Causes of the disease
Cerebral palsy is a common disease.
Its frequency is approximately 2 children per 1000 births, and data may vary depending on the region. The cause of the disorder, like any other cerebral palsy, is pathological changes in the cerebral cortex, subcortical structures, capsules or brain stem. The difference between cerebral palsy and other similar disorders is only in the time of its diagnosis (postnatal period) and the disturbance in the manifestation of reflexes. Cerebral palsy is the result of abnormal development of brain structures or damage to a healthy brain. The process can occur both during pregnancy and childbirth, and in the early neonatal period.
Among the causes of this disease are the following:
- premature birth or birth trauma;
- multiple pregnancy;
- infectious diseases suffered by the mother during pregnancy, as well as mercury poisoning;
- traumatic brain injuries in the early neonatal period or in the first few years of life.
Cerebral palsy is not considered a genetic disease, since most of its cases occur in pathologies of pregnancy and childbirth. However, in 2% of cases inheritance is traced to an autosomal recessive type. Up to half of children with a similar diagnosis were born prematurely. The remaining patients were twins in multiple pregnancies, had low birth weight, or were born by instrumental delivery or emergency cesarean section. It is believed that asphyxia (insufficient oxygen supply to the brain) is one of the factors that can trigger cerebral palsy.
Cerebral palsy can also develop in children born at term. Among the causes that cause such pathologies, birth trauma comes first. In the early neonatal period, they can be caused by brain injuries and other types of brain dysfunction. Heavy metal poisoning, jaundice, stroke - all these factors lead to impaired blood circulation in the cerebral cortex, which affects their normal development. In a healthy child, cerebral palsy can be a consequence of drowning or other cases in which temporary cessation of breathing occurs, as well as inflammatory diseases of the brain, including those of infectious origin.
Is cerebral palsy transmitted from father and mother?
The cause of cerebral palsy is many factors, but they all boil down to the main thing - when the brain does not receive oxygen for a long time, irreversible processes occur that can have serious consequences for the body. Typically, cerebral palsy occurs due to an illness, such as polio. But many diseases are dependent on heredity, the question arises - how do genes influence the possibility of contracting this serious illness, is cerebral palsy inherited?
Scientific research
With cerebral palsy, the child’s gait and movements are impaired, involuntary movements are possible, and muscle stiffness is also observed, which leads to stiffness of the limbs.
The severity can vary - from barely noticeable to the inability to move independently; there are also accompanying diseases, such as epilepsy.
Modern science claims that the cause of cerebral palsy is damage to the child’s immature brain; this damage can be due to toxins, infections, or injuries.
But with genetics it's not so simple. After all, diseases may not be directly transmitted, but still the body may have genetic characteristics that, under certain circumstances, can affect the occurrence and development of the disease.
Some dependence was identified by Pakistani scientists who studied many people with cerebral palsy and found that there is a slight pattern of recurrence of the disease, with a probability of about 10 percent. Researchers in Sweden and England concluded that cerebral palsy has a 2% dependence on hereditary factors, but this statistic was not associated with complications during childbirth.
It is possible that the risk of the disease in twins is due to the fact that it is more difficult for them to develop in utero, and the difficulties are often mechanical in nature and associated with limited space.
But all studies may indicate that a person is genetically more prone to something, but we cannot talk about direct dependence, since this is not a genetic disease, and it cannot be obtained directly from relatives. But still, let’s try to explain the reasons for the potential possibility of getting sick from heredity.
The role of genes
The disease itself is not hereditary, but characteristics of the body that can influence the course of the disease and its severity can be transmitted at the genetic level. Here we can talk about the endurance of the nervous system, its resistance to possible unfavorable factors.
Sometimes the symptoms of cerebral palsy resemble certain diseases of the nerves and muscles that are inherited. Among the genetic factors that influence cerebral palsy, one can identify possible disorders of the blood supply to the brain, spina bifida, blastomatous processes, epileptic, hysterical attacks, and stuttering.
These symptoms are observed both in hereditary diseases and in patients who have acquired cerebral palsy due to a childhood disease.
The fact is that medical diagnostics at the neuromuscular level is labor-intensive and not very developed due to a lack of specialists and equipment, so doctors can identify diseases of the central nervous system that are similar to infantile paralysis with cerebral palsy.
Editor's note: What hormones are produced by the pituitary gland?
Sometimes cerebral palsy is confused with paralysis resulting from polio, but cerebral palsy is mainly associated with oxygen deprivation of the child in the womb or with complications during childbirth; due to a lack of oxygen, brain function can be impaired.
The connection between cerebral palsy and genetics is that the disease can affect that part of the body that is weakened due to heredity. It is at this point that there may be an intersection of hereditary factors and disease.
No direct connection was found between the genetics of the parents and the child’s illness.
Forms of cerebral palsy and their clinical manifestations
In the first days and months of life, a child with cerebral palsy may not differ from his peers, and symptoms of the disease appear later. Their severity depends on the degree of brain damage, as well as the timeliness of diagnosis and treatment.
The clinical picture of cerebral palsy may include the following disorders:
- increase or decrease in the tone of certain muscles;
- skeletal deformity;
- long-term preservation of reflexes, which normally disappear between the ages of 6 and 8 months;
- impaired reflexes, including swallowing;
- mental retardation, hearing and vision problems;
- convulsive syndrome.
Doctors at the Clinical Brain Institute argue that any changes in a child’s behavior should be a reason for additional examination. Currently, to determine an accurate diagnosis, a generally accepted classification is used, which identifies 5 main forms of cerebral palsy.
Forms of the disease
Cerebral palsy does not progress, because organic brain damage occurs during pregnancy. But in the absence of rehabilitation, these complications become permanent, and a person has to live with them all his life. The main signs of cerebral palsy are movement disorders, weakening of muscle tone, the appearance of pathological reflexes, and speech impairment. All these disorders can be significantly compensated for if a rehabilitation program is started in time.
Before starting treatment, the doctor determines the form of the disease:
- spastic diplegia - damage to the muscles of the back, legs and arms, rigidity of the lower extremities is more pronounced;
- double hemiplegia – the muscles of the arms are most affected, and mental retardation is observed;
- atonic-astatic type of pathology - deterioration of muscle tone throughout the body due to damage to the cerebellum and its pathways;
- hemiparetic form - unilateral lesion with predominant weakening of the upper extremities.
How is the rehabilitation of cerebral palsy carried out? – the first two forms are more amenable to correction than others, but with constant treatment and training, even with the most severe course of paralysis, good results can be achieved.
Psycho-emotional and personal development of the child
The degree to which a child’s psycho-emotional development deviates from normal indicators depends on many factors. And first of all, this is the mental development of the child and the degree of damage to his brain. However, the attitude of the people around the child is no less important.
Psycho-emotional abnormalities in children with cerebral palsy can manifest themselves in different ways. Thus, some children are overly irritable, excitable, and are characterized by sudden changes in mood throughout the day.
Some guys, on the contrary, are shy, fearful, they have difficulty making contact with others, and do not show initiative in their actions.
Most children are characterized by delayed mental development of the infantilism type. This means that they exhibit underdevelopment of the emotional-volitional sphere of personality.
Intelligence in such cases may correspond to the norm. However, it is the emotional sphere that is revealed to be immature.
Parents of a sick child should know that all responsibility for his mental development, for the formation of his character, etc. lies with them. Excessive care and compassion will ultimately lead to the fact that he will withdraw into himself even more and will not develop as a person.
Exercise therapy
Therapeutic exercises help restore lost functions, normalize tone and prevent muscle wasting. It is recommended to perform exercises from an early age - this will help you quickly cope with weak tone and restore self-care.
The following program is recommended:
- physical exercises with a trainer - to develop a specific muscle group;
- kinesitherapy - “treatment with movement” and constant physical activity;
- mechanotherapy – performing approaches on specialized simulators in rehabilitation centers.
The main feature of the rehabilitation of children with cerebral palsy is that the effect appears only with systematic training. That is why you need to fully follow all the doctor’s recommendations and engage in physical therapy.
The nature of children's behavior
In cases of mental development disorders associated with cerebral palsy, the following features in the behavior of children are observed:
- the child is guided mainly by emotions associated with pleasure;
- Children with cerebral palsy are characterized by egocentricity;
- they cannot work purposefully in a team;
- they do not know how to correlate their own interests with the interests of the people around them;
- there are elements of infantility in behavior;
- even at high school age, such children have an increased interest in games;
- they are extremely suggestible, incapable of volitional efforts on themselves;
- behavior is also characterized by instability of emotions, disinhibition;
- children tend to get tired quickly;
- they have difficulty adapting to new conditions, they have various fears - most often fear of heights, darkness, etc.;
- children are very sensitive to the mood and behavior of others, which is reflected in increased impressionability: incidents that are neutral for other children can cause a violent reaction in them.
- Sleep disturbances, nightmares, and nighttime anxiety are common.
Recovery stages
The first steps in the treatment of cerebral palsy are the most difficult - the child has lesions in the cerebral structures, which cause motor impairments. In the future, it will be easier to cope with pathology; as neural connections are restored and formed, it will be easier for the nervous system to adapt to new conditions.
There are several stages of recovery; such rehabilitation is carried out for cerebral palsy from an early age. It includes:
- preparing the nervous system for upcoming loads and movements;
- biomechanical effects to destroy neural connections and restore muscle tone;
- consolidation of the results obtained, stabilization of coordination of movements and self-care.
The second stage is the most difficult; many difficulties arise during this period. A complete restructuring of the nervous system is coming - the child will actually have to learn to walk again, talk normally and deal with stress.
Features of physical development
Impaired motor activity in cerebral palsy leads to curvature of the spine, contractures and other pathologies of internal organs. To prevent complications, it is very important to form muscle tone.
All work and attention of parents should be directed to the correct formation of motor functions. The most appropriate interventions would be massage and therapeutic exercises.
The main thing in classes is their early start, as well as continuity. The success of treatment will depend on this.
A set of exercises is selected depending on the severity of the disease and individual developmental characteristics. Corrective work comes down to the formation of vital skills, such as the ability to walk and take care of oneself.
The acquired skills must be adapted to everyday life, constantly practiced until they become automatic.
Features of motor development of children with cerebral palsy:
- it is necessary to stimulate his interest in outdoor games;
- you need to develop fine motor skills;
- it is also necessary to form a correct image of your body;
- It is also important to stimulate communication with others;
- At every opportunity, it is necessary to develop the child’s self-care skills.
Development of fine motor skills in children with cerebral palsy:
Recovery methods
Rehabilitation methods for children with cerebral palsy are varied, they include ongoing treatment, physical therapy and training. Medicines are used as basic therapy, exercises and procedures help develop new skills and consolidate the results. To obtain a pronounced effect, the impact must be complex and targeted, therefore, to prescribe a program, you should contact specialized centers. A doctor in such an institution will be able to observe the patient and, if necessary, adjust rehabilitation.
Factors influencing the child's will
Factors influencing the will of the child can be divided into:
- external, which include the conditions and nature of the disease, the attitude of others towards the sick child;
- and internal ones, such as the child’s attitude towards himself and his own illness.
Weakness of will in most children suffering from cerebral palsy is directly related to the characteristics of their upbringing. Very often in a family with a sick child, one can observe the following picture: the attention of loved ones is focused exclusively on his illness, parents show concern about every issue, limit the child’s independence, fearing that he may get hurt or fall, or be awkward. In such a situation, the child himself will inevitably be overly restless and anxious. Even infants subtly feel the mood of loved ones and the atmosphere of the space around them, which are fully transmitted to them. This axiom is true for all children - both sick and healthy. What can we say about children suffering from musculoskeletal disorders, who are distinguished by increased impressionability and acuteness of feelings?
Or another picture: an unhappy mother who, while caring for her child, forgets about her own life and becomes a hostage to illness. She looks tired and unhappy. But any child needs a happy mother, capable of giving love and warmth, and not her health and nerves. For a sick baby, this need is a thousand times greater.
All this leads to the fact that the child grows up lacking initiative, unsure of his strengths and capabilities, and timid. He resigns himself to his illness and does not strive for independence. He expects in advance that those around him will do everything for him. Over time, the child gets used to this state of affairs and finds it comfortable. And from here comes a pronounced egocentrism, the desire to manipulate people.
The importance of the educational position of parents in relation to children with cerebral palsy is confirmed by the fact that the children among them with a high level of volitional development come from families that are prosperous in terms of the psychological climate. In such families, parents are not fixated on the child’s illness. They stimulate and encourage his independence within acceptable limits. They try to form adequate self-esteem in the child. Their attitude can be expressed by the formula: “If you are not like others, this does not mean that you are worse.”
We must not lose sight of the child’s own attitude towards the illness. It is obvious that he is also significantly influenced by the situation in the family. Studies have shown that awareness of the defect in children with cerebral palsy manifests itself by the age of 7-8 years and is associated with their worries about the unkind attitude of others and lack of communication.
Children can react to the current situation in different ways:
- the child withdraws into himself, becomes overly timid, vulnerable, and strives for solitude;
- the child becomes aggressive and easily enters into conflict.
The difficult task of forming a child’s attitude towards his own physical defect again falls on the shoulders of the parents. Obviously, this difficult period of development requires special patience and understanding from them. The help of specialists should not be neglected. For example, it is quite possible to overcome a child’s worries about his appearance thanks to well-organized psychological work with him.
Thus, the characteristics of the development of the personality and emotional-volitional sphere of a child with cerebral palsy largely depend not only on the specifics of the disease, but primarily on the attitude of parents and relatives towards the child. Therefore, you should not assume that the reason for all the failures and difficulties of upbringing is the baby’s illness. Believe me, you have enough opportunities in your hands to make your baby a full-fledged personality and just a happy person.
Cerebral palsy and weak genes
There is no doubt about the strong relationship between the state of the nervous system of the patient and the severity of the clinical picture, as it is also known that every person has genes that most directly affect the state and characteristics of the functioning of the central nervous system. In connection with this knowledge, a reasonable question arises: to what extent can we assume that cerebral palsy is inherited?
Does this give us the right to assert that so-called “broken” DNA can become a kind of catalysts that increase the risk of morbidity several times? It is possible, because some people have a weak nervous system precisely due to genetic predisposition. Perhaps it is this fact that can explain the fact that under an equally unfavorable combination of circumstances (for example, prematurity, asphyxia, fetal hypoxia), one child recovers and develops without any harmful consequences, while the other receives a brand name for life. Is it really possible to blame fate if the fault lies solely with heredity, which transmits the nervous system as a weak link due to “clumsy” genes?
Thus, in some cases, the clinical picture of cerebral palsy is a phenocopy of some hereditary neuromuscular diseases. There is reason to assert that a combination of hereditary factors can influence:
- cerebral circulatory disorders;
- development of blastomatous processes and spina bifida;
- the origin of stuttering, hysteria, epilepsy and narcolepsy, etc.
Most of the above manifestations are observed with different degrees of severity of cerebral palsy, however, it is not so easy to differentiate hereditary diseases of the central nervous system from forms of infantile paralysis. That is why spastic paraparesis, for example, observed with spastic paraplegia, which is hereditary, is classified as cerebral palsy. This is due to the lack of adequate diagnostic parameters for various forms of neuromuscular diseases and the fact that about a tenth of the total number of children are not actually biological relatives of the putative fathers.
To summarize, it should be noted that the implementation of the genetic factor depends on violations of immunochemical mechanisms under the control of genes, the weakness of which is of no small importance in the genesis of cerebral palsy. The search for that very “main gene” responsible for childhood paralysis has not stopped to this day, and this path is quite difficult not only from the point of view of analysis as such, but also, first of all, the interpretation of the results obtained
After all, whatever they are, it is inappropriate to say that cerebral palsy is inherited and the disease will definitely manifest itself, because the essence of the brain processes that form that very “predisposed” nervous system remains unknown.
From the editor: Forms, causes and symptoms of encephalitis
Practical recommendations
- If your child has sleep disturbances, try to adjust his daily routine. It is necessary to create a calm environment for him, to refuse overly active, noisy games before bedtime. As far as possible, reduce the effect of external stimuli on his senses. Stop listening to music, or let it be soft, unobtrusive instrumental compositions. (Songs with lyrics in a language familiar to the child will be an additional burden for perception, and, therefore, another irritant that prevents the child from relaxing and falling asleep.) Limit watching TV.
- In order for a child to develop an adequate assessment of himself and the world, parents and loved ones, it is necessary to abandon excessive guardianship towards him. The strength of the child’s volitional qualities will depend on how the family perceives the child – as a disabled person who is unable to achieve success in life, or as a person, albeit in some ways different from those around him, but taking an active life position.
- If in the process of working with a child you notice that he is tired - has become irritable, aggressive, or, on the contrary, is overly withdrawn - you should not try to continue working. In order for work with a child to be fruitful, he himself must first of all be interested in it. It's better to take a break, offer him something to play, or just leave him alone for a while. It is likely that after some time the baby will regain energy, and you will be able to continue your activities with renewed vigor.
The need for the development and education of children with cerebral palsy
Even 20 years ago, they did not always agree to educate such children; there were very few boarding schools for them. The problem of this disease and the adaptation of children in society fell entirely on the parents, who often did not have special knowledge and did not fully understand the essence of the diagnosis. Because of this, the child's life was deplorable. There is no opportunity to learn, communicate, develop - this only aggravated the condition. Society's attitude to the problem was negative: children were pitied while they were small, but teenagers and adults with cerebral palsy were simply not accepted into educational institutions or to work. They remained unclaimed.
Recently, the problem of social adaptation of children with disabilities has been treated differently. Of course, at any time, left without any opportunities for development, such a baby will sharply deteriorate. Even if he retains his intellectual function, he loses many opportunities and loses his personality. Children must be given opportunities for learning, communication, games, and normal children's activities. Of course, as much as possible.
Unfortunately, among the causes of childhood disability, cerebral palsy occupies one of the leading positions. From birth, children need constant adult help, supervision, and care. Many of them find it difficult to enter society and begin to communicate even at the simplest level. This is often due to the special behavior of such children: they are irritable, whiny, and sometimes aggressive.
Psychophysiological characteristics of children with cerebral palsy
Psychophysiological characteristics of children with cerebral palsy
Author: Popova S.M., primary school teacher, School No. 34, Nevsky District, St. Petersburg
Relevance.
This article is devoted to the psychophysiological characteristics of children with cerebral palsy, its causes, the specifics of the cognitive and emotional-personal development of children with cerebral palsy.
Cerebral palsy (CP) refers to a group of movement disorders that occur when the motor systems of the brain are damaged and manifest as insufficient or absent nervous system control of voluntary movements.
Currently, the problem of cerebral palsy is acquiring not only medical, but also socio-psychological significance, since psychomotor impairments, motor limitations, and increased irritability prevent such children from adapting to life in society and mastering the school curriculum. Under unfavorable circumstances, such children cannot realize their abilities and do not have the opportunity to become full members of society. Therefore, the problem of correcting the negative manifestations of cerebral palsy is particularly relevant.
The problem of cerebral palsy is considered in the works of: Arkhipova E.F. (1989), Badalyan J.O., Zhurby L.T., Timonina O.V. (1989), Danilova L.A. (1997), Lalaeva R.I. (1990), Mastyukova E.M. (2005), Shipitsina L.M., Mamaichuk L.M. (2001) and others.
The term cerebral palsy (CP) refers to a group of movement disorders that occur when the motor systems of the brain are damaged and are manifested in the lack or absence of control by the nervous system over voluntary movements.
With cerebral palsy, there is early, usually intrauterine damage or underdevelopment of the brain. The causes of these disorders can be different: these are various chronic diseases of the expectant mother, as well as infectious diseases she has suffered, especially viral diseases, intoxications, incompatibility of mother and fetus according to the Rh factor or group affiliation, etc. Predisposing factors may be prematurity or distortion of the fetus.
In some cases, the cause of cerebral palsy may be obstetric trauma, as well as protracted labor with the umbilical cord entwined around the fetal neck, which leads to damage to the nerve cells of the child's brain due to; lack of oxygen. Sometimes cerebral palsy occurs after birth as a result of infectious diseases, complicated by encephalitis (inflammation of the brain matter), after severe head injuries. Cerebral palsy, as a rule, is not a hereditary disease.
When differential diagnosis of cerebral palsy with various movement disorders, first of all, the anamnesis data should be taken into account. The history of children suffering from cerebral palsy often contains indications of a pathological pregnancy in the mother and birth trauma with the use of obstetric methods of delivery.
A child is usually born with asphyxia, often with signs of intracranial injury: the Apgar score is low - 2-6 points, with an optimal score of 9-10 points (Mastyukova E.M., 1999).
During the newborn period, children with cerebral palsy often experience general anxiety, tremor (trembling of the arms, chin), an increase or, on the contrary, a sharp decrease in muscle tone, sometimes there is an increase in the size of the head, increased tendon reflexes, absence or weakness of cry, and disturbances in sucking due to weakness sucking reflex, convulsions often occur.
Already in the first months of life, a lag in psychomotor development appears, which is combined with a delay in the extinction of unconditionally reflex motor automatisms, among which the so-called postural reflexes are of greatest importance. With normal development, by 3 months of life these reflexes no longer appear, which creates favorable conditions for the development of voluntary movements. The preservation of even individual elements of these reflexes after 3-4 months of life is a symptom of risk or a sign of damage to the central nervous system. X
Among the reflexes that adversely affect the development of motor skills, the following are of greatest importance.
Labyrinthine tonic reflex, which manifests itself when the position of the child’s head in space changes. Thus, in the supine position, when this reflex is expressed, the tone of the extensor muscles increases. This determines the characteristic position of the child on his back: the head is thrown back, the hips are adducted, turned inward, and in severe forms of cerebral palsy - crossed; the arms are extended at the elbow joints, the palms are turned down, the fingers are clenched into fists.
If the labyrinthine tonic reflex is pronounced in the supine position, the child does not raise his head or does it with great difficulty. He cannot stretch his arms forward and take an object, pull himself up and sit down, or bring his hand or spoon to his mouth. This prevents the development of skills in sitting, standing, walking, self-service, and voluntary grasping of an object under visual control (Mastyukova E.M., Moskovkina A.G., 2002).
In the position of the child on the stomach, the influence of this reflex is manifested in an increase in the tone of the flexor muscles, which determines the characteristic posture: the head and back are bent, the shoulders are pulled forward and down, the arms are bent under the chest, the hands are clenched into fists, the hips and shins are abducted and
bent, the pelvic region of the body is raised. This forced position inhibits the development of voluntary movements: lying on his stomach, the child cannot raise his head, turn it to the side, stretch out his arms for support, kneel down, take a vertical position, or turn from his stomach to his back.
Delayed motor development and disturbances of voluntary movements constitute the structure of the leading defect and are associated with damage to the motor areas and adductor pathways of the brain.
Depending on the severity of the lesion, a complete or partial absence of certain movements may be observed. In this case, first of all, the most subtle differentiated movements suffer: turning the palms and forearms up (supination), differentiated movements of the fingers. Restriction of voluntary movements in cerebral palsy is always combined with a decrease in muscle strength (Mastyukova E.M., Moskovkina A.G., 2002).
The limitation or impossibility of voluntary movements delays the development of static and locomotor functions.
In children with cerebral palsy, the age sequence of development of motor skills is disrupted. Motor development in children with cerebral palsy is not just delayed, but qualitatively impaired at every age stage. There are several forms of cerebral palsy depending on the damage to certain brain systems.
Children with cerebral palsy are characterized by a variety of emotional and speech disorders. Emotional disorders manifest themselves in the form of increased emotional excitability, increased sensitivity to common environmental stimuli, and a tendency to mood swings. Increased emotional lability is combined with inertia of emotional reactions.
Increased emotional excitability can be combined with a joyful, elevated, complacent mood (euphoria), with a decrease in criticism. Often this excitability is accompanied by fears, especially the fear of heights.
Also, increased emotional excitability can be combined with behavioral disorders in the form of motor disinhibition, affective outbursts, sometimes with aggressive manifestations, and protest reactions towards adults. All these manifestations intensify with fatigue, in a new environment for the child, and may be one of the reasons for school and social maladjustment. With excessive physical and intellectual stress, and errors in education, these reactions are reinforced and there is a threat of the formation of a pathological character.
Specific disturbances in activity and communication in cerebral palsy can contribute to the unique formation of personality (Lalaeva R.I., 1990).
The most often observed is a disproportionate variant of personality development. This is manifested in the fact that sufficient intellectual development is combined with a lack of self-confidence, independence, and increased suggestibility. Personal immaturity is manifested in egocentrism, naivety of judgment, poor orientation in everyday and practical issues of life. Moreover, this dissociation usually increases with age. The child easily develops dependent attitudes, inability and unwillingness to engage in independent practical activities; Thus, a child, even with intact manual activity, does not master self-care skills for a long time.
—
When raising a child with cerebral palsy, it is important
development of his emotional-volitional sphere, prevention of neurotic
and neurosis-like disorders, especially fears, increased excitability combined with lack of self-confidence.
A child with cerebral palsy often experiences a peculiar development similar to mental infantilism. To prevent mental infantilism, it is important to develop the child’s will and self-confidence.
In addition to motor and speech disorders, the structure of the defect in cerebral palsy includes specific deviations in mental development. They can be associated both with primary brain damage and with a delay in its postnatal maturation.
Motor, speech and sensory disorders play a major role in mental developmental abnormalities in children with cerebral palsy. Thus, oculomotor disorders, underdevelopment and delay in the formation of the most important motor functions (holding the head, sitting, etc.) contribute to the limitation of visual fields, which, in turn, impoverishes the process of perception of the environment, leading to a lack of voluntary attention, spatial perception and cognitive processes (Shipitsina JI.M., Mamaichuk JI.M., 2001).
Motor impairments limit subject-related practical activities. The latter causes insufficient development of objective perception. Motor impairment makes it difficult to manipulate objects and perceive them by touch. The combination of these disorders with underdevelopment of visual-motor coordination and speech impedes the development of cognitive activity.
Deviations in mental development in children with cerebral palsy are largely due to a lack of practical activity and social experience, communicative connections with others and the impossibility of full-fledged play activities.
Motor disorders and limited practical experience may be one of the reasons for the insufficiency of higher cortical functions and, first of all, the lack of formation of spatial concepts. Speech disorders also play a major role in cognitive impairment in children with cerebral palsy.
The characteristics of mental disorders largely depend on the location of the brain lesion.
Impaired mental performance in children with cerebral palsy manifests itself in the form of irritable weakness syndrome. This syndrome includes two main components: on the one hand, it is increased exhaustion of mental processes, fatigue, on the other hand, extreme irritability, tearfulness, and moodiness.
Sometimes more persistent dysthymic changes in mood are observed (decreased background mood with a tinge of dissatisfaction). Children with cerebral palsy are persistently mentally exhausted, insufficiently productive, and incapable of prolonged intellectual stress (Danilova L.A., 1997).
Irritable weakness syndrome is usually combined in these children with increased sensitivity to various external stimuli (loud sounds, bright lights, various touches, etc.). A certain role in the aggravation of these disorders belongs to social factors, in particular overprotective upbringing.
As a result, underdevelopment of the motivational basis of mental activity may occur. In these cases, asthenoadynamic syndrome is more clearly manifested. Children with this syndrome are lethargic and inhibited. They are inactive when performing any type of activity; they have difficulty completing tasks, moving, and speaking. Their thought processes are extremely slow (Badalyan L.O., 1989).
Asthenoadynamic syndrome is mostly observed in children with spastic diplegia (damage to the lower and upper extremities, with a clear predominance of damage to the legs), as well as with the atonic-astatic form of cerebral palsy (against the background of low muscle tone, clear impairments of coordination and balance are noted).
In the hyperkinetic form, when the child primarily experiences involuntary movements - hyperkinesis, asthenohyperdynamic syndrome is often observed with manifestations of motor restlessness, increased irritability and fussiness.
Cerebrasthenic syndromes begin to manifest themselves most clearly in older preschool age, when systematic pedagogical classes begin with the child. There is a sharp lack of attention, memory and other cortical functions. In addition, the specific features of mental activity become more clear.
Violations of mental activity are manifested in the delayed formation of conceptual, abstract thinking. Despite the fact that
many children may have formally sufficient
vocabulary, there is a delayed formation of the word as a concept, there is a limited, often highly individual, sometimes distorted understanding of the meaning of individual words. This is due, first of all, to the child’s limited practical experience. It can be assumed that generalizing concepts formed outside of practical activity do not adequately contribute to the development of intelligence and the general strategy of cognition.
The peculiarities of thinking in children with cerebral palsy are most clearly revealed when performing tasks that require the simultaneous nature of intellectual processes, i.e., a holistic intellectual operation based on the interaction of analyzing systems.
Children with cerebral palsy usually have not only a small supply of knowledge and ideas due to the poverty of their practical experience, but also specific difficulties in processing information obtained in the process of subject-related practical activity.
These specific features of thinking are often combined with impaired dynamics of thought processes. The most common slowness of thinking and some inertia are observed. Some children show insufficient consistency and purposefulness of thinking, sometimes with a tendency to reasoning and side associations. Slowness of thinking is usually combined with the severity of cerebrasthenic syndrome.
In all cases, there is a relationship between disorders of thinking and speech activity.
In terms of intelligence, children with cerebral palsy represent an extremely heterogeneous category: some have normal intelligence, many have a kind of mental retardation, and some have mental retardation (Arkhipova E.F., 1989).
Children with cerebral palsy are also characterized by disturbances in the formation of higher cortical functions. Optical-spatial disturbances are most often observed. In this case, it is difficult for children
copy geometric shapes, draw and write.
*
Insufficiency of higher cortical functions can also manifest itself in a delay in the formation of spatial and temporal representations, phonemic analysis and synthesis, stereognosis (recognition of objects by touch).
With intellectual disabilities, personality development features are combined with low cognitive interest and insufficient criticality.
Features of the mental development of children with cerebral palsy in conjunction with the specifics of speech disorders should be taken into account when preparing them for education. For the development of speech and thinking of children with cerebral palsy, it is important to expand their horizons and enrich their life experience. Work on speech development is carried out step by step in close connection with the development of motor skills and the correction of movement disorders.
Thus, an analysis of modern approaches to organizing the psychocorrection process with the participation of children with cerebral palsy allows us to conclude that it is necessary to include various forms and methods. Thus, the most complete scheme of psychological correction is described in the works of E.M. Mastyukova (Education and training of children with developmental disorders. M., 2005), as well as L.A. Danilova (Methodology for correcting speech and mental development in children with cerebral palsy. M., 1997).
A general system of work may include the following aspects:
- Physical rehabilitation.
- Self-regulation skills training.
- Development of cognitive qualities and communication skills.
- Correction of negative emotions.
- Development of deficit functions in the diagnostic system.
Physical rehabilitation of children with cerebral palsy should be aimed at developing bodily sensations, developing coordination of movements, their consistency, and developing the ability to voluntarily relax skeletal and respiratory muscles.
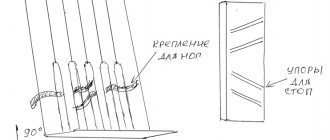
The nervous system of these children is designed in such a way that both emotional and physical overload contribute to an even greater development of undirected irritability, which is a symptom of fatigue. Children with cerebral palsy need early comprehensive treatment and correction work. Along with physical therapy and massage, in most cases special orthopedic measures are necessary (special placements, staged plaster casts, various devices for holding the head, sitting, standing and walking: gurney frames, weighted carts, walkers, walking sticks, etc.).
List of sources
- Arkhipova E.F. Corrective work with children with cerebral palsy. M., 1989.
- Badalyan JI.O., Zhurba JI.T., Timonina O.V. Cerebral palsy. M., 1989.
- Danilova JI.A. Methods for correcting speech and mental development in children with cerebral palsy. M., 1997.
- Lalaeva R.I. Methodology for the psycholinguistic study of speech disorders in abnormal children. St. Petersburg, 1990.
- Mastyukova E.M. Speech disorders in students with a hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy and medical justification for speech therapy measures // Defectology. 1999. No. 3.
- Mastyukova E.M. Physical education of children with cerebral palsy. M., 1991.
- Mastyukova E.M., Ippolitova M.V. Speech disorders in children with cerebral palsy. M., 1995.
- Mastyukova E.M., Moskovkina A.G. What is the most important thing in raising a child with cerebral palsy? // Raising and teaching children with developmental disorders. 2002. No. 2.
- Shipitsina JI.M., Mamaichuk JI.M. Cerebral palsy. St. Petersburg, 2001.
Determination of mental readiness for learning
Children with cerebral palsy undergo regular examinations by a doctor. Based on the physical condition and mental development of the child, the doctor determines whether he can study at school. Next comes choosing the type of school. If the intellect is well preserved and the degree of damage to the nervous system is minimal, then such children can study in a regular school. They may not be the best students, but it is quite possible to finish school. Then they are offered the opportunity to undergo specialized training and find a job.
If your mental state or the severity of your physical condition does not allow you to attend a regular school, then doctors recommend special educational institutions. In extreme cases, the child is considered unteachable. Such situations are rare, with severe damage to the nervous system.
The main parameters for determining the possibility of learning are the personal, intellectual and volitional characteristics of the development of children. Every component is important.
Home schooling
This type of training is preferable. There is a familiar atmosphere here, there are opportunities for relaxation, breaks for sleep and food. The school definitely cannot offer this. On the other hand, there must be someone who is constantly with the child and supervises the activities. Teachers will come to the student. Here he is deprived of the function of communicating with other children, which is not very good: he will not have full social experience, like other children. Such children develop worse speech, and their behavior becomes even more unstable. Parents and teachers make concessions to him and often indulge his desires - this has a negative impact on personal development.
Education is not all that children with cerebral palsy need. You will need the supervision of a doctor, and sometimes the presence of a nurse. Massages and a swimming pool are very helpful in relieving stress and pain from muscle tension. They will also have to be visited regularly. This is also an opportunity to develop your child according to an individual program.
Of course, a child or teenager feels comfortable at home, they are surrounded by the care of their parents. If upbringing is done correctly, children can be quite gentle and understanding. The better the intellect is preserved, the easier it is to cultivate normal moral qualities. The main thing for adults to remember is that their child will not always remain small. We need to prepare him for adult life as much as possible.
Studying at a regular school
Some schools accept children with similar problems. But there are many “buts” that need to be taken into account before the baby sits down at the desk with everyone else.
It all depends on several factors:
- physical and intellectual learning ability;
- permission from a doctor to attend an educational institution;
- minimal student aggression;
- the school's ability to accommodate a disabled child;
- availability of qualified teachers in the field of defectology.
Unfortunately, it does not often happen that all these factors are met and a student with cerebral palsy can attend a regular school. Most often, he is sent to home-based training, external studies. It is also very important to choose a special program and approach to the baby. The usual situation: a class of 20-30 people, one teacher - it is impossible to pay attention to everyone. And a child with such a disease needs the constant participation and help of a teacher.
In addition, he cannot always move around on his own, climb stairs, or go to the toilet. His mother or nurse should be with him. This also makes attending a regular school very difficult. Here, non-acceptance by the team comes into the background, but it is no less important. Your baby, like anyone else, wants to have friends and normal relationships. Due to the problems and physical manifestations of the disease, he may be the object of ridicule and even bullying. Parents should take this into account, even if they have the opportunity to attend school and have a normal level of intelligence.
Why a regular school is not always suitable
Traditional public school is most often not suitable for children with disabilities, and here are the main reasons:
- the infrastructure of the school grounds and classrooms may not be suitable, for example, there are often no ramps and elevators;
- the pace of study brings discomfort and takes a lot of energy, for example, in high school the daily schedule consists of 7-8 lessons;
- The format of a public school does not allow a child to be productive - the requirements of the program do not correlate with the student’s capabilities, and children with disabilities may find it more difficult to write by hand, keep up with the teacher’s speaking speed, or focus on one task for a long time.
Distance learning for children with disabilities can solve these problems, as it makes the educational process more individualized. An online school can adapt to the needs of a child with a disability and provide the most comfortable conditions for classes.
Specialized boarding schools
Such boarding schools usually accept pupils for 5-6 days a week, and their parents pick them up only on weekends and holidays. Most often, their recipients are patients with severe cerebral palsy. This sounds very harsh and is equivalent to abandoning a sick child. But not every person has the time, means and energy to care for their child, and therefore it is better to place him in a boarding school, where he will communicate with the same “special” children and under the constant supervision of teachers and doctors.
As a rule, everyone is divided into groups depending on their capabilities and skills. And after completing the training, each graduate receives a certificate, lessons are held as in a regular school. In addition to general education subjects, physical education and classes are conducted that promote the development of many skills. There is a nanny and a doctor; if necessary, you can sign up for a massage.
Extra education
In addition to the fact that a child needs to learn to read, write, and count, it is also necessary to develop his other skills, such as motor skills. For patients diagnosed with cerebral palsy, it is necessary to undergo regular massages, which eliminates pain from muscle tension. It is also necessary to learn to swim, which will have a positive effect on the development of the nervous system.
A diagnosis of cerebral palsy does not mean that your child will never learn to speak, wash himself, brush his teeth and understand others. It all depends on how it is dealt with, what programs and methods are used for development. But educational technologies do not stand still; a lot of programs have been invented for children with this diagnosis that are easy to use at home.
Bobath method
This method of neurodevelopmental treatment was named after its creators, Bertha and Karel Bobath. The approach to treating patients with cerebral palsy is based on knowledge and development of the nervous system and its pathologies:
- sensory-motor;
- emotional and social development of young children;
- perceptual;
The program is completely individualized and applied exclusively by the hands of a therapist. The focus is on natural sensory nutritional feedback and musculoskeletal control training.
The principles of treatment are:
- learning to sense movement;
- motor pattern training;
- facilitating the natural movement pattern and inhibiting pathology;
- setting goals, taking into account the stage at which motor ability is, the age and abilities of the child, always occurs in close connection with the family;
- assistance in the development of normal motor skills of the child;
The success of achieving goals affects the development of the child’s fine motor skills and speech. Close cooperation with the family is a must.
Parental help
If a child has cerebral palsy, the main task of education lies with the parents. No educational institution, no certified teacher, no even the noblest state education system can replace parental care and control. But you shouldn’t think that caring for a child, even one with disabilities, is some kind of difficult task - all the necessary skills and desire to care are inherent in parents by nature. But not only do parents have natural potential, the child also has abilities that are given to him from birth; the task of parents is to reveal the abilities of their daughter or son and help him adapt to life.
Mother's love overcomes barriers
Parents and teachers need to pay attention to psychological and pedagogical points:
- It is necessary to pay less attention to the illness, and more to the development of the child himself, to the assertion of his independence and responsibility. Show that his presence in your life gives you happiness, and the child will respond with redoubled efforts, being active in the right direction, just to bring satisfaction and praise from his parents. Also develop courage, perseverance and other character traits needed to achieve success in life.
- Teach your child that all people are different, and just because he is special does not mean that he is worse. You can emphasize that if a person doesn’t do something better than others, then something else can work out better. The human body tends to compensate for deficiencies; if difficulties arise, a person can achieve results in other ways. For example, if a person cannot earn money through physical labor, he can be diligent and earn much more through mental labor.
- It takes daily focused work. If you want to achieve a certain result in your studies or physical development, you need to take small steps - every day you need to put a brick in the building that you want to build. Don’t put it off “for later” because “later” never comes.
- Physical deficiencies can be compensated for by more significant qualities - intelligence, moral values. But physically, there is no need to be upset - if an ordinary person can become an Olympic champion, then a person, even with significant physical limitations, can lead a completely ordinary life through training and fully take care of himself.
- There is no need to have pity for the child, not only in terms of physical assistance, but there is no need to even look at him with pity. Be demanding without regard to illness, and the child will feel healthy. Even if it is difficult, he will be grateful that at least in the family he is treated as a full-fledged member of society, and he will transfer these feelings into real adult life.
- Being demanding does not mean demanding the impossible. The child is sick, there is no need to deny this, one must constantly strive for recovery, but if one does not accept the disease for what it is, then one does not strive to eliminate it. If the disease progresses or does not recede at an insufficient rate, you need to treat treatment as an integral work that needs to be done daily.
Is psoriasis inherited?
As has already been proven, psoriasis is not a contagious disease.
A person suffering from skin lesions can come into contact with others without the risk of transmitting the disease. As for its nature, the gene is not always inherited, but even if a person received it, the causes of symptoms are rarely congenital. For example, he may become ill as a result of a sharp decrease in immunity or a violation of lipid metabolism in the body.
Often the appearance of plaques is caused by hormonal imbalance, prolonged use of certain medications, or violation of the rules for taking them. Among these drugs are drugs of the antimalarial group, drugs with lithium salts, and beta blockers.
Sometimes pathology begins to develop if a person has suffered from infectious and some other diseases: sinusitis, otitis media, sore throat. There have also been cases of the disease being diagnosed in people infected with HIV.
Lifestyle is a serious factor. Those who visit the solarium too often or spend a long time in the open sun are at particular risk.
Another reason for the development of the disease can be skin injuries: burns, cuts, insect bites. Finally, strong feelings can provoke the appearance of unpleasant symptoms. Moreover, these are not only troubles and severe stress, but also positive emotions if they are expressed too strongly.
From father to child
In some cases, a father can pass on the psoriasis gene to his baby. The risk of inheritance with paternal predisposition to skin diseases ranges from 14 to 19%.
When twins are born, the risk that one of the children will begin to show symptoms of the disease reaches 70%. Approximately the same possibility exists when both parents have psoriasis.
If the baby becomes a carrier of the gene, symptoms may not appear until many years later. But this does not always happen: if there are no other provocateurs, psoriasis is usually dormant and does not cause any inconvenience.
From mother to daughter or son
The situation when a son or daughter can inherit a disease from their mother also occurs quite often. In this regard, women need to take into account several nuances:
From the editor: Comprehensive brain development
- During the period of bearing a child, the disease calms down, and symptoms manifest themselves extremely rarely. An exception may be the first trimester of pregnancy, when the body undergoes restructuring;
- During menopause, hormonal fluctuations occur and the disease worsens. By the way, due to hormonal imbalances, psoriasis often appears during puberty;
- When preparing for conception, it is better to consult a dermatologist. The doctor can adjust the treatment or recommend preventive measures, which will allow you to give birth to a healthy baby.
Breastfeeding has its own characteristics. As a rule, at this time, instead of using strong drugs, the specialist selects gentle therapy.
Positive emotions
Social educators and psychologists are very good. You need to listen to their advice and draw conclusions. But the child also needs to be given the opportunity to go to church, where he will improve both in the short and long term. Christianity cannot be considered only as a moral teaching; it is also healing, both spiritual and very real, physical.
It is also very important for a child to expand his horizons. It’s good, of course, if you have a computer at home, and it can be used both for games and for learning and work. But we must not forget that children love to play with their peers. It would be good if he had friends, and real ones, and not through social networks. An ordinary club will not work, but perhaps in the city there is an opportunity to spend time with other children with cerebral palsy, and even better - with healthy children. Even if he cannot draw, sing, dance, sometimes it is enough just to look at other children from the outside, and not only new impressions and emotions will arise, but a desire to improve his own life will arise.
Going to exhibitions, theaters, performances, dance competitions, various crowded events, city holidays - this should be present in life on a regular basis. But man does not live by only one culture. No matter how difficult it may be, you need to get out into nature - fishing, a beach holiday by the river or local lake. If possible, organize a resort vacation. Of course, all this is problematic, but we must take into account that these efforts have a good effect not only on the child, but also on the parents - there is an opportunity to communicate more closely with the child, and his positive emotions, his joy will pass on to the father and mother, who, caring about the child, they automatically take care of themselves.
Can cerebral palsy be cured?
Cerebral palsy is an umbrella term for a group of non-progressive conditions that are associated with damage to the brain early in its development (in utero, during childbirth, or in the first two years of life).
It follows from this that it is impossible to “cure” cerebral palsy, since we cannot eliminate the cause of the motor deficit - structural disorders in the central nervous system.
But the consequences of this damage can be compensated to varying (sometimes significant!) degrees.
In order to properly organize the movement of a child with cerebral palsy, it is necessary, first of all, to normalize muscle tone, make maximum use of sensory information, and carry out competent correction of motor disorders.
This requires long-term rehabilitation.
There are many methods, but the basis for successful recovery is exercise therapy, exercise therapy, massages, classes with a speech therapist, speech pathologist, and psychologist.
Work with children diagnosed with cerebral palsy must be comprehensive. And, of course, medication support is needed, which is prescribed by a doctor.
Small conclusion
Thus, inclusive education, at its core, is an excellent opportunity for children with special needs to enter an atmosphere of social communication. We can only hope that it will be fully implemented in the post-Soviet space.
The opportunity for different children, with different abilities, to be together, make friends, play, learn to help each other, take care of each other and understand that all people are different, but everyone lives together on the same Planet and under the same sky. It’s just that among them there are those who are the same as the others, only they have fewer opportunities, but they have the opportunity to say - I’m learning!