are observed by neurologists and neurosurgeons. Rehabilitation is carried out by psychologists, defectologists, speech therapists, neuropsychologists, and psychiatrists.
The 30% chance of a favorable outcome that doctors give for such defects depends on the hard everyday work of the parents. It is necessary to deal with both physical and speech, psychomotor, and mental development.
The child will not always want to study. He can get tired quickly, become moody, absent-minded, even aggressive.
Agenesis
Agenesis of the corpus callosum in the fetus is the complete or partial absence of the main commissural commissure between the hemispheres. It can be either an independent disease or part of other congenital defects, for example, Aicardi syndrome.
Reasons for the absence of the corpus callosum:
- Genetic anomaly. A chromosomal mutation can be hereditary (not necessarily in the next generations, it is quite possible that the precedent was in the 5th-6th generation or earlier). An accurate diagnosis can be made by a geneticist after an examination.
- Intrauterine infection. Three decades ago, the term TORCH appeared, which unites the most common infections dangerous to the fetus - toxoplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, syphilis, rubella, cytomegalovirus and herpes. Unfortunately, they lead to serious developmental defects, miscarriage and death of newborns.
Partial agenesis of the corpus callosum is not so dangerous. The functions of the missing areas are taken over by the neighboring segments, as well as the anterior and posterior commissures. However, it also requires constant monitoring of the baby’s condition and drug treatment.
Usually the deviation is visible on ultrasound, but sometimes the disease goes unnoticed. In the first few months of life, the problem becomes obvious. Symptoms of agenesis of the corpus callosum:
- Functions of vision and hearing are impaired. The baby hears poorly or does not perceive sounds at all, and does not focus his gaze on an object. This is noticeable already at 1.5-2 months.
- The size of the head, and therefore the brain, is smaller than normal. During a routine consultation, a neurologist measures the circumference of the child’s head with a centimeter.
- Disturbances in the structure of the bones of the facial part of the skull are especially pronounced in the area of the eyes and nose.
- Various forms of epilepsy - convulsions, freezing, loss of consciousness.
- Delayed mental, psychomotor and speech development.
Parents can notice these symptoms themselves and consult a doctor. There are several signs that can only be detected through examinations:
- tumors, neoplasms, cysts - both at the site of the corpus callosum and in other organs, most often in the stomach and intestines;
- adhesions and characteristic spots on the fundus;
- disturbances in the electroencephalogram can appear only during functional tests, although sometimes the EEG in such children represents a variant of the norm.
It represents disturbances in the development of tissues of both a separate area of the corpus callosum and the entire organ. It is caused by the same reasons as agenesis - chromosomal abnormalities, intrauterine infections and poor lifestyle of the expectant mother.
Smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs lead to improper formation of the fetal neural tube.
MT dysgenesis is not life-threatening, but problems are inevitable. First of all, such children have problems with oral and written speech, perception of light signals and reaction to external stimuli.
Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum of the brain is a general underdevelopment of the brain. Hypoplasia, like other developmental anomalies of the corpus callosum, can be an independent disease or be associated with other developmental defects.
Main features:
- disproportionate skull. As a rule, this is noticeable, but deviations can sometimes be insignificant;
- the structure of the convolutions is changed - they become flat;
- muscular dystonia. The baby's movements are uncertain, infants do not hold their heads well and do not lean on their arms. If the disease was overlooked in the first months of life, then at an older age awkwardness and clumsiness are noted. Children often fall and drop objects;
- disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system. Sometimes it is very difficult to predict the reaction of a sick baby to a particular stimulus;
- developmental delay. The baby begins to walk later than others and has difficulty mastering speech.
Usually, abnormalities in the structure of the brain are visible on ultrasound during pregnancy. But poor quality equipment, low qualifications of the doctor, and the specific position of the fetus during the examination can make it difficult to make a diagnosis in the early stages.
Up to two years of age, children with hypoplasia of the corpus callosum can develop on par with their peers, and only after this age do symptoms begin to appear.
There are several ways to define both hypoplasia and dysplasia:
- Magnetic resonance imaging - allows you to see organic lesions of the brain and all its parts.
- Electroencephalogram - shows how the patient reacts to certain stimuli and records epiactivity.
- Neurosonography - ultrasound of the brain through the fontanel. Possible only in the first 1.5 years, then the connective tissue is replaced by bone.
All we can do is hope and pray
Although agenesis of the corpus callosum is not an extremely rare disease, it has been poorly studied.
Today, doctors do not have sufficient knowledge about the causes of its occurrence in each specific case; only factors that can serve as an impetus for the development of this pathology have been identified.
Also, no effective methods for treating this condition have been found and it is carried out only according to the symptoms of those disorders that were caused by agenesis. In this case, all measures are aimed at the effect, but do not in any way affect the cause.
From this we can conclude that there are no effective measures to prevent agenesis of the corpus callosum.