16 September 2020
64124
0
4.1 out of 5
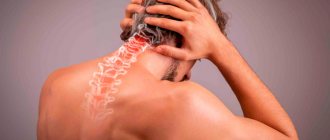
Radicular syndrome is not a separate disease, but is a complex set of symptoms that occur when spinal nerves are compressed at the points where they branch from the spinal cord. This can be observed in many diseases, but in any case, the appearance of radicular syndrome requires immediate diagnosis of the causes of development and the beginning of treatment adequate to the situation. Indeed, in addition to the fact that it is accompanied by severe pain, prolonged compression or compression of the nerve roots can lead to irreversible changes and ultimately necrosis of the nerve fibers, resulting in loss of sensitivity and motor disorders in those parts of the body for the innervation of which they were responsible.
Causes of the disease
In general, all reasons can be divided into two groups. Namely:
- Mechanical damage.
- Degenerative processes.
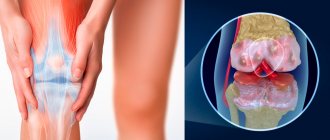
In the first case, it is enough to turn or bend over unsuccessfully to encounter manifestations of pinching. Also, sometimes pathology is provoked by excessive physical exertion and lack of dosage of work and rest. Degenerative processes include scoliosis, osteochondrosis and other diseases. They lead to disturbances in the structure of the vertebrae and the cartilage between them, accompanied by severe pain and a host of other manifestations.
Physical exercise
Symptoms of a pinched nerve in the thoracic spine can easily arise if, for example, you take on a load that is too heavy for you. You may experience pain if you lift a load too quickly or if you lift it incorrectly and put strain on your back.
Osteochondrosis
It is a dangerous disease, the manifestation of which is often a pinched nerve in the thoracic spine. The pathology causes the cartilage tissue between the vertebrae to wear out and become thinner, which significantly impairs shock absorption. Untimely treated osteochondrosis can lead not only to pinched nerves, but also to the occurrence of intervertebral hernia.
Sensitivity of nerves
The sensitivity of the nerves tends to change over time, and the position of the spine changes in the same way. There are cases when, with age, people experience various types of curvature of the spinal column, which provokes pinched nerves. To eliminate this condition, you will need to stop the displacement and strengthen your back muscles.
Causes
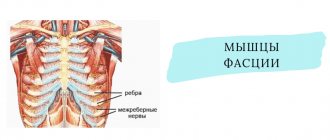
The spinal cord is an organ of the central nervous system. It is located in the spinal canal, on one side formed by the vertebral bodies together with the cartilaginous layers separating them (intervertebral discs), and on the other by the bony processes of the vertebrae. Thus, nature took care of protecting such a delicate and important organ for human life as the spinal cord.
The vertebral processes connect at several points, thereby forming natural openings called foraminal openings, through which the nerve roots extending from the spinal cord exit. They are large nerve fibers. As they move away from the spinal cord, they branch more and more into smaller fibers and reach all organs and parts of the human body, ensuring the transmission of appropriate signals to them that regulate their functioning.
Each spinal root is formed by sensory and motor nerve fibers. The first ones depart from the spinal cord from the side of the vertebral processes, i.e., closer to the back of the body and are therefore called posterior. The motor roots are located almost adjacent to the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs and are called anterior. Thus, from their names it is clear that the anterior roots are responsible for motor capabilities and are responsible for muscle contraction, while the posterior ones transmit signals to receptors that must respond to the action of various kinds of irritating factors: touch, rough blows, etc.
As already mentioned, the spinal roots exit on both sides of the spine through natural openings formed by the arches and processes of the vertebrae. Therefore, any changes in the condition of the spine and the surrounding soft tissues can affect the condition of such important nerves and lead to the development of radicular syndrome.
The bulk of cases of radiculopathy occur in diseases accompanied by degenerative changes or inflammatory processes in the spine and surrounding tissues. In the latter case, it is provoked by a reflex muscle spasm that occurs in response to pain, or swelling of the soft tissues.
The most common causes of radicular syndrome are:
- osteochondrosis;
- protrusion and intervertebral hernia;
- spondylosis;
- spondyloarthrosis;
- spondylolisthesis;
- traumatic injury to the spine;
- infectious diseases of the spine;
- neoplasms.
The significant “rejuvenation” of radicular syndrome is largely due to changes in the lifestyle of modern people for the worse. It is excess weight, a sedentary lifestyle, bad habits, stress and lack of habit of maintaining posture that become the main reasons for the development of the above diseases, which in turn cause the occurrence of radiculopathy. All of them contribute to poor circulation, which becomes a “trigger” for the occurrence of degenerative changes in the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs and the development of corresponding pathologies.
Osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a chronic disease in which there is a gradual destruction of the intervertebral discs against the background of degenerative-dystrophic changes occurring in them, i.e., the cartilage located between the vertebral bodies, acting as shock absorbers and ensuring the flexibility of the spine. They gradually become thinner and lose their natural elasticity. This leads to the fact that the bodies of neighboring vertebrae come closer together, and the diameter of the foraminal openings decreases, which can result in pinching of the spinal roots.
Protrusions and intervertebral hernias
Protrusions and hernias are one of the consequences of osteochondrosis, accompanied by deformation of the shape of the intervertebral disc and its protrusion. Initially, a protrusion is formed. This means that the disc is already deformed, but its outer shell (annulus fibrosus) still retains its integrity. If untreated, it ruptures in the most vulnerable place, which leads to the loss of internal contents (nucleus pulposus) into the spinal canal or the area from the front of the spine, i.e. the formation of a full-fledged intervertebral hernia.
Both protrusion and hernia can compress the spinal roots, either just one of them or both at once. This directly determines on which side neurological disorders will be observed. Large hernias and sequestered ones, that is, separated from the intervertebral disc, can also compress the spinal cord itself, which is fraught with serious complications. If the sequester begins to move along the spinal canal, this will be accompanied by the appearance of signs of damage to those nerve roots to the level of which it descends. If it reaches the lumbosacral region and the large bundle of nerves located there, called the cauda equina, it can lead to paresis and paralysis of the lower extremities.
Spondylosis
Spondylosis is another complication of osteochondrosis, in which the intervertebral discs wear out and become so thin that the vertebrae come together to a critically close distance. Against this background, their deformation occurs, which is accompanied by the formation of bone outgrowths called osteophytes on their edges. Over time, adjacent vertebral bodies can firmly fuse together, which leads to severe pinching of the spinal roots.
Spondyloarthrosis
This disease means the destruction of the facet joints, i.e., the place where the processes of the vertebrae meet. It involves damage to all elements of the joint, including its capsule, ligaments, surfaces and even periarticular muscles. This may also be accompanied by the formation of osteophytes and pinched nerve roots.
Spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis is a pathology of the spine in which the body of one or more vertebrae is displaced relative to the underlying one by a certain distance. Since this disrupts the spinal axis and displaces all the anatomical structures in this area, this leads to compression of the spinal cord roots or even the spinal cord itself.
Traumatic injuries
Spinal injuries are far from uncommon. Strong blows, falls from heights, road traffic accidents and other factors can lead to vertebral subluxations, fragmentation and compression fractures, which is almost always accompanied by the development of radicular syndrome.
Infectious diseases
From the point of view of the occurrence of radiculopathy, the greatest danger is posed by syphilitic and tuberculosis infections, as well as osteomyelitis and nonspecific bacterial meningitis. In such cases, damage to the nerves by pathogenic viruses and bacteria may occur, which will lead to their inflammation.
Neoplasms
The spine and spinal cord, just like other organs, can be subject to the formation of benign and malignant tumors. In addition, with oncological diseases of other organs, metastases can separate from the maternal tumor, which, through the bloodstream, enter the tissues surrounding the spine and can also provoke pinching of the nerve roots and the occurrence of corresponding symptoms.
One of the very common benign tumors of the spine is hemangioma. Many people are already born with such a vascular neoplasm located in the vertebral body, or acquire it with age. It is not dangerous, but it significantly increases the risk of spinal compression fracture.
Symptoms
The symptoms of this phenomenon can be either obvious or disguised as diseases of internal organs and other pathologies. Often, treatment for a pinched nerve in the thoracic spine is needed by people who have gone to the doctor with complaints about the heart, stomach and other internal organs, since the pain innervates them. It is worth knowing how a pinched nerve manifests itself in order to recognize the condition in time and consult a neurologist
.
Chest pain
Symptoms of pinching in the thoracic spine are often very similar to symptoms of an angina attack. The person complains about the following:
- there is severe pain and burning under the shoulder blade and in the chest;
- there is not enough air and you can’t breathe in completely;
- hands go numb;
- Cold sweat appears on the body.
To exclude the condition that occurs with angina pectoris, you can put two nitroglycerin tablets under your tongue. If you have heart problems, this remedy will eliminate them within 5 minutes, but if you have a pinched nerve, then the situation will not improve. In this case, there will be severe pain in the vertebral area.
Problems with the gastrointestinal tract
A person who is experiencing digestive problems due to back pain may need to find out what the symptoms and treatment of pinched thoracic spine may be. A person may note:
- Pain in the intestines when trying to change position.
- Spasmodic pain in the abdomen.
- Stool disorders.
Such symptoms may indicate not only pinching, but also a more serious condition - prolapsed intervertebral hernia or displacement of the vertebrae.
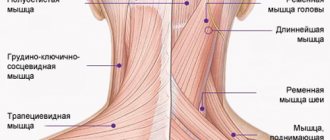
Pain in the shoulder blades: what could be the causes?
The average person is well aware of what the scapula is - a flat triangular paired bone in the upper back. But why does it hurt?
The most likely reasons could be:
- Spinal problems, injuries. Poor posture, curvature of the spinal column, and osteochondrosis lead to compression of nerve endings and the occurrence of pain symptoms.
- Diseases of the internal organs: pneumonia (pneumonia), pleurisy, angina pectoris, pericarditis, gastritis and gastric perforation due to ulcers are accompanied by severe pain in the upper back.
- Muscle problems: myalgia, muscle inflammation (myositis) cause nagging pain in the shoulder blades.
Why does my back hurt in the shoulder blade area? In addition to the above, pregnant women may experience pain in the shoulder blades at different stages, which is normal for them. But the problem can be more serious - neoplasms (both benign and malignant) in the chest or abdominal cavity can give similar symptoms. However, do not rush to panic and sound the alarm - even stress can indirectly lead to pain in the shoulder blades due to muscle strain and stooping. Such symptoms can be caused by excess weight, poor posture at work or while sleeping.
Types of pain between the shoulder blades
The symptom itself - that is, the nature of the pain in the shoulder blades - says a lot about the underlying disease. Pain can be acute, paroxysmal or chronic (constant), and it also varies in type and intensity.
Aching pain in the shoulder blade
In most cases, aching pain between the shoulder blades indicates pathology of the vertebrae and spine. Scoliotic deformities of the spinal column, osteochondrosis or herniated disc cause such symptoms. A peptic ulcer can also manifest itself as aching pain - in this case, you cannot do without a gastroenterologist.
Burning in the area of the shoulder blades
The occurrence of burning pain in the shoulder blades tells us about potential heart problems, for example, coronary heart disease. Such pain does not depend on movement, rarely lasts long and goes away soon after taking nitroglycerin. The second option is pinching of the nerve by intervertebral discs. Nitroglycerin will not help here, but non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs will help. Relief comes if you change your body position to a more comfortable one. In addition to the above, a burning symptom occurs when gastric contents reflux into the esophagus (reflux esophagitis).
Dull pain between the shoulder blades
As a rule, patients describe the pain that occurs due to pathology of tendons, ligaments and muscles with the word “dull.” The same characteristic is given to painful sensations in diseases of internal organs - cholecystitis or cholelithiasis.
Throbbing pain in the shoulder blade
Injury to the ribs, shoulder blades or vertebrae provokes the appearance of characteristic throbbing pain in the area of the shoulder blades. These painful symptoms may become more pronounced when sneezing or coughing. You should not hesitate to deal with such symptoms - you need to quickly contact a traumatologist.
Pressing pain in the shoulder blade
With inflammation in the muscles surrounding the scapula, a feeling of compression may occur. In addition to severe pain, myositis (inflammation of the muscle) leads to limited mobility of the shoulder and arm.
Sharp, sharp pain between the shoulder blades
An incipient stomach ulcer, an attack of biliary colic or pyelonephritis is manifested by a stabbing, sharp pain. In case of perforation of the ulcer, the pain begins in the stomach, accompanied by nausea, heartburn and bloating. With pleurisy, the patient will also notice a sharp pain in the area of the shoulder blades, but it will be complemented by a cough.
Pain when inhaling
If pain appears or intensifies during inhalation, this may signal us about lung disease or intercostal neuralgia. The pain with neuralgia has a shooting, encircling character. And with lung diseases, as a rule, the pain is accompanied by a cough, poor general health, weakness and fever.
Whatever the nature of the pain between the shoulder blades, if it does not subside within 1-1.5 days, it is recommended to visit a doctor.
Which doctor should I consult for back pain between the shoulder blades?
Since the etiology of pain between the shoulder blades is quite varied, the first thing you need to do is make an appointment with a therapist. The doctor will assess the situation, collect anamnesis, conduct an initial diagnostic examination and advise which specialist to contact for the most effective relief from pain in this localization.
Further treatment can be carried out by a traumatologist, orthopedist, neurologist, gastroenterologist, cardiologist, pulmonologist and other highly specialized specialists.
How is pain in the shoulder blades diagnosed?
In addition to collecting complaints, examining and carefully palpating (feeling) the causative area, the doctor may need to carry out a number of additional diagnostic measures:
- General and biochemical blood test, urine test.
- X-ray examination (if a deeper study is necessary, computed tomography (CT)).
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to assess the condition of internal organs, ligaments, tendons.
- Ultrasound diagnostics may be useful in determining kidney and bowel function.
- Electrocardiogram for diagnosing heart disease.
- Fluorography for suspected pulmonary problems.
- Gastroscopy to study the function of the stomach.
Back pain between the shoulder blades: treatment methods
How to treat?
It is necessary to choose a treatment method depending on what preceded the pinched nerve in the thoracic spine. However, there are general rules for treating pinched nerve roots that will help you get rid of the unpleasant condition.
Drug treatment
If you go to the doctor with complaints of back pain and you are found to have an injury, you will be prescribed a list of medications. These will be:
- antispasmodics;
- drugs to improve blood circulation;
- medications for inflammation;
- vaso-strengthening.
Additionally, painkillers may be prescribed depending on the general condition of the patient. As soon as the condition improves, other treatment methods can be used.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is combined with gymnastic exercises, which allow you to recover and prevent recurrent injuries in the future. If you are experiencing pinching in the thoracic spine, you may be prescribed physical therapy:
- ultrasonic;
- laser;
- electrical stimulation of muscle tissue.
However, all these treatment methods can be used only after the patient’s general condition has improved and pain has been relieved.
Surgical intervention
As a rule, during the treatment of pinched nerve tissue, surgical interventions are avoided. But they will be indicated in a number of cases when there is no improvement in the condition for a long time, and the situation is getting worse. Radical treatment methods will be indicated if:
- conservative treatment was not effective;
- the pain spread further;
- the muscles began to atrophy;
- complications have appeared that affect the functioning of internal organs;
- pathological processes occurred in the intervertebral discs.
In such a situation, in addition to surgically eliminating the cause of the pain, surgery may be necessary to enlarge the hole in the intervertebral disc. But most often, treatment with medications and exercises for severe pinching of the thoracic spine can achieve the desired result, and surgery is a last resort.
The main symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
Chest pain with osteochondrosis is the main symptom of the clinical picture. However, considering the general symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, we can also highlight:
- difficulty breathing, chest tightness;
- difficulty in bending;
- periodic occurrence of a feeling of freezing of the extremities due to circulatory failure;
- brittle nails and hair;
- nausea, digestive disorders;
- pain that is easily confused with that that accompanies cardiovascular diseases;
- soreness of the mammary glands in women;
- discomfort and difficulty swallowing, cough.
The manifestation of several symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis requires immediate consultation and a full examination by a specialist in order to make an accurate diagnosis and determine a treatment plan for thoracic osteochondrosis.
Prevention
In order not to think about how to remove pinching in the thoracic spine, prevent pathology. Maintain good posture, keep your weight under control, lift weights correctly - do not bend over, but squat. If your work involves a computer or long periods of sitting at a desk, do exercises and breaks. In addition, you need to monitor your diet, adequate intake of vitamins and minerals, basic physical activity, and lead the healthiest lifestyle possible. In this case, it will be possible to maintain the health of the spine even in old age.