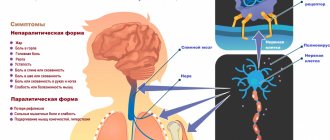
Autism is a psychomotor development disorder characterized by impairments in social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, accompanied by restricted behavior and stereotypical actions. The first clinical signs begin to appear, as a rule, in the first two years of a child’s life, actively progress until the age of 12, then they are characterized by some regression - the patient seems to “outgrow” the disorder.
How does autism manifest?
As already noted, symptoms most often begin to appear in childhood. Parents, for their part, should devote more time to the baby and carefully monitor his behavior. In this article we will talk about the signs of autism in adult women and men:
- Senseless, erratic movements of the arms, head and other parts of the body.
- The patient makes up his own rules and strictly follows them. For example, he puts things in a strictly certain order.
- Increased irritability and manifestation of aggression to any changes in his usual environment. For example, rearranging furniture in a room.
- Strict adherence to certain regimes and routines.
- The patient often repeats actions and sees only one direction.
- Sometimes there is an excessively high level of activity, reaching the point of insanity; the patient can easily bite or hit himself.
Of course, such symptoms can also be observed in a completely healthy person. But here we are talking about pronounced, permanent signs. And this is the first alarm call.
When it comes to depression, we imagine a gloomy, apathetic person. His judgments are negative, his mood is decadent, his self-esteem is low, and his outlook on life is quite sad. Read more in the article: “hidden depression: symptoms.”
Experts are actively studying this problem and monitoring patients for a long time. Research has identified additional symptoms of autism in adults:
- almost all patients with pathology have a low level of intelligence;
- seizures of various types are observed in a quarter of patients;
- a person suffering from autism cannot concentrate for a long time, lack of perseverance;
- unjustified outbursts of anger usually arise as a result of an attempt to explain something or a misunderstanding of the interlocutor’s arguments;
- violation of the usual eating regimen, lack of appetite, requirement of the same diet, identical arrangement of plates and other utensils;
- sleep disorders, most often expressed in insomnia, that is, a person takes a long time to fall asleep, gets up in the middle of the night, wakes up too early, etc.
Diagnosis of autism
The diagnosis of autism in adults is made by a qualified doctor based on anamnesis, a survey and the results of an instrumental examination. Instrumental examination (electroencephalography) allows us to exclude the possibility of concomitant pathologies and carry out differential diagnosis. Differential diagnosis of autism in adults is carried out if schizophrenia or depressive disorders are suspected.
The most commonly used diagnostic methods are:
- EEG to detect seizure activity;
- MRI and ultrasound to detect changes in the brain.
Consultations with a psychiatrist, neurologist, and audiologist are also prescribed. JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg), located in the central district a stone's throw from the metro stations "Mayakovskaya", "Chekhovskaya", "Novoslobodskaya" has the latest laboratory and diagnostic equipment for conducting a comprehensive examination.
Autism syndromes and their features
Autism is a general name for several syndromes that are characterized by common features, but also have their own characteristics and characteristic behavioral patterns.
Kanner syndrome
The disease is characterized by obvious lesions of the cerebral cortex, due to which the patient has serious problems with communication, there are speech defects, aggressive behavior is noted, intellectual data is poorly expressed, and it is almost impossible to find a common language with the person. Able to exist normally only in one familiar environment. No more than two out of ten thousand people suffer from this syndrome; it can be diagnosed in childhood.
Pathologies of the respiratory tract that provoke aphonia (lack of voice) are a common reaction to infections, poor environment, stress and other factors. Read more in the article: “my voice is gone, my throat does not hurt and there is no fever.”
Asperger's syndrome
Asperger's syndrome - as a form of autism, expressed in a pronounced deficit in social interaction and communication, is characterized by limited interests and the same type of actions. Asperger's syndrome is often diagnosed in children of primary school age. As a form of autism, Asperger's syndrome is a dysfunction that affects a person's perception of the world, processing information and relationships with other people.
Rett syndrome
Rett syndrome is a congenital brain pathology characterized by defective mental development with intellectual impairment and leading to social maladjustment. This neuropsychiatric genetic disease is caused by gene mutation. It is manifested by progressive mental retardation mainly in girls, muscle hypotonicity, unsteadiness of gait, scoliosis, constipation, loss of acquired skills, respiratory disorders, paresis and paralysis. The mechanism of inheritance of Rett syndrome is dominant, linked to the X chromosome. The syndrome is extremely rare in boys. For them it is incompatible with life.
Video - Autism in adults: symptoms, causes, forms, diagnosis, treatment
Autism
4693 23 June
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Definition
Autism, or more precisely, autism spectrum disorders (ASD), is a group of mental disorders that are characterized by impairments in social interaction and communication - the process of communicating and transmitting information to other people. In autism, restricted, stereotypical, repetitive behavior is observed. In different patients, the disorders are expressed to varying degrees, and they may or may not be accompanied by disturbances in speech and intellectual development.
The first signs of the disease are observed already in infancy or early childhood, anomalies in social functioning and behavioral characteristics persist throughout life.
Causes of autism
The causes of autism spectrum disorder are not fully understood, but genetic factors are believed to play a major role. It is known that the risk of having a child with ASD increases with the age of the parents.
There is a possible connection between the occurrence of ASD in a child and features of the course of pregnancy: prematurity of the fetus, the use of valproic acid by the mother during pregnancy to treat epilepsy, manic-depressive psychosis, migraine, as well as gestational diabetes in the mother (diabetes mellitus that develops during pregnancy). It is unlikely that any of these factors is critical in the development of ASD, but can be realized in interaction with genetic predisposition.
Autism is more often diagnosed in boys, with a gender ratio of approximately 3:1.
Since the mid-1990s, there have been concerns about the possible link between vaccination and ASD. Current epidemiological data indicate that there is no such association. Moreover, there is no evidence of an association between vaccine use and the risk of ASD, even when vaccinating children at risk - siblings of children with ASD. It has been proven that the preservative thiomersal and aluminum adjuvant contained in inactivated vaccines do not increase the likelihood of ASD in vaccinated children. According to many international studies, changes in the vaccination schedule, withdrawal of any vaccines and their components did not affect the incidence of ASD.
Classification of the disease
Depending on the number of symptoms and their severity, there are three main types of ASD: childhood autism, atypical autism and Asperger's syndrome.
Asperger's syndrome is the mildest form of ASD - intelligence is not affected, changes can be regarded as personality traits and do not interfere with a person's professional development and social adaptation.
There is a division of ASD depending on the presence or absence of intellectual disabilities and the person's ability to use spoken or written language as a means of expressing needs or desires.
Symptoms of Autism
The main manifestations of ASD are impairments in social interaction, communication (anomalies in communication) and limited, stereotypical, repetitive behavior. In addition, patients often have other nonspecific problems: various phobias (fears), sleep and eating disorders, aggression and auto-aggression (aggression directed at oneself). Contrary to popular belief, autism spectrum disorders are not associated with high levels of intelligence in most cases, although some patients may have extraordinary abilities in some area of knowledge.
Let us dwell in more detail on the description of the main manifestations of the disease.
Disorders of social interaction and social communication. Parents pay attention to the fact that the child rarely uses eye contact, gestures, facial expressions and posture to regulate social interaction; he has reduced interest in interacting with peers and adults. The child may not speak or begin to speak with a strong delay, and if he does speak, he does not start a conversation, does not ask questions, communicates exclusively on topics that interest him; may repeat the same words and phrases over and over again. The baby has no desire to be held; he does not always distinguish his parents from other people. Such children do not look at the interlocutor, may not respond to speech addressed to them, to requests, may not respond to names, they do not or are reluctant to enter into dialogue, and do not smile in response.
Often, unusual behavior can be observed in a child with autism, for example, violation of bodily boundaries, lack of embarrassment or excessive anxiety when interacting with new people, monotonous scenarios in communication.
After the age of 7 years, some children with ASD remain speechless or have a minimal vocabulary. Other children, when starting to communicate, are unable to build long-term friendships and respect social rules. The problem for many older children and adults with autism is the inability to understand and feel the state of other people, their mood.
People with ASD are characterized by naivety and simple-mindedness, they do not understand irony and humor well, and have difficulty maintaining a dialogue and understanding the rules of behavior.
Many patients with ASD retain excessive or, conversely, absent gesticulation, unstable or excessive eye contact.
Stereotypical, repetitive behavior, limited interests and hobbies. With the exception of Asperger's syndrome, most patients have a decrease in intelligence of varying degrees of severity. Children with ASD are characterized by unique play activities; for example, a child may use toys in an unusual way: throw them around, lick them, or perform other monotonous manipulations. Already in early childhood, selective interests often manifest themselves - for example, this can be the study of moving objects, a passion for narrow topics (interest in the alphabet, numbers, names and individual characteristics of objects). Such children experience significant difficulties when it is necessary to switch attention.
With age, the set of symptoms may change in content and severity. Many older children and adults are characterized by inflexibility of thinking, manifested by a lack of response to changing environmental conditions, difficulty in assimilation and use of new information, practical skills, and an excessive tendency to detail.
Diagnosis of autism
When collecting complaints and examining the patient, the doctor pays attention to the patient’s behavioral characteristics and assesses the current psychiatric status and level of development.
To clarify the diagnosis and increase the accuracy of clinical diagnosis, additional standardized methods related to the “gold standard” are used: ADOS-II and ADI-R.
ADOS-II is a test administered by a child or adult psychiatrist or clinical psychologist. It consists of observing the patient performing certain tasks in a playful manner. Depending on age, ability to speak and play, the doctor chooses one or another module - a type of testing. Modules vary in the complexity of the proposed games, activities and the presence of speech tasks. Module 1 is used for children speaking in separate words. 2nd - for children using sentences of several words. 3rd – for children who communicate freely. 4th – for freely communicating teenagers and adults. Using a certain set of toys and objects, the specialist creates various play situations. He observes the work being done, evaluating facial expressions, words, and methods of solving the proposed tasks. Completing the tasks lasts about an hour, after which the specialist processes the test results and draws up a conclusion. Usually the test is recorded on video, which helps make a more accurate diagnosis and provides an opportunity for other specialists to assess the child’s condition.
ADOS-II is not the only criterion for diagnosis. The ADI-R screening may be used as an additional test to collect more data.
ADI-R - an interview containing about 100 questions, conducted by a psychologist or psychiatrist; but not with the patient, but with his parents or other close people. Questions aimed at assessing:
- quality of social contact;
- quality of communication and speech characteristics,
- patterns of behavior (repetitive, restricted or stereotyped actions).
To clarify the direct cause of ASD, genetic testing may be recommended for children and adolescents with an already established diagnosis.
It is compiled according to an individual plan with the involvement of geneticists or other specialists. Instrumental examination methods are of secondary importance and are not leading in the diagnosis of ASD. Electroencephalography (EEG), computed tomography (CT) of the brain, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain are not recommended for all children and adolescents with ASD or suspected ASD. On the one hand, this is due to the fact that difficulties may arise during the examination due to ASD-specific impairments in the patient’s communication and behavioral skills. On the other hand, these studies cannot confirm or refute the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder, but can be indicated for making a diagnosis and determining treatment tactics if the presence of other disorders is suspected, for example, epilepsy or a brain tumor.
Which doctors should I contact?
Autism may be suspected. Confirms the diagnosis, prescribes therapy and observes patients for children, and then for adults, a psychiatrist, neurologist, and psychologist.
Treatment of autism
There is currently no direct treatment for ASD. Prescribed medications, for example, from the group of antidepressants, can help solve various nonspecific problems - sleep and eating disorders, increased irritability, attacks of aggression directed at oneself or others. The main treatment methods for ASD are predominantly non-pharmacological. They include educational and psychological assistance aimed at socializing a person with ASD - the earlier assistance is started, the better the child’s development prognosis.
There are many methods of treating and helping patients with ASD that have no proven effectiveness: gluten-free and casein-free diets, brain micropolarization, the Tomatis method, bioacoustic correction, art therapy, as well as hippotherapy, dolphin therapy and many others. If parents insist on using these methods, it is important to understand that they should not be used in place of a primary treatment program.
Nootropic and peptide drugs are often used in the treatment of patients with ASD. There is currently no convincing evidence of their ability to influence the development of cognitive and language skills. At the same time, they can increase motor activity, cause disinhibition and sleep disorders.
Complications of the disease
With autism, various damages are possible that the patient inflicts on himself and others.
Due to impaired cognitive functions, speech, and difficulties in interacting with others, patients with ASD, with the exception of patients with Asperger syndrome, in most cases cannot live independently, study and work.
Due to the high pain threshold and behavioral characteristics of those suffering from ASD, diagnosis and treatment of other diseases is difficult.
Prevention of autism
There are currently no specific measures to prevent ASD. However, early diagnosis is a necessary condition for organizing early comprehensive care for the child, which can improve the prognosis.
Sources:
- Clinical recommendations. Autism spectrum disorders. Developer of the clinical recommendation Association of Psychiatrists and Psychologists for Evidence-Based Practice Approved by the Scientific and Practical Council of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, 2021. – p. 52.
- Bozhkova E.D., Balandina O.V., Konovalov A.A. Autism spectrum disorders: current state of the problem (review). Modern technologies in medicine. T. 12, No. 2, 2021. pp. 111-120.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Frequency of symptoms of autism
| Sign | Frequency of occurrence |
| Desire for isolation | Often |
| Difficulties in communication | Often |
| The desire to do one thing | Rarely |
| Retardation of activity | Often |
| Hearing impairment | Rarely |
| External defects | Often |
| Aggression | Rarely |
| Difficulty understanding information | Often |
| Emotional disruptions | Often |
| The difficulty of understanding another person's emotions | Often |
This table was compiled using only 100 patients, so results may vary slightly in a larger study.
Examples of autism tests for adults
The tests are used only during the initial screening of an adult patient to determine the need for further evaluation. The most popular and most frequently used diagnostics will be discussed below.
AspieQuiz
The technique consists of 150 questions that affect personal, professional and social areas of life. Examples of questions are: is it difficult for a person to be around strangers, do you have problems with asexuality, how passionate are you about your business, and so on. After answering all the questions, testing will assess your intellectual, social characteristics and ability to accept incoming information.
RAADS-R testing
This testing can only be completed in a specialist’s office, since the online tests offered cannot give an accurate result. The peculiarity of this test is that it absolutely does not give false positive results, since during the examination behavioral characteristics are taken into account not only at the present moment, but also up to 16 years of age. In psychology, this age is critical and marks a kind of transition from puberty to adulthood.
TAS20
This test is designed to test the sick person’s ability to perceive the emotions of the interlocutor. According to previous studies, only 20% of people with autism can understand another speaker. Moreover, this recognition may be somewhat inhibited. The test consists of three scales: how well a person recognizes the emotions shown to him, how well he can describe them, as well as features of externally oriented thinking.
Which test to take for a particular patient is determined by the attending physician. You are only allowed to take the ASPIE on your own on the Internet, but with its results it is still better to contact a psychologist or psychotherapist.
"Awakening"
Typically, parents begin to worry about their child's development when he or she approaches two years of age. Before this, any lags and deviations can be explained by the individual characteristics of the baby, and one can hope that they will gradually smooth out. By the age of two, an ordinary child, as a rule, masters the simplest skills, but even when this does not happen, he still understands what adults want from him. It’s the same with language: even if he doesn’t speak yet, he understands speech addressed to him quite well, as can be judged by his reactions.
table
Let's try to list the oddities in the development and behavior of the child that cause concern among parents:
- the child does not make eye contact;
- speaks about himself in the third (he) or second (you) person;
- repeats words and phrases all the time;
- the child began to speak the first words, but speech disappeared;
- does not utter words, hums;
- is not interested in toys, peers, does not play with other children;
- the child is distant, ignores the mother, does not respond to requests, does not respond to his name;
- shakes his head, hands, sways;
- walks on tiptoes;
- chews fingers, hands;
- hits himself in the face;
- the child has hysterics, attacks of aggression;
- afraid of strangers/strangers;
- gets scared by sounds, shudders;
- afraid of light, turns it off all the time.
If any of these traits are present in your child, it is not necessarily autism. However, it's worth worrying about. There is a short diagnostic test consisting of three questions:
- Does your child look in the same direction as you when you try to get his attention to something interesting?
- Does your child point at something to get your attention, not to get what you want, but to share your interest in the subject?
- Does he play with toys, imitating the actions of adults? (Pours tea into a toy cup, puts the doll to sleep, not just rolls the car back and forth, but carries the blocks in a truck to the construction site).
If the answer to all three questions is negative, the parents of a 2-3 year old child have reason to show him to a specialist. If, on the contrary, it is positive, then most likely the delay in speech development and the acquisition of skills has another reason, not autism.
Diagnosis of autism is carried out according to certain criteria, in comparison with which the attending physician can evaluate the behavior and condition of the patient. Early diagnosis and timely treatment will improve the quality of life.
A variety of autism tests are administered to children, adolescents, and adults to identify specific developmental delays. You can take any test yourself (for example, an online test on the Internet) by filling out a questionnaire and determining the result based on the number of points scored. The data obtained is not a final diagnosis.
Types of tests for autism:
- Screening (M-CHAT, CARS, ASSQ),
- Diagnostic (ADOS, ADI-R, ABC),
- Assessment of disease control (ATEC) indicators.
Screening tests
Autism tests are required to identify signs of the disorder in children, adolescents and adults. They are intended for objective self-diagnosis and determining the need to contact a specialist.
M-CHAT – Modified Autism Screening Test for Young Children. Used for screening to identify children at risk of developing the disease between the ages of 1.5 and 2.5 years. It can be carried out both during a medical examination and at a specialist’s appointment. Using the test, a preliminary diagnosis is made.
The test consists of 23 questions, the answers to which can be obtained from parental observation of the child. There are several answer options for each question. Two or more matches with the proposed options are a serious reason to seek advice from a specialist in this profile.
TAKE THE M-CHAT TEST
CARS – Diagnostic Scale for Early Childhood Autism. This is one of the most common tests for autism in the United States. Serves as an initial screening for disease signs and severity. The basis for the answers is the child’s behavior, communication and games.
The test is recommended for children from 2 to 6 years old. The questions are divided into 15 groups. For each of them, 4 answer options are given with a different number of points, allowing you to more fully identify the picture of the deviation. Testing requires the participation of the child’s entire immediate environment.
The resulting sum of points determines the severity of the disease:
- 15–30 – autism is excluded;
- 30–37 – mild or moderate autism;
- over 37 – severe degree of autism.
When several people take the test (parents, older generation, teachers), the average score is taken. To confirm the diagnosis, you need to see a doctor and undergo additional tests to rule out organic brain damage.
TAKE THE CARS TEST
ASSQ – used to detect signs of autism in children and adolescents from 6 to 16 years of age. Parents or the patient answer the questions for self-diagnosis. The test consists of 27 questions covering communication with peers, behavior, and games. Each question has 3 answers.
The result is determined by the sum of points:
- up to 19 – absence of disease;
- 19–22 – there is a possibility of illness;
- from 22 and above – autism.
TAKE THE ASSQ TEST
Diagnostic tests
Autism tests are used to determine the extent of the disorder and overall impairment of developmental and verbal communication skills. Suitable for all age groups.
ADOS – Autism Diagnostic Observation Scale. This technique is recommended for diagnosing the disease, regardless of the patient’s age and development of speech communication. The ADOS test consists of 4 modules, each of which takes approximately 40 minutes to complete.
Determining the required module is individual and depends on the patient’s age and speech skills:
- Module 1 – for children speaking in separate words;
- Module 2 – for children using multi-word sentences;
- Module 3 – for freely communicating children;
- Module 4 – for freely communicating teenagers and adults.
During modules 1 and 2, the child and the doctor move around the room. Testing takes place in a game form. For teenagers and adults, table conversation is enough.
ADI-R - Autism Diagnostic Interview. This is a questionnaire, the answers to which provide all the information necessary to detect the developmental features characteristic of autism. To carry out the procedure, you need an experienced psychologist and a patient representative (parents, guardian, educator), who is well aware of the developmental history and behavior of the subject. The limitation of the interview is the level of mental development (at least 2 years). It takes 1.5–2 hours to conduct the interview and sum up the results.
Evaluation of Disease Control (ATEC)
ATEC is a test to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment for autism. This online test is designed to evaluate the results of any technique. ATEK questions are divided into 4 parts (speech and communication, socialization, sensory and cognitive abilities, health and behavior), points are scored depending on the answer to them.
The total number of points is also calculated. Test results:
- 10–15 – no autism;
- 15–30 – slight developmental delay;
- 30–40 – mild degree of autism;
- 40–60 – average degree;
- 60 and above – severe.
TAKE THE ATEC TEST
Treatment of autism
The disease cannot be ignored, as it can progress and can lead to complete isolation and severe aggression of the patient. First, you need to choose an individual approach to the patient, becoming a good friend for him. After this, through conversations and activities to develop fine motor skills, intellectual stimulation, with the help of even the most ordinary mosaics and pictures, the IQ level will gradually increase.
If treatment is successful, the patient will begin to make contact with other people and try to perceive incoming information. If this does not help or does not bring the desired result, medications are prescribed. If severe anxiety and panic attacks occur, the patient will be prescribed antidepressants.
If a patient exhibits severe aggression, he should take antipsychotics, which can suppress irritation by blocking the activity of nerve endings. But it is worth understanding that because of this, the patient can become very slow and poorly perceive incoming information. In this case, analeptics will be prescribed that will increase attentiveness and the ability to think.
An autistic teenager: what you need to know about him
School plays a significant role in the life of an autistic person. Moreover, it concerns not only the education part, but also communication. Children with autism are often bullied by their classmates. Because of this, a warm atmosphere in the family is simply necessary.
Parents should not create already tense conditions.
Firstly , there is no need to look for special manifestations of ASD (autism spectrum disorder) in the child. If he has become more withdrawn, constantly plays computer games and shares less secrets with mom and dad, then most likely this is just a manifestation of the child growing up.
You should not focus on the fact that the child is “different”, is sick with something and develops differently than others. A complex teenager who daily faces relationship problems at school, personal flaws and body changes can withdraw even deeper into himself and distance himself from his family.
How adapted is an autistic person to life?
The disease cannot be ignored, as it can progress and can lead to complete isolation and severe aggression of the patient. First, you need to choose an individual approach to the patient, becoming a good friend for him. After this, through conversations and activities to develop fine motor skills, intellectual stimulation, with the help of even the most ordinary mosaics and pictures, the IQ level will gradually increase.
If treatment is successful, the patient will begin to make contact with other people and try to perceive incoming information. If this does not help or does not bring the desired result, medications are prescribed. If severe anxiety and panic attacks occur, the patient will be prescribed antidepressants.
No matter how strange it may seem, autistic people quite often achieve success in the fields of mathematics and physics. They can ponder over some formula for quite a long time; thanks to their perseverance, they observe rare processes that subsequently lead to discoveries and breakthroughs in science. In addition, people with a mild form of the syndrome can become talented musicians, scientists, directors, models and actors. Bob Dylan, Isaac Newton and even the twentieth US President James Garfield are all examples of autism, which did not prevent it from becoming a legend and history.
If studies have shown that you suffer from autism, or your loved one is faced with this problem, you should not immediately think that life ends there. In conditions of normal social communication, in which there are understanding people and friends who are close in spirit to the sick person, a patient with a similar diagnosis can fully realize himself in the professional and personal sphere.