What does the rash look like (types of rash)
The most common skin rashes are formed by the following elements:
- stains
_ A spot is a reddened area that does not protrude above the level of the surrounding skin. Redness is associated with excess blood flow. When you press on it with your finger, the stain disappears, and after the pressure stops it appears again; - nodules
(papules) are compacted areas that protrude slightly above the skin level. Most often, papules are round or conical in shape. Papules can merge with each other, forming plaques, sometimes quite large in area (for example, the size of a palm). When pressed, the papule also loses its color; - bubbles
(vesicles). A vesicle is an element, usually round in shape, rising above the level of the skin and representing a cavity filled with a clear, cloudy or bloody liquid; - pustules
(pustules). A pustule is a vesicle with purulent contents. The skin at the base of the pustule may also become inflamed; - blisters
are hollow elements of a round or oval shape, slightly rising above the skin level, resulting from limited and acute swelling.
The above elements are called primary
, since they occur on clean skin.
During the course of the disease, secondary elements
:
- areas of hyperpigmentation
or
depigmentation
(skin loses its natural color, becoming either darker or discolored); - peeling
(scales are formed - particles of the dying top layer of skin); - erosion
(superficial damage to the skin resulting from the opening of a vesicle and abscess). In severe cases, ulcers may occur - a violation of the integrity of the skin, involving all layers of the skin - up to the subcutaneous fatty tissue; - when scratching - abrasions
, both superficial and deep; - crust
(formed as a result of drying of sections of a weeping surface - for example, at the site of burst blisters, pustules, as well as ulcers and erosions); - areas of lichenification
(thickening of the skin with an increase in its pattern), etc.
Rash due to infectious diseases
The appearance of a rash on the skin is typical of infectious diseases that mainly affect children: chickenpox (chickenpox), rubella, scarlet fever, measles.
For chicken pox
rashes are found throughout the body, including on the scalp, on the mucous membranes, and sometimes even on the palms and soles. The elements of the rash first look like pink or red spots of a round shape. Then bubbles form in this place. After 2-3 days, the bubbles dry out and crusts form after them. At the same time, elements of the rash at different stages may be adjacent to the body. In general, the rash lasts 5-10 days.
For rubella
the rash consists of small pink-red spots of a round or oval shape. Usually the rash appears first on the face and then spreads throughout the body. The rash usually lasts from 2 to 4 days (sometimes up to 7 days), then disappears - without pigmentation or peeling.
Measles
characterized by a dark red (purple) rash. Unlike the rubella rash, the elements of the measles rash can merge. The rash appears sequentially: first - on the face, neck and behind the ears; the next day - on the torso, on the third day the rash covers the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs, including the fingers. The skin affected by the rash becomes rough. From the fourth day after its appearance, the rash begins to fade in the same order as it appeared. Brown, scaly spots remain at the site of the rash for another week and a half.
Scarlet fever rash
appears as numerous very small red dots that stand out against the background of redness of the skin. The rash covers the entire body, but is most intense in the natural folds of the skin, in the lower abdomen and on the sides of the torso. A characteristic feature of scarlet fever is normal skin color and the absence of rashes in the so-called nasolabial triangle (the area formed by the base of the bridge of the nose and the corners of the mouth). The rash fades away after 3-7 days, leaving no pigmentation behind. After the rash disappears, the skin begins to peel off, and comes off in layers on the palms and soles.
Also, a rash on the body is observed with herpes ,
enterovirus infection, syphilis, tuberculosis and some other infectious diseases.
If the rash is caused by an infectious disease, the skin rash is usually accompanied by other symptoms, primarily fever and intoxication. However, you should not try to make a diagnosis yourself, including by the type of rash. Currently, diseases quite often occur in atypical (“blurred”) forms, many symptoms may be absent, and manifestations of the rash may be mild. However, the very appearance of a rash against the background of other symptoms indicates the severity of the disease.
The most alarming thing is the appearance of a hemorrhagic rash. Such rashes are caused by rupture of surface capillaries and represent pinpoint hemorrhages. When pressed, the elements of the hemorrhagic rash do not disappear and do not even turn pale. This rash may indicate meningococcal infection.
(meningococcal sepsis - blood poisoning). This disease is deadly and develops rapidly. Its initial symptoms are similar to the flu (high fever, vomiting). If a rash is detected against this background, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Stress rash: how stress affects our skin
For most people, stress is an integral part of everyday life.
Skin rashes can be a symptom of stress. In this article, we'll look at the causes of stress rashes and explore how they are identified, treated, and prevented. The effects of stress on the skin Although stress is commonly thought of as a psychological problem, it can also have physical manifestations, such as on the skin. Stress can affect the skin in a variety of ways.
Stress-induced hives
Stress can cause hives Stress can trigger an outbreak of hives. Hives are raised red spots or welts. They come in different sizes and can be located on any part of the body. Areas affected by hives are itchy. In some cases, when touched, they cause a tingling or burning sensation. Hives can occur for a number of reasons, such as:
- Exposure to cold or heat
- Infection
- Certain medications, including antibiotics
The most common cause of hives is an allergen that enters the body. For example, a person with hay fever may develop hives as a result of exposure to pollen. Emotional stress can also cause hives. In response to stress, a number of hormonal and chemical changes occur in the body. These changes can cause blood vessels to dilate, resulting in red, swollen patches of skin. The skin condition with urticaria may worsen for the following reasons:
- Alcohol or caffeine consumption
- Exposure to high temperatures
Stress makes your skin worse Stress can prevent existing skin problems from healing properly. For example, stress negatively affects psoriasis and eczema. When to Seek Help A rash outbreak may be considered acute if it has resolved in less than 6 weeks. If the urticaria does not go away longer, it may be chronic. As a rule, the rash goes away within a few days, in which case there is no need to prescribe treatment. In other cases, you should consult a doctor. Sometimes hives may cover the entire body or be accompanied by:
- Peeling skin
- The appearance of blisters
- Fever
- Pain
Each of these symptoms may indicate a more serious problem or allergy, so don't hesitate to see a doctor.
Treatment
A cold compress can help relieve the itching Treatment for stress rash can usually be done at home using over-the-counter antihistamines. They should help relieve the itching. Cooling the skin can also relieve itching. You can do this by taking a cool bath or using a cold compress. In more severe cases, the doctor may prescribe a short course:
- Strong antihistamines
- Steroids
- Antibacterial drugs
The rash may be associated with the development of other conditions such as angioedema or anaphylaxis. In this case, treatment will be prescribed taking into account the nature of the complications.
Alternative causes of the disease The cause of the rash may be eczema, which appears as red spots on the skin. The rash may appear due to factors other than stress, such as:
- Heat rash. Exposure to hot and humid climates can cause heat rash to develop.
- Eczema. This chronic condition can occur at any age. It is characterized by small bumps on the skin that spread to form dense red patches known as plaques.
- Contact dermatitis. This condition is caused by an allergen, such as certain soaps or gemstones, that comes into contact with the skin.
- Pityriasis rosea. A skin condition with large rashes, often surrounded by small bumps or rashes.
- Rosacea. This rash often appears on the face and can last for weeks or months. It may recur despite treatment.
Prevention
Meditation is an excellent stress preventative. The best way to prevent stress rashes is to reduce your exposure to stress. Unfortunately, this is not always possible. Certain stressors may be unavoidable. For example, work situations or relationship problems. However, there are methods that can help a person cope with stress. You can minimize the impact of stress in one of these ways or a combination of them:
- Regular physical activity
- Healthy, balanced diet
- Meditation or relaxation
When stress occurs, it is important to minimize the discomfort that accompanies it and prevent the condition from worsening.
Skin rash due to allergic diseases
A rash is a common allergic reaction. The rash has an allergic nature in the form of red swollen spots on the abdomen, chest, limbs, less often on the face, which quickly arise, change shape and location, and are accompanied by severe itching. This disease is called urticaria. Contact dermatitis appears as a rash in areas where the skin came into contact with an allergenic substance. Food allergies and allergies to medications (antibiotics, sulfonamide drugs, hormonal drugs, vitamins, etc.) can also manifest themselves in the form of a skin rash.
Types of nerve rash
Nervous allergy is a hypersensitive reaction in the absence of the allergen itself. The inflammatory reaction develops due to irritation of nerve endings - sensitive receptors. At the same time, the same substances as in allergies are released into the surrounding tissues and cause similar changes: itching, swelling, rash and redness. This process is involved in the formation of symptoms of skin diseases (eczema and psoriasis), as well as asthma, migraines, and vasomotor rhinitis.
Urticaria is a disease in which there is redness of the skin, itching and a characteristic rash in the form of irregularly shaped tubercles that can merge with each other. Such changes are provoked by contact with an allergen, exposure to cold, sun, pressure on the skin, as well as emotional stress. Nervous urticaria is quite rare and usually goes away once the stressor is removed. Treatment uses sedatives, as well as drugs that affect the functioning of the autonomic nervous system.
Nervous scabies, or neurogenic itch, is a condition that forms in the brain, while the skin is not affected by the disease. Itching can originate from the brain, or from peripheral nerves and receptors. Central neurogenic includes, for example, a feeling of itching in the amputated limb. The nerves may be pinched by a tight muscle or misaligned bone, causing itching. With shingles, there may also be itching in the area of the affected nerve. In the treatment of nervous scabies, glucocorticoids and antihistamines are ineffective. In case of nerve damage, local anesthetics and capsaicin (a red pepper alkaloid that affects pain receptors) help. If the cause is in the brain, medications are prescribed that act on the pain processing centers in the central nervous system. These are pregabalin and gabapentin.
Rash due to skin diseases
A rash on the body can also be a manifestation of skin diseases such as:
- acne (acne) - manifests itself in the form of papules and pustules on the skin of the forehead, cheeks, nose and chin;
- psoriasis;
- fungal diseases;
- scabies (caused by microscopic parasites).
Redness of the skin is also caused by prickly heat (for infants - a typical reaction to overheating), insect bites, etc.
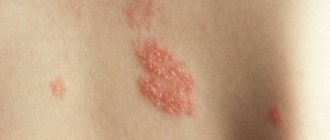
Skin rashes due to nerve damage (shingles)
Skin rashes with nerve damage are most often associated with viral aggression. The appearance of skin rashes indicates a decrease in the body's immune defense. Our task is to relieve you of skin rashes and improve the functioning of the immune system so as to stop the viral attack. Read more about the treatment of herpes zoster
Skin rashes with herpetic lesions of peripheral nerves (herpes zoster) appear on the skin in the area of the nerve affected by the virus.
Symptoms of herpes zoster:
- severe pain that gets worse when touching the skin,
- bubbles giving way to crusts,
- redness,
- severe itching is possible.
Where to treat the rash
When trying to independently determine the nature of the rash, it is easy to make a mistake. Therefore, in case of skin rashes, you should consult a dermatologist or general practitioner (pediatrician, family doctor or internist).
If there is sufficient reason to suspect the allergic origin of the rash, you should see an allergist-immunologist. By taking antihistamines on your own, you can achieve the disappearance of skin rashes, but it is worth remembering that in this case the cause of the allergy remains unknown, complex treatment is not carried out, which means that more acute allergic reactions should most likely be expected in the future.
By contacting the “Family Doctor”, you will receive qualified assistance from experienced dermatologists, allergists-immunologists, and pediatricians who will determine the cause of the rash and prescribe an effective course of treatment.