Examples of abstract thinking
Abstract thinking will help prepare a child for adult life. For example, in childhood there is only the awareness that in the future you will have to work, since money is necessary. The child does not yet understand what he will do and does not realize what exactly he wants to do. But he accepts the inevitability of getting a job. Therefore, when he grows up, it is not difficult for him to accept this fact. The child thought about this, so he easily accepted this fact, although he had not encountered this before. The same applies to plans for the future. It is impossible to know what awaits in life in a few years. Fantasies and plans will help you achieve your goals. The future does not yet exist, but there is a desire to make it the way it appears.
Fantasies
Abstract thinking forms the basis of exact sciences, for example, physics and mathematics. Without assumptions and reasoning, it is impossible to prove the theorems on which knowledge is based. A person deals with objects that he cannot see and cannot touch. Numbers and formulas are abstract concepts. Calculations are carried out with them, they are compared, measured, and worked with. Research leads to conclusions
Abstract-symbolic thinking is important for people of science to assimilate information using codes and formulas
Signs that you have developed abstract thinking:
1. You spend a lot of time thinking about big questions such as “What is the meaning of life?” or “What is the nature of consciousness?”
2. You are constantly surprised and wondering why. Most likely, as a child, you annoyed others with your endless questions.
3. You don't like doing anything unless you see a good reason for it. This “just like that” option doesn’t suit you.
4. You really don't like following step-by-step instructions and, most likely, you will figure everything out on your own.
5. You don't like routine and get tired easily if you do the same thing over and over again.
6. When you think about something new, you often compare it with what you already know, even if these ideas seem unrelated to you at first.
7. You can come up with metaphors and analogies and connect ideas in new ways.
Tests to determine the severity of abstract thinking
Before answering the question of how to develop abstract thinking, you need to determine the level of its expression in a person. Psychologists offer a number of techniques that will help determine the level of this reasoning skill in a person. Such techniques include:
- a technique to determine the type of thinking ability. A positive result is an indicator of the predominance of an abstract-logical mindset. Such tests are issued in the form of questionnaires. As a rule, in them a person needs to choose the statement that is most suitable for him. It is also possible to work with various pictures;
- testing to identify cause-and-effect relationships. In these techniques, the subject is given certain conditions on the basis of which he must draw a logically correct conclusion. Typically, such tests are used as terms of non-existent words to determine a person's level of abstraction from explicit details;
- techniques for analyzing proposed word combinations. In the course of such studies, the subject must identify the correct pattern due to which various verbal combinations are combined with each other. Then they need to be extended to the following phrases.
To get accurate results, experts recommend going through several techniques. As a rule, abstract thinking is typical for people prone to self-development. This is owned by people who have dedicated their lives to science:
- mathematics;
- theoretical physicists;
- programmers.
Those with this kind of thinking start from distant concepts and rely on general information. Due to the specifics of such thinking, based only on hypotheses, scientists have made many discoveries in all branches of science.
Specifics of abstract thinking
Scientists identify two main pieces of information about abstraction; in other words, we are talking about a process when the ability to think gradually moves to the awareness of abstract concepts:
- Abstraction within empirical psychology. The participants in this teaching brought the abstract only to the sensual.
- Abstraction within the framework of realistic psychology. Scientists who thought in this direction separated the abstract from the sensual. At the same time, they said that it is thought that generates the abstract content of a phenomenon.
Watch a video about the abstract thinking test.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=vnt0QeQwNao
Based on this, we can conclude that abstract thinking is characteristic only of people. Speaking about abstract thinking and its forms, one cannot help but talk about the goals this thinking is aimed at. There are two main goals:
- Formal. In this case, it is meant to identify the main properties that are most important for theoretical analysis.
- Meaningful. In this case, the calculation of qualities that are of practical importance occurs.
Basic signs of abstract thinking
When studying the issue of abstract thinking, you should pay a lot of attention to becoming familiar with its main features:
- the ability to make the correct conclusion remotely without direct contact with the object;
- synthesis and analysis;
- the ability to find relationships and analyze them;
- identifying precise cause-and-effect relationships;
- the ability to easily operate with concepts that do not exist in the real world;
- there is no need to interact with the external environment in order to identify its patterns;
- searching for the relationship between qualitative and quantitative changes in an object;
- clear systematization of the information received.
Abstract thinking is considered the main tool in logic. Scientists claim that this concept originated within the framework of this science. The main aspect of this type of thinking can be called the possibility of reflection. It is seen as an analysis of one’s own thoughts and behavior patterns as someone else’s in order to rethink them.
A person with developed abstract thinking can:
- think logically;
- make correct conclusions;
- argue reasonedly;
- look for connections between events and objects;
- successfully find favorable conditions for acquiring new knowledge;
- look for rational methods in solving various problems.
Thus, the main feature of this type of thinking is the ability to realize the features of one’s thoughts during active cognitive activity.
Share your opinion on the topic at what age abstract thinking is formed and what its role is in human psychology, in. And also watch a video about the need for abstract thinking.
Types of abstractions
As you remember, abstract logical thinking involves manipulation of abstractions (units of specific patterns). And in order to get closer to understanding abstract thinking and its mechanism, it is necessary to talk about the types of abstractions and their purposes.
There are six types of abstractions:
- isolating abstraction – allows you to highlight the components of phenomena on which attention is focused;
- generalizing abstraction – allows you to highlight a general characteristic in a specific phenomenon, cutting off individual characteristics;
- constructivization – allows you to give clearer forms to phenomena with “blurred” boundaries;
- idealizing abstraction - allows you to replace the real properties of a phenomenon with an ideal template that eliminates shortcomings;
- abstraction of actual infinity - allows you to define infinite sets as finite;
- primitive sensory abstraction - allows you to highlight some properties of a phenomenon and ignore others.
In addition, abstractions are also divided by purpose:
- formal abstractions - necessary for considering phenomena based on external manifestations, without these phenomena not existing;
- meaningful abstractions - necessary for isolating from phenomena properties that can exist outside these phenomena - autonomously.
By operating with abstractions of all kinds (and thanks to the possibilities they provide), we can “select” from the world around us what cannot be recognized using the natural senses. The general patterns of all phenomena are conveyed through special linguistic expressions. With them, we no longer need to identify different concepts each time, because we learn about them from the very beginning of life - from parents, educators, teachers, etc. And it is here that we need to talk about the forms of abstract thinking.
Forms of abstract thinking
Through abstract thinking, a person, in the process of reasoning, discovers new facets of the object being studied and expands his knowledge about the surrounding reality.
Forms of abstract thinking:
- concept;
- judgment;
- inference.
Concept
The concept reflects the result of human intellectual activity, as a result of which a general understanding of the essence of an object is formed based on its essential features. Essential features are those features that allow an object to be classified into a particular group. For example, the concept “Car” has a number of insignificant features, such as color, brand, engine power. These signs vary from car to car. It doesn't matter what color the car is, it's still a car. But this concept also has essential features that allow it to be classified in the “Cars” group: the presence of an engine and four wheels.
The definition of a concept is the establishment of all essential features. Separately, the features are necessary, but together they are considered sufficient for the formation of a concept.
For example, the presence of an engine and four wheels separately are necessary signs - a car will not move without wheels, without a motor it is no longer a car, but a trolley. Together, these signs are sufficient to call an object on wheels with a motor a car.
A concept can be everyday, obtained from personal experience, and scientific, obtained through teaching by someone.
Ways to define concepts:
- analysis - decomposition of the subject being studied into individual components;
- synthesis - composing a whole object from disparate parts;
- generalization - the unification of objects that are similar in certain characteristics;
- comparison - determining the differences or similarities of objects;
- abstraction - concentration on some properties and removal from others.
Rice. 2. Basic mental operations: analysis, synthesis, generalization, comparison, abstraction.
Judgment
Judgment is a form of thinking that reproduces not a set of properties of an object, as a concept, but connections and interactions between objects. Judgments are expressed in the form of affirmation or denial.
Judgments can be simple, for example, “Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky is a composer,” or complex, “Spring has come, migratory birds have returned from warmer climes.”
A proposition can be said to be true or false.
Inference
An inference allows you to construct a new conclusion from one or more premises.
For example, “Vegetables can be eaten,” “Onions are a vegetable,” “Onions can be eaten.”
What tools does abstract thinking use: types and examples
Formal methods use three main modes of mental activity. However, this is not all. To gain deeper knowledge about the subject of research, a lot of auxiliary tools are used.
Analysis
The process of speculative division of an entire object, phenomenon or process into its component parts. Depending on the subspecies used, it is then possible to study each individual component or highlight the most significant features. An example of the first is the concept of crime in law. Includes objective and subjective sides, object and subject. It is possible to separate a very real object during analysis, to physically separate its parts. In the study of mechanisms, human organs, tissues within the framework of anatomy, pathological anatomy, etc.
If we talk about the second subtype, the most typical example is the development of a definition of a concept, the derivation of a definition. For example, a person. What properties can be identified? Walks upright, has two pairs of limbs, eyes, hearing organs, is intelligent, has the ability to think and speak, etc. When analyzing the second type, only essential features need to be highlighted. What is important in this case? Speech ability, mental activity, upright posture. This is how this technique is used.
Synthesis
The opposite phenomenon to analysis. The process of combining component parts into a whole. It is especially actively used in scientific practice, in the application of legal norms by specialists in the field of jurisprudence, doctors when conducting diagnostics and drawing up a unified clinical picture (then hypotheses regarding the disease are put forward). Mental operations are closely related to everyday life.
Systematization (or classification)
Distribution of a group of concepts or real objects into classes. It has a formal basis - that is, the line along which the distinction is made. An example is geometric shapes. The criterion is the number of angles. Absent - ovals, ellipses, circles. Three is a triangle. Four - square, parallelogram, rectangle. And so on. The most productive use of classification is in scientific practice and statistics.
Comparison or comparative analysis
It consists of comparing two structures and objects. In identifying similarities and differences. It only makes sense when the objects are truly similar. There is no point in comparing people and fruits, it is absurd and will not bring any new knowledge, since the essence is already well understood. But the comparison of humans and primates, humans and animals, and so on, makes sense in the context of evolutionary concepts, biological, anatomical knowledge.
Specification
Or the deductive method. Based on the transition from general knowledge to a particular case of the existence of the same phenomenon. To take an example: in European countries it is hot in the summer. Ukraine is a European country. Consequently, it is hot in Ukraine in summer. Essentially this is a type of inference.
Induction
There is also the opposite phenomenon. When a movement is made from private knowledge to general knowledge. It would be fair to give this option here. It's hot in Ukraine in the summer. Ukraine is part of Europe. Consequently, European countries are hot in summer. There's a big problem here. While deductive inferences are mostly true, inductive inferences are likely to be false. Because the law of sufficient reason is violated. Generalizations are made with great caution and require empirical confirmation.
Analogy
Transferring the properties of one object to another. Such a transfer also requires a careful approach, since the truth is not always the case. However, this is a bold technique; it allows you to take a fresh look at familiar things. It is used not only in scientific activities, but also in applied fields. Based on this principle, some laws of aerodynamics were determined, aircraft were designed, etc. The basis was studies of the life activity of birds and biological creatures.
These tools, when used correctly, provide a wealth of information. Allows you to achieve high-quality results in research and practical activities. The areas can be very different. Forms of abstract thinking in such a context also act as tools, only more general ones.
Upon analysis, the difference between abstract and concrete thinking becomes clear. If the first deals with logical constructions and follows clear laws, the second is spontaneous and based on experience, working with specific objects here and now (although the logical variety can also deal with specific objects if they have meaning within the context of the situation).
Components of logical thinking
Having realized the tasks and forms of logical thinking, we can clearly formulate a definition of this concept. This is a process with evidentiary properties. The goal is to obtain a conclusion from the premises. You should also consider its types in detail.
Figurative-logical thinking
This variety is otherwise called visual-figurative thinking. The situation is presented visually, operations are performed on the images of the objects included in it. In essence, it is imagination, which allows you to give a variety of vivid characteristics. Such mental activity and logical thinking begin to develop from the age of 1.5 years in childhood. You can check the level of development using the Raven Test - an auxiliary questionnaire. It allows you to derive your IQ, which is essentially a diagnostic of logical thinking with an objective assessment.
Development from 1936 by D. Raven and R. Penrose calculates IQ without depending on a person’s education or social affiliation. The progressive matrix scale is based on images of figures and does not include text. There are 60 tables with pictures connected by some dependence. The missing figure is located at the bottom of the image among 6 - 8 others. A person must establish a pattern, choose the right element that is missing. Tables are offered according to the principle of increasing task complexity.
Abstract logical thinking
This type uses non-existent categories - abstractions through which they think. Relationships are modeled not only for real objects, but also between created figurative representations. It is this kind of thinking that includes the forms: concept, judgment, inference.
Verbal and logical thinking
This type uses speech structures and language means. Verbal or verbal-logical thinking involves the ability to speak competently with the skillful use of the thought process. These are public appearances, arguments, and other situations where thoughts are expressed verbally.
Development methods for people of different age groups
Children
Abstract thinking develops automatically in children . To improve this process, parents work with the child. How to develop the ability for abstract thinking? It is important to begin development in the first years of life when the brain is forming and growing. The child must move from working with specific objects to operating with conventional concepts and expand his horizons.
The following exercises will be useful for this::
- Spread a blot on a sheet of paper with ink or paints. Together with your child, create a drawing from it: the sun, a person’s face or a flower.
- Come up with original names together with your baby. While walking down the street, give the object 3 interesting names. This can be applied to animals and people.
- Create a home theater. For performances, you can create costumes together from scrap materials.
- Playing shadow theater is an effective remedy.
In addition to exercises, crosswords, puzzles, anagrams, and riddles will be useful. Logical games will also develop abstract thinking (from low to intermediate level, etc.): chess, checkers, puzzles, dominoes.
At first it will be difficult for the child to study, but constant training will quickly lead to the necessary skills: the level of abstract thinking in children develops much faster than in adults. Read the article on how to develop verbal and logical thinking in a child.
How to develop abstract thinking in preschoolers, watch the video:
Adults
Logic and abstraction in thought processes develop more complexly in an adult than in a child : it has already formed and has lost its initial flexibility.
It is more difficult for an adult to perceive and assimilate knowledge (can lead to a low level of thinking). Performing special exercises will develop creativity and the ability to think abstractly. They must be performed with your eyes closed:
- Introduce the people you had a chance to communicate with during the day. If possible, remember in the smallest detail what they were wearing, how they spoke and gesticulated, what pitch and timbre their voice was, what facial expression they spoke with. At the same time, reproduce your own feelings.
- Begin to imagine emotions: happiness, joy, anger, disappointment, melancholy, tenderness, calm. The image of each emotion must be recreated in the brain.
- Provide an image of terms, concepts or ideas that are interesting to a person. At the same time, you need to monitor the emotions and sensations that accompany fantasies.
The exercises should be supplemented by solving puzzles, logical problems, Sudoku, and rebuses. It’s worth inventing new words that don’t exist, or drawing.
Books will help adults effectively and quickly improve their ability to think abstractly:
- Kirill Berendeev “Abstract thinking”.
- Andrey Rodionov "Intellect-training".
- Philip Carter "Grow Your Mind"
- Edward de Bono "Teach yourself to think."
- John Medina "Brain Rules"
An interesting practice is to read books diagonally, upside down, from the last page to the first. These methods help develop the ability to think abstractly.
Where is it used?
Children, with the help of abstract thinking, draw, design, sculpt, understand the meaning of riddles, can solve problems, and coherently express their thoughts when describing events. During school years, this type of mental activity helps schoolchildren master mathematics, which requires the ability to operate with a lot of data, divide them into groups, and look for relationships.
Abstract thinking is used in logic, physics, astronomy and other exact sciences, where one must be able to measure, count, calculate, and combine elements into one group. It is necessary for psychologists, philosophers, writers, engineers. Time management is unthinkable without it.
In everyday life, people also constantly use abstract-logical mental activity. Examples of abstract thinking reflect everyday human thought processes. Planning often intersects in the imagination with dreams and fantasies. Young people looking for a job can come up with so many things that, when faced with reality, they cannot stand the conditions offered to them. So girls, waiting for a prince on a white horse, mentally endow their future chosen one with unrealistic traits. This inevitably leads to disappointment in the future.
Peculiarities
Abstract thinking is used by children from the first years of life. It begins to appear along with the development of articulate speech. A younger child fantasizes, thinks about unusual things, explores the world, compares his toys, using abstraction skills. They are underdeveloped, but you can still use them.
School age is combined with an increase in the importance of abstract thinking. The student will need to think outside the box when faced with solving various problems. This is especially true in mathematics, where abstraction plays a big role. Later, when the teenager is in high school, the importance of such thinking will become even greater.
Abstract thinking is also used in philosophy, writing, engineering, managerial psychology, time management and many other areas. Its good development allows you to achieve success in any field.
Signs
Thinking with abstraction has its own characteristic features. They allow us to distinguish it from other thought processes and better understand why abstraction is so useful for a person.
Signs:
- Reflection of the surrounding world without using the senses. A person does not need to use his senses or contact an object to obtain information about it. It is abstraction that allows you to use old existing knowledge to solve a particular problem.
- Generalization of phenomena. By generalizing various objects and identifying their characteristic features, a person is able to quickly access his knowledge. If he is able to identify certain patterns and similarities, then in the future it will be much easier to remember and find the necessary information in memory.
- Linguistic expression. All thoughts are easily expressed in the form of internal dialogue, which can be translated into real life. In this case, abstract concepts can be thought through in the head without the use of linguistic expression at all, and the result will be a final judgment that will be easy to express in speech.
The development of abstract thinking allows you to improve all of the characteristics listed above, which are also useful skills, without which it is difficult to achieve success.
Impact on humans
It is difficult for the average person to imagine exactly what someone with highly developed abstract thinking looks like. Such people, as a rule, always achieve their goals, they are successful and happy. At the same time, something is always happening in their heads: they reason, think about events, imagine the future figuratively, and solve difficult problems. Most often, they speak a complex language, which causes difficulties in communication. Their high efficiency allows them to occupy high positions, and their developed intelligence makes them very important for any company.
Such people may face a number of problems. They are often too selfish, which makes it difficult for them to find true friends. At the same time, people with developed abstract thinking cannot show enough physical activity and are passive in practical work. Sometimes they are careless in appearance, which alienates others.
Most often, men in technical professions have developed abstract thinking.
Examples of abstract thinking
The clearest example of abstract thinking is the exact sciences, such as astronomy, physics and mathematics, etc. Most often it serves as their base. A person does not see numbers and formulas as such, but he can calculate, measure, count, combine objects into groups and find their quantity.
The same goes for life itself. What is life? This is when there is a body in which consciousness functions. We cannot give an exact definition of the concept of “life,” but we can say with precision when a person is alive and when he is dead.
Abstract thinking manifests itself no less clearly when we look to the future. We don't know what awaits us, but we have plans and goals, aspirations and desires. If we couldn't dream and imagine, we wouldn't be able to make plans for the future. Now we are making efforts to achieve results. Our movement through life has a direction. Abstract thinking gives us tactics and strategy that lead to the desired future. This reality does not exist yet, but we are trying to make it correspond to our ideas.
When considering examples of abstract thinking, one cannot help but recall idealization. Many idealize both the world in which they live and the people who surround them. There are, for example, men who dream of “possessing” a woman, and at the same time do not even think that one can only possess an inanimate object or a non-thinking being. There are also women who are waiting for a “prince on a white horse” and do not pay attention to what many “princes” are like in real life.
There is also an excellent example of false judgments. Let's touch on relationships again: some women believe that all men are “bad,” but this judgment is based on bitter experience - situations in which men betrayed these women. In any case, a woman identifies men as a separate class with its own specific properties, and therefore she can attribute to all of them what was manifested in one representative.
From false judgments, among other things, false conclusions often arise. For example, a house may be called “dysfunctional” because of faulty wiring, poor heating, or unfriendly neighbors. Based on his emotional discomfort that arises in the current conditions, a person makes unambiguous judgments, from which conclusions are formed that form a conclusion that distorts reality - after all, the house may well be “normal”, you just need to bring everything in it to mind.
There are many similar examples that can be given, but they will all say that abstract thinking (including the false judgments and inferences that arise from it) constitutes a colossal part of our everyday thought process. It manifests differently for everyone, and there will always be components that require development. Someone may be good at systematizing information, but find it difficult to isolate individual elements of events. Someone can perfectly find correspondences between the particular and the general, but have difficulty specifying something, etc. And in order to train your brain and improve your intellectual abilities, you need to develop abstract thinking.
Why develop abstract thinking in children
Are you convinced that a certain level of abstract thinking is necessary for success in school? Have you realized that your child has problems in the ability to think logically and find non-standard solutions? Do you want to form forms of abstraction in your little schoolchild? Then you need to listen to the opinion of experts. Thus, psychologists warn that the development of thinking is a rather long process and requires daily work. One child may not be able to quickly and efficiently master abstract operations. Therefore, parents need to help him develop abstraction skills. In psychological and pedagogical practice, many methods have been developed for the formation of abstract processes in primary schoolchildren. Parents can focus on the one that seems most accessible and acceptable to them for homeschooling.
Exercises and games for logical thinking
Gaming activities still remain important for younger schoolchildren, so games and exercises are successfully used in the development of abstract thinking. This method is accessible and interesting for children; with its help, you can do complex work to improve forms of abstraction. Each adult can come up with game tasks independently for their child. The main thing is your creativity and ingenuity! To prevent games from getting boring, they can be easily “revitalized” with elements of outdoor games (running, jumping, clapping) or sports objects (ball, skittles, rope). A competitive moment (who can name it faster...) and forfeits are good options. What can you offer for home use?
Synonyms - antonyms
The classic game of matching synonyms and antonyms always attracts children. They enjoy the competition of “who can come up with the first word (synonym or antonym).” You can play verbally, or you can throw the ball to each other with the chosen word. Approximate synonyms (close in meaning): stingy - greedy, throw - throw, dog - dog, slacker - lazy, friend - buddy, damp - wet, lie - not true.
A simpler task for children is to select antonyms (words with opposite meanings). It is carried out similarly to the previous one, for example: friend - enemy, brave - cowardly, future - past, good - evil, grief - joy, beautiful - ugly. Interest in the game can be maintained by introducing game moments: for an incorrect answer, the player gives a forfeit, and then redeems it with the help of a certain task: sing, dance, say a tongue twister, guess a riddle.
Finish the sentence
Similar to the previous game, an exercise is carried out to complete sentences. Players must catch the ball with the beginning of the phrase, and return it with the ending, for example: dogs bark and cats... (meow), in winter it is frosty, and in summer it is... (heat), the car drives, and the plane... (flies). A more complex option - you need to end a complex sentence with a subordinate clause, for example: in winter it’s cold, ... (because it’s frost); the student received an A, ... (because he learned the lessons) and the like.
Decipher it!
Such an exercise must be prepared in advance; at first, pictures or words written on cards are used. Subsequently, when the student learns to divide a word into syllables mentally, it can be carried out in the form of a word game. The essence of the exercise is the following:
- highlight the first syllables of each word and compose a new one (decipher): de lo, river , water (tree); strength la, nor na, queen (tit); ma ma, thorns , Na tasha (car);
- highlight the last syllables and create a new word: airplane , ball ( pilot); bara ban , ut ka (bank); dere vo , lavan da (water).
Three effective methods for developing abstract thinking
Association game
Associations (connections between phenomena and concepts) are considered the most accessible and simple method of developing abstract thinking in children. It is easy to use in everyday life if you invite your child to find various connections between objects and phenomena that surround him. For example, during a walk together, or while traveling to the country, or over evening tea, you can play a word association game. The point of the game is that one concept or image entails another. An adult pronounces a concept, and children must choose words that are in any way related to it. For example, umbrella - rain - puddles - boots - roof; car - trip - passenger car - truck - motor - wheel; summer - sun - warm - fun - swim - sunbathe - vacation. The player can name any word, the main thing is to prove that the words are related. It is interesting to involve all family members in the action and reward the winner who has found and proven the most associations.
As a variant of such a game, you can invite participants to create an associative chain according to a given attribute, for example, yellow and warm - sun - lantern - lamp, etc. Or original associations, for example, hedgehog - Christmas tree - needles - burdock - brush.
The older the child, the more complex the concepts from which associations are built should be. These can be words denoting various relationships in the world around us: between people (family, mom, dad, sister, brother, society, friendship, school); in living and inanimate nature (winter, summer, water, thunderstorm, any animals, forest, tree, fruit, vegetables); emotional processes (joy, grief, love, success, envy, sympathy); phenomena of social life (homeland, peace, war, country) and other concepts that make up the world around us.
Shadow play
The most popular and interesting way to develop abstract thinking, somewhat similar to an association game. With its help, various images are created, by playing with which the child uses all mental processes (memory, attention, thinking, imagination, speech). Shadow theater is easy and simple to organize at home and make it a family tradition. To organize, you will need a sheet, a table lamp, character figures cut out of cardboard or plywood, or a variety of hand movements. The lamp is installed so that it creates a shadow. You can act out any works familiar to children, but not only - performances can be improvised. The main thing is that the child must see the image depicted and be able to act out it. Shadow theater promotes the development of abstract thinking in the child, develops the ability to use and understand symbols: hand movements are concrete, real, and an image is created from shadows on the screen. You have to imagine that these are no longer fingers, but animals that move.
Mental arithmetic
Experts consider mental arithmetic a more effective way to develop abstract thinking - a program for developing mental abilities and creative potential using arithmetic calculations on special accounts (soroban). The technique is designed for children and schoolchildren from four to sixteen years old. Instructions for this technique can be found in more detail on the Internet, in special courses for schoolchildren.
As you can see, it is not so difficult to form abstract thinking in a child at home if you follow the recommendations of specialists. And most importantly, show parental love, care, and attention. Help your little schoolchild see the world around him from all sides and show his abilities.
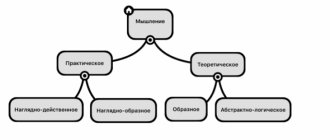
1.6. Types of thinking
Thinking is a complex and multifaceted mental activity, so its types are distinguished on different grounds.
Firstly, depending on the extent to which the thought process is based on perception, idea or concept, three main types of thinking are distinguished:
objective-effective (or visually-effective), visual-figurative and abstract.
These are not only stages in the development of thinking, but also its different forms that are inherent in an adult and play an important role in mental activity. You can speed up and intensify the passage of certain stages of the development of thinking, but you cannot bypass any of them without damaging the mental make-up of the individual as a whole:
- objective-active thinking - thinking associated with practical, direct actions with an object (for young children, thinking about objects means acting, manipulating with them);
– visual-figurative thinking, which is based on perception or representation (typical for preschoolers and partly for younger schoolchildren);
– abstract thinking with concepts devoid of direct clarity inherent in perception and ideas (characterizes older schoolchildren and adults).
Secondly, by the nature of the thinking process we can talk about inferential thinking; which goes step by step, and intuitive thinking, where the final result is achieved without knowing or thinking through the intermediate stages.
Thirdly, if we take the nature of the results of thinking as a basis, then we can have reproductive thinking (when we clearly follow the train of thought of another person, for example, the proof of a mathematical theorem in a textbook, we perfectly understand the flow and logic of the thought of a writer, scientist, we understand the most complex modern knowledge etc.) and creative thinking (if we create new ideas, objects, original solutions and evidence).
Fourthly, thinking is divided according to the effectiveness of control into critical and non-critical.
Fifthly, depending on the focus on practice or theory, we can talk about theoretical and practical thinking. B.M. Teplov showed that theoretical and practical thinking are differently related to practice. And the point is not that one of them is connected with practice and the other is not, but that the nature of this connection is different. The work of theoretical thinking is aimed mainly at finding general patterns and principles of development, organization and other phenomena and facts of reality. The work of practical thinking is mainly aimed at solving particular, specific problems of any scale.
That is, in most cases we have to process and organize information in such a way as to cope with the everyday difficulties that confront us in the most logical way. In this case, the role of thinking is to develop mental strategies based on symbolic procedures.
Abstract-logical thinking as the highest form of the thought process
Human thinking is the result of a long evolution; it has gone through several stages in its development. Abstract thinking today is considered its highest form. Perhaps this is not the last stage in the development of human cognitive processes, but so far other, more advanced forms of mental activity are unknown.
Three stages of thinking development
The formation of abstract thinking is a process of development and complication of cognitive activity. Its main patterns are characteristic of both anthropogenesis (the development of humanity) and ontogenesis (the development of a child). In both cases, thinking goes through three stages, increasingly increasing the degree of abstraction or abstraction.
- This form of cognitive processes begins its journey with visual and effective thinking. It is specific in nature and associated with objective activity. In fact, it is carried out only in the process of manipulating objects, and abstract reflection is impossible for it.
- The second stage of development is figurative thinking, which is characterized by operations with sensory images. It can already be abstract and is the basis for the process of creating new images, that is, imagination. At this stage, both generalization and systematization appear, but still imaginative thinking is limited to direct, concrete experience.
- The possibility of overcoming the framework of concreteness appears only at the stage of abstract thinking. It is this type of mental activity that allows one to achieve a high level of generalization and operate not with images, but with abstract signs - concepts. Therefore, abstract thinking is also called conceptual thinking.
Imaginative thinking is divergent in nature, that is, it resembles circles diverging in different directions from a stone thrown into a lake - the central image. It is quite chaotic, the images intertwine, interact, and evoke associations. In contrast, abstract thinking is linear; thoughts in it are arranged in a certain sequence, subject to a strict law. The laws of abstract thinking were discovered back in Antiquity and combined into a special field of knowledge called logic. Therefore, abstract thinking is also called logical.
Abstract Thinking Tools
If figurative thinking operates with images, then abstract thinking operates with concepts. Words are his main tool, and this type of thinking exists in speech form. It is the verbal formulation of thoughts that allows you to build them logically and consistently.
Words organize and facilitate thinking. If you don’t understand something, try to talk through the problem, or even better, explain it to someone. And believe me, in the process of this explanation you yourself will understand even a very complex issue. And if there is no one willing to listen to your reasoning, then explain to your reflection in the mirror. This is even better and more effective, since the reflection does not interrupt, and you also don’t have to be shy in your expressions.
Clarity and clarity of speech directly affects mental activity and vice versa - a well-formulated statement presupposes its comprehension and internal elaboration. Therefore, abstract thinking is sometimes called inner speech, which, although it also uses words, is still different from ordinary, auditory speech:
- it consists not only of words, but also includes images and emotions;
- internal speech is more chaotic and broken, especially if a person does not try to specifically organize his thinking;
- it is condensed, when some words are skipped and attention is focused on key, significant concepts.
Inner speech resembles the statements of a small child 2-3 years old. Children at this age also designate only key concepts; the rest of their minds are occupied by images that they have not yet learned to name in words. For example, as soon as a baby wakes up, he joyfully exclaims: “Bye-bye – woman!” Translated into “adult” language, this means: “It’s great that while I was sleeping, my grandmother came to us.”
Fragmentation and conciseness of internal speech is one of the obstacles to the clarity of abstract logical thinking. Therefore, it is necessary to train not only external, but also internal speech, achieving the most accurate mental formulations in the process of solving complex problems. Such ordered internal speech is also called internal pronunciation.
The use of words in thinking is a manifestation of the sign function of consciousness - that which distinguishes it from the primitive thinking of animals. Each word is a sign, that is, an abstraction associated with a real object or phenomenon with meaning. Marshak has a poem “Cat House”, and there is this phrase: “This is a chair - they sit on it, this is a table - they eat at it.” This is a very good illustration of meaning - the connection of a word with an object. This connection exists only in a person’s head; in reality, the combination of sounds “table” has nothing to do with the real object. In another language, a completely different combination of sounds is endowed with this meaning.
Establishing such connections, and even more so operating in the mind not with concrete images, but with abstract signs - words, numbers, formulas - is a very complex mental process. Therefore, people master it gradually until adolescence, and even then not all and not to the fullest extent.
How to develop abstract thinking. What is it and why, 101!
You need to think abstractly, broadly. What does it mean? Dont clear. In the article 1timer.ru we will consider what abstract thinking is in simple language.
Concrete thinking is unambiguous. Example: Vasya, if you don’t remove this brick from the edge, then Andryukha will hit it with his elbow and we will smash those cars down there.
Abstract thinking is ambiguous, imprecise. Example: It is possible to die from a brick falling on your head, bricks are heavy and due to negligence people are killed every day.
The product of abstract thinking is conclusions that come from generalizations. Unnecessary information is cut off. This speeds up the process of analyzing the situation with the brain.
When thinking abstractly:
- A person tries to connect the general properties of various phenomena, events and objects into a logical chain;
- The thinking process is limited by the amount of knowledge a person has. It represents "internal dialogue."
By processing the information received, a person forms new knowledge and consolidates it in his memory. During abstract thinking, a person uses tools: concepts, evaluation criteria, generalizations, analysis, information, knowledge.
Abstract thinking tools help build cause-and-effect relationships. Abstract thinking allows you to find correspondences between seemingly unrelated objects and phenomena.
A distinctive feature of abstract thinking is the ability to separate from conventions and particulars, to evaluate the situation honestly.
If you don't develop abstract thinking, you're a fool!
Why celebrate the little things and ignore the big things if it doesn't produce results? People with high intelligence possess abstract thinking; thanks to abstract thinking, the horizon of perception of the surrounding world expands. It pushes the boundaries of judgment, inference and conclusions.
6 types of abstraction that everyone needs to know
Abstract thinking is closely related to imagination. Their origins are sensory knowledge. In psychology, there are various classifications of types of abstraction. All of them are based on 2 processes: distraction and replenishment. There are abstractions:
Isolating or analytical. Record the properties of objects. For example, “heat capacity”, “moisture resistance”, “truthful”, etc.;
Generalizing. Formulate the general properties of objects. Example: “sour”, “green”, “hard”, etc.;
Constructivism. Develops realistic ways to solve problems;
Idealizing. Exaggerating the merits of objects: “absolutely pure water”, “ideal figure”, etc.;
Actual-infinite. Eliminates the possibility of fixing anything;
Primitively sensual
During the process of thinking, they divert attention from some feelings and concentrate it on other emotions.
Practical examples of abstract logical thinking
In the life of every person you can find many examples of abstract thinking. All of them show an extraordinary approach to solving a particular problem. A striking illustration of abstract thinking is the example of how Winnie the Pooh in a balloon tried to get honey from the hollow of the “wrong” bees. You can find examples of abstract thinking not only in the lives of fairy-tale characters.
Abstract thinking example #1. Numbers
Mathematical calculations on paper are described using various numbers and symbols. How do calculations happen in a person’s head without paper and pen? The result of the calculations arises from playing with images. Many people don't even try to visualize a picture of step-by-step calculations.
Abstract thinking example #2. Life planning
This element of human life always includes elements of fantasy. For example, someone bought a lottery ticket and, even before the drawing begins, begins to make plans to spend the unearned winnings.
Abstract thinking example #3. Idealization
It happens that men and women endow their partners with qualities that they do not have (and never had). The ideal image he comes up with can live in their minds for the rest of their lives.
Concept
Abstract thinking is one of the forms of mental activity in which the analysis and understanding of information, as well as the identification of relationships and patterns, occurs without direct contact with material objects, time and space.
In simple words, this is the ability to think not only about things, events and phenomena that are in front of us here and now, but also about general categories, principles, properties, concepts, ideas. To think abstractly, a person uses previously acquired knowledge as a basis, and thinks out the rest using his imagination.
Without abstract thinking, we would not be able to recognize smells, tastes, sounds, tactile sensations, predict future events, or create something new.
A simple example from life: an abstract thinker, looking at an apple lying on the table, is able to think not only about this particular apple, but about all the apples on the planet, about metaphors, about the role of the forbidden fruit in the Old Testament story, etc.
A person operates with logical thinking when he knows the facts and data, when he clearly understands what is happening. The abstract works in any opposite situation, when you have to guess, draw general conclusions, moving away from specifics, rules and dogmas. This approach is often used in philosophy, literature, psychology, and political science.
How abstract thinking differs from other types of thinking:
- Abstractions cannot be seen or touched with human vision, they can only be imagined. While material things are always tangible and concrete.
- Only humans are endowed with abstract thinking. Even the most developed animal is not capable of such a process.
According to the Swiss psychologist Jean Piaget, the first rudiments of abstract thinking appear in a child between the ages of 2 and 7 years. But only by the age of 12–15 does it begin to fully form, which indicates a transition to a conscious lifestyle.
To one degree or another, abstract thinking is developed in all people. Exceptions include cases of dementia, some forms of autism or schizophrenia, and mental retardation.
Visually effective type
This is the earliest form of mental activity that develops in humans. It is typical for children under 3 years of age. Mental operations are based on manipulations with really existing tangible objects. Each problem is solved immediately at the practical stage, during manipulations with objects. Thinking disorders of this type are rare. Mainly with severe mental retardation. They lead to the fact that the process of development of brain activity as a whole slows down or stops.
How and when does developmental disorder develop?
This is the first stage in the development of mental activity. The time frame for its development to begin varies. Some experts indicate that a child is capable of simple mental operations from birth. Others say that the development of mental processes is closely related to the ability to move and appears simultaneously with a decrease in muscle hypertonicity. Estimated time frame: 6 months – 1 year.
Vivid and uncontrolled manifestations of visual-effective thinking in children over 3 years of age, adolescents and adults indicate serious mental disorders - mental retardation, regression in psychosis. The patient exhibits a pronounced desire to grab, break and hide surrounding objects.
Manual or visual-effective thinking of children and ways of its development
This type of solving life problems got its name due to the fact that the child constantly performs some kind of manipulation with surrounding objects. The most striking manifestations are the baby grabbing toys, knocking them, testing them, licking them, trying to take them apart and put them back together.
It makes no sense to wean a child from these manipulations; a much more important task for parents is to provide the child with toys that he can disassemble and assemble without damaging them. An excellent option is sorters. This educational toy has many functions and modifications. The principle of operation is usually similar - assemble, disassemble, correlate colors, edges, shapes. This is both a puzzle and a construction set in one toy. Check out the selection of smart toys in different prices and variations.
Visually effective type of thinking in adults
In adults, such mental operations are involved in cases where the result of actions cannot be predicted on the basis of existing inferences. A striking example is mastering an unfamiliar technique. Arrangement of furniture in the room or objects on the table, selection of necessary materials according to shape, texture, subjective sensations.
Exercises for children
It is easiest to develop in childhood. At this time, the brain is open to external influences and can undergo any changes. Exercises for children differ from those offered to adults, but are no less effective.
Best exercises:
- Reverse reading of inscriptions. Parents should invite their child to play a game in which they read the signs they see in reverse order. It will be very difficult to do this with all the advertising posters. Therefore, additional conditions should be negotiated (for example, read only red signs).
- Drawing unusual animals. The child must draw an animal consisting of parts of other animals. When the drawing is ready, you need to come up with an unusual name for the new species.
- Shadow play. With the help of his hands, on which the light from a lamp falls in the dark, the child must create unusual shadows depicting certain things. You can even invite him to act out his favorite fairy tale using shadows.
- Mental arithmetic. The child will be required to calculate simple examples using special abacus called an abacus. Such training will also develop perseverance and general intelligence.
- Puzzles. You need to choose puzzles, rebuses, anagrams, etc. games, taking into account the baby's preferences. His task will be to solve all the problems provided. At an older age, you can add crosswords to them.
- Studying clouds. The child should look at the clouds together with his parents and name what exactly he sees. The ability to visually evaluate each cloud for its similarity to different objects or animals increases the chances of successful development.
- Construction. Parents need to give their baby a task, which involves building certain objects from toy blocks. This will help develop imaginative thinking and creativity.
- Associations. The baby needs to come up with associations for everything he sees or feels. You can also ask him to imagine animals by hearing the sounds they make.
- Classification. The child needs to sort all available things or toys according to certain criteria. For example, by shape, weight or purpose. Parents should monitor the process and give hints if necessary.
- Questions. Parents should ask their child “why?” and “what if?” questions. etc. to make him think and analyze the situation. You can ask at any time.
Such simple exercises will allow you to achieve good results in a few weeks of training. It is recommended to combine them with other activities that will be aimed at developing general intelligence.
Editorial: Ways to develop emotional intelligenceThinking is considered the highest level of human cognition
. The development of thinking is the mental process of creating obvious, non-proving patterns of the surrounding world. This is a mental activity that has a goal, motive, actions (operations) and a result.