Definition of disease
DE
– this is rather a collective concept in medicine, since there is no such definition in the ICD tenth revision. Therefore, due to its similarity with clinical symptoms, it is most often associated with cerebral ischemia.
Methods for diagnosing dyscirculatory encephalopathy:
| Methods | Description |
| Angiography of head and neck vessels with contrast | Allows you to identify affected areas of blood vessels |
| Electroencephalography | Provides insight into the functional capacity of brain neurons |
| Magnetic resonance imaging | The most informative method for diagnosing microstrokes in ischemic areas |
| Fundus examination | Hemorrhages in the ocular retina and acute swelling of the optic nerve are detected, indicating intracranial hypertension |
| Doppler ultrasound | Allows you to identify blood clots and blocked areas in blood vessels |
The difficulty in determining the disease lies in the fact that several disease factors may play a role in one patient, such as:
- Excessive hypervasoconstriction of cerebral arteries. When, in response to an increase in systemic blood pressure, not a physiological reaction occurs - arterial spasm, but hyperconstriction, which exceeds this physiological reaction in severity.
- Cerebral microangiopathy. Which plays a role in hypertension, but can also be in diabetes mellitus, and in CVD - cerebrovascular disease.
- Insufficiency of collateral circulation. When even minor stenoses of the main vessels of the head can lead to cerebral ischemia.
- Deterioration of the rheological properties of blood.
- Impaired microcirculation at the cerebral level.
- The appearance of microemboli on the main vessels of the head. When a substrate (embolus) forms from an atherosclerotic plaque and clogs the small arteries of the brain, causing the formation of a lacunar infarction.
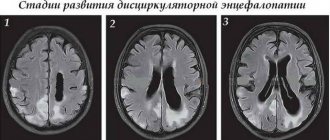
All these factors affect blood circulation in the brain, change the structure of the tissue, which affects its function. In this regard, three stages of the disease are determined, as well as several of its types, depending on the causes:
- Venous DE
. It is caused by stagnation of blood during outflow from the brain, which causes swelling of the brain vessels. - Hypertensive DE
. Characterized by frequent hypertensive crises. - Atherosclerotic DE
. The cause is cerebral atherosclerosis. The most common form of the disease.
DE of mixed type is a disease of complex genesis that combines several forms of the disease.
[media=
https://youtu.be/4hWZJpiFWq0
]
Main causes of dyscirculatory encephalopathy
A decrease in the functionality of brain vessels leads to disruption of blood flow in the tissues. Certain areas begin to experience a deficiency of oxygen and nutrients, which is why cell colonies first die, and then large areas of the brain matter. At first, the functions of these areas are taken over by neighboring zones, but in the absence of treatment this connection is lost.
The causes of the disease depend on its form:
- atherosclerotic - harmful protein and lipid compounds accumulate on the walls of blood vessels, narrowing their lumen. Hypoxia of the brain develops, the organ ceases to perform its functions to the required extent. Pathology is often a consequence of poor nutrition, leading to increased cholesterol levels;
You will learn about atherosclerosis and its impact on the development of various pathologies here.
- venous - the result of compression of the veins through which blood, along with metabolic products, is removed from the brain. The tissues are literally poisoned by toxins, and inflammatory processes develop. The risk of this form appearing in a person increases if there is a history of heart or pulmonary failure, tumors, or surges in blood pressure;
- hypertensive – characterized by acute development against the background of a sharp increase in blood pressure. This phenomenon leads to spasm of blood vessels, which try to maintain integrity and not burst. Over time, the channels begin to thicken inward, which narrows their lumen. The risk group includes patients with hypertension, glomerulonephritis, liver failure, and Cushing's disease.
You will learn about the symptoms of hypertension and possible complications of the pathology here.
Smoking and alcohol are factors in the development of dyscirculatory encephalopathy
The disease can also be a consequence of VSD, smoking and alcohol abuse, blood disorders, toxin poisoning and osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. A separate group includes DEP of mixed origin, in which several factors are to blame for the development of the pathology. Most often there is a combination of atherosclerotic and hypertensive forms. This type of disease progresses most quickly and is typical for older people.
Initial stage of the disease
Symptoms of discirculatory encephalopathy at the initial stage are hardly noticeable, since the function of dead cells is taken over by nearby neurons. In this case, minor signs appear that are not clearly expressed:
- headaches with a feeling of fullness;
- dizziness;
- memory loss;
- noises in the head;
- irritability;
- emotional instability.
At this stage of the disease, with timely treatment, remission for decades is possible, and in some cases, complete recovery.
Multiple sclerosis is often mistakenly called memory loss in old age. In fact, this is a disease of young people, difficult to treat, and its consequences are very serious. Read more in the article: “multiple sclerosis symptoms and causes.”
Disability at the second stage
The third disability group is given to those patients with dyscirculatory encephalopathy who are able to perform everyday and professional activities, but this is difficult for them. At the same time, living with the disease is possible without constant monitoring from loved ones or specialists. In general, each specific case requires an individual approach and consideration.
The second group is given to people whose condition is not limited to cephalgic syndrome (headache, tinnitus, nausea and vomiting). Due to deterioration of memory, attention, and tremors of the limbs, they are unable to maintain their ability to work. Impaired functioning is obvious, but it does not necessarily mean that the patient is completely unable to care for himself.
Second stage of the disease
When decompensation occurs and the lesions become significant, in addition the following symptoms begin to appear:
- lack of control over one's own movements;
- inhibited articulation, the person seems to forget how to speak.
Stage 2 of the disease develops, which can also manifest itself in various variants of psychopathological syndromes:
- asthenodepressive;
- asthenohypochondriacal;
- paranoid;
- affective.
The cephalgic syndrome becomes especially pronounced, in which severe headaches are felt, often vomiting and nausea. The patient may experience sudden changes in mood due to loss of communication between neurons in the brain. Speech becomes sluggish, and the patient does not always remember what he is talking about.
Treatment must be carried out immediately, otherwise the disease progresses very quickly.
At this stage of the disease, disability is already assumed, although the person is still able to take care of himself and does not lose cause-and-effect relationships.
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is a diagnostic procedure that helps determine the exact parameters of internal organs: their location, size, structure and condition. Read more in the article: “ultrasound of the abdominal organs: preparation for the procedure.”
Prognosis for the second stage of the disease
Many people are interested in the question of how long you can live with dyscirculatory encephalopathy of the 2nd degree. There is no clear answer, and there is no statistical data on this matter. In our country, as well as abroad, there is no information about the epidemiological prevalence of this disease.
Patients with degree 2 encelopathy can live a long time - up to 20 years
, and maintaining mental activity until the end. It all depends on the patient’s lifestyle, the characteristics of the course of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment, the goal of which is to prevent the disease from developing to the third stage. Conditions such as degenerative changes in the brain, high blood sugar levels, and frequently recurring hypertensive crises worsen the prognosis.
Disability groups for dyscirculatory encephalopathy:
| Group | Description |
| First group | With DE stage 3 with completely absent ability to self-care. With severe disorders of the musculoskeletal system, blood circulation and severe dementia. |
| Second group | At stages 2-3 DE with significant memory loss and neurological/mental disorders. |
| Third group | At stage 2 DE with moderate neurological and mental disorders. The patient is capable of self-care. |
At the last stage of the disease, brain damage is irreversible, the person loses all connection with the world around him. The diagnosis, unfortunately, is disappointing - how long such a patient can live depends on the care of the medical staff.
Symptoms of dyscirculatory encephalopathy of the second degree
The sooner treatment for stage 2 DEP begins, the higher the chances of preventing irreversible consequences and complications of the pathology.
Therefore, it is important to understand what signs may indicate the onset of organic changes in the brain. Depending on the form of the disease, the classic clinical picture is supplemented by specific manifestations. In hypertensive DEP, persistent arterial hypertension is observed. If the cause of the disease is atherosclerosis of the cerebral vessels, then initially the patient complains of tinnitus, dizziness, fatigue and fatigue. List of classic symptoms of the second stage of dyscirculatory encephalopathy:
- constant and obsessive headaches;
- nausea and vomiting for no apparent reason;
- dizziness, staggering when walking;
- deterioration in sleep quality;
- vasodilation during fundus examination;
- change in the patient’s facial expression due to pallor and deterioration in the functioning of the facial muscles;
- problems with coordination of movements that do not allow performing actions that require the use of fine motor skills of the hands;
- hearing and memory impairment, speech problems, minor twitching of the limbs;
- tearfulness and moodiness, mood swings, irritability and aggressiveness, feelings of fear for no apparent reason.
The symptoms that characterize grade 2 dyscirculatory encephalopathy can appear constantly or at the end of the day. Often, patients experience not individual symptoms, but entire syndromes.
Within their framework, specific manifestations turn into functional failure. Some people suffer the most from their thinking, while others experience serious disturbances in sleep or motor activity.
Treatment and prevention
Prevention of ischemic diseases of the brain must begin at a very early age. To do this you need:
- protect yourself from stress;
- control your own weight;
- prevent the process of obesity;
- adjust nutrition;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- engage in active sports.
Treatment is carried out with various drugs aimed at improving cerebral circulation:
- vasoactive;
- cerebroprotective;
- neuromodulatory;
- antioxidant.
In addition to medications, various physical procedures are prescribed, such as therapeutic massage, exercise therapy, and laser therapy. Such patients are treated under the supervision of a neurologist in a hospital.
With timely diagnosis and adequate volume therapy, the progression of dyscirculatory encephalopathy can be stopped, and the prognosis will be favorable.
The complex of therapy also includes special diets and spa treatment
. Traditional recipes using herbs - soothing baths and infusions - will also give a good effect. If these methods are insufficiently effective, surgical intervention is indicated to restore vascular patency.
Diagnosis of pathology
Making a preliminary diagnosis begins with collecting complete information about the situation. The clinical picture of second-degree DEP is often similar to other forms of brain damage. In order to identify real pathology, neurologists conduct tests that identify problems with coordination and cognitive impairment. Blood pressure indicators are assessed and cholesterol levels in the blood are determined.
To confirm the diagnosis of grade 2 dyscirculatory encephalopathy, the following studies are carried out:
- CT or MRI – identifying the area of tissue damage;
- Doppler ultrasound and rheoencephalography – assessment of the condition of cerebral vessels;
- neuropsychological study - identifying damage to the higher functions of the nervous system;
- identifying neurological manifestations of the disease by checking reflexes.
You can learn more about diagnostics using rheoencephalography here.
A comprehensive diagnosis of stage 2 DEP allows not only to confirm the presence of problems, but also to determine the degree of their severity. Based on the research results, therapy is prescribed aimed at overall improvement of the condition of the blood vessels in the brain, combating individual symptoms and causes of decreased functionality of the blood channels.