Head injuries include damage to the skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscles, skull bones and brain matter. These are particularly dangerous injuries for the human body, since soft tissue injuries are often accompanied by heavy bleeding, and bone fractures are complicated by brain damage, which in injury statistics accounts for half of all injuries. A quarter of the victims die from cardiac arrest due to untimely or ill-provided medical care.
Causes of head injuries
Head injuries occur as a result of such events:
- • injuries in everyday life, fights;
- • injuries at work;
- • use of firearms;
- • injuries during an accident.
Classification of head injuries
The following types of head injuries are distinguished:
- injury to the skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscles,
- fractures of the skull bones.
All injuries can be closed (bruise) or open (wounds). There are also fractures of the skull (vault and base) and facial skull (the most common are fractures of the upper and lower jaw, the temporal bone).
Treatment of trauma to the occipital part of the head
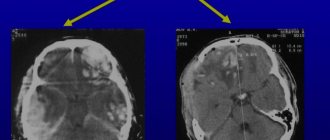
In case of injury in the back of the head, a medical examination and a calm regime are necessary. According to the dynamics of subjective symptoms and objective neurological results, a CT scan is sometimes performed, an examination that can detect increases in brain depression, subdural or epidural hematoma. In this case, neurosurgical intervention is necessary - elimination of the hematoma. Rare post-traumatic hydrocephalus is usually resolved by inserting a shunt. The cervical spine is secured with a cervical collar. Appropriate medications are used to suppress other associated symptoms of neck injury:
- symptomatic analgesics;
- weak opioids;
- NSAIDs;
- tricyclic antidepressants.
Rehabilitation treatment is added later.
Important! If you hit the back of your head, a difficult-to-control protracted pseudoneurasthenic syndrome sometimes develops.
If you hit the back of your head and there is a suspicion of damage to the cervical spine, you need to be careful in your actions to prevent deterioration of your general condition during manipulation.
It is advisable to relieve increasing pain from the very beginning with medications from the NSAID group (Brufen, Ibalgin, Ibuprofen). If pain persists, consult a doctor.
If no serious damage is found during the inspection, the following measures may help:
- Massage. After determining the location of the injury, massage of a specific group of muscles in the back of the head effectively eliminates the consequences of the injury. The correct technique of the procedure is important, so massage is performed only by a professional.
- Physiotherapy. The physiotherapist creates a combination of suitable exercises designed to involve all injured muscles and ligaments in the back of the head. Therapeutic exercise improves blood circulation, which provides good results in eliminating and preventing the consequences of injury.
- Physiotherapy. Physiotherapeutic methods include magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, ultrasound or laser treatment.
- Chiropractic. Carrying out this method belongs only to the hands of a specialist!
- Acupuncture. This therapeutic method is advisable when signs of neuralgia appear.
- Regime measures. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is an important part of treating the consequences of neck injuries.
Prescribing treatment without proper examination, determining the causes and localization of damage is unacceptable!
Pharmacotherapy
In recent years, pharmacotherapy has been overused and often inappropriately. Without careful clinical evaluation, drug treatment is useless. In addition, drug treatment primarily does not affect the underlying cause of the disease, but only its consequences. Therefore, proper rehabilitation is a much better solution. For acute painful symptoms after a blow to the back of the head and injury to the cervical spine, NSAIDs are most often used in combination with muscle relaxants. The essence of this therapy is the analgesic effect and the effect on reflex muscle spasms.
Muscle relaxants help relax muscle spasms and relax skeletal muscles. Depending on the mechanism of action, they are divided into 2 groups:
- peripheral;
- central.
Peripheral muscle relaxants block the action of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. They are used in anesthesia or when short muscle relaxation is necessary. In contrast, central muscle relaxants are active in the brain stem and spinal cord, where they dampen reflexes. They are often used to treat acute painful muscle spasms after injuries to the back of the head or when spinal problems occur.
Signs of head injuries
All types of head injuries have their own symptoms and mechanisms, knowledge of which will allow you to provide competent assistance to the victim at the scene of the incident. A bruise occurs when struck by a hard object. It can manifest as subcutaneous limited or diffuse hemorrhage, characterized by the presence of fluctuation (softening).
Head wounds can be penetrating (in which the dura mater is damaged) and non-penetrating (without damaging it). Depending on the wounding object, they are divided into cut, chopped, stabbed, bruised, and gunshot wounds.
Cut wounds are inflicted with a knife, blade and other sharp objects. They are accompanied by pain, heavy bleeding; their edges are even, smooth, and gape widely. Chopped wounds occur when struck by a sharp heavy weapon, deep; As a rule, the substance of the brain is damaged. Puncture wounds have a deep channel and are dangerous for the development of anaerobic infection. Bruised wounds are less dangerous, however, they are accompanied by severe damage to surrounding tissues with their further necrosis. Scalped wounds are characterized by damage to surrounding tissue and heavy bleeding. Gunshot wounds are superficial (without damage to the bone) and deep (non-penetrating and penetrating - with damage to the bone, meninges and brain substance).
Fractures of the facial bones reach 4% of skeletal fractures, but the most common are fractures of the lower jaw. With such a fracture, the following signs are determined:
- the patient has difficulty chewing and swallowing;
- the jaw is tilted to the side,
- speech is impaired,
- pain and pathological mobility of fragments are noted.
A calvarial fracture occurs after strong impacts with depression and rupture of the skull bones. It is characterized by:
- the presence of deformation, depression or protrusions,
- mobility of bone fragments and crepitus (a sound reminiscent of that heard when walking on snow in cold weather).
- with an open fracture, brain matter can be seen in the wound.
Fracture of the base of the skull appears:
- leakage of blood and cerebrospinal fluid (cerebrospinal fluid) from the nose and ear,
- symptom of “spectacles” - hemorrhage into the tissue around both eyes,
- exophthalmos (displacement of the eyeball forward).
It must be remembered that the severity of the victim’s condition will be determined not by a bone fracture, but by a traumatic brain injury.
Types of hematoma
A hematoma forms after a strong blow that ruptures blood vessels and collects blood under the skin. The victim may experience mild pain, swelling, and a bluish-purple hue at the site of the injury.
A hematoma can be:
- Subcutaneously. Occurs when the forehead is bruised without damaging the surface of the epidermis. Post-concussion hemorrhage occurs under the skin.
- Intramuscularly. It is formed in the muscles of the head itself after injury.
After examining the hematoma, you can assess the condition of the victim. If only soft tissue is damaged, there is no need to see a doctor. A cause for concern is fragmentation at the site of the bruise or visual changes in the frontal bone, indicating a fracture. In this case, an urgent visit to a trauma surgeon is necessary.
First aid for head injury
In case of a soft tissue bruise, you need to put a bag of snow, ice or water on the victim's head. You can also moisten several layers of gauze with cold water, squeeze well and apply to the bruised area. The edges of the wound should be treated with a 1% alcohol solution of iodine or a 5% alcohol solution of brilliant green and cover it with a sterile gauze bandage; bleeding is stopped with a pressure bandage. If there are signs of fractures of the cranial vault, then the bandage is applied very carefully. Pieces of bones, metal, and fragments protruding from the wound are not removed to avoid bleeding. If brain matter is visible in the wound, do not press it down; several sterile napkins are placed on the wound, and a roller is placed around them, which is rolled up from cotton wool and gauze like a donut. A bandage should be applied on top. If the base of the skull is fractured, the victim is laid horizontally, with the head turned to the side. In case of a fracture of the lower jaw, stop the bleeding using tampons and a sterile bandage; bleeding can also be stopped by pressing the artery with a finger to the angle of the lower jaw. You can also bandage the lower jaw to the head with a sling bandage. The victim's mouth must be cleared of knocked out teeth, vomit and blood clots. If there are no wounds, apply cold to the damaged area. If necessary, perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
The life of a victim with a head injury depends on who is nearby at the time of the incident: a person can be saved only when the injury is recognized in a timely manner and qualified first aid is provided. After providing first aid, be sure to call an ambulance.
Forehead bruise: medicinal ointments
The following ointments help combat the effects of bleeding:
- "Troxevasin".
- "Lyoton."
- Hepatrin ointment.
Homeopathic remedy - Traumeel S.
ethnoscience
Medicinal ointments should be applied to the bruised forehead several times a day. You can also get rid of the tumor using traditional medicine.
- You can speed up the process of resorption of a tumor on the forehead using the following time-tested methods:
- Apply finely chopped or crushed sycamore leaves to the tumor for 10 minutes.
- Mix water and alcohol in equal quantities, moisten gauze and apply to the tumor for 15 minutes. This compress is recommended to be used 2 days after the injury.
- In the morning for half an hour, and in the evening apply a compress of finely grated raw potatoes to the lump.
- Chop the cabbage leaf and boil in milk. Cool slightly until warm, wrap in a napkin and use for an hour 2 times a day.
An iodine mesh will help remove a bump on the forehead.
A compress of raw potatoes, grated on a fine grater, is a good remedy for bruises on the forehead.
Warning signs
Signs of a concussion
Regardless of age, a child who has fallen and hit his forehead on the floor requires close attention for at least the first two days.
Severe crying and hysterics, a bruise and a bump on the forehead after a fall are not alarming symptoms. The baby may cry not from pain, but from fear. If he continues to cry a lot for 20-40 minutes. after hitting your head, medical attention is required. This may be the first sign of injury.
A hematoma or bump, as well as an abrasion, a small dent or wound, is not a reason to be alarmed. There are more dangerous signs of TBI.
If a child hits his forehead against a wall, radiator or other metal objects, or falls headfirst from a bed or sofa, parents should be alerted to the appearance of the following symptoms:
- short-term clouding of consciousness, dizziness, unsteady gait, disorientation in space;
- changes in behavior, speech impairment, functioning of the senses (lack of smell, deterioration of vision, hearing);
- dilation or constriction of the pupils, pupils of different sizes, the appearance of bruises in the whites;
- drowsiness that is not typical for a child, or vice versa, the baby cannot fall asleep;
- the appearance of dark or dark blue circles under the eyes, behind the ears;
- severe headache, which young children notify their parents about by crying, anxiety, and moodiness;
- ear or nosebleeds, other discharge from the nose or ears;
- repeated vomiting or frequent regurgitation;
- a sharp increase in body temperature.
The most dangerous symptom is loss of consciousness, even if it is short-term, as well as convulsions and partial paralysis, for example, the inability to move an arm or leg. These signs indicate serious brain damage.
The presence of at least one alarming symptom indicates that the child needs medical attention. But even if the baby feels well, it is better to show him to the doctor.
After a child has fallen and hit his head or hit his temple or forehead on a frame, it is necessary to provide him with complete rest and not allow him to play active games, run, or jump. You shouldn’t put her to bed; it’s better to be nearby in order to notice possible negative changes in time.
Danger of forehead impact
A blow to the forehead can lead to a concussion; you need to observe the child’s behavior.
Every child in childhood hit his forehead on a bed, table, chair, got bruises on his temples without hitting the door, or bumps on his head when falling from a bicycle. Superficial head injuries are assigned an ICD-10 code of S00.
Such injuries always cause concern among parents, and this is partly justified, says pediatrician Evgeniy Komarovsky. A popular pediatrician in the country says that most head contusions in infants end well, since the bones of the skull are soft, mobile, and the fontanelle provides shock absorption, reducing the force of the impact and the likelihood of negative consequences.
You should be more concerned about the condition of children older than one year, since complications after strokes appear more often. If a one-year-old child hits his forehead on concrete, tiles, asphalt, a radiator, or falls from a great height upside down, the following consequences may occur:
- concussion;
- bleeding in the cranial cavity;
- soft tissue bruise;
- compression, bruise, swelling of the brain;
- fracture of the base of the skull.
For traumatic brain injury, care must be provided within the first 24 hours, otherwise neurological complications will develop. The severity of the consequences of TBI depends on the degree of brain damage, impairment of brain functions, and the speed of providing qualified assistance.
Causes
If you have a headache after a fight, it is better to immediately seek medical help. Contusion of the brain and bone structures of the skull occurs due to a direct blow to the skull area, mechanical impact with acceleration, and compression of the cranial structures. Common situations associated with injury:
- Road accidents.
- Falling from height.
- Industrial injuries.
- Traumatic injuries as a result of a fight or attack.
- Sports activities.
Depending on the strength of the traumatic impact, damage of varying degrees of severity occurs - reversible disorders (concussions of the brain) and irreversible (foci of crushed brain structures). The crush site is a variable area of the cerebral hemispheres, in the area of which the meninges are ruptured and particles of alternative brain matter are present.
The crush site is characterized by a functional and structural change in the nervous tissue (neurons, gliocytes, nerve fibers, synapses) and elements of the vascular system, in the area of which multiple hematomas appear. Bruises of the skull are usually accompanied by the formation of foci of hemorrhage.
The crush site in the acute period of TBI manifests itself clinically as an intracranial space-occupying process (hematoma, tumor) and contributes to the progression of hypertensive-dislocation syndrome. As a result, life-threatening conditions associated with pinching and compression of the brain stem may develop.