Many citizens often forget certain events, actions or expressions. Moreover, such symptoms may indicate the development of some serious psycho-neurological disease, which in the early stages can still be treated.
Amnesia or memory loss can be caused by various reasons and, accordingly, has different forms and types.
People of any age and gender should know what the peculiarity of retrograde amnesia is, what symptoms it is accompanied by, how it is diagnosed, how treatment is carried out and the necessary prevention.
What it is?
The peculiarity of retrograde amnesia lies in the following: the patient experiences a memory failure, and it is difficult for him to remember exactly those life episodes that happened immediately before the attack or injury.
This kind of oblivion can occur as a result of some neurological disease, brain injury or serious mental damage. According to ICD-10 coding, this type of amnesia is designated R41.2.
The first who paid attention and began to study this form of this disease was the Russian-born psychiatrist S.S. Korsakov. He noted disturbances and memory lapses in people who had severe alcohol poisoning, which is why this form of amnesia was previously also called “Korsakoff syndrome.”
Then, at the beginning of the 20th century, M. Bekhterev identified this disease in people who had suffered a stroke, and it had a paroxysmal manifestation.
Adults are most susceptible to this disease, and it often appears unexpectedly, but under exceptional circumstances it can develop gradually together with some other serious diseases.
Forms, types, causes of the disease
Any person is at risk, since this type of disease develops for the following reasons:
- there are acute infectious diseases (encephalitis) affecting the cells of the central brain organ;
- received any severity of head injury;
- blood supply disturbances occur that are dangerous to the brain;
- tumor formations of any origin were diagnosed, not only in the soft, but also in the hard tissues of the head;
- severe intoxication with drugs, gases and alcohol occurred;
- received electrical injuries, which were accompanied by temporary cessation of breathing;
- suffered an emotional state of shock;
- have serious mental illnesses, such as histrionic personality disorder.
There are several criteria for classifying retrograde amnesia. Due to memory loss there are :
- Limited, which is associated with head injuries, previous diseases that affect the normal functioning of the brain, severe intoxication of the body with various substances, including alcohol.
- Psychogenic, caused by mental damage.
Based on the volume of lost memories, there are:
- partial - there are some fragments of events in the memory, some vague images, while the orientation in space and time is disturbed;
- complete – all episodes relating to a certain time period are lost;
- temporary - develops after traumatic brain or electrical injuries, and only seconds or entire months can be lost;
- permanent - develops with long-term brain damage from electroconvulsive therapy or serious diseases (stroke, encephalitis).
According to the course of the pathological process, they are distinguished:
- acute, which appears suddenly after some unforeseen reasons, for example, injury, stroke, intoxication and others;
- gradually increasing, developing together with other mental, oncological or degenerative diseases.
Find out more about types of amnesia:
- anterograde and its manifestations;
- rare transient global;
- childish (infantile) - inherent in each of us;
- memory loss after alcohol.
Fixation amnesia as an element of Korsakoff's Syndrome, difficulties in diagnosis
The human brain has enormous potential, thanks to which we perform meaningful actions, think logically, and analyze a large amount of information.
Thinking and memory are the most complex mental processes. Only memory is capable of preserving our experience and restoring knowledge, skills and abilities in certain conditions. Memory is multifaceted in nature: sensory, emotional, motor and verbal-semantic.
It happens that a person loses this ability to remember and restore events. Memory loss is a disease that affects both young and old people. This phenomenon may occur slowly or affect the memory suddenly, but the outcome of treatment is completely unpredictable.
From the editor: Why do you feel dizzy when turning?
A person who has lost his memory is immersed in complex experiences, and therefore often needs special attention and care. The quality of life is significantly reduced, personal and professional growth stops.
Three main types of memory based on information storage time:
- Immediate (a few seconds);
- Intermediate (from a few seconds to several days);
- Long-term (events of the long past).
Greater brain plasticity provides children with stronger memories and increased success in the learning process. Based on memories, a person grows throughout his adult life.
The properties of memory have been studied since ancient times, but to this day all aspects have unknown areas.
The phenomenon of memory loss is often used in films and TV series to add poignancy and drama to the plot. The main character is cured by love or he starts his whole life with a clean slate. In real life everything is more complicated.
Definition of amnesia
What is amnesia? A persistent disease that occurs under the influence of physical or mental aspects, based on a violation of remembering and reproducing information is called amnesia.
Amnesia is a disorder of cognitive memory function.
The most severe forms of complete or partial amnesia were described by Professor Korsakov in his works; this diagnosis was later called Korsakov's Syndrome. A person loses information from his past, does not remember new information, but, as a rule, remembers personal data (name, main milestones of his biography), and also retains skills and abilities.
Causes of Memory Loss
- Organic (head injuries, brain diseases, alcoholism, drug addiction, chemical poisoning, epilepsy, migraines, tumors and hemorrhages, amyloid accumulations in brain structures - Alzheimer's disease).
- Psychological or psychogenic (mental and psychological trauma, stress), an attempt to repress memories of trauma.
Types of amnesia according to the nature of the course
Let's look at the main types of amnesia:
- Retrograde - events that occurred before amnesia are forgotten.
- Anterograde - events that occurred after amnesia are not retained in memory. If the hippocampus is affected, one person can have both amnesias at the same time.
- Traumatic - amnesia as a result of head injury, often temporary.
- Dissociated - facts from personal life are forgotten, but universal knowledge is preserved. It is based on mental trauma.
- Dissociative fugue is a serious illness involving the loss of information from one's biography, including personal data, often with movement to unfamiliar territories.
- Childhood – a common loss of memory about infant and early events in one’s life. It is a protective function of the body.
- Post-hypnotic - everything that happened during the hypnosis session is forgotten. This is the same protective function of the psyche.
- Fixation - memory is impaired for the current time by events for more than a few minutes. Fixation amnesia is one of the elements of Korsakoff's syndrome.
Symptoms, additional signs, course of the disease
A person has lost his memory over a period of time - the first symptom.
A person has difficulty remembering immediate events - the second symptom.
The presence of false memories in a person, an attempt to replace them with fantasies or fictitious events is the third symptom.
In parallel, indirect signs may be observed: headache, impaired coordination of movements, drowsiness, attacks of cardiac arrhythmia, confusion, partial or complete loss of knowledge, visual impairment.
According to the course of the disease, amnesia is defined as:
- progressive type (slow gradual erasure of memories, difficulty remembering);
- regressive type (temporary memory loss followed by functional restoration);
- stationary type (sustained loss of a specific stage or event).
Clinical picture and specific manifestations
When a person enters a medical facility with an illness such as retrograde amnesia, he usually cannot explain to others why he ended up here.
Those. The main symptom of this type of amnesia is the inability to reproduce those events and actions that immediately preceded the attack or brain injury.
It is also common for patients to:
- manifestation of isolation and detachment;
- the presence of constraint in behavior and confusion;
- disturbance of orientation both in space and time;
- repetition of the same questions with a certain frequency;
- during an attack or for a short period after the injury, they do not remember events, actions and phrases, but then the function of reproducing brain memories is normalized.
If the brain injury is mild, the patient cannot remember the few seconds, minutes or hours preceding the injury.
In severe cases, events of a longer period are lost, and patients usually do not perceive information and ask it again several times .
Despite the loss of previous memories, the patient can easily reproduce particularly vivid events of the distant past, for example, a birthday, anniversary, and others.
Some patients, due to their inability to remember recent past episodes, develop pseudomemories, or begin to invent them in order to restore missing moments of life. The main thing in such circumstances is not to pay attention to this, since over time the function of reproducing memorable information will be restored, and the patient will gradually remember the missing points .
What signs are not symptoms of the disease?
Often, a person susceptible to this disease may experience symptoms such as dizziness and headaches, nausea and even vomiting, convulsions, visual disturbances, light and sound sensitivity, weakness, pain and aches throughout the body, high blood pressure and temperature, and others.
These signs do not in any way characterize retrograde amnesia, but are symptoms of the underlying disease or injury that caused such memory impairment.
Memory loss after alcohol
It is believed that even at the first stage of alcohol dependence, amnesia may occur. Sudden amnesia due to excessive alcoholic libation becomes stressful for the individual. However, not everyone experiences memory loss after drinking alcoholic liquids. For temporary amnesia to occur, it is necessary to “comply” with the following conditions: the number of drinks consumed, the degree of alcohol, the simultaneous consumption of a variety of alcoholic beverages, drinking alcohol on an empty stomach, the combination of alcoholic beverages with medications.
Editor's note: What characterizes simple schizophrenia?
How severely the connections between brain cells are damaged when drinking alcohol-containing liquids depends on the amount of ethyl alcohol that enters the body. It is believed that small doses of alcohol do not lead to loss of memories. However, the influence of alcoholic drinks on people is quite individual: firstly, the very concept of a small dose is different for different people, and secondly, the gender of the drinker, his age and general health are of great importance.
There is also a pattern: the higher the degree of alcoholic drink, the greater the likelihood that the drinking individual will have memory lapses.
The simultaneous consumption of different drinks containing different alcohols sharply increases the likelihood of amnesia.
Drinking on an empty stomach promotes instant absorption of liquid in the body, as a result of which almost all of the ethanol immediately enters the blood, which leads to rapid intoxication, which has the most destructive effect.
When drinking alcohol while undergoing drug treatment or combining the use of alcohol-containing liquids with drugs or smoking, the likelihood of amnesia increases several times.
Of the three types of memory, alcohol can only affect short-term memory; in other words, an individual’s memories “fall out” of a period of time.
Memory loss during alcohol intoxication occurs after palimpsest. A characteristic sign of the described condition is considered to be minor memory lapses, that is, the subject cannot remember some minor details or episodes of what happened during alcohol intoxication.
Memory loss in young people due to alcoholism occurs due to the occurrence of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. This syndrome is observed when an individual’s body is exposed to prolonged intoxication in the absence of adequate nutrition and a lack of vitamins B and C.
Step-by-step diagnostic algorithm
Diagnosis of this disease is carried out in several stages:
- Preliminary diagnosis based on examination and collected medical history, conducting special tests designed to test memory, communicating with loved ones and eyewitnesses to determine the causes and influencing events.
- Laboratory studies and examinations using special instruments, as well as consultations with highly specialized specialists.
- Establishing diagnosis.
The patient needs to consult several medical specialists: a neurologist, an infectious disease specialist, a narcologist, a psychiatrist and a neurosurgeon. You may also need a report from a traumatologist or surgeon.
Laboratory tests include blood sampling for general and biochemical analysis, toxicology.
Instrumental examinations include: radiography of the skull, showing violations of the integrity of bone structures, tomographic examination (MRI/CT) of the brain, allowing to identify pathological changes in its structure, and electroencephalography (EEG), showing the electrical activity of brain areas.
After analyzing all the findings obtained, a diagnosis is made and appropriate treatment is prescribed.
What is the treatment?
This form of amnesia is usually treatable, which is based on eliminating the underlying cause - a serious illness or injury.
The patient is prescribed for therapeutic purposes:
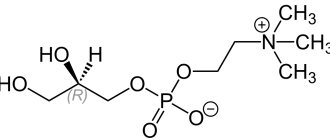
- drugs that help improve blood circulation in the damaged brain organ;
- nootropic (cerebralysin) and neuroprotective (glycine) drugs;
- antioxidants;
- vitamins (especially group B) and microelements;
- drugs that normalize the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
It is also recommended to undergo a course of physical procedures (electrical stimulation of the cerebral cortex, color therapy), regularly perform exercises aimed at improving and strengthening memory, and attend psychotherapeutic sessions in order to restore lost episodes, since the information has not disappeared from memory.
If this kind of illness is caused by various types of formations that require surgical intervention, then the necessary operations are performed.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for memory recovery is based on the causes and extent of brain damage, as well as the timeliness of providing the necessary drug treatment.
If the damage is minor, recovery is often predicted within a few days after the start of therapy. In cases where there are organic disorders of the brain, the prognosis for the restoration of lost information is not comforting - usually the memory does not return and becomes worse with the progression of the underlying disease.
Prevention of this kind of illness is aimed at preventing and timely diagnosing diseases that can provoke its development, therefore it is recommended:
- Do not refuse to undergo routine medical examinations, take the necessary tests and undergo hardware diagnostics of the nervous system.
- Follow safety precautions and try to avoid head injuries, and if injured, immediately contact a medical facility.
- Use alcohol and tobacco with caution, or better yet, avoid it.
- Maintain a normal daily routine and eat properly, consuming the required amount of vitamins and microelements.
Such disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system, which are associated with memory loss, require timely diagnosis and treatment in order to try to restore lost events and cause complications for the body. At the same time, people should follow the recommendations in order to prevent such a disease as retrograde amnesia.
Retrograde amnesia: treatment
In most cases, retrograde memory loss is reversible. This is due to the fact that with this type of amnesia, most often only the process of reproducing information is disrupted, while perception and storage remain normal. Psychotherapy sessions help replenish lost episodes. Electrical stimulation of the nervous system is also used to treat retrograde amnesia.
In order to fully restore memory, it is necessary to fight the immediate cause of the disease. For this purpose, medications that improve cerebral circulation (Cerebrolysin, Curantil), nootropics, and antihypertensive drugs are prescribed. For neoplasms, surgical treatment is indicated. Giving up bad habits is a necessary condition for therapy.