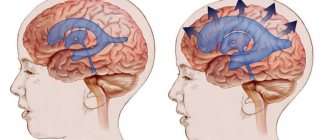
Clinical manifestations
Regardless of the nature of its occurrence, the clinical picture of meningitis has a set of common symptoms:
- General infectious symptoms - the most serious symptom is the occurrence of intoxication, which leads to the development of various disorders in the body (for example, hormonal disorders, water-salt disorders, etc.).
- Meningeal syndrome - this process is caused by the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the meninges. Conventionally, it is divided into general cerebral symptoms (photophobia, dizziness, headache) and meningeal symptoms (Kernig's, Brudzinski's symptoms, etc.).
- Changes in the cerebrospinal fluid (for example, with purulent meningitis, turbidity of the cerebrospinal fluid is observed, the amount of protein increases, etc.).
Why do spots appear?
The appearance of spots on a child's skin is a very dangerous symptom of meningitis .
This phenomenon is called meningeal rash, and, as a rule, begins from the legs, gradually rising higher and higher. The main reason for the appearance of spots lies in the harmful effects of meningococci on the child’s body. As a rule, the appearance of a rash is characteristic of purulent meningitis, so it is necessary to begin treatment urgently, otherwise the consequences can be very dire.
Does it happen without fever?
It should be noted that often not always a child may experience a full set of symptoms characteristic of meningitis . In particular, an increase in body temperature is not necessary. It may remain at the same level.
IMPORTANT : However, in any case, at the slightest suspicion that a child has this disease, it is necessary to urgently contact a medical institution, since sometimes the count may not be days, but hours.
You should especially carefully monitor the condition of infants, since they cannot express in words what exactly is bothering them.
Graft
Are children vaccinated against meningitis?
Vaccination against meningitis is not included in the standard list of vaccinations in the Russian Federation. In total, doctors note about 90 types of varieties of this disease on the planet, but only 15 of them can be fatal, which affects up to 80% of children.
It is transmitted by airborne droplets , so no one can be protected from meningitis without vaccination. The vast majority of experts believe that a child should certainly be vaccinated against this serious disease. This will protect him from serious illness. The vaccine is especially needed if the child will go to kindergarten or attend large gatherings of children of his age.
Don't skimp on your child's health!
Much to our disappointment, the Ministry of Health of our country does not agree with this issue, since the vaccination against meningitis has not yet been mandatory. But this may soon change dramatically.
Expert opinion
Zemlyanukhina Tatyana Vyacheslavovna
Ambulance and emergency paramedic at the Clinical Emergency Hospital #7 in Volgograd.
Ask an expert
Despite the fact that compulsory vaccination is not prescribed at the legislative level, parents should take care of their child’s health on their own. The effectiveness of the vaccine reaches 90%, the formation of immunity takes no more than a week, and the effect lasts for 3-5 years.
At what age should children be vaccinated?
Depending on your region of residence, the vaccination period may vary greatly . In Russia, children are vaccinated against this terrible disease only at the age of two years, but in neighboring Ukraine, children are given the vaccine at the age of:
3;- 4;
- 5 months.
But at the age of 18 months they carry out revaccination. If the child is as active and friendly as possible, and not a homebody, then it is best to vaccinate him at the age of 1.5 years. This will strengthen his immunity to serious illness just at the moment when he begins to actively run and play.
Now you know at what age a child is vaccinated against meningitis.
Do they do it for up to a year?
This question is quite difficult to answer, since in fact it all depends not on the personal preferences of the doctor, but only on the type of vaccine used .
Some foreign drugs that have undergone clinical trials make it possible to vaccinate children who have not reached the age of one year, but most doctors do not recommend using the vaccine at this age, since it will be meaningless. The thing is that the mother's milk that is fed to the baby contains all the necessary microelements that help protect and maintain the baby's immunity at the proper level.
Starting from the age of 1.5 years, the effect of this natural phenomenon disappears, so the child is left alone with viral diseases, and it is precisely at this moment that it is necessary to support his health with the help of a vaccine.
Where is it held?
Unfortunately, children are not vaccinated against meningitis in regular clinics or hospitals . For this purpose, there are special private clinics that specialize in this particular area of activity.
IMPORTANT ! There is no need to choose a cheaper vaccine. The main thing is the child’s health, so it is best to agree to the option suggested by the attending physician.
Such private clinics can be found in almost every major city. You can find out more about them at the city hospital, where doctors will refer parents to the address.
How long does the action last?
Again, it all depends only on the vaccine itself .
But, despite this fact, many experts recommend revaccination every three years. The thing is that some drugs do not use as a basis the virus itself in small proportions, which is absorbed in the body, but the immune system finds an element of fight against this disease. Many drugs, on the contrary, are based on antibodies, which leave the body over time.
Possible side effects
Often, the vast majority of children tolerate meningitis vaccination stably and without any visible consequences. Minor complications may occur, but they cannot compare with the severity of the disease itself.
Common complications include:
- Fever.
- Slight redness at the grafting sites.
- Drowsiness.
This is a small price to pay for a healthy child.
Vaccine names and prices
Among the wide variety of meningitis vaccinations for children, in our country you can find only a few basic drugs that are used by private companies. The names of the vaccines are as follows:
- The meningococcal vaccine is produced by Russian experts. The composition includes serogroups A and C, which allow you to develop immunity to meningococci. The average price on the market reaches 1400 rubles.
- The “Meningo A + C” vaccination is produced in France, therefore it is considered to be of higher quality. The main composition of serogroups A and C allows protection against cerebrospinal meningitis. Intended for children over 18 months. The average cost reaches 2,200 rubles.
- “Mencevax ACWY” is produced by a joint company from Belgium and the UK. Thanks to its serogroup components, ACWY allows the formation of bactericidal antibodies. Intended for children over two years old. The average cost is about 3,100 rubles.
- “Menactra” is produced by a company from the USA and is considered to be the highest quality today. It includes serogroups A, C, Y and W-135. Allows you to actively produce antibodies to fight the disease. Recommended for use by children over two years of age and adults up to 55 years of age. The average cost on the market reaches 3,500 rubles.
How to recognize at home?
There are several of the most striking childhood symptoms of meningitis, the appearance of which directly signals a developing disease. As mentioned above, these symptoms are called meningeal. Thus, knowing the meningeal symptoms, you can check for meningitis in your child at home . So, let's look at them in detail.
Kernig's symptom - is expressed in the fact that the patient, lying on his back with his leg bent at the knee and also at the hip joint, cannot straighten it due to the fact that the muscles of the back of the thigh are in severe spasm. At the same time, trying to bend one leg, the second also begins to reflexively bend.
Brudzinski's symptoms contain a set of signs indicating damage to the membranes of the brain.
So, there are the following 4 symptoms that can be used to identify meningitis in a child, even at home:
The upper Brudzinski symptom is expressed in the fact that when trying to bring the patient’s chin closer to the chest, there is strong resistance from the neck muscles, as well as flexion of both legs at the knee and hip joint.- The average Brudzinski symptom is when light pressure is applied to the patient’s pubic bone, and the leg is pulled toward the abdomen. This is a positive sign.
- The lower Brudzinski symptom is a kind of Kering symptom. If, when trying to bend the patient’s leg at a right angle at the knee and hip joints, the second leg involuntarily begins to be pulled towards the stomach, then, accordingly, the lower sign can be considered positive.
- Brudzinski's buccal symptom - if, when pressing on a point located just below the zygomatic arch, the patient bends the arm at the elbow joint and raises the wrist, then accordingly this sign can be considered positive.
Brudzinski's symptoms in children at an early age are usually very mild.
Ankylosing spondylitis's symptom is called the zygomatic symptom , and is expressed in the fact that when lightly tapping the cheekbones with a hammer, the patient experiences a severe headache, and a painful grimace appears on the face. This indicates pathological processes occurring in the brain.
Expert opinion
Zemlyanukhina Tatyana Vyacheslavovna
Ambulance and emergency paramedic at the Clinical Emergency Hospital #7 in Volgograd.
Ask an expert
Meningitis has its own set of symptoms by which you can determine the presence of the disease at home. But most often, especially in children, the disease begins asymptomatically or is accompanied by such nonspecific manifestations as irritability or drowsiness.
Recognizing symptoms at home
Meningitis in a child under 10-12 years of age is determined by the characteristic manifestations of headache and vomiting, but it is often mistaken for an acute cold and acute respiratory viral infection. To clarify an independent diagnosis at home, the following tests are performed:
Determination of the tone of the occipital muscle by tilting the head . With meningitis, the chin cannot be brought to the chest.- Brudzinski's sign . The child is placed in a supine position. One leg straightens and the other begins to bend. Spontaneous bending and straightening of the leg indicates the presence of a symptom of the disease.
- Kernig's sign . The child should be placed on his back. If noticeable resistance appears when bending the leg at the knee joint, pathology can be suspected.
Additional tests can be performed for pain symptoms:
- Light tapping on the cheekbones on both sides causes a sharp facial contraction (Bechterew's symptom).
- Light tapping on the skull causes a painful sensation (Pulatov's symptom).
- Palpation in the area of the ear canal causes pain (Mendelian symptom).
Symptoms in infants
REFERENCE! Meningitis in infants occurs in 1 child out of 100; children under one year of age are most often affected. Half of the sick die.
It's also worth reading about the MSD Handbook.
The first signs in children under one year old
During the incubation period of meningitis, infants develop symptoms:
- headache, bursting pain;
- body temperature rises;
- the child feels sick and vomits;
- the baby is weak, lethargic;
- drowsiness;
- the skin is unnaturally pale;
- body aches;
- bright light and loud sounds are poorly tolerated;
- constant, high-pitched crying.
When the disease begins to develop, the temperature of the infant rises quickly. In 3-4 hours it rises to 40 degrees. With timely measures taken, the temperature subsides on the third day.
Headache in the forehead, eyes, nose. At elevated temperatures, nausea and vomiting begin. The cause of vomiting is that the vomiting center of the brain swells. Vomiting is not associated with food; the child begins to vomit when he is turned over or the headaches intensify.
Main manifestations
The child refuses to eat, the respiratory rhythm is changed, and he suffers from convulsions. Consciousness is lost, the fontanel thickens. Fever, poor appetite and vomiting do not indicate that it is meningitis. Such signs are also characteristic of other diseases. An accurate diagnosis is made if there are the following symptoms of meningitis in infants:
- The neck muscles become numb.
- Buccal symptom.
- Muscles are tense.
- The baby lies on its side, head thrown back and knees bent to the stomach.
What to do if warning signs of the disease appear?
If a child under one year of age develops symptoms of meningitis, an ambulance is quickly called. Only the doctor knows what measures to take for treatment. You cannot act independently.
Why is self-medication dangerous?
Traditional methods of treatment are unacceptable. The disease is acute and passes with lightning speed. The baby’s immune system is not able to cope with the pathology on its own; self-medication methods will not bring a positive effect.
Self-medication with medications is also dangerous. There are medications that are incompatible with other medications. The dosage of the drug depends on the weight of the child; only the pediatrician can determine this accurately. The duration of taking medications is determined by the doctor.
IMPORTANT: incorrectly chosen medications lead to gastrointestinal disorders. The child feels nauseous, has problems with bowel movements, and has a bloated stomach.
If traditional treatment is not started in a timely manner, consequences and complications arise:
- excess fluid accumulates in the brain;
- intoxication of the body leads to toxic shock;
- the brain swells;
- hearing deteriorates.
In a hospital, “establishing the exact nature of the illness may take several days. This is a necessary delay, so the doctor usually prescribes an antibiotic immediately, without waiting for diagnostic results.” EMC (European Medical Center)
What are the symptoms of meningitis?
As Dr. Komarovsky says, if parents carefully monitor the health of their child, they will be able to quickly identify the presence of the first symptoms.
Headache in a child
It is enough to pay attention to the main signs, which include:
- Attacks of severe headaches in a patient, which are provoked by serious intoxication of the body. Toxins have a negative effect on the lining of the brain, causing pain as intracranial pressure increases significantly. Painful sensations can be sharp, pressing, bursting and sharp.
- The pain spreads throughout the head, so the child will not be able to indicate the location of the pain. Doctors note that these painful sensations do not subside with the use of painkillers, so if a child experiences this symptom, you should immediately call an ambulance.
- The child becomes very sensitive to bright light and loud sounds, the patient reacts negatively to light touches, as the sensitivity of the skin increases.
- Dizziness occurs and vomiting may occur. The described symptoms appear in the second and third stages of meningitis development.
Newborns may react slightly differently to the development of a dangerous disease; such babies experience additional symptoms:
- the baby becomes more whiny and nervous, or he sleeps a lot, but periodically cries out for no reason;
- there is a disturbance in the functioning of the digestive system, this manifests itself in the form of diarrhea, regurgitation and flatulence;
- in the later stages of the disease, the child experiences seizures.
It is worth noting the most dangerous symptoms of meningitis in children, these include the appearance of rashes and seizures. The fact is that the rash occurs due to the death of skin cells and tissues, which is triggered by the development of sepsis.
In this case, the disease develops rapidly and can be fatal. When the body temperature rises, spots appear on the child’s body, and convulsions occur, parents should immediately seek help from specialists.
Up to a year
First signs
The first signs of meningitis in children under one year of age are the same as in other neonatal infections:
- lethargy, weakness, passivity;
- frequent regurgitation and vomiting;
- difficulty breathing;
- breast refusal, loss of appetite;
- fluctuations in body temperature.
Infants weighing more than two kilograms may develop a sudden rise in temperature.
In premature babies, the first symptoms may not be so obvious. These are the symptoms of meningitis in children under one year of age:
- fever;
- monotonous crying;
- swelling of the fontanel.
Now you know about the signs of the disease in newborns and infants.
How to recognize houses?
Note! If there is a suspicion of meningitis, then the fontanel should be examined. When meningitis occurs, it becomes inflamed and pulsates.
You can also check for Lesage's sign. To do this, you need to grab the baby by the armpit area. If there is meningitis, the baby involuntarily pulls his legs towards his stomach and throws his head back.
Differences from ARVI
Meningitis is very dangerous because its initial symptoms also occur in less dangerous diseases. However, in the following cases, you should immediately seek professional help, because: there is a possibility that the baby fell ill with meningitis:
- prolonged headache due to a current infectious disease;
- at high temperatures, pain appears in the back and neck, which will intensify when moving the head;
- nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, confusion;
- cramps, no matter how long they lasted or how severe they were;
- a rash that appears at high temperatures.
Signs in children 1-2 years old
How to recognize at the initial stage?
The danger of meningitis lies in the fact that at the initial stage its manifestations are not typical and resemble the symptoms of colds. However, attentive parents can consider the disease at an early stage.
First signs
Let's talk about the signs of meningitis in children 2 years of age and under 1 year of age.
There are manifestations by which the parents of the baby may suspect the development of this infectious disease. These include:
Increased body temperature up to 40 degrees: the baby’s body reacts to the introduction of the microorganism with fever. In this case, antipyretic drugs have no effect.- Lethargy, drowsiness, loss of strength of the child.
- Pale skin and bluish nasolabial triangle.
- Development of sound and photophobia: a small patient tries to close himself off from the light source and turns away from loud sounds.
- Confused consciousness: the baby does not respond to the parents’ appeal.
- The appearance of vomiting.
- If the baby's condition worsens, seizures and spasms are likely to occur.
Basic
Inflammation of the meninges is complicated by the fact that children 1-2 years old are not able to explain their complaints to an adult. For this reason, diagnosing the disease requires extreme care so as not to miss a single sign.
General infectious syndrome
Such manifestations do not indicate the appearance of meningitis, but indicate the presence of an infectious disease in the child. These include:
- Fever with high body temperature.
- Loss of strength, lethargy.
- Extreme thirst: the baby greedily drinks large quantities of water.
- The appearance of a runny nose, redness of the throat.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
General cerebral
These symptoms in 1-year-old children are characteristic of the development of a pathological process in the brain and spinal cord . These include:
- The appearance of vomiting in the baby.
- Confusion: the child does not respond to the words of an adult.
- Headaches with the appearance of fear of light and sound: the baby covers himself with a blanket and turns to the wall.
- The occurrence of seizures associated with increased intracranial pressure.
Meningeal
To identify inflammation of the meninges, the specialist uses specific techniques that confirm meningitis. Let's take a closer look at each of them.
Kernig's symptom is considered the most famous test for diagnosing the disease in children and adults. It is carried out by passive flexion of the lower limb at the hip and knee joints with the patient lying on his back. The doctor cannot straighten the leg due to excessive tension in the muscles.- Stiff neck – the doctor tries to press the chin to the chest, but instead there is resistance in the back of the head, leading to limited movement.
- Brudzinski's sign - the baby lies on his back, and the specialist flexes the knee joint of 1 lower limb. Together with it, the other leg reflexively tightens.
- Ankylosing spondylitis symptom - the doctor taps on the cheekbone of a small patient, and the facial muscles contract to form a kind of grimace. This is explained by the appearance of severe pain even with the slightest tapping.
- Mendel's sign - a specialist inserts a finger into the external auditory canal and then presses on the ear. This is accompanied by a sharp increase in headache, causing the patient to grimace in pain. The technique is especially useful in cases where classical tests raise doubts among the doctor.
- Hermann's sign: the child lies on his back with his limbs straightened. The doctor performs a passive tilt of the head, and at this time the baby’s first toe spontaneously extends.
- Flatau's symptom - in a patient with meningitis, dilated pupils are detected when the head is tilted.
First signs
Viral meningitis begins very acutely. At the end of the incubation period, the child develops a strong fever, the body temperature rises to 40 degrees, and sometimes exceeds this figure. At the same time, a fever breaks out and the child begins to become delirious.
Immediately after the child’s temperature rises, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted. After 23 hours, all the characteristic symptoms for this infection appear: stiffness of the neck muscles, Kernig’s and Brudzinski’s symptoms.
After a day, the following symptoms can be observed:
- intoxication of the body;
- nausea in a child, often ending in repeated vomiting without obvious improvement after the gag reflex;
- dizziness that cannot be relieved with painkillers;
- skin sensitivity, bone pain, joint and muscle problems;
- cough;
- due to digestive disorders, rashes appear on the body.
Important! The disease is characterized by successive waves of increasing symptoms. Initially, the temperature rises, vomiting appears, then other symptoms appear. After 7 days, clinical signs cease their progressive effect for 2–3 days and appear again.
As a rule, the disease lasts on average from 14 to 17 days. If during this period the characteristic signs of the disease cannot be extinguished, then more serious measures are taken, including hospitalization of the child.
There are a number of specific characteristic signs by which parents can independently understand whether their baby has viral meningitis or some other disease:
- Body posture. During illness, it is convenient for the baby to lie on his side and at the same time throw back his head and pull his legs to his stomach.
- When trying to bend the leg at the hip joint, the child becomes unable to straighten it at the knee.
- If you put your baby on his back and ask him to tilt his head to his chest, you may notice an involuntary bending of the legs at the knees.
- Strong muscle tension in the back of the head. A child lying on his back is unable to touch his chin to his chest.
For children 4 years old
In childhood, the disease manifests itself as a respiratory disease. The baby has a fever, a sore throat and a headache. The nature and strength of symptoms depends on the type of infection.
A child who is about 4 years old can tell what is bothering him, which will allow him to recognize the disease based on a number of symptoms. The first signs of meningitis are fever and headache. Other symptoms include:
- Hallucinations, confusion, delirium.
- Cramping in the abdomen, similar to an intestinal infection.
- Vomiting and nausea.
- Yellow tint to the whites and swelling of the face.
- Sore throat, redness and looseness of the palate.
- Spasms and cramps, numbness of the skin.
We diagnose at home
The main task of parents is to promptly recognize the appearance of meningitis in a child 1-2 years old by signs and symptoms and seek qualified help from a medical institution.
We recommend using the step-by-step steps below.
Take the baby's temperature: with meningitis it is high and is accompanied by the child's lethargy and weakness.- Pay attention to the baby’s consciousness: when inflammation of the meninges develops, it is confused, and he does not make contact with an adult.
- See if there is any strange position of the baby's body. Meningitis is characterized by a peculiar position when he lies on his side for a long time, bending his knees and pressing them to his body, while his head is thrown back.
- If convulsions occur , they may indicate a serious condition.
Important! Don't wait for your child to get worse. At the slightest suspicion of the development of meningitis, consult a specialist immediately!
Differences from ARVI
Serous and meningococcal forms at an early stage often resemble colds. They are accompanied by elevated body temperature and the appearance of weakness, as with ARVI.
However, parents should be wary if the disease develops rapidly. The baby is capricious and refuses to eat. Loud noises and bright lights irritate him.
When a child has a cold, he takes a characteristic position : on his side in a lying position, he brings his legs to his stomach and throws his head back. Any change in posture is accompanied by the appearance of wild pain.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor performs tests to confirm inflammation of the meninges. The most common test for neck stiffness is that the doctor places one hand on the upper chest and the other on the back of the baby's head. Then the specialist presses on the back of the head, bending the neck, and the chin reaches the palm that lies on the chest. If a baby develops meningitis, such a test cannot be performed.
Treatment
Attention! Even if parents independently determine the signs of viral meningitis in a child, they should immediately show him to a pediatrician. Self-medication is unacceptable, as it can lead to a number of negative consequences and be fatal.
The doctor prescribes the following complex treatment:
- To prevent intoxication of the body, a saline solution is injected intravenously, with Prednesolone and vitamin C added in a single dose.
- To stop vomiting, you need to take medications containing Metoclopramide.
- Regularly reduce the temperature with Panadol, Nurofen.
- It is useful for the gastrointestinal tract to drink enzyme preparations and follow a dairy-free diet.
- For abdominal pain, the child is given Drotaverine.
- Convulsions go away after taking Seduxen or Domosedan.
Providing first aid to a child
The first thing the baby’s parents must do is call an ambulance. There is no need to put off calling, much less try to treat your child on your own!
Remember: the faster quality, qualified assistance is provided, the greater the child’s chances of recovery.
Before the arrival of specialists, it is necessary to provide the little patient with peace, silence and darkness. You should not let your child get up.
If he needs to go to the toilet, provide a bedpan or put on a diaper. The baby should be given drinks more often. If vomiting occurs, it is necessary to turn the child's head to the side to prevent vomit from entering the respiratory tract.
The same technique should be carried out in the case when a small patient experiences convulsions. This will protect the baby during an attack from the tongue retracting and blocking the respiratory tract.