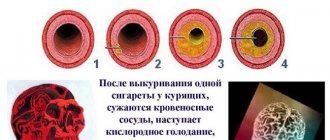
Deadly consequences of smoking
Since nicotine enters the human body in small doses, addiction develops, and there are no symptoms of acute poisoning1. During his life, a smoker smokes about 15 thousand lethal doses of nicotine. Urine harms almost all organ systems1.
This addiction increases the risk of coronary heart disease and hypertension by 4-6 times, and lung cancer by 101. Smokers are 5-8 times more likely to die from cardiovascular diseases and live on average 8-10 years less than non-smokers people1.
Every year, nicotine kills almost 5.5 million people in the world; on average, one person in the world dies from smoking every 6 seconds3. Smoking harms the health of not only those who smoke, but also those around them. Inhalation of cigarette smoke - passive smoking - annually leads to the death of 600 thousand non-smokers in the world4.
Next, we will look in detail at how smoking affects the body .
Up to contents
Physiological effects of nicotine
Nicotine can be consumed in many ways, but smoking cigarettes is the most common. During smoking, most of the nicotine is burned in the flame, but the small amount of nicotine inhaled is compensated by the gigantic surface of the lungs, through which it is absorbed into the blood. When chewing tobacco is used, nicotine concentrations in saliva are up to 6 orders of magnitude higher than the concentration in lung fluids after one cigarette.
Nicotine entering the body in one way or another stimulates nicotinic receptors not only in the brain, but also in all other tissues. In the lungs, nicotine stimulates the division of mucosal cells by activating the corresponding receptor. Excessive division, combined with DNA damage caused by tobacco carcinogens, can lead to lung carcinoma. Similar phenomena are observed in cells throughout the body, which is why nicotine consumption (even not through smoking) increases the risk of breast, uterine and food tract cancers.
The effect of tobacco smoke and nicotine on the immune system is extremely interesting and controversial. Depending on the frequency, length of smoking, and individual differences, tobacco smoke (TS) can either stimulate or suppress the immune system. For example, TD is rich in reactive oxygen species, which cause chronic inflammation of the lungs, that is, it generally stimulates the immune system. And although some studies have shown that TD activates immune T cells, this does not mean that tobacco is good for the immune system: medical statistics say that smokers suffer more often and more seriously from colds, pneumonia and tuberculosis than non-smokers [11]. In addition, in other studies, where more attention is paid specifically to antiviral immunity, it was shown that TD reduces the body’s resistance to viruses [12].
Smoking also affects the course of autoimmune diseases [13]. Smoking is known to aggravate rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease (but alleviate ulcerative colitis!) [14] and contribute to the development of emphysema. Relatively recently, people began to understand the reasons for this: activated T cells begin to produce antibodies to the structural protein of the lungs, arteries and skin - elastin [15]. Such antibodies target the smoker’s immunity to his own body. The autoimmune aspect is one example of the irreversible impact of TD on health, since once formed, antibodies will continue to be synthesized even years after quitting smoking.
You can often hear that smoking leads to diseases of the cardiovascular system. In many ways, these diseases are triggered by the factors already mentioned: oxidative stress and inflammation.
Reactive oxygen species TD reduce the activity of the enzyme responsible for relaxing blood vessels and lowering blood pressure - NO synthase. This enzyme produces nitric oxide NO, which, when reacted with reactive oxygen species, becomes the toxic molecule peroxynitrite [16]. Thus, by reducing NO levels, smoking leads to hypertension, the main cause of ischemic diseases. Smoking causes impotence through the same mechanism: a lack of NO leads to vasoconstriction and reduced blood flow in all organs.
Another problem that only male smokers may experience is the loss of the male Y chromosome. Swedish scientists have discovered that the blood of smokers contains 3-4 more cells that have lost this purely male part of the genome. This phenomenon may be related to general genetic instability caused by tobacco smoke mutagens and is very likely to contribute to the development of cancer [17].
Chronic pneumonia in smokers activates leukocytes throughout the body, including in the blood. Against the background of this inflammation, the number of endothelial progenitor cells decreases, which ensure the restoration of damaged vessels [18], and blood clotting increases [19].
How does smoking affect the oral cavity?
Tobacco consumption causes a range of dental diseases and side effects. The effects of smoking on cavity are as follows:
- change in taste sensitivity;
- dark brown or black "smoker's plaque" on the teeth ;
- bad breath;
- gum diseases (periodontitis);
- leukoplakia of the mucous membrane (inflammation of the keratinization type);
- Oral cancer5 .
This effect of smoking on the oral cavity is due to the following factors:
- chemical—cigarette smoke contains more than 4,000 toxic compounds 5;
- thermal - due to high temperature (300°C for smoldering tobacco, 900-1000°C at the time of puffing and 40-60°C for tobacco smoke6), the blood supply to the gums is disrupted, which leads to hardening of blood vessels and atrophy of gum tissue5;
Smoking can lead to an unpleasant mouth condition called halitosis. The reasons for this are as follows:
- nicotine, tar and other products of tobacco combustion that linger in the oral cavity have a specific odor;
- a decrease in the amount of oxygen in the oral cavity caused by smoking leads to an increase in the number of anaerobic microbes, as well as to the breakdown of proteins;
- in smokers, the mucous membrane becomes dry - its desquamation increases;
- Smoking is a risk factor for the development of inflammation in periodontal tissues and the appearance of tartar6.
Smokers have an increased content of pathogenic microbes in cavity that affect periodontal tissue. A feature of the clinical picture of periodontitis is minor external signs of inflammation and at the same time a sharply progressive loss of bone tissue5.
It has also been proven that constant tobacco consumption increases the growth of fungi of the genus Candida, which leads to the development of candidiasis in cavity (identified in 60% of men and women with this bad habit)7.
Oral diseases in smokers have a worse prognosis, including cancer, not only because of the local influence of tobacco, but also because of the effect on the immune system - the content of immunoglobulins IgG and IgA in the blood decreases 6 .
Up to contents
What should everyone know about the dangers of smoking?
Smoking and skin conditions
Undoubtedly, smoking is always associated with bad skin. Due to vasoconstriction and constant oxygen starvation of tissues, the skin is insufficiently supplied with blood. The necessary portions of oxygen and various nutrients do not reach the dermis. In the worst case, the following changes are observed:
- dehydration and tired skin;
- gray skin tone;
- early loss of elasticity;
- premature formation of facial wrinkles.
If there is any doubt that tobacco consumption affects the skin, then you can look at those who have been smoking actively for a long time. Over the years it becomes noticeable that this habit has left its mark on the whole body, and most importantly on the skin of the face.
Smoking and figure
The myth that cigarettes help you lose weight has long been dispelled. In practice, it is clear that such weight loss is often associated with general exhaustion and many other factors. On the contrary, the natural process of fat deposition may be disrupted. It should be noted that fat often accumulates more in the chest and waist area, while the least amount of fat is deposited in the hip area. That is why a person who smokes regularly, as a rule, has a disproportionate figure.
Smoking and the nervous system
Toxic tobacco smoke, which is familiar to many, has a destructive effect on the human body, affecting organs and systems. Associated phenomena with a significant smoking history are:
- fast fatiguability;
- memory problems;
- increased irritability;
- headaches and dizziness due to narrowing of blood vessels in the brain.
Doctors say that cigarettes can significantly harm the nervous system. The overall energy level drops. So to speak, vitality decreases. At the same time, it is interesting that smokers themselves often do not notice any decline, since they no longer remember what their normal energy reserve is.
Smoking and the senses
Of course, the senses may be affected. For a smoker:
- the perception of tastes is distorted;
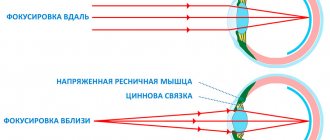
- against the background of damage to the optic nerve, vision decreases and the ability for normal color perception is lost;
- Due to the negative effect of toxic substances on the auditory nerve, hearing is dulled.
Smoking gradually destroys the peripheral nervous system. Tobacco has the worst effect on people with existing pathologies of the nervous system.
Smoking and the respiratory system
Cigarettes cause the greatest harm to the human respiratory system. For example, chronic inflammation of the nasopharynx develops. The chemical composition of smoke irritates not only the tissues of the larynx, but also the trachea, lungs, and bronchi, which continuously inflames the airways. Smoking is often accompanied by bronchitis. Gray sputum comes out with the cough.
Constant irritation causes changes in the vocal cords, causing the voice to become rougher and dissonant. Due to the clogging of the lungs with tar and a decrease in their elasticity, emphysema develops. In any case, the lungs do not work properly and are extremely vulnerable to infections. Among other things, smoking very often provokes:
- malignant neoplasms in the lungs;
- stomach cancer;
- tuberculosis.
Smoking and the cardiovascular system
The human heart contracts more often and works under enormous overload if the body is regularly poisoned with cigarette smoke. Research shows that smoking:
- the risk of hypertension increases;
- narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels occurs, causing all organs to receive insufficient blood supply;
- atherosclerosis develops, that is, the vessels from the inside become clogged with plaque and plaque.
The main causes of coronary heart disease are hypertension and atherosclerosis, both diseases develop many times more often against the background of smoking.
Smoking and gastrointestinal tract
It should also be noted that the digestive organs, tooth enamel, pharynx, gums and tongue are seriously affected. Usually everyone notices that a smoking person always has an extremely unpleasant odor coming from his mouth. All tobacco users are automatically at risk for developing the following pathologies:
- tongue cancer;
- lip cancer;
- chronic gastritis and other gastrointestinal diseases;
- deterioration of intestinal motor activity;
- slow digestion and poor appetite;
- poor liver function;
- pancreatic diseases.
What turns many people away from cigarettes is the fact that with constant smoking, the enamel of teeth inevitably turns yellow and even discolors the gums.
Smoking and the endocrine system
Doctors believe that smoking causes a range of disorders in the human endocrine system, here are the most common consequences of these disruptions:
- sexual impotence in men;
- miscarriages, toxicosis and menstrual irregularities in women;
- improper functioning of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland.
In fact, no one guarantees that when smoking a person will or will not develop this or that disease. Scientists only talk about a certain trend and draw conclusions based on research. The realities of life are such that the body of each of us is unique, so one of us very soon develops health problems when starting to smoke, while another’s body condition worsens only after decades of experience.
The adaptive capabilities of the body and resistance to tobacco poisons play an important role. Today, smoking and the human body have been studied quite deeply, so there are many ways to give up the bad habit.
The effect of smoking on the respiratory system
Tobacco tar, consisting of liquid and solid fractions, settles on the walls of the airways, accumulating in the alveoli of the lungs. Some of these compounds are released when coughing along with sputum, and some are absorbed into the tissues and enter the bloodstream6.
The lungs of smokers function worse than those of non-smokers. There is a narrowing of the bronchi, a violation of gas exchange develops and, as a result, oxygen deficiency8. According to the data described, as a result of pathological studies it was established that the lungs of a forty-year-old smoker look like the lungs of a non-smoker aged 75-80 years8.
The main symptoms of impaired functioning of the respiratory system due to smoking are chronic shortness of breath and cough with sputum. Often tobacco smoke is the cause of persistent breathing 9.
Bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, tuberculosis and pneumonia are what smoking can to . Tobacco negatively affects the course of these diseases: it contributes to the appearance of extensive damage to lung tissue and pronounced destructive changes9.
In recent years, there has been an increase in the incidence of lung cancer due to nicotine consumption, due to an increase in the number of not only active, but also passive smokers9.
There is a relationship between the frequency of consumption of tobacco products and the development of oncology of the respiratory system. Heavy smokers lung cancer 70 times more often than non-smokers10.
Up to contents
Risk of developing cancer due to smoking
The main harm of smoking (cigarettes, cigars and pipes) is their ability to cause cancer. This addiction can lead to malignant neoplasms 11:
- lungs;
- lips, tongue and other parts of the oral cavity;
- pharynx;
- larynx;
- esophagus;
- stomach;
- pancreas;
- liver;
- Bladder;
- kidney;
- cervix;
- colon.
In 30-35% of cases, nicotine is the main cause of the development of the above diseases11.
Tobacco smoke is the most common known carcinogen12 Smoking causes irreparable harm to the body : components of cigarette smoke are capable of forming mutagenic compounds with DNA, which lead to gene damage, the occurrence of mutations and the subsequent development of cancer12.
Tobacco consumption not only increases the risk of tumors , but also reduces life expectancy after cancer and increases the risk of relapse13.
Thus, quitting tobacco products helps prevent cancer: it helps prevent the emergence of new mutations , and also has a beneficial effect on the prognosis of existing cancers13.
Up to contents
The effect of smoking on the psyche
Human health also depends on the state of the psyche, which determines the level of intelligence, memory, personality traits, emotional background, and behavior.
One of the powerful factors that has a destructive effect on a person’s mental health is smoking. This is due to the active impact of various substances contained in tobacco smoke on the functioning of the brain and nervous system14.
In the first 10 seconds after inhaling smoke, nicotine penetrates the brain and begins to affect neurons - the working cells of the nervous system14. Nicotine acts as a master key, causing the brain to produce:
- Norepinephrine (NA) – acts as a stimulant. It determines the level of wakefulness of the brain and is responsible for concentration. NA increases blood pressure, increases heart rate and breathing, which contributes to the working mobilization of the body. This is why people who smoke believe that cigarettes help them concentrate better and improve their performance. However, without nicotine, smokers begin to experience difficulty concentrating.
- Serotonin is a neurotransmitter responsible for emotional stability. With its deficiency, a person becomes irritable, feels a lack of positive emotions, and has problems sleeping. Unexpected and unexplained tears and suicidal thoughts and actions may be associated with serotonin deficiency.
- Dopamine is commonly called the neurotransmitter of pleasure. This substance is produced at the moment when a person experiences satisfaction from what is happening. Dopamine is also responsible for kind feelings towards other people. With a lack of this neurotransmitter, a person perceives life as joyless and colorless, experiences an inability to love, and does not feel remorse about his own behavior.
- Gamma-aminobutyric acid is a substance that causes a feeling of calm. A lack of GABA leads to “free-floating anxiety” and panic attacks14.
When people start smoking, they experience a bitter taste in the mouth, a sore throat and cough, dizziness and headache, increased heart rate, and increased sweating. All this is a protective reaction of the body, as well as symptoms of nicotine poisoning. Gradually, the smoker adapts to this substance, the signs of intoxication disappear, and the need for a cigarette develops into a conditioned reflex, prompting the person to further self-poisoning. Each subsequent dose of nicotine, in turn, strengthens the acquired reflex. Thus, a vicious circle is created, the way out of which is to give up the bad habit14.
Up to contents
The effect of smoking on performance and the negative impact of smoking on the nervous system
Effect of smoking on performance
There is an opinion that smoking enhances performance, and many are deceived by this myth.
In fact, nicotine has a stimulating effect for a very short time, then quickly reduces and impairs performance, both physical and mental.
Physical activity increases the body's need for oxygen. During work, especially when associated with significant stress, it is not always possible for the required amount of oxygen to reach the organs and tissues. At the same time, incomplete oxidation products accumulate in the body, which contribute to the development of fatigue. During rest, these products oxidize. During smoking, a large amount of carboxyhemoglobin is formed and the amount of oxygen supplied to various organs and tissues decreases. The heart is forced to work with great tension. It takes a smoker longer to regain normalcy than a non-smoker. Along with increased heart rate and increased blood pressure during physical activity, after smoking one cigarette, the recovery period lengthens, which indicates a violation of the body's functional ability. In the future, if smoking continues, this also occurs with relatively moderate physical activity. With long-term smoking, impaired lung function increases the discrepancy between the need for oxygen and its delivery to the heart. The adaptive capabilities of the heart decrease.
Studies have shown that 10-15 minutes after smoking, muscle strength decreases by 15%. Systematic smokers also experience 15% more muscle fatigue than non-smokers. Coordination (accuracy) of movements is impaired. Thus, the number of hits with the ball on the target after smoking one cigarette decreased by 12%, after two - by 14.5%. Smoking also reduces visual acuity. The sniper, who scored 96 points out of a possible 100, scored only 40 points after smoking several cigarettes.
A connection has been identified between heavy tobacco smoking and occupational injuries. Smoking slows down reactions and makes them less clear. Attention and memory weaken, intelligence decreases
. People whose professions require memory, attention, and quick reactions (office workers, transport drivers, pilots, sailors, etc.) must remember that smoking reduces their professional performance.
Tobacco smoke reduces the amount of negatively charged ions in the air, which help improve body tone and performance. Labor productivity when smoking also drops because a lot of time is spent on so-called smoking breaks.
The effect of smoking on the nervous system
The components of tobacco smoke, in particular nicotine, actively affect all nervous functions, but the central nervous system and, above all, brain cells are especially sensitive to it. Those who smoke should remember that under the influence of nicotine, cerebral blood vessels narrow.
, and consequently, blood flow to the nervous tissue decreases.
In this regard frequent headaches
and
memory weakens
.
Smoking has a negative effect on any manifestation of nervous activity (and primarily in connection with hypoxia). The great German poet Goethe said: “Smoking makes you stupid. It is not compatible with creative work.” It is known that nerve cells generate biocurrents that can be recorded using an electroencephalograph. Scientists have found that when smoking, changes appear on the electroencephalogram indicating a weakening of the bioelectrical activity of brain cells
. In this case, the degree of attenuation of bioelectrical activity is proportional to the number of cigarettes smoked by a person.
Under the influence of smoking, disorders of both the central and peripheral nervous systems can occur. Smokers often experience inflammation of the nerve trunks - neuritis, polyneuritis, radiculitis, etc. Smoking is especially harmful for people who suffer from any nervous diseases or have suffered a trauma to the nervous system, such as contusion or concussion.
Disturbances in higher nervous activity are also common in smokers. Due to disruption of the correct flow of nervous processes, a person becomes irritable and quarrelsome
, he develops, as they say, a “difficult character.”
Disorders of nervous activity as a result of smoking can lead to more severe consequences. Statistics show the undoubted role of smoking in the occurrence of a number of nervous disorders.
| Think about it, is it worth risking your health? You decide. But if you still need to improve your performance and at the same time maintain your health, remember that we have an alternative, effective and absolutely safe solution to any of your problems related to intellectual and emotional stress. Intellectual program: Excellent memory, high performance, restful sleep Find out more about the program... Find out more... | Russian scientists have developed a program that has a complex effect, providing a quick and long-lasting effect.
|
The effect of smoking on the cardiovascular system
Smoking and healthy blood vessels are two incompatible concepts. Nicotine increases the development of cardiovascular diseases such as:
- atherosclerosis;
- coronary heart disease (CHD);
- hypertension15.
Nicotine causes vasospasm, thereby increasing blood pressure. The walls of blood vessels are damaged, and cholesterol plaques are deposited on them. These factors are the main cause of the development of cardiovascular diseases, including myocardial infarction. The blood vessels in the smoker’s brain are also damaged - due to deterioration of blood supply, memory decreases and the risk of paralysis increases15.
Up to contents