Why do leg cramps occur?
Crumpy syndrome
Represents short-term painful muscle contractions.
It is extremely widespread, according to various sources, detected in 20-90% of adults, more common in old age. It can occur as a physiological reaction to various external influences, be idiopathic or symptomatic. In the vast majority of cases, the calf muscles are affected. During a cramp, sharp pain and plantar flexion of the foot are noted. Manifestations persist for several seconds or minutes and decrease with walking, massage, and passive extension of the foot. After the attack, minor pain and increased sensitivity of the calves are observed for 1-2 days. The syndrome often appears at night and is preceded by fasciculations. Provoked by the following circumstances:
- Physical factors.
Spasms in the legs bother you after unusual intense exercise - long walking, training on exercise equipment. They develop in water, especially cold water, which is associated with the danger of drowning. Other irritants include dehydration, hypothermia, and consumption of salty foods. - Idiopathic cramps.
They appear for no apparent reason and are detected both at rest and during movement. Observed daily or several times a week. May be associated with hereditary predisposition (detected in several members of the same family). - Somatic diseases.
Cramps are potentiated by chronic renal failure, liver cirrhosis, chronic heart failure, and rarely by glycogenosis and paraneoplastic syndrome. - Neurological diseases.
The syndrome occurs against the background of pathologies with hypertonicity and spontaneous muscle activity: ALS, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's syndrome, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, crampie-fasciculation syndrome. Sometimes accompanied by osteochondrosis, mono- and polyneuropathy.
Flat feet
Leg cramps are detected in all types of flat feet: longitudinal, transverse, mixed. They are caused by improper load distribution, which entails constant overwork of the muscles of the distal limbs. They are more often observed in the afternoon and develop after prolonged standing or walking. May disturb you at night.
Vascular diseases
Spasms in vascular diseases are caused by deterioration of metabolic processes, hypoxia, and a decrease in the amount of ATP in cells. Detected in the following pathologies:
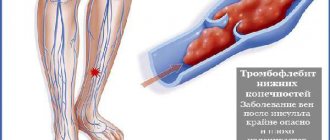
- Varicose veins.
The symptom is disturbing mainly in the stage of decompensation, more often observed at night. It is combined with increased fatigue, swelling, dull pain, constant heaviness in the legs, pronounced external changes in the veins, and trophic disorders. - Obliterating atherosclerosis.
More often diagnosed in older people. Pain and cramps in the calf muscles are preceded by numbness of the feet, burning, chilliness, and increased sensitivity to cold. After a certain period of time (usually insignificant), intermittent claudication is added to the listed symptoms. - Obliterating endarteritis.
Young men predominate among the patients. Symptoms resemble the clinical picture of atherosclerosis and include chilliness, numbness of the fingers, paresthesia, spasms in the feet and calf muscles, and intermittent claudication. A less favorable course and rapid development of trophic disorders are characteristic. - Thromboangiitis obliterans.
Always two-sided. Along with cramps, pain, increased sensitivity of the feet, hemorrhages in the toes, Raynaud's syndrome and migratory thrombophlebitis of the distal legs are detected. As it progresses, severe trophic disorders occur.
Endocrine diseases
Convulsive syndrome is most typical for hypoparathyroidism and is caused by increased neuromuscular excitability with low levels of parathyroid hormone. As a rule, the arms are symmetrically involved first, then the legs, and the flexors are predominantly affected. Sometimes spasms spread to the facial muscles, muscles of the trunk, and internal organs. In mild cases, attacks last 1-2 minutes and are repeated 1-2 times a week. In severe cases, there are many daily paroxysms lasting up to several hours.
In some cases, spasms bother patients with severe dysfunction of the thyroid gland due to hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. May be combined with myoclonus, cognitive and behavioral disorders. In diabetes mellitus, the cause of cramps in the legs is diabetic macroangiopathy, which occurs 10-15 years after the manifestation of the disease and is found in approximately 10% of patients. The symptom is complemented by chilliness, numbness of the feet, swelling, sharp pain in the legs, thighs, and sometimes buttocks, which intensifies with movement.
Fluid and electrolyte disturbances
Tonic convulsions caused by changes in electrolyte balance occur in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (malabsorption, condition after resection of the stomach and intestines), kidney diseases, endocrinopathies. The cause can also be external and internal bleeding, intestinal infections, poisoning, accompanied by repeated vomiting and frequent diarrhea. The symptom is determined in such conditions as:
- Hypocalcemia.
Foot cramps are combined with spasms of the hands, facial and chewing muscles. - Hypomagnesemia.
Carpopedal spasm is complemented by trembling of the limbs, hyperreflexia, tetany, weakness, drowsiness, and dyspeptic disorders. - Hyperkalemia.
Convulsive attacks are short-lived and quickly replaced by decreased muscle tone. Bradycardia, arrhythmias, and pain in the epigastric region are detected. - Hyper- and hyponatremia.
Unlike other conditions, the symptom is generalized. Paroxysm is preceded by respiratory distress, nausea, and vomiting.
Hypovitaminosis
Disorders of muscle contractile function are most often found with a deficiency of B vitamins:
- Hypovitaminosis B1.
Cramps in the lower leg muscles are characteristic of the dry form of beriberi. Neuritis and changes in pain and temperature sensitivity of the lower extremities are noted. - Hypovitaminosis B2.
Neurological disorders are determined during a long course of the disease, including spasms, paresthesia, ataxia, hyperreflexia. The listed symptoms are preceded by weakness, damage to the eyes, skin and mucous membranes. - Hypovitaminosis B6.
Convulsive syndrome develops at night. Complemented by decreased vision, conjunctivitis, dry skin. The tongue becomes crimson and takes on a varnished appearance.
Intoxication and poisoning
Spontaneous cramps in the legs and other parts of the body are associated with a drug overdose or an individual reaction to the drug. The cause of the symptom is most often drugs from the group of calcium channel blockers, beta blockers, statins, and diuretics. Sometimes the symptom develops under the influence of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, steroid hormones, nootropics, and a number of psychotropic and antibacterial drugs.
In some patients, convulsive syndrome appears upon recovery from anesthesia using muscle relaxants. The list of toxic substances that can provoke local (including in the legs) or generalized cramps includes dichlorvos, other insecticides, and pesticides. Arsenic, formaldehyde, phenol, as well as ergot, belladonna and fly agarics have a similar effect.
Pathologies of pregnancy
Convulsions caused by inferior vena cava syndrome appear in the 2-3 trimester of pregnancy. They are caused by compression of the vessel by the enlarging uterus and, as a result, poor circulation in the legs. The symptom is detected in the supine position, in the later stages it is combined with postural hypertension, dizziness, palpitations, and increased fetal movements.
In eclampsia, convulsions are generalized. They begin with small twitching of the facial muscles, turn into spasms of the muscles of the upper and lower extremities and end with convulsions that cover the entire body. They develop once or in “series” of several attacks. Then a coma forms, which is replaced by a gradual restoration of consciousness or deterioration of the condition, followed by death.
Other reasons
There are many conditions in which leg cramps occur but are not a specific symptom or, as in eclampsia, become generalized. Spasmodic contractions are possible with sunstroke and heatstroke. They can be detected in patients with posthemorrhagic anemia caused by massive blood loss. Found in epilepsy, head injury, and cerebral tumors. Occurs in tetany, myotonia, and some myopathies.
Cramps of the lower extremities
More often, convulsive contractions are observed in the calf muscles of the legs. Pain appears suddenly and often develops at night. Old people and children can experience excruciating pain. Statistics show that spasms mainly affect older people. The essence of the acquired state of muscle tissue is in a disturbed mechanism:
- muscle tissue consists of cells that have an electrical charge;
- there are sodium ions outside the cell, potassium ions inside;
- the balance of chemical elements lies in the contraction of cell membranes;
- if nerve impulses lose strength and intensity, calcium ions enter the cell;
- Subsequently, sodium enters the cell, displacing potassium.
The mechanism of convulsive contractions is formed with the help of opposite reflex displacements of sodium.
Convulsive contraction in the leg
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures are carried out by a neurologist. According to indications, patients are referred to an orthopedist, vascular surgeon, obstetrician-gynecologist, and other specialists. The examination program includes the following methods:
- Survey.
The doctor clarifies when the spasms first appeared, how often they recur, and what provokes the attacks. Investigates other complaints. Asks about existing diseases, lifestyle habits, and medications taken to determine possible causes of the symptom. - Physical examination.
During the examination, the specialist identifies changes in the legs: signs of flat feet, hypertrophy or increased muscle tone, fasciculations, dilated superficial veins, swelling. Evaluates pulsation, examines sensitivity and reflexes. - Electrophysiological studies.
Electroneurography and electromyography help determine the state of neuromuscular transmission, the speed of passage of nerve impulses, the presence or absence of spontaneous muscle activity, which in some cases indicates a possible cause of seizures. - Lab tests.
The screening examination includes CBC, TAM, determination of glucose, creatinine, urea, liver enzymes, and blood proteins. In case of water and electrolyte disorders, the level of electrolytes is examined, in case of hypovitaminosis, the content of vitamins is assessed, and in case of endocrine pathologies, hormone tests are performed. In case of poisoning, toxicological tests are performed. - Hardware techniques.
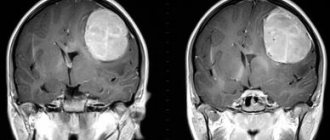
Patients with vascular diseases are advised to undergo ultrasound examinations (Dopplerography, duplex scanning) of the vessels of the lower extremities. For patients with flat feet, weight-bearing radiography of the feet is recommended. For endocrine diseases, ultrasound of the endocrine glands is performed; for organ lesions, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and kidneys is performed. To exclude neurological pathologies, an MRI of the brain is performed.
Night leg cramps in children
Often accompany a period of active growth of the baby. Since the concept of a “cramp” is unfamiliar and incomprehensible to the child, the sudden onset of muscle contractions causes significant anxiety, fear and crying. The main causes of nighttime leg cramps in a child are:
- keeping the leg in an awkward position, in one position for a long time;
- hypothermia of the lower extremities;
- lack of microelements (magnesium, potassium and calcium) in the body;
- flat feet.
The last 2 reasons are likely with regular, disturbing convulsions for a long time.
Treatment
Conservative therapy
Therapeutic tactics are determined by the cause of leg cramps. Taking into account the characteristics of the pathology, the following methods are used:
- Crumpy syndrome.
For symptomatic spasms, therapy for the underlying disease is indicated. To eliminate seizure activity, antiepileptic drugs, calcium channel blockers, and quinine are used. To stop attacks, muscle relaxants are prescribed. For severe pain, NSAIDs are included in the treatment regimen; for sleep disorders, mild sleeping pills are included. - Flat feet.
Non-drug methods play a leading role. Patients are advised to normalize their weight, choose comfortable shoes, and avoid prolonged static loads. To strengthen the arch of the foot, walking on small stones, massage, special exercises, SMT, magnetic therapy, and other physiotherapeutic procedures are useful. If necessary, select orthopedic shoes. - Vascular diseases.
Therapy for varicose veins is carried out using venotonics, physical therapy, elastic compression, and compression sclerotherapy methods. It is necessary to reduce the load on your legs. Drug treatment of obliterating diseases of the arteries is carried out with antispasmodics, anticoagulants, thrombolytics, and analgesics. Non-drug therapy includes ILBI, ozone therapy, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, balneological and physiotherapeutic procedures. - Endocrine diseases.
Hypoparathyroidism is corrected by diet, taking calcium and vitamin D supplements, sedatives, and anticonvulsants. UFO is useful. For hypothyroidism, hormone replacement therapy is carried out; patients with hyperthyroidism are prescribed thyreostatics. In diabetes with macroangiopathy, insulin therapy in combination with antiplatelet agents is necessary.
Violations of water and electrolyte balance are eliminated by intravenous administration of electrolyte solutions. Vitamin preparations are recommended for patients with hypovitaminosis. In case of intoxication, detoxification therapy is required. Pregnant women with NSAIDs are advised to sleep on their left side and moderate physical activity. Eclampsia is an indication for complex resuscitation measures.
Exercises for leg cramps
Surgery
Patients with seizures may undergo the following operations:
- Flat feet:
various options for correction of Hallux valgus, tendon transplantation, resection of bone sections. - Varicose veins:
phlebectomy, miniphlebectomy, adhesive obliteration, laser and radiofrequency coagulation, cryophlebectomy. - Obliterating vascular diseases:
endarterectomy, stenting, dilatation or prosthetics of arteries, shunt interventions, arterialization of the veins of the foot, profundoplasty, thromboembolectomy. - Endocrine pathologies:
resection of the thyroid gland in patients with hyperthyroidism, endarterectomy and plastic surgery of trophic ulcers in diabetic macroangiopathy.
Varicose veins and leg cramps
Leg cramps are one of the most common symptoms of varicose veins. Often it is the appearance of leg cramps that forces a person to visit a doctor.
Cramps in the lower extremities
Leg cramps with varicose veins are an involuntary contraction of the lower leg muscles, most often the calf muscles, occurring in the evening and at night. These leg cramps are painful, make movement difficult, and last from a few seconds to several minutes.
Cramping feet: reasons
All the reasons for cramping the feet can be divided into two large groups:
- primary – this includes muscle spasms that are not pathological in origin;
- secondary - seizures are always associated with pathologies in the body.
Lack of microelements in the body
If there is a deficiency of magnesium, calcium and potassium, then foot spasms can bother a person regularly. This happens against the background of the presence of provoking factors:
- adherence to strict diets, unbalanced nutrition;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- forced to take certain medications (for medical reasons);
- period of bearing a child.
It is especially common for feet to cramp when an imbalance of microelements has been present in the body for a long time. Another reason for the lack of elements important for neural impulses is dehydration, which can occur against the background of prolonged diarrhea, during the summer heat and profuse sweating.
Cold, forced use of medications
One of the most common causes of foot cramps is hypothermia of the lower extremities. In this case, the arch of the foot “pulls”, this happens against the background of an acute circulatory disorder - the person wears shoes that are out of season, spends a long time in cool water, or his work activity takes place outside at any time of the year.
If a person must take certain medications for a long time or on a constant basis, then he will be bothered by cramps of the soles of his feet - the excitability of the nerve endings is impaired. And this happens most often when diuretics (drugs with a diuretic effect) and antidepressants are used for therapy - useful microelements are simply “washed out”, blood flow becomes slow.
Physical inactivity
A sedentary lifestyle leads to shortening of ligaments and their atrophy, reducing the elasticity of muscle fibers, but moderate and regular physical activity is definitely necessary. The absence of the latter leads to stagnation of blood in the vessels - it flows slowly, nutrients stop flowing to the tissues in the required volume. As a result, foot cramps begin to bother you not only when walking, but also at rest.
If physical inactivity has been present in a person’s life for a long time and is burdened by excess weight, then not only the feet, but also the ankle and calf muscles will experience spasms.
Excessive stress on the legs
Although physical inactivity is a trigger for foot spasms, excessive exercise can have the same effect. And we’re not just talking about those people who play sports professionally or are forced to stand for long periods of time (for example, due to the nature of their work) - often the load becomes too heavy when wearing high-heeled shoes or narrow, tight models.
If you periodically tighten your feet, and in the evenings both your right and left legs cramp, then you should pay attention to your shoes. If possible, it is enough to replace the existing models with more comfortable, convenient ones, and after 7-10 days the negative sensations will stop bothering you.
At night
Convulsive syndrome that bothers you at night can often be explained by pathological conditions:
- sudden disruptions in the functionality of the central nervous system;
- flat feet;
- late stages of pregnancy;
- pathologies of blood vessels and metabolic processes that lead to circulatory disorders;
- chronic kidney and spinal column diseases.
The listed pathologies cause extensive swelling, which compresses the nerve endings - this causes a disruption in the transmission of neural impulses from the brain to muscle fibers. Depending on what disease caused the cramps, only the heel or the entire arch of the foot will cramp.
In water
If your feet cramp in water, then this condition can be explained by a sudden change in the external temperature. Such convulsions last several minutes, are always accompanied by severe pain, and they are often the cause of death of a person on the water.
Infrequently, convulsive syndrome can occur in warm water - prolonged exposure to such a body of water provokes pressure on the muscles, and an insufficient level of physical fitness only increases the likelihood of developing a spasm.
During pregnancy
Foot cramps begin to bother pregnant women in the second trimester, which is easy to explain - the veins in the pelvis and abdominal cavity are compressed, chronic or secondary varicose veins progress, an imbalance of microelements occurs, and swelling of the lower extremities is almost always present.
If these provoking factors are eliminated from a woman’s life or made less pronounced, then convulsive attacks will be extremely rare or will disappear altogether.
Chronic diseases
Convulsive twitching of the feet and a feeling that they are “cramped” may occur against the background of:
- Diabetes mellitus. A sharp cramp in both lower extremities occurs when there is a sharp drop in blood sugar levels. This can be caused by improperly administered therapy or an unbalanced diet.
- Varicose veins and other vascular diseases. Blood clots and trophic ulcers, which provide the patient with the almost constant presence of muscle fiber spasms, are considered especially dangerous. They cannot be eliminated using standard methods; long-term drug therapy or surgery will be required.
- Hormonal “swings”. This applies to women who have irregular menstrual cycles, even complete absence of periods, excessive estrogen production, and problems with the reproductive system.
- Heart diseases. They are almost always accompanied by thinning of the walls of blood vessels and their fragility, and impaired circulation. Cramps will occur both day and night, at rest and while walking.
Cramping feet: causes and treatment
If your feet cramp regularly, you must first find out the true causes of this condition, after which you can carry out treatment. For this, it is recommended to contact a therapist who will conduct an initial examination of the patient and, as part of the diagnosis, prescribe:
- general blood and urine tests - will help to exclude or confirm inflammatory processes in internal organs;
- laboratory blood test for sugar - makes it possible to diagnose the onset of diabetes mellitus;
- Ultrasound examination of the veins of the lower extremities - the condition of the walls of blood vessels is assessed, blood clots and areas of narrowing are identified;
- hormone tests - prescribed only if the doctor suspects a hormonal imbalance in the patient;
- blood test to check the level of vitamins and minerals.
After making an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe targeted therapy. As soon as the patient’s condition stabilizes and the pathological process stops progressing, the convulsive spasms of the feet will stop.
Symptomatic therapy
Treatment of the identified disease can take several weeks or even months, and in order to alleviate the patient’s condition and eliminate pain and discomfort, the doctor may prescribe symptomatic therapy:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - can be taken in any convenient pharmacological form (tablets, injections), are selected taking into account the underlying and concomitant diseases, relieve pain and have an anti-inflammatory effect;
- barbiturates – have a relaxing effect on nerve conduction, neutralize spasmodic contractions of muscle fibers, and are strictly prohibited for use in childhood;
- muscle relaxants – relax muscle tissue as much as possible, have a large list of side effects (nausea, severe weakness, drowsiness, “lethargy”), are prohibited for long-term use (they are addictive);
- complexes with vitamins and minerals (magnesium, potassium, folic acid, calcium, and so on) - most often prescribed to pregnant women, this is a good prevention of foot cramps.
If seizures are associated with impaired blood flow in the vessels of the lower extremities, then experts recommend that patients wear special compression garments that will reduce the load on the legs.
As part of drug therapy, the following are often prescribed:
- venotonics - drugs that increase the tone of the veins and have a positive effect on blood circulation in the vessels of the lower extremities;
- vitamins C and P - in addition to the already prescribed vitamin and mineral complexes, if you need to strengthen the walls of blood vessels and reduce their fragility;
- medications that lower blood sugar levels - help only if diabetes mellitus is confirmed during diagnostic measures;
- means for normalization and stabilization of myocardial functionality.
ethnoscience
You can use remedies from the “traditional medicine” category only after consulting a doctor - you need to exclude the possibility of worsening the condition. If permission for such therapy has been obtained, then you should use:
- Complex infusion. Anise, thyme and mint are mixed in equal proportions, then 2 tablespoons of the mixture are poured into 500 ml of boiling water. The infusion should be kept in a sealed container for 5-8 hours. After the specified time, the product is filtered and taken throughout the day in small portions.
- Celandine juice. It is “extracted” from a fresh plant - you just need to chop the green mass and squeeze it through a gauze napkin. The product is added to medical Vaseline in the proportion of 1 teaspoon of juice per 1 tablespoon of the drug. The prepared mixture is rubbed into the skin of the feet 1-2 times a day.
Exercises
If you perform certain exercises 2 times a day, they will help prevent the appearance of new spasms. The complex consists of only 5 exercises, the number of repetitions for each execution must be increased:
- Stand against the wall, leaning your back against it. Lean on the outside of your foot and stay in this position for a few seconds (5-10). Then return to your usual position and repeat after 3 seconds.
- Without changing the previous starting position, stand on your toes and after 3-5 seconds sharply lower onto your heels (stand on your full foot). Repeat at least 5 times.
- Sit on a chair or sofa. Stretch your legs forward and slightly raise them above the floor. Intensely squeeze and unclench your toes for 10 seconds. Then take a comfortable position and repeat the exercise again after 5-15 seconds.
- Without changing the starting position from the previous exercise, rotate your feet first in one direction, then in the other, ending with rotating your feet in different directions.
- Take 5-10 small steps forward, slightly raising your leg above the floor and stretching your toes down (imitate a ballerina's foot).
Preventing foot cramps
To prevent repeated convulsive attacks, you need to follow the simplest rules for preventing such spasms:
- adjust your diet by adding fresh fruits and vegetables, fish and seafood to the menu;
- eliminate medications with a diuretic effect, and if this is not possible (medical indications), then add more foods rich in calcium, magnesium and potassium to the menu;
- Perform a set of leg exercises daily, which will take 10-15 minutes;
- if necessary, reduce the level of load during sports training;
- if there is a history of varicose veins, then take a contrast shower daily;
- change the level of mobility of life - combat physical inactivity by walking in the fresh air.
Foot cramps can be disturbing not only as a symptom of internal pathology, but also against the background of provoking factors that do not pose a danger to human health and life. You can get rid of cramps using simple “home” methods, and it will be possible to prevent a recurrence of the situation only after examination by doctors, treatment, and compliance with preventive measures.