The private clinic "Kordia" in Moscow provides treatment and prevention of all types of dementia. The center's doctors and psychologists have extensive experience working with people with dementia and know how to help them. If there is a person near you who has dementia, and treatment seems completely ineffective, be sure to call the specialists at our institution. They know what to do even in difficult stages. Center phone number: +7 (495) 268-09-02.
GET A FREE CONSULTATION
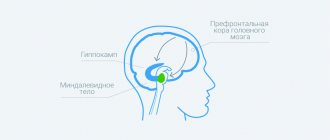
Causes of dementia
This disease is an acquired form of dementia. When it occurs, a person loses previously acquired skills. In the last stages of dementia, patients are not able to use acquired knowledge, care for themselves, or communicate normally with others.
The disease develops due to organic brain damage. It can also be the result of an injury or disease that negatively affects brain function. Today, doctors name more than two hundred factors contributing to the onset of dementia.
Among them:
- Alzheimer's disease;
- hypertension;
- malignant and benign neoplasms of the skull;
- atherosclerosis.
In young people, dementia can be a consequence of prolonged use of drugs, alcoholism, neurosyphilis, AIDS, viral encephalitis, chronic meningitis. In rare cases, symptoms occur with autoimmune pathologies and endocrine disorders.
The many faces of dementia
The most common cause of weakening memory and intelligence in the elderly is Alzheimer's disease. In addition to Alzheimer's disease, dementia can also be caused by: vascular brain damage, dementia with Lewy bodies, frontotemporal degeneration and dementia associated with other diseases (Parkinson's disease, brain tumors, multiple sclerosis, stroke, intoxication, infections, alcoholism, head injuries etc.). There is also reversible dementia associated with a deficiency of certain vitamins. And each of them is treated differently, so it is very important to establish the correct diagnosis.
Article on the topic
Is dementia a death sentence? Who is at risk and can the disease be avoided? The course of different types of dementia is also different. For example, with Alzheimer's disease, orientation disturbances, problems with counting and speech (difficulties in finding words) occur; a person remembers well what happened to him many years ago, and does not remember what he did yesterday. Dementia with Lewy bodies is often accompanied by visual illusions and hallucinations, sleep disturbances, confusion, loss of spatial orientation, as well as autonomic symptoms (fainting, low blood pressure, urinary and bowel motility disorders). Frontotemporal dementia, which accounts for only 5% of all other similar disorders and is associated with a family history in 30–40% of cases, usually occurs at an earlier age (from 50 to 60 years) and is manifested by thinking, behavioral and speech problems that progress over time violations. A sick person's character and behavior can change dramatically: a kind grandmother becomes quarrelsome and aggressive, and a previously quiet grandfather begins to blatantly pester a young neighbor. Vascular dementia, associated with atherosclerosis and accounting for only 10% of all cases, manifests itself in the form of mental slowdown and decreased mental activity, a strong narrowing of the range of interests, increasing selfishness and increasing talkativeness. Writing is often impaired and the gait becomes shuffling.
Click to enlarge
COST OF TREATMENT FOR MENTAL DISEASES
The duration of treatment in a hospital is from 14 to 90 days, depending on the severity of the disease.
TREATMENT IN A HOSPITAL.
AMBULATORY TREATMENT
TREATMENT IN A HOSPITAL
Inpatient treatment – accommodation options
| Accommodation in a triple room | 10,000 rub./day |
| Double room | RUB 13,800/day |
| Single room of increased comfort | 16,000 rub./day |
| Treatment in a single VIP ward | 25,000 rub./day |
AMBULATORY TREATMENT
Ambulatory treatment
| psychiatrist | FOR FREE |
| Consultation with a psychiatrist (first appointment) – free of charge during hospitalization | 3,000 rub. |
| Full psychodiagnostics (all tests and procedures) | from 5,000 rub. |
| Appointment with the head physician of the clinic | 4,500 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychiatrist at home | from 4,000 rub. |
FREE CONSULTATION
The most common symptoms of dementia
Symptoms are determined by the location of the affected area of the brain and the cause of dementia. With a mild degree of impairment, the patient can perform household work, he retains the ability to think critically. As the disease progresses, brain activity is impaired. Then the person notices that his intellectual abilities have noticeably decreased. It is difficult for him to take care of himself. He finds it difficult to use standard household appliances. It gets to the point where he doesn’t understand how to answer the phone or open the front door. In severe forms, there is a complete collapse of the personality. The patient no longer notices that something is wrong with him, although he constantly behaves inappropriately. Relatives suffer more. They are the ones who seek qualified medical help.
First signs of illness
The symptoms and signs of the disease are similar.
The first thing relatives may notice:
- problems with remembering and reproducing information;
- loss of interest in what is happening around;
- difficulties with orientation in space;
- reducing the patient’s criticality of their own behavior.
According to experts, if you ignore dangerous symptoms for a long time, dementia will progress rapidly. Hallucinations and delusions will appear. Then very quickly the person will be lost to society.
Stages of dementia disease
The disease is progressive.
Doctors distinguish three stages:
- The first one. The symptoms are mild, although significant negative changes have already occurred in the intellectual sphere. The patient is able to understand that he needs to be treated and take medication. He is worried about the peculiarities of his condition.
- Second . Symptoms appear moderately. Intellectual impairments become more severe. It is difficult for a sick person to take care of himself. He may forget to turn off the gas, put a boiling kettle in the refrigerator, etc.
- Third. The most difficult stage. The patient is not able to eat on his own, it is difficult for him to chew food, and he does not always recognize relatives and friends. The ability to think logically is lost.
To prevent a rapid transition from the first to the third stage, you need to start therapy as early as possible and strictly follow all medical prescriptions.
Causes of the disease
This phenomenon has a medical explanation. The fact is that with age, brain cells receive less nutrition and atrophy. This leads to a disruption of established neural connections, which means that all those mental operations that were previously easy and accessible are forgotten and turn into a real test for the brain. In medical practice, this is called senile dementia or dementia.
Among the factors that increase the risk of developing dementia are not only old age, but also others:
- persistently depressed mood;
- alcoholism and other harmful addictions;
- depressed state of mind;
- low level of quality of life;
- weakened immune system.
According to available medical evidence, maintaining an active lifestyle, healthy eating, and maintaining a daily routine significantly reduces the risk of developing dementia in older people.
This disease is difficult, but treatable, so you need to contact a specialist as early as possible. Its first manifestations may go unnoticed, but you should not brush them aside if they are repeated regularly. In this case, timely measures taken can significantly slow down the development of the disease.
Methods and methods of treatment
Problems that doctors solve when providing care to dementia patients:
- blocking and minimizing behavioral disorders;
- increasing cognitive abilities;
- improving quality of life.
The client can be treated on an outpatient basis or in a hospital - much depends on the severity of his condition.
During the work, the following techniques are used:
- Social therapy. Doctors advise relatives on the patient’s condition and the characteristics of his care.
- Psychotherapy. Both demented individuals and their immediate environment participate in the sessions. Particular attention is paid to practices that improve attention and memory characteristics.
- Pharmacotherapy. Medicines are selected that support normal brain activity.
- Psychopharmacotherapy. Drugs are used that alleviate the disorders associated with dementia.
In the case of inpatient therapy, patients attend exercise therapy, physiotherapy, massage sessions, and medicinal baths. This comprehensive treatment allows you to achieve the best results.
Does your relative have a mental disorder?
Refuses hospitalization? Are you afraid that he will harm himself and others? Call or request a free consultation.
URGENT CONSULTATION
The doctor will arrive within 1 hour . We'll take you to the hospital ourselves. Emergency hospitalization - around the clock!
Drugs to treat dementia
Medicines for dementia help reduce anxiety, improve well-being, and slow the progression of the disease. Remember, now there are no miracle drugs that could restore memory. Be careful!
The main goals of treating dementia:
- improvement of cognitive functions
- maintaining functional activity
- reducing the severity of behavioral disorders.
The choice of therapy depends on:
- from the individual clinical symptoms of each specific patient
- from the presence of concomitant diseases,
- on drug tolerance and a number of other parameters.
Three groups of drugs:
GROUP 1 Cholinergic drugs - acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChE): rivastigmine, donepezil, galantamine
Cholinesterase inhibitors are a group of drugs aimed at inhibiting enzymes that destroy acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft. In accordance with their mechanisms of action, there are 2 classes of cholinesterase inhibitors:
I class
- acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (Reminyl (galantamine), Aricept (donepezil)
class II
- acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors (Exelon, rivastigmine)
GROUP 2 drugs interacting with NMDA receptors (memantine)
In case of emotional, affective and psychotic reactions in patients
the doctor may prescribe appropriate concomitant therapy. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the compatibility of drugs, as well as the likelihood of adverse events.
Caution must be exercised
when prescribing neuroleptics (antipsychotics) to patients with dementia, since in dementia with Lewy bodies, which has a similar clinical picture to Alzheimer's disease, the use of antipsychotics is contraindicated and can lead to a worsening of the condition.
How is dementia treated?
Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia are currently considered incurable diseases. But over the past decades, the advent of drug treatment has made it possible to alleviate the severity of the main symptoms of dementia and delay the onset of irreversible decline for a significant period of time.
Drugs proven to be effective in treating dementia
- drugs of first choice are acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (active substance: rivastigmine or galantamine or donepezil). Recommended for the treatment of all stages of the disease in guidelines for the treatment of dementia in Europe and the USA.
- second choice drugs are NMDA-glutamate receptor antagonists (active substance - memantine). They are added to first-choice drugs when the effectiveness of therapy decreases or are prescribed to patients who consult a doctor late (with moderate and severe stages of dementia)
About treatment options for your relative, consult your doctor or the Altsrus Hotline . Our expert physicians will not be able to prescribe medications for you, but will be able to provide a second opinion on the therapy your loved one is prescribed and other advice.
Important to remember!
- the earlier treatment is started, the better the result can be obtained
- slowing down the progression of the disease achieved with medication means that many brain functions can be preserved for a longer period of time
- as a result of timely and correct treatment, the patient will be able to maintain independence longer, better navigate everyday life, and accordingly, the burden on relatives will be reduced
Additional medications
In the early stages of the disease, depression, anxiety, and agitation may occur in the patient. For these conditions, the following drugs may be additionally prescribed:
- mood improvers (antidepressants)
- drugs to relieve anxiety and agitation (neuroleptics)
The dosage of these drugs must be approached very carefully, taking into account the many complicating factors inherent in elderly patients, such as diabetes mellitus, rheumatism, high blood pressure and other diseases of the cardiovascular system.
The regimen and dosage must be agreed with your doctor!
Drug treatment of the disease - medications used
Traditional treatment for dementia is pointless - specialized medications must be used. Doctors at the Cordia clinic select them taking into account the stage of the disease and the severity of its course.
Help with dementia disorders:
- Drugs that improve brain activity. This refers to anticholinesterase medications and NMDA glutamate receptor blockers. They have neuroprotective properties, do not allow neurons to be destroyed, and enhance the transmission of nerve impulses. With their help, it is possible to improve memory and increase focus.
- Neuroleptics. Used to correct behavioral abnormalities. Reduce psychomotor excitability, perception deception, delirium. Since medications in this group often cause unwanted side effects, they can only be used under constant medical supervision.
- Antidepressants. Fighting depression. May contain fluoxetine, mianserin, fluvoxamine maleate and other active substances. The selection of a suitable medicine can only be carried out by a qualified doctor.
Since patients with dementia often complain of light sleep and insomnia, many are additionally prescribed sleeping pills.
Prescribed medications
Basic drugs
Chakhava Vasily Otarovich
Psychiatrist and psychotherapist
Candidate of Medical Sciences
32 years of experience
The cost of admission is 7000 rubles.
Make an appointment
- Memantine (Akatinol memantine. Prescribed to improve metabolic processes in the brain. Has a positive effect on memory, concentration, performance of habitual skills, thinking. Has a minimal number of side effects;
- Rivastigmine (Exelon). Aimed at slowing down the destruction of acetylcholine. It has a beneficial effect on its accumulation in the cortex and hippocampus.
The drug improves memory, attention, speech, reaction. Reduces the level of mental and behavioral disorders. A patch with rivastigmine is prescribed so that the drug smoothly enters the blood throughout the day in a certain dosage. The patch must be applied once a day to the back, chest, or shoulders. It should always be glued at the same time, but on different parts of the body and skin. When taking a bath or shower, you can leave it on, this will not affect its functions. The only limitation is visiting the sauna.
- Nicergoline (Sermion). the drug improves blood circulation in the brain, increases the resistance of nerve cells to oxygen starvation and deficiency of nutrients, reduces vascular resistance in the lungs, upper and lower extremities, reduces platelet aggregation, and also reduces systemic blood pressure.
Additional drugs
- Cerebrolysin. A multidisciplinary organ-specific drug with an effect on the brain. Aimed at protecting neurons and regulating metabolism. Helps improve memory and simplify everyday activities.
Taken intravenously in a dropper for at least 4 weeks. It retains its therapeutic properties for a long time and has no side effects. Suitable for the treatment of dementia of all types;
- Actovegin. Has a similar effect to Cerebrolysin. Aimed at improving blood transport function. This helps to increase the energy potential of neurons.
Reduces the severity of signs of dementia, thereby reducing a person’s need for others. The first few weeks the drug is taken in a dropper, after which the pills begin.
How are patients treated in a hospital?
Hospitalization is indicated at any stage of the disease. At the initial stages, it is needed to select the optimal treatment that will slow down the progression of dementia. In the later form, doctors take measures to alleviate the patient’s condition, provide him with high-quality and complete care, and improve his quality of life.
At the Cordia hospital, patients are monitored around the clock. For each applicant, specialists develop unique treatment programs that allow them to achieve positive results in a short time.
It is important to understand that it is impossible to completely cure dementia, but it is possible to stop its progression. To do this, you need to be observed by experienced doctors. Make an appointment with Cordia doctors by calling +7 (495) 268-09-02 . We are ready to help you and your loved ones.
How to prolong the life of a person with dementia?
Dementia is an irreversible process. According to medical studies, patients can live with this diagnosis for up to 10 years. Relatives are faced with a task: if mom, dad, grandma or grandpa has senile dementia, how can they help their loved one and try to preserve the remnants of their intellect?
In the initial stages of the disease, you need to intensively train the brain: solve crossword puzzles with the patient, solve problems from the school curriculum, watch TV quiz shows and offer your own answers. It is recommended to engage in gentle physical exercise and walk more in the fresh air. There are special simple exercises for dementia for the elderly; they are easy to perform, but they require concentration, which is very useful for such patients.
Communication with well-known people is welcome. Conversations, discussions, telephone conversations are useful. Despite the manifestations of the disease, relatives need to remember that in front of them is the same beloved and close person whom they are accustomed to knowing all their lives. All changes in character occur not by his will, but under the influence of an incurable disease. Dementia cannot be cured, but its progression can be delayed and delayed.