There is no need to say that drinking large quantities of strong alcoholic beverages negatively affects the health of the drinker. The biggest blow falls on the human nervous system. Alcoholic dementia is one of the natural outcomes of alcoholism, and its first symptoms can appear quite early. Although this disease is also characterized by dementia, like other forms of the disorder, it has its own characteristics. They concern both the external manifestation of the disease and methods of its treatment, prognosis and much more.
What is alcoholic dementia
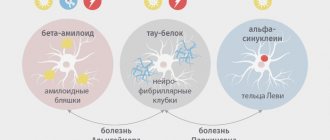
Alcoholic dementia, in simple terms, is severe damage to the tissues and blood vessels of the brain due to constant or frequent alcohol intoxication. As for the external manifestations, in this case they do not differ from any other organic dementia. Here, in the same way, there is a slow change in personality, behavioral reactions, emotional sphere, mental abilities, but this always happens under the influence of alcohol and its products on the entire nervous system.
Important: Alcoholic dementia develops much faster than organic dementia. No more than 5 years pass from the appearance of the first symptoms to the development of the last stage.
This disease cannot be called rare - to one degree or another, dementia always develops in alcoholics. If no therapeutic measures are taken, it often leads to disability and complete loss of self-care. What really distinguishes this form of disorder from others is the age of its onset and gender. If the classic variant is more common in women over the age of 70, then alcoholic dementia is more common in men of pre-retirement age. The first symptoms can be observed as early as 45 years of age.
Complications
Alcohol-induced dementia has severe consequences. The brain atrophies, most of its functions turn off. The patient is exhausted, the body mass index reaches critical values.
Ethyl alcohol toxins affect all organs. The liver suffers, it becomes inflamed, alcoholic hepatitis begins, which ends with necrosis of the organ parenchyma and its complete failure.
Since fluid is eliminated from the body through the kidneys, toxins also affect them. The glomeruli stop working to filter blood plasma. Toxins accumulate in the body. Renal failure develops, which leads to failure of one and then both kidneys.
Accumulated toxins affect the pulmonary and cardiovascular systems, causing failure of these organs.
Damage to the brain ends with inhibition of reflexes, mental and speech activity. The connection with the outside world is completely lost. Gradually the patient falls into a vegetative state.
Life expectancy is sharply reduced. Most alcoholics live in unsanitary conditions, so they often develop infectious, viral and fungal diseases.
Symptoms of alcoholic dementia
The symptoms and treatment of alcoholic dementia are similar to other types of organic brain damage. The disease also develops gradually; more and more signs of destruction of the nervous system are added every day, but they go unnoticed by the alcoholic himself.
For starters, Korsakoff syndrome appears. It is characterized by memory problems. Events of the recent past are erased from memory, and in their place so-called false memories arise. This stage cannot yet be called alcoholic dementia, but it is a sure sign that the brain can no longer cope with the constant effects of poison and is about to begin to deteriorate.
Then the true symptoms of alcoholic dementia appear, namely:
- Intellectual decline. Thinking slows down, it becomes difficult to concentrate on one thing, as well as switch to another topic.
- Excessive irritability appears, and it primarily concerns something new. People are increasingly nostalgic for the old days.
- Amnesia is constantly evolving. It becomes more difficult for a person to remember even the events of yesterday, not to mention the remote past.
- The ability to analyze and generalize is deteriorating, even the imagination is working worse and worse. In this way, all mental processes are affected.
- The circle of interests is narrowing. It becomes important for a person only to satisfy primary needs and consume a new portion of alcohol.
- Egoism develops and against its background the ability to empathize is lost. Moral principles don't matter anymore.
- Criticism in thinking is completely absent. A person becomes absolutely immune to other people’s comments and does not see problems in himself.
- The control of impulses is impaired.
All of the listed signs of alcoholic dementia can only be called initial; gradually the disease becomes more and more similar to the last stages of the classical form of the disorder: a person loses the ability to navigate in space and time, does not recognize relatives, becomes unable to care for himself, and motor skills are lost. As a result, a fairly young 45-50 year old person becomes like a decrepit old man.
Causes and symptoms
The only cause of AD is drinking excessive amounts of alcohol over a long period of time. There are people from risk groups (those mentioned above) in whom alcoholism has a more severe clinical course and dementia comes earlier.
Symptoms
There are symptoms of alcoholic dementia that a neurologist and psychiatrist can use to make a diagnosis:
- Memory change. The function of long-term memory is impaired, the patient does not recognize loved ones, does not remember important moments in life. Short-term memory gradually fades, that is, he does not remember his actions that he just performed.
- Behavior change. An alcoholic experiences frequent mood swings, he becomes aggressive, childish, and cannot be controlled by doctors. Talking to himself. His personality changes completely and lethargy appears. Attachment to loved ones disappears. Actions become thoughtless.
- Depression is common in the early stages of dementia. At the same time, others take this for a state of fatigue.
- Disorientation in time and space. The patient does not understand where he is, confuses places and people, does not realize what time it is at the moment, confuses day and night.
- Periodic enlightenment of consciousness. It does not happen often and only in the early stages of alcoholism. In case of a more serious disorder, it occurs after treatment.
- Loss of concentration in later stages. The patient cannot engage in any activity; the information transmitted to him is not perceived. Simple actions become impossible for him.
- The boundaries of morality are blurred. A person does not care what happens around him. He doesn't feel close to people. The range of his interests comes down only to alcohol.
- A constant, insatiable feeling of hunger that occurs after the body has passed through intoxication.
- Loss of skills that the patient previously possessed. He cannot serve himself. Stops cooking, washing, washing dishes, cleaning.
- Some representatives develop uncontrolled collecting. They take everything they see home.
- Sleep disturbance. The period of sleep can last only a few hours, and the period of wakefulness can last for several days in a row. This leads to even more severe disorders of brain activity.
- Clinical symptoms of central nervous system disorders. Tremors (shaking) of the hands appear, muscle strength is reduced, and the reaction of the pupils to light is less pronounced than in a healthy person. The gait changes, it becomes uncertain, shaky, sometimes the patient cannot stand up. Speech function is impaired (incoherent words, mooing). These conditions cannot be treated because the neuron function is completely lost.
Diagnosis of the disease
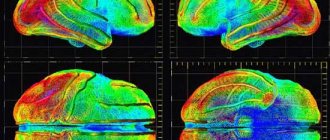
Sometimes alcoholic dementia in dementia appears so early that doctors attribute the problem to other diseases. Similar symptoms may appear due to mental disorders, tumors, and intracranial hematomas. To confirm that alcohol was the cause of the disease, and the brain has already begun to deteriorate, it is necessary to perform an MRI or CT scan.
Treatment will depend on the location of the lesions, the extent of the disorder, and the presence of concomitant diseases, so ultimately consultation with several specialists may be required. Usually a therapist, narcologist, neurologist, and psychiatrist are involved. They conduct additional examinations in accordance with their specialization, after which they make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment measures.
Diagnostics
In order to diagnose AD, it is necessary to exclude other causes of brain damage: tumors, stroke, hemorrhage, infections, fungi, metabolic disorders affecting the brain.
Upon admission to an appointment with a neurologist, an anamnesis is collected, that is, a questioning of the patient or his guardian about symptoms and complaints. The doctor asks additional questions to help him make a diagnosis. After this, an instrumental examination of the patient’s body is carried out, the reflexes of the pupils and the musculoskeletal system are checked. The doctor looks at how a person speaks, whether his speech is connected, what his ability to think and perceive information is.
After collecting an anamnesis and examination, laboratory tests are prescribed: general analysis of urine and blood, puncture of cerebrospinal fluid (if an infection in the brain is suspected), scatological examination (stool analysis). These tests are also prescribed when a diagnosis of alcoholic dementia has already been established, since most alcoholics live in conditions of poor hygiene and may contract an infection or fungus.
In severe cases, MRI and CT are performed. Data from these studies will show how much brain damage progresses. The doctor assesses how much brain activity has been preserved and which centers are damaged. This is necessary for drug therapy.
After a diagnosis of alcoholic dementia is made, internal organs are diagnosed to determine how badly they are damaged. For this purpose, data from blood tests, urine tests, ultrasound of the peritoneum and pelvis are used.
Treatment of alcoholic dementia
As in the case of organic dementia, treatment of alcoholic dementia comes down to relieving the symptoms of the disease and slowing down its development.
Work is being carried out in several directions, presented in the table below. Directions for drug treatment of alcoholic dementia
| Disease stage | Main symptoms | Treatment |
| Lightweight |
| Prescribing medications to improve the functioning of blood vessels, cerebral circulation, antidepressants, vitamins. |
| Moderate |
| Prescribing medications to relieve psychopathic symptoms in addition to those used for mild disorders. |
| Heavy |
| Prescription of sedative and neuroleptic drugs. |
Treatment of alcoholic dementia at any stage is impossible without complete abstinence from alcohol. As additional therapy, a special diet, physiotherapy, psychotherapy, and the creation of comfortable conditions are prescribed. Particular attention is paid to concomitant diseases, such as diabetes mellitus and hypertension, as they can seriously worsen the patient’s general condition. It is recommended to carry out treatment in a hospital setting, at least in the first months.
Treatment
For the treatment of alcoholic dementia, the main principle is a ban on the use of alcohol, cigarettes, and drugs. Any addiction will lead the alcoholic to start drinking alcohol again. In order to stop drinking faster, you need to see a psychotherapist or psychiatrist. Weekly counseling will help you quickly learn to live without alcohol. The psychiatrist will recommend a coding method. It comes in the following types:
- The medical route, based on the intravenous administration of drugs that cause aversion to alcoholic beverages, therapy is considered the most effective.
- Introduction of medications that block the entry of ethyl alcohol and its toxins into organs and systems at the biochemical level.
- Laser therapy based on acupuncture, that is, the beam acts on certain points that are located inside organs or blood vessels, causing healing, activating the function of damaged tissue and stopping the use of ethyl alcohol (the method appeared recently, so reviews about it are not widespread).
- Psychiatric treatment based on the use of methods that restore psychological health that was damaged during alcohol abuse (suggestion, hypnosis, talking), their choice depends on the degree of decomposition of the patient’s moral foundations (the more serious the violation, the more active the doctor chooses, for example, hypnosis in the acute phase).
- Physiotherapy with the help of devices, that is, devices are used that restore internal organs without chemical medications, but thanks to physiotherapy.
After completely quitting alcohol, it is necessary to restore internal organs. For this purpose, drug therapy methods are used:
- nootropic drugs - enhance brain nutrition and function;
- neuroprotectors - protect neurons from the effects of pathogenic factors;
- antioxidants - remove free radicals and toxins from the body that cause tissue damage;
- drugs that improve coronary blood flow (that is, to the vessels of the heart), this is necessary in case of complications in the heart and insufficiency of its work;
- since blood flows poorly from the portal vein of the liver, and the pressure in it increases, drugs are prescribed that reduce the risk of hypertension and rupture of the vessel wall (angioprotectors, hypotension);
- sedatives, in severe cases with severe patient aggression, tranquilizers are used;
- sleeping pills for sleep disorders, insomnia (this allows the body to rest and recuperate).
After completion of treatment and complete cessation of alcohol, in some cases additional medicinal support of the body is necessary to avoid the risk of relapse. For this purpose, drugs are used that cause disgust from the effects of alcoholic beverages. If the patient uses these drugs and drinks alcohol, headache, nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, and increased sweating will occur.
Prognosis for treatment of alcoholic dementia
In most cases, damage to the nervous system in general and the brain in particular is irreversible. A relatively favorable prognosis for alcoholic dementia can only be given if treatment was started at the initial stage and the patient follows all the doctor’s recommendations.
If gross changes in personality have already occurred, it will not be possible to reverse them - all that remains is to relieve the most severe symptoms of the disease and provide maximum care. Doing this at home is quite difficult, as is the case with other types of dementia, so patients are usually placed in special boarding houses and hospitals. If psychotic deviations occur, treatment is carried out in a psychoneurological dispensary.
Prevention
A person who drinks alcohol in moderation should adhere to rules that reduce the risk of developing addiction. Doctors trace a hereditary predisposition to alcohol dependence in those people in whose family there were such cases.
In order to avoid such effects, it is necessary to adhere to a healthy lifestyle (play sports, eat healthy foods), treat emerging diseases completely, prevent their chronic course, self-development, be in society more often, and prevent the development of depression.
Alcohol should be consumed in moderation or avoided completely if there is a possibility of addiction.
Alcohol-induced dementia is a serious disease that requires urgent medical attention and therapy. People who have developed this condition do not turn to a specialist themselves. They need help from loved ones. Treatment depends on the severity of the central nervous system disorder. Most people with alcohol-related dementia are unable to care for themselves and require 24-hour care. Self-medication is impossible; drug therapy is required, which will not only eliminate addiction, but also help with withdrawal symptoms.
What can contribute to the development of alcohol-related dementia?
Dementia and alcohol don't always go together, but many factors can increase your chances of developing the disorder. The following are guaranteed to be at risk:
- People who have relatives who are alcoholics.
- People who have suffered traumatic brain injuries or have other neurological problems.
- Patients with diabetes mellitus and other endocrinological diseases.
- People with disorders of the cardiovascular system.
- Persons leading a sedentary lifestyle, as well as those who refuse intellectual training.
If a patient has a potential predisposition to developing alcoholic dementia, it is better to stop drinking alcohol completely, since the disease can make itself felt at any time.
Important. Like other forms of the disease, dementia due to alcoholism is irreversible. It can only be slowed down by completely abstaining from alcoholic beverages and prescribing treatment.
The danger of alcoholic dementia and alcoholism is, in principle, known all over the world, but residents of the former Soviet republics, Finland and Asian countries are especially susceptible to the disease. They should pay special attention to their lifestyle, strive for a healthy diet and high activity. If you notice the first symptoms of the disease, you must immediately seek medical help, including drug treatment and psychiatric help. Otherwise, it will be impossible to avoid brain damage, as well as restore it.
Stages of development
The stages of development of alcoholic dementia are stepwise.
- First stage. Signs of a central nervous system disorder are not visible. Depression begins and detachment from people is observed.
- Mild dementia. Information is difficult to assimilate. Interest in the outside world is lost. An alcoholic sometimes forgets where he is and stops performing everyday tasks.
- Moderate dementia. Loss of mental activity, speech impairment, complete withdrawal from the world.
- Severe dementia. The patient does not recognize loved ones, does not know what year or time of day. Insomnia is progressing. A person stops serving himself. Doctors define this condition as acute alcoholic dementia.
Reasons for development
The main provoking factor is considered to be the constant impact of alcohol breakdown products on the brain structures and blood supply of the central nervous system. In the liver, ethanol is oxidized to acetaldehyde, a toxic intermediate compound that has a negative effect on many body systems.
Under the influence of this substance, the structure of the walls of the cerebral arteries changes, which leads to chronic oxygen starvation of nerve cells. The walls of blood vessels become less durable, which increases the risk of hemorrhage. As a result of hypoxia and exposure to toxins, degeneration and then death of neurons occurs. The risk of developing dementia increases if you have the following conditions:
- arterial hypertension;
- cerebral atherosclerosis;
- alcoholic encephalopathy;
- metabolic diseases;
- endocrine pathologies.
Predisposing circumstances are previous traumatic brain injuries, cerebrovascular accidents (stroke, transient stroke), cerebral tumors. Hereditary predisposition is important (the presence of close relatives with dementia of any origin, especially alcoholic).
Alcoholic dementia: causes, consequences
Dementia can erase all accumulated skills, knowledge, and abilities from memory. Alcohol intoxication of the brain causes not only intellectual, but also personal pathologies, social connections and family life are destroyed.
Elderly people lose the ability to self-care and become disabled.
Alcohol is an aggressive substance that, when used regularly, poisons brain cells, disrupts blood flow, destroys blood vessels, and damages the structures of the nervous system. Ethanol immediately penetrates the circulatory system and spreads throughout the internal organs, releasing acetaldehyde, which has a destructive effect on nerve cells. In this case, alcoholic polyneuropathy is often observed, occurring together with dementia.
The development of dementia is facilitated by concomitant traumatic factors, brain tumors, age-related changes, infectious, endocrinological, autoimmune diseases, diabetes mellitus, genetic predisposition, heart and vascular disease, physical inactivity, and lack of intellectual activity.
Stages of the disease
The rate of development of alcoholic dementia depends on many factors: the amount of alcohol consumed, concomitant diseases, genetic inheritance, drug use. This means that dementia can develop differently in different patients, but still, as a rule, the disease goes through four main stages:
- Stage one: initial. The only external sign is emotional disorders - the appearance of isolation, the predominance of depressive moods, the loss of previous interests and hobbies.
- Stage two: easy. Mild dysfunctions of memory, attention and logical thinking are observed: patients find it difficult to remember or concentrate, and any intellectual stress comes at the cost of noticeable effort.
- Stage three: middle. Symptomatically repeats the second stage, but the disturbances are much more pronounced: patients clearly do not control their attention, cannot remember anything, have difficulty remembering past events, and intellectually demonstrate violations of logical coherence, consistency of judgments or inferences.
- Stage four: severe. There is a complete disintegration of the personality with disruption of all mental functions, loss of moral principles and the development of various mental disorders.
And in the end
At the last, initial stage, patients are exhausted, cachectic, lying in bed in the fetal position, muttering something inaudibly. The main difficulty is that dementia does not develop in reverse
. You can only stop it at the stage from which massive and expensive treatment began - and this is provided that alcohol is completely excluded from the diet. Therefore, all efforts to correct the situation must be made earlier, much earlier. Ideally, even before the stage at which signs of Korsakov’s syndrome appear. What to do with a person who is already at the stage of alcoholic dementia is up to the relatives to decide: either provide constant care and vigilant control, or send them to a boarding school for psychochronic patients.
Tags:
- Alcohol
- Brain