Self-esteem conflict
Your image is your internal idea of yourself, for example, “My name is Ivan. I am a patient, loving and compassionate person. I'm a disorganized artist who supports animal rights, etc." Internal conflict occurs when we are confronted with evidence that contradicts our beliefs about ourselves. For example, a person who believes he is honest may lie on his resume to get his dream job. Someone who is for a healthy diet cannot give up smoking. A person who identifies as an empath may experience constant resentment towards another person.
Types and forms of intrapersonal conflicts
Since there are many causes and conditions for the emergence of intrapersonal conflicts, they can only be classified conditionally. In real life, a huge number of conflicts of this type arise every day, so experts have come to the conclusion that it is necessary to find one specific basis for classification. This basis for dividing internal conflicts into types was the value-motivational sphere of the individual, since it is this sphere that is directly related to the internal conflict of the individual.
There are six types of intrapersonal conflicts: adaptation conflict, conflict of unsatisfied desire, role conflict, conflict of biased (inadequate) self-esteem, moral conflict, motivational conflict.
If any of the six types of conflicts are not resolved over a long period of time, then it transforms into a neurotic intrapersonal conflict.
1. Adaptation conflict is a contradiction between an individual and the reality around him. This type of intrapersonal conflict also arises when disruptions occur in the process of social or professional adaptation.
Examples: a new employee cannot perform his job duties properly; the recruit cannot adapt to the army regime, etc.
2. A conflict of unsatisfied desire is a contradiction between the desires of an individual and the surrounding reality that prevents their satisfaction. This type of conflict most often occurs in people with an inferiority complex.
Examples: an individual dreams of being like the celebrity he adores, but has a completely different appearance; a person dreams of living in abundance, but the real state of affairs does not allow him to realize this desire, etc.
3. Role conflict is problems that arise in the process of understanding the requirements imposed by the individual to fulfill a particular role or the inability of an individual to implement several roles at the same time.
Examples: A police officer has difficulty arresting his good friend; the teacher may not know how to behave in a particular case with a student who is her son, etc.
4. The conflict of biased (inadequate) self-esteem is a contradiction between the claims of an individual and his real internal potential.
Examples: a person has high or low self-esteem; a person wants to engage in self-improvement, but does not want to leave his usual comfort zone, etc.
5. Moral conflict is a contradiction between the desires of an individual and his responsibilities, between personal attachments and moral and social principles and norms.
Examples: a married man has the opportunity to start a relationship with a girl to whom he feels attraction and interest; a pacifist needs to take up arms and protect his loved ones, otherwise they will be killed, etc.
6. Motivational conflict is a contradiction of motives of different nature, a struggle between the unconscious aspirations of the individual and existing security considerations.
Examples: a man experiences certain difficulties because he cannot make a choice between meeting with school friends and going for a walk with his wife; the guy wants to start doing martial arts, but is afraid of bruises and injuries, etc.
Each of the above types of intrapersonal conflicts is expressed in one of six existing forms.
The forms of expression of intrapersonal conflicts are such forms as:
- neurasthenia (insomnia, depression, decreased level of performance),
- rationalism (justification of lifestyle, actions and deeds),
- euphoria (laughter through tears, increased mood in public),
- nomadism (the desire to comprehensively change the environment),
- regression (primitivism and refusal of responsibility),
- projection (negative and negative attitude towards the world around us, use of excessive criticism).
Forms and methods of solving the problem
Click to enlarge
Understanding the forms of manifestation and ways to resolve internal conflicts is an important task for every person. We have already talked about forms, now we can move on to the topic of resolving the situation
The point is, if a person does not find a positive solution for himself, this will lead to a protracted confrontation and, as a consequence, to a suicidal situation, a nervous breakdown, or the development of psychological disorders. That is why it is important to know how to act in the current conditions. Moreover, if you calmly figure it out, it’s not so difficult.
To resolve intrapersonal conflict as quickly as possible, you should pay attention to the following points:
- Care. Try to let go of the difficult situation and switch to another topic. Sometimes a problem cannot be solved with existing skills and capabilities. Therefore, it is worth accepting;
- Compromise. If there is a choice, try to come to a compromise and immediately begin to act;
- Sublimation. In cases where you cannot solve a problem, switch to another activity that brings you pleasure. For example, a hobby, sports or creativity where you can achieve results. Later you will return to the unresolved problem with renewed vigor;
- Reorientation. Change your attitude towards a person or object;
- Idealization. If reality is very bad, turn on some music and try to daydream. Break away from reality. Watch a comedy or movie that you like best;
- Correction. Try to be objective about your Self;
- Crowding out. If desires are unrealistic, try to suppress them or push them into the future, switching to more achievable ones.
Peculiarities
In conflictology, sociology and psychology, intrapersonal conflict occupies a special place due to its most important features:
- Unusual nature (the person himself and his personality are simultaneously the subject and object of the conflict, comes into conflict with himself, and not with “alien” actors - another person or an entire group).
- The difficulty of identifying a contradiction - this symptom is also called latency: lies in the fact that the individual often does not notice that he is in a conflict situation.
Latent personal contradiction can be accompanied by the following phenomena:
- simulation, sabotage, denial of problems and the need to solve them;
- sublimation;
- compensation (as an option - extreme development in another area);
- escapism - escape from reality into dreams;
- nomadism - radical changes in life;
- self-justification;
- idealization, abstraction - attempts to convince oneself that everything is in order;
- regression, which includes suppressing desires, avoiding making decisions that will entail responsibility;
- projection (attributing one's own negative qualities and traits to another person).
3. Specific forms of manifestation, course - accompanied by suffering, up to biochemical disorders, for example, endogenous depression.
Application of knowledge about conflicts
As already mentioned, we live in a world in which all kinds of disagreements, disputes, clashes, contradictions, etc. often arise. And even if the situation around you now is positive or at least neutral, it is not a fact that everything will continue to go like clockwork and no conflict situation will arise. Even such a superficial look tells us that conflicts need to be resolved.
But let's talk more specifically about why you need to apply knowledge about conflicts:
- If a person has an intrapersonal conflict, it is very dangerous for his mental health, and in some cases for his life. Knowing how to manage one’s intrapersonal conflict, a person is able to understand oneself, neutralize serious experiences, promote one’s positive attitude and good mental health;
- The ability to behave with dignity in conflict situations is one of the indicators of an adult, mature personality, good manners, adequacy, constructive perception of reality and a mood for productive interaction with society. If a person is used to solving everything with his fists, and only knows how to argue and snap, this indicates that his inner core is weak, his psyche is unstable, and he lacks the ability to communicate competently and find a common language;
- Peace with oneself and the people around you is, first of all, a positive mental state, and science has long proven that the mental state is reflected in the physical plane. Consciousness, soul and body are directly interconnected with each other. Internal conflicts can cause serious physical illnesses, not to mention mental ones. And conflicts with other people can result in injuries, injuries, etc. If a person knows how to apply conflict management skills, he can prevent situations that are dangerous to both his physical and mental health;
- The ability to resolve conflict and behave appropriately in conflict situations indicates that a person is inclined to show kindness, a positive attitude towards people, and respect. It also says that a person thinks not only about himself and his interests, does not prioritize only himself and his own desires, but also thinks about others. The attitude of those around such a person will almost always be similar, i.e. he will be valued, respected, appreciated, and his opinion taken into account. In addition, there are always more good events in the lives of positively minded people than in those who are negatively minded;
- Skillful application of knowledge about conflicts is an integral part of the path to harmony with oneself, the people around you and the surrounding reality.
The benefits of applying knowledge about conflicts are obvious. But it would not be superfluous to note that these are not all the advantages of this skill. In fact, there are much more of them, including a positive influence on the future generation, in other words, on one’s children, because, as is known, the skills and abilities acquired by a person are passed on to his children in the form of predispositions at the genetic level. So, by studying conflict management, you can be sure that you are making not only your life better, but also the lives of your sons, daughters and even grandchildren.
The positive impact of intrapersonal conflict on a person’s future
Despite the danger of a person developing a severe form of neurotic disease, intrapersonal conflict is an excellent opportunity to rethink values by adjusting one’s own worldview. Practitioners working with such patients identify the following positive changes in the psyche of people who have coped with disagreements:
Forced mobilization of hidden personal resources, with the help of which it is possible to solve the problem that has arisen. A “sober” look from the outside at the desired and actual, haunting the patient’s inner world. Increased self-esteem, because a person copes with a serious mental disorder, overcoming a number of fears. The appearance of rational thinking, which helps him make decisions in controversial and especially difficult situations. Knowledge of one’s own “I”, which improves a person’s attitude towards society. In the process of searching for a solution to a problem, brilliant thoughts appear and effective ways to realize hidden potential are found.
The main thing is to contact a psychologist in time, who can correctly diagnose the cause of internal disagreements. It is extremely rare for people susceptible to neurotic illness to solve such a problem on their own. Too many subconscious “interlocutors” are present in the patient’s head, directing the true personality along the wrong path.
The problem from the point of view of Western psychologists
Both Western and domestic researchers have taken a thorough approach to studying the problem of intrapersonal conflict. Let us mention the most famous theories.
According to Freud
Freud analyzed intrapersonal conflict within the framework of his own theory of psychoanalysis. In his understanding, this kind of contradiction is inevitable, since the base interests of a person are related to the satisfaction of his biological needs, while the social and cultural sphere imposes certain restrictions on the individual. Thus, intrapersonal conflict is a confrontation between the conscious and unconscious.
According to Maslow
The theory of the American psychologist A. Maslow is that an individual has a rank of needs, from biological to spiritual, the top of which is the need for self-realization (self-actualization). Intrapersonal conflict manifests itself right at the top of Maslow’s pyramid, when a person suffers from the results of self-realization and his own expectations if they diverge from each other.
Works of Soviet psychologists
The Soviet school also paid close attention to the study of intrapersonal conflicts. Classic theories include the works of A
Luria, V. Merlin and A. Leontiev.
A. Luria considered this as a significant destructive factor in the functioning of a person’s personality. As its components, he identified two tendencies, opposite in their direction, but equal in strength, as a result of which it is difficult for a person to make a decision.
V. Merlin considered intrapersonal conflict as a state of personality disintegration, which is expressed in the aggravation of contradictions (or the emergence of new ones) between various aspects, characteristics and personality traits, as a result of which the individual feels deeply dissatisfied in the most important aspects of development.
According to A. Leontiev, the diverse relationships that a person enters into in various situations are objectively contradictory, which brings Leontiev’s concept closer to Freud’s theory. Accordingly, the motives that underlie various areas of an individual’s activity may also come into confrontation with each other, which leads to the generation of conflicts. A. Leontyev considered them an integral part of human life.
Manifestation of internal conflicts
Intrapersonal conflict manifests itself in cognitive, behavioral and emotional areas. Some experts also identify a fourth type of manifestation of intrapersonal conflicts - integral indicators.
» The cognitive area is problems with self-esteem and self-identification, obstacles that negatively affect the adoption of the optimal decision and its implementation.
Examples: a person’s self-esteem decreases; the individual experiences certain difficulties in making decisions; the individual experiences doubts about his own principles, motives and aspirations; a person experiences inconsistency in the perception of his own image, etc.
» Intrapersonal conflict in the behavioral area manifests itself in the form of a lack of satisfaction in the activity being carried out, rude communication with other people and other negative changes in the individual’s behavior.
Examples: a person’s level of productivity decreases, and the quality of work drops significantly; the individual experiences dissatisfaction with his own activities; a person begins to communicate rudely and in a raised voice with colleagues and relatives, etc.
“ In the emotional area, conflicts of this type arise in the form of negative thinking, cynicism, nihilism, and an increase in the level of emotional tension. A person experiences psycho-emotional stress and serious experiences that are negative.
Examples: a person loses interest in life; the individual becomes apathetic; the person becomes depressed; the individual lives in constant stress, etc.
» The manifestation of intrapersonal conflicts in the form of integral indicators is a complex disorder of the individual’s psyche.
Examples: a person experiences increased psychological or emotional stress;
the individual has disturbances in the adaptation mechanism; the individual has long-term disturbances that prevent him from adapting to new circumstances, etc.
What creates conflict within a person?
Cognitive dissonance occurs when a person is unable to achieve what he wants. This is prevented not by external obstacles, but by internal circumstances. The psyche determines two ways out of the situation, but neither of them is usually suitable. We are unable to change our desires. A girl cannot easily put down and stop loving a guy she really likes, even if she understands that he is completely unsuitable.
During the period of confrontation, two strong opposing sides arise - from the mind and from emotions, they have equal strength, so the intrapersonal battle lasts for quite a long time and because of this the individual cannot live a normal, familiar life.
What creates conflict within a person?
Cognitive dissonance occurs when a person is unable to achieve what he wants. This is prevented not by external obstacles, but by internal circumstances. The psyche determines two ways out of the situation, but neither of them is usually suitable. We are unable to change our desires. A girl cannot easily put down and stop loving a guy she really likes, even if she understands that he is completely unsuitable.
During the period of confrontation, two strong opposing sides arise - from the mind and from emotions, they have equal strength, so the intrapersonal battle lasts for quite a long time and because of this the individual cannot live a normal, familiar life.
Types and structure ↑
The types of conflicts are very diverse and wide; their classification can be presented as follows.
1. Depending on the area in which conflicts arise:
- family (occur in the sphere of family relationships, between parents, children, various relatives);
- production (exist in teams and groups regarding work processes and discipline, between managers, subordinates, employees in general);
- social (manifested in the intense interaction of various social groups and entities: government, people, public organizations).
2. According to the sources of occurrence, conflicts manifest themselves as:
- business – arise in the structure of various institutions and organizations due to shortcomings in the structure and distribution of responsibilities;
- emotional - appear due to the individual psychological characteristics of each person, when people are incompatible in types of temperament or character, manifestations of the emotional-volitional sphere.
3. Depending on how exactly a person perceives conflicts at a subjective level, they can be:
- erroneous - there are no real reasons for confrontation, but the person subjectively perceives the situation as a conflict;
- potential – when the prerequisites for a conflict have already emerged, but the conflict itself has not yet arisen;
- true (real) - a “classical” conflict with open confrontation between its participants.
4. Based on the subjects who take part in the conflict, conflicts are divided into:
- intrapersonal (conflicts with oneself);
- interpersonal (between two individuals);
- intragroup (between spheres of influence in a particular group);
- intergroup (between different groups with conflicting positions and goals).
The structural elements of the conflict process look like this:
- parties (subjects, participants) of the conflict - all those who are directly or indirectly involved in conflict interaction;
- conditions of the conflict – acute and painful, quiet and sluggish;
- images of a conflict situation (the subject of the conflict) - the participants’ ideas about what exactly caused the confrontation;
- the results of a conflict situation - how the conflict ended, what its consequences are for each of the participants.
Forms of manifestation
Infantility in men - what does it mean, signs and causes
You can determine if a person has a mental disorder based on several signs:
- Neurasthenia, manifested by excessive nervousness. Such people suffer from insomnia and completely lose the ability to relax in their free time. They experience a sharp decrease in performance and general fatigue of the body. A person suffering from a conflict with himself closes himself off from the world, becomes uncommunicative, responds sharply to treatment, and is rude.
- Euphoria, which is characterized by inappropriate active behavior. About this form of manifestation we can say “laughter through tears,” reminiscent of hysterics.
- Regression. When this form manifests itself, a person tends to ignore difficulties. He, like an ostrich who hides his head in the sand, avoids responsibility.
Head in the sand
- Projection. A person suffering from internal contradictions takes out his anger and feelings on others. This manifests itself in endless nagging and destructive criticism.
- Nomadism as the desire to change the main aspects and foundations. People approach the issue critically, change their place of residence, work, and circle of friends. Often behavior can change to antisocial, as a manifestation of protest against a forced life situation.
- Rationalism is the desire to explain to oneself and others the reasons for one’s actions in order to justify oneself in society and before one’s conscience.
Interesting. It is the whitewashing of one’s behavior to oneself that can give rise to a slight disorder of consciousness, when deep emotional experiences force the subconscious to protect the body from negativity, drawing a parallel reality in which a person exists happy and satisfied.
Intrapersonal conflict
Intrapersonal conflict is considered an extremely difficult to resolve contradiction that occurs precisely in the inner world of a person. It may be considered a serious psychological problem that will require prompt resolution. This type of confrontation helps to simultaneously accelerate the process associated with self-development (see How to grow personally), mobilization of one’s own potential and harm to a person due to inhibition of the process of self-knowledge, as a result of which self-affirmation is unrealized. It is worth talking about the emergence of intrapersonal conflict when existing needs, interests and various drives collide. They differ from each other in equal importance.
Basis and features of intrapersonal conflict
Click to enlarge
As mentioned above, the basis of such a conflict is, first of all, disagreements experienced within the individual. This conflict flares up inside a person, and he, as a rule, does not take it out into the world around him. The individual finds himself in a situation where he needs to rethink his values and, if this can be done, he acquires new useful qualities and a vision of the world. However, in reality it is not always possible to cope with the situation, which leads to even greater isolation and asociality. The characteristics of such conflicts are such that they cause stress, frustration and anxiety.
Anxiety manifests itself even before a certain situation unfolds. It, in turn, is divided into situational and personal. Situational anxiety develops due to external circumstances, but if a person does not have time to cope with it, it immediately turns into personal anxiety. Remember how in childhood we were scolded for failing and threatened with punishment. When a child receives a negative assessment, situational anxiety occurs (external circumstances have turned out badly), after which he remembers his parents and the expected consequences. Thus, internal anxiety begins to appear. At these moments, internal dialogues begin that can develop into something more, for example, into intrapersonal conflicts or frustration.
Frustration is a state in which a person experiences great disappointment. It arises in cases where it is not possible to solve a complex problem for subjective or objective reasons. The same child cannot avoid scandal at home; this leads him to oppression and frustration. In adults, this condition occurs most often when setting a goal and failing to achieve it. When an individual throws all his strength and resources into solving a problem, but it turns out to be unsolvable at a given moment in time. As a result, a person experiences great disappointment, powerlessness, and his desires do not coincide with his capabilities.
Further, if the individual fails to cope with the developing internal negativity, stress may occur, which covers even more topics related to life in general and one’s position in it. Let's return to the topic of goal setting. Let's say an individual set a goal to earn much more money, and, as usually happens, overestimated his capabilities. However, he wants to have an expensive car, new housing and beautiful things. As a result, all forces are mobilized and after some time he realizes that he can’t achieve anything and gives up his idea. A small conflict flares up within the individual, the person begins to blame himself, and then the entire world around him, for injustice. You can often come across statements that life is unpleasant, only bad people are lucky, there is deception and corruption all around. Although most often these problems do not directly affect the individual and have only a minor impact on his life.
Concept
What is intrapersonal conflict in psychology?
Intrapersonal is a person's communication with himself.
Intrapersonal conflict is understood as a contradiction that arises as a result of such communication.
A person perceives this conflict as a serious problem that requires the fastest possible solution.
The inability to resolve a situation or the lack of ability to make a decision can provoke various disorders, for example, insomnia due to constant thinking.
Intrapersonal conflict can direct a person into one of the following scenarios:
- The problem will direct him to self-development, he will begin to mobilize his strength, and he will begin to take measures to improve his life.
- The problem, on the contrary, will force him to slow down, which will disrupt the process of development and self-knowledge.
In intrapersonal conflict, a collision occurs between two or more interests, needs or desires that are equal in importance and opposite in meaning.
It is difficult for a person to make a decision and make a choice.
By occupying one side, he is deprived of the advantage of the other side.
Awareness of this leads to doubts, hesitations, and the inability to make a decision.
Depending on the importance of the issue that a person cannot resolve, conflict can provoke various problems and frustrations. Being in confrontation with oneself, a person increases the risk of developing various pathologies, both psychological and physiological. Having solved the problem, he takes the path of healing and liberation from such adverse reactions.
Having solved the problem, he takes the path of healing and liberation from such adverse reactions.
Being in confrontation with oneself, a person increases the risk of developing various pathologies, both psychological and physiological. Having solved the problem, he takes the path of healing and liberation from such adverse reactions.
What characterizes a person as a person? Find out about this from our article.
Consequences for humans
Nervous breakdown and related diseases of internal organs are the most common consequences of deep intrapersonal conflicts. In medicine, there is an opinion that mutation of body cells, causing their uncontrolled reproduction, which leads to the development of cancer, is one of the consequences of mental torment. The trials that come along everyone's path in life can shake the balance of a person, and as a result, a person loses friends, love, and profession.
There are many examples in literature describing the internal conflicts of strong people, as a result of which geniuses went crazy. The soul can also hurt, and it, like the organs, needs to be treated. Otherwise, a person faces a severe form of depression, and in rare cases, suicide.
Depression
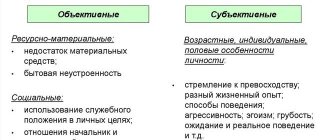
Causes of intrapersonal conflict
Like any conflict, this one also has its reasons. These reasons usually affect a person’s attitude towards his own personality. When we even subconsciously do not approve of some of our actions and even thoughts, we gradually learn to remain more and more dissatisfied with ourselves.
Unjustified expectations
Numerous demands are put forward to modern man in society. Sometimes a false impression is created that a successful person never gets tired and always does his job efficiently. In fact, this is just an appearance, an image imposed by society, which everyone is trying to unconditionally follow. A person cannot constantly exist at the limit of his capabilities. Gradually, she accustoms herself to the fact that she lives incorrectly, not like other people. Unjustified expectations are the main reason why intrapersonal conflict begins to develop. A person feels that he does not meet some standards and cannot influence the situation that oppresses him.
Disappointment in yourself
A common reason for the development of intrapersonal conflict, which makes you give up. It seems to a person that he is not capable of anything, but can only make various mistakes. Disappointment in oneself can arise as a result of failure in meaningful activities. Problems at work unsettle you for a long time and deprive you of self-confidence. If a project fails, thoughts about your own insolvency often come to mind. Disappointment in oneself contributes to the aggravation of intrapersonal conflict. People often drive themselves into terrible experiences precisely because they want to achieve great results, but in fact they deprive themselves of moral strength.
Social norms and personal needs
These categories often come into significant conflict with each other. Conflict is formed when a person feels unable to realize his own desires for one reason or another. Many people consider it necessary to conform to the laws of society, even if these requirements run counter to their own ideas about life. For some, social norms are too important and significant to ignore. In this case, the personality often remains lost and unclaimed. When individual needs are not met, most simply give up and no longer want to make even the slightest attempt to try to change their lives.
Low self-esteem
This is a serious problem, which in itself provokes intrapersonal conflict. If for some reason a person cannot realize his potential, then this circumstance puts extreme pressure on him and makes him doubt himself. Low self-esteem does not allow you to achieve success. Even if a person is talented enough, he does not find within himself the resource for achievement. She has to constantly be in an internal struggle, proving to herself the right to self-expression, and this circumstance is very mentally exhausting. The inability to value oneself is a common reason for the formation of conflict.
How to prevent the emergence of intrapersonal conflict
In order to avoid the development of severe forms of conflict situations within the individual, you need to:
- Get to know yourself as best you can. Analyze your daily choices, imagine your decisions in fictitious situations. The more a person knows himself, the easier it is for him to make choices.
- When choosing your social circle, you should not rely on the rule that opposite charges attract. People are not metal; it is more correct to communicate with those who are close in spirit and hobbies, without thereby creating a reason for organizing your own mental discomfort.
- Learn to give in and not go ahead to the point of a conflict of interests. Flexibility of character will protect you from contradictions.
- Learn not to be afraid of conflict situations. There are a great many of them throughout your life; if you don’t master your emotions in time and don’t fall into depression, you can maintain your mental and psychological health.