Neurologist
Chudinskaya
Galina Nikolaevna
Experience 29 years
Neurologist, member of the Association of Interdisciplinary Medicine
Make an appointment
Plexopathy is damage to the nerve plexuses due to disease or injury. The most commonly affected nerves are the lumbosacral, brachial, or cervical nerves. Plexopathy has ICD-10 code G54. With a long course of the disease, a person loses his ability to work, and in the most severe cases, muscle paralysis occurs. If detected at an early stage, hand plexopathy is completely curable with the help of manual therapy and other modern treatment methods.
Symptoms and signs of plexopathy
Brachial plexopathy according to ICD-10 is classified into several other types depending on the location of damage to the nerve plexuses. Based on this criterion, the most common types of disease are identified:
- brachial plexopathy (G54.0). Of all types, it is more common than others, mainly occurring after injury;
- Duchenne Erb plexopathy (G54.1). Develops when the roots C5 and C6 are affected, manifested in paralysis of the infraspinatus, biceps brachii and deltoid muscles of the shoulder;
- sacral plexopathy and lumbar plexopathy (G1). In most cases, it develops against the background of degenerative processes in the intervertebral discs with protrusions or hernias;
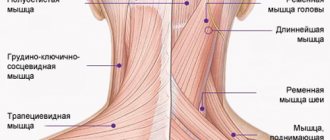
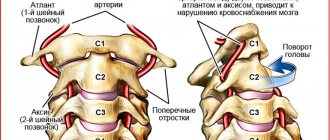
- cervical plexopathy (G2). Damage to the nerve plexuses at the level of C2-C3, which are responsible for the muscles of the shoulder girdle and back of the neck, partially the face and scalp.
Brachial plexus plexopathy according to ICD 10 is the very first one, since it is more common than others. This is explained by the location of the nerve ganglion - it is located in such a place that it is constantly at high risk of injury. This is why post-traumatic brachial plexopathy is diagnosed in most patients who present with characteristic complaints.
Plexopathy occurs in 2 stages:
- neuralgic. It suggests the appearance of spontaneous pain, which intensifies when the affected plexus is compressed, in particular, with various movements;
- paralytic. At this stage, paresis and paralysis occur. They affect only those muscles that are innervated by the affected nerve plexuses.
At the second stage, reflexes also worsen, tactile sensitivity is impaired, swelling and vasomotor disorders appear. Post-traumatic brachial plexopathy most often causes pain in the supraclavicular and infraclavicular region, which radiates to the arm. As the disease progresses, swelling of the hand, pallor and cyanosis of the hands, and sweating of the palms occur.
Plexitis (plexopathy)
Signs
Cervical plexitis is manifested by pain in the neck, most often in the front and side, pain in the ear area.
The pain may radiate to the back of the head. Paralysis of the cervical muscles, paralysis of the phrenic nerve and, as a result, respiratory failure may occur. Often with cervical plexitis, the patient cannot cough, speak loudly, and his abdominal muscles do not work enough. Hiccups appear. With brachial plexitis, the patient feels pain in the collarbone area with radiation to the arm, sensitivity in the arm is impaired, and paralysis may even develop. The hand swells, its skin turns pale. Often in this case the hand hangs like a whip, but the patient can move his fingers.
With lumbosacral plexitis, pain occurs in the lumbar region, but the hips, legs and feet also hurt. The legs swell, their sensitivity is impaired, and paralysis may develop.
With lumbosacral and brachial plexitis, dystrophy of the nails of the toes and hands develops.
Description
With plexitis, sensory, motor or trophic disorders occur. Moreover, damage to the plexus can be partial, when individual trunks and branches are damaged, or complete. The severity of symptoms depends on the degree of damage.
During the course of the disease, two stages are distinguished - neuralgic and paralytic. At the first stage, the patient experiences pain that intensifies with movement or compression of the plexus. And at the second stage, paralysis and paresis of muscles develop, which are innervated by the branches of the affected plexus. At the same stage, the organs innervated by the branches of this plexus swell, their sensitivity decreases, nutrition deteriorates, and their dystrophy develops.
Plexits can be
- traumatic, occurring after fractures, sprains, joint dislocations, bruises, compression of the plexus, birth injuries;
- infectious, occurring after influenza, tuberculosis, syphilis, tonsillitis, brucellosis;
- infectious-allergic, for example, post-vaccination plexitis;
- compression-ischemic, occurring when the plexus is compressed by bone fragments during a fracture or tumor.
Also, the cause of this disease can be metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, gout), osteochondrosis and intoxication.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis of plexitis, you need to interview the patient, do electroneuromyography and x-ray examination. A computed tomography (CT) scan may be needed.
Shoulder plexitis must be differentiated from diseases of the shoulder joint. Lumbosacral plexitis must be differentiated from radiculitis, sacroleitis (inflammation of the sacroiliac joint) and psoitis (inflammation of the iliopsoas muscle).
Treatment
The main task in treating plexitis is to eliminate the cause of the disease. For infectious plexitis, antibacterial or antiviral therapy is carried out. For traumatic and compression plexitis, surgical intervention is performed to remove compression and restore conductivity of the plexus branches. For intoxication and infectious-allergic plexitis, detoxification is carried out.
In all cases, painkillers, physiotherapy (UHF, iontophoresis), vitamins B1 and B12, balneotherapy, massage, reflexology and physical therapy are prescribed. Mud therapy also has a good effect. Swimming is very useful during the recovery period.
If treatment is started in a timely manner and carried out correctly, the prognosis of the disease is favorable.
Lifestyle
Physical overexertion, working with toxic substances and hypothermia are contraindicated for those suffering from plexitis. You should avoid staying in the same position for a long time and do not wear tight clothes.
When the disease enters the remission stage, sanatorium-resort treatment in specialized sanatoriums is indicated. These are sanatoriums
- Kislovodsk (“Villa Arnest”, “Jinal”, “Zarya”, “named after Dimitrov”, “named after Kirov”, “named after Ordzhonikidze”, “Moscow”, “Narzan”, Picket, “Plaza”, “Solnechny”);
- Essentukov (“Victoria”, “Valley of Narzanov”, “Pearl of the Caucasus”, “Istok”, “named after Andzhievsky”, “named after Pavlov”, “Metallurgist”, “Nadezhda”, “Healing Key”, “Miner”);
- Pyatigorsk (“Palace Gallery”, “named after Lermontov”, “Lenin Rocks”, “Forest Glade”, “Spring”);
- Zheleznovodsk (“named after Kirov”, “named after Thälmann”, “named after the 30th anniversary of the Victory”, “Elbrus”);
- Belarus (“Alesya”, “Berestye”, “Bug”, “Borovoe”, “Berezka”, “Berezina”, “Golden Sands”, “Crane”, “Forest Lakes”, “Nadzeya”, “Silver Keys”, “ Pridneprovsky", "Praleska", "Sosnovy Bor").
Prevention
To prevent plexitis, you need to dress appropriately for the weather, avoid overcooling, and promptly and correctly treat infectious diseases and metabolic disorders. You need to play sports, as it improves coordination and forms the muscle corset, thereby protecting against injuries.
© Dr. Peter
Causes and risk factors of plexopathy
Brachial plexopathy most often occurs after some kind of trauma, such as carrying heavy objects for a long time, a dislocated shoulder, birth injuries, or after a car accident. Post-traumatic plexopathy is always associated with some kind of mechanical impact on the shoulder area.
In some cases, the nerve plexuses in the shoulder suffer from compression by the tumor. Then compression plexopathy is diagnosed. In the cervical region, pathology is relatively rare.
The second most common type is lumbosacral plexopathy. It can be connected:
- with a space-occupying formation behind the peritoneum;
- fracture of the pelvic bones;
- hemorrhage caused by an overdose of anticoagulants or hemophilia;
- surgery on the hip joint;
- aneurysm of the aorta or iliac artery.
Main features
This disease usually occurs on one side. The elbow hurts, the discomfort radiates to different parts of the body. It depends on which nerve is affected. At night and when moving, the pain intensifies. It is necessary to buy Nucleo ampoules for treatment. If left untreated, plexitis causes paralysis. Sometimes doctors detect decreased tone and muscle wasting, paresis, and decreased tendon reflexes. All types of sensitivity suffer from this pathology, in addition, trophic disorders are observed. When the inflammatory process subsides, the disease enters the recovery stage, which can last a very long time, sometimes until the end of life. In the absence of complete reversibility, residual effects remain for many years. The patient is concerned about atrophy, paresis, contracture.
When to see a doctor
Already when the first symptoms of plexopathy appear, it is necessary to consult a doctor, because the earlier the disease is detected, the more effective the prescribed treatment will be. A neurologist diagnoses this disease. JSC "Medicine" (academician Roitberg's clinic) in the center of Moscow has a whole staff of doctors in this specialization. Our patients receive high-quality treatment and psychological support, which, combined with timely rehabilitation, allows them to quickly return to a healthy life.
Treatment
Treatment of brachial plexopathy, depending on the patient’s condition, can be carried out on an outpatient or inpatient basis. Therapy is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease. If it is an infection, antibiotics are prescribed, if it is a tumor, it is removed, etc.
Upper plexopathy at an early stage can be treated through manual therapy. First of all, this is a spinal traction procedure, which allows you to cope with the effect of compression. As a result, the nerve fiber begins to receive sufficient nutrition and is completely regenerated.
The following medications are prescribed to the patient:
- anticholinesterase;
- B vitamins;
- painkillers;
- trophic means;
- improving microcirculation;
- steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
In addition to medications, the following methods are used:
- massage – after acute inflammation subsides;
- physiotherapy: ultrasound, electrophoresis, ozokerite, magnetic therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- balneotherapy, cryotherapy, reflexology, laser therapy.
Erb's plexopathy can also be treated with surgery if pharmacological drugs do not produce the desired results. In such cases, neurosurgical operations are performed to restore the integrity of the nerve column or eliminate its compression (squeezing).
Complex treatment of plexitis of the nerve of the shoulder joint
Treatment of brachial plexitis should be comprehensive. At the initial consultation in our manual therapy clinic, the neurologist gives individual recommendations to each patient. They are aimed at eliminating negative influence factors. A treatment plan is then developed individually.
It may include various techniques. To treat plexitis of the shoulder joint, the following therapeutic conservative methods can be used:
- traction traction of the spinal column, if plexitis is caused by osteochondrosis and its complications;
- osteopathy and massage to restore microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid;
- reflexology – by influencing biologically active points on the human body it is possible to start the process of tissue regeneration;
- therapeutic exercises and kinesiotherapy restore muscle strength and the ability to perform any movements of the upper limbs;
- physiotherapy, laser treatment, electromyostimulation.
If you need effective and safe treatment for brachial nerve plexitis, you can schedule a free initial consultation with a neurologist at our manual therapy clinic. Here you will be given a preliminary diagnosis, a special examination will be recommended and information about treatment options will be provided.
Home remedies
Shoulder plexopathy allows the use of traditional methods of treatment, but only after consultation with the doctor and exclusively as a complement to the main therapy. Some effective home remedies include:
- ointment with propolis. Melt 15 g of animal fat in a water bath, then add 1 g of propolis. Mix everything and leave to cool. Use to massage the sore area 2-3 times a day;
- bath with mint. Pour 5-7 tablespoons of mint leaves into 1 liter of boiling water, leave for 2-3 minutes, then pour into a warm bath. Take it within 15-20 minutes.
Myths and dangerous misconceptions in the treatment of plexopathy
Many patients do not attach much importance to such a treatment method as gymnastics. Medicines only help relieve symptoms in their acute stage, but do not help create a strong muscle corset and ensure good blood flow in the musculoskeletal system.
Only a sufficient level of physical activity, agreed with your doctor, will help with this. The same applies to bed rest during the acute period - 2-3 days are enough, after which it is necessary to get up and begin to engage in physical activity.