Breathing exercises for sleep: what is it?
Breathing exercises before bed should be performed daily . Only under this condition will it be as effective as possible. But infrequent exercise is unlikely to bring tangible benefits.
Relaxing gymnastics were invented by American doctors. Their goal was to create a training method that would help fall asleep in just a couple of minutes.
Breathing exercises for sleep are based on the practice of ancient Indian yogis and are called “4-7-8” . These numbers mean how much time you need to spend on each stage of breathing. In other words, while performing the exercise, you need to inhale for 4 counts, hold your breath for 7 counts, and exhale deeply through your mouth for 8 counts. In this case, you need to take several such breaths. And preferably at least 10.
The advantage of such gymnastics is that it can be performed anywhere, at any time . Moreover, you don’t need any improvised means for this. Just lie down or sit down and start doing the exercises.
According to experts, to quickly fall asleep, you need to do gymnastics twice a day - in the morning and in the evening. Thanks to classes 2 times a day, you will notice positive changes after the first week of such practice.
Note that breathing exercises for sleep are aimed at creating inner peace, as well as complete relaxation of the soul and body.
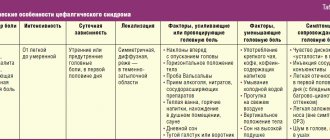
Symptoms of sleep diseases
Finding the reason that prevents you from sleeping well at night can be difficult. After all, the same symptoms may indicate both sleep diseases (insomnia or insomnia, obstructive apnea syndrome), and other diseases (bronchial asthma, chronic heart failure), as well as problems of a psychological nature (anxiety, depression) or inappropriate condition bedrooms and non-compliance with the rules of going to bed - violation of sleep hygiene.
Symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea
The most extensive symptoms are inherent in obstructive apnea syndrome. During rest, the soft tissues of the upper respiratory tract relax and vibrate as air passes through. This causes an unpleasant acoustic phenomenon - snoring.
Snoring in itself does not warrant a diagnosis. However, regular loud snoring should be a reason for a visit to a somnologist
During intense vibrations, the walls of the pharynx close completely, which prevents air from entering the lungs. One of the reasons for such obstruction is a low position of the soft palate or an enlarged uvula. Patients with similar problems often describe their feelings like this:
- uvula interferes
Smoking, allergies, trauma to the mucous membrane - all this can cause additional swelling of the uvula, as well as loss of tone. As a result, it hangs even more over the root of the tongue, practically touching it. The airway clearance decreases, snoring increases and this leads to more frequent episodes of sleep apnea.
Repeated stops in breathing cause oxygen starvation. The body reacts to such stress by releasing anxiety hormones - adrenaline and norepinephrine. This makes the heart beat faster and provokes vasospasm. Regular hypoxia coupled with the body’s stress response leads to the following unpleasant consequences:
- persistent increase in blood pressure;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- chest pain
, indicating the development of angina and coronary heart disease.
Patients with obstructive sleep apnea often experience a persistent increase in blood pressure. It can increase especially strongly at night and in the morning.
A rapid heartbeat and high intensity of work of the respiratory muscles lead to changes in the body similar to the reaction to severe physical activity or stress. Examples include:
- increased sweating
(the head sweats especially heavily).
The lack of oxygen forces the brain to wake up for a split second and command it to take several frequent and deep breaths to replenish the lack of oxygen. Forced breathing causes such phenomena as:
- dyspnea;
- suffocation
(extreme shortness of breath).
Episodic increased breathing or shortness of breath is a mandatory symptom of sleep apnea, but often the patient does not remember this, since he does not fully wake up during episodes of respiratory arrest, but only goes into a state of drowsiness for a few seconds.
Deep and frequent breathing dries out the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, making it sensitive to irritating factors - saliva flowing into the throat and the beating of the walls of the respiratory tract against each other during snoring. Regular trauma to the mucous membrane contributes to the development of inflammation and swelling. The reaction to stimuli may be as follows:
- night cough;
- dry mouth;
- voice hoarse by morning;
- a sore throat.
Frequent breathing after an episode of apnea dries out the mucous membrane, making it susceptible to external irritants. Therefore, snorers often have sore throats and coughs.
Frequent breathing after an episode of apnea dries out the mucous membrane, making it susceptible to external irritants. Therefore, snorers often have sore throats and coughs.
As soon as breathing is restored, the person falls asleep, and the walls of the throat again lose their tone. Snoring in men and women resumes, and everything repeats again. Hypoxia and nocturnal hypertension lead to headaches
.
Micro-awakenings after episodes of apnea disrupt the structure of night rest, since there are practically no stages of deep sleep. But they are the ones responsible for restoring the body’s resources. As a result, apnea becomes the source of the following problems:
- difficulty waking up;
- daytime sleepiness;
- fatigue and weakness;
- irritability, nervousness, depression.
The psycho-emotional state is aggravated by the fact that numerous awakenings increase anxiety and provoke nightmares
.
Stopping breathing also affects the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. During an episode of apnea, intrathoracic and intra-abdominal pressure fluctuates. The stomach contracts and its contents are thrown into the esophagus. Gastric acid irritates the mucous membrane and appears:
- heartburn
(including chest pain caused by heartburn); - belching
.
Sleep affects almost all body systems, including the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract
With massive reflux, microparticles of gastric contents can reach the upper respiratory tract and cause spasm of the vocal cords. As a result, a person wakes up from:
- severely difficult wheezing;
- lack of air;
- cough.
Obstructive apnea also affects the urinary system, causing frequent urination at night.
.
An increase in intrathoracic pressure during an attack of apnea makes it difficult for the heart to work and causes stagnation of blood in its right sections, followed by stretching of the heart chambers. This produces a special hormone that affects the renal blood flow and accelerates the excretion of sodium and water from the body. This leads to more intense urine production, and, consequently, frequent visits to the toilet at night.
Rules for performing breathing exercises
The rules for performing breathing exercises are not limited to inhaling for 4 counts, holding your breath for 7 counts, and exhaling for 8 counts. It is very important to breathe slowly , since fast breathing no longer relaxes, but invigorates a person.
Note that when performing gymnastics, you should inhale through your nose and exhale exclusively through your mouth . Moreover, the exhalation must be “warm”. That is, when you exhale, you seem to warm the air in the room, while making a noisy sound “HA”.
In the first week of classes, it is enough to take only 2-3 breaths in the morning and 2-3 breaths in the evening. This is quite enough to get started. There is no need to do more in the first 2 days, since you may feel dizzy from an excess of oxygen.
Try to increase your oxygen load every day. Do one more repetition every day until you reach at least 50 reps . This will help you achieve a sleeping effect faster after the exercise.
You can do gymnastics in any body position . You can choose from: sitting, standing and even lying down. At the beginning, we recommend performing the exercise in a sitting position, leaning back in a chair. This way, you can breathe as deeply as possible, which is very good for complete relaxation.
Important point: Make sure that your stomach is fully protruded when you inhale, and pulled in as much as possible when you exhale. This breathing style trains the diaphragm, the muscle that separates the chest and abdominal cavity.
It is worth emphasizing that breathing exercises for sleep are carried out slowly, and all exercises and movements are performed slowly. According to the creators of this complex, unhurried execution makes each breath as effective as possible for quickly falling asleep.
Symptoms of poor sleep habits and hygiene
The quality of a night's rest can be impaired by poor bedroom conditions and too little or too much sleep. Let us list the most common signs of violation of rest routine and hygiene.
Sometimes, to normalize your sleep, it’s enough just to change the pillow and carefully monitor the level of humidity and temperature in the bedroom
- Headache.
Often bothers those who sleep in a stuffy room with low humidity. The pillow is also important: if the head is thrown back during rest, this impairs blood circulation in the vessels of the neck, prevents the flow of blood to the brain and leads to oxygen starvation. And hypoxia is a prerequisite for the occurrence of migraines. - Sweating.
This problem, as a rule, can be solved by using a moderately warm blanket, ventilation, and monitoring the level of humidity. - Allergy.
Common allergens are house dust, laundry detergent, lint in pillows, and animal hair (including wool blankets). Night allergies manifest themselves as a dry, non-productive cough, difficulty breathing, sneezing, lacrimation, and rhinitis. - Night cough.
If the air is too dry, the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract does not have time to restore the protective film of moisture. This leads to irritation and causes a defensive reaction - coughing. Low temperature and dusty air lead to a similar problem. - Edema.
The cause of this trouble is excess or lack of sleep. With “lack of sleep” the changes are insignificant and are explained by mild metabolic disorders. When “oversleeping,” a person is in a horizontal position for a long time, which negatively affects blood circulation, causing stagnation of blood and the release of its liquid part into the tissue. The use of high pillows also affects the development of edema.
Symptoms of insomnia (insomnia)
Decreased quality of night rest and constant lack of sleep causes deterioration in physical and mental health. In a state of stress, the body produces anxiety hormones that speed up the heart, which, as in the case of apnea syndrome, often leads to hypertension
.
The inability to fall asleep at night keeps a person tense, which also leads to problems of a physiological and psychological nature.
Excitation of the autonomic nervous system leads to increased blood pressure and rapid heart rate. The patient is in a lying position and practically does not move, but his body experiences stress, as during physical exercise, which provokes sweating
.
And even if you manage to fall asleep, a person still wakes up several times a night due to minor extraneous sounds or disturbing dreams. After each awakening, you have to make an effort again to fall asleep. Therefore, insomnia is often accompanied by complaints of:
- light sleep;
- nightmares.
With a reduction in the quantity and deterioration in the quality of rest, sleep does not provide the necessary feeling of vigor and freshness. As a result, the patient experiences:
- difficulty waking up;
- fatigue and weakness;
- headache;
- irritability;
- daytime sleepiness.
Facial gymnastics for women and men with insomnia
To fall asleep, facial gymnastics for women and men is often used, which can quickly put you to sleep. The essence of this exercise is to relax the facial muscles, the tension of which can cause insomnia. Typically used for relaxation:
- Temple massage . To perform this exercise, you need to place two fingers on your temples and move them clockwise, pressing slightly on the skin. The duration of this exercise is at least 1 minute;
- Eyelid massage . To perform it, you should make circular movements, as if circling your eyes with the fingers of both hands. The eyes, of course, should be closed. Do 7-10 such movements;
- Forehead massage . To do this, place the fingertips of both hands on the middle of your forehead. And then massage it with rubbing movements, moving the fingers of your left hand from the center of the forehead to the left temple, and the fingers of your right hand to the right. To relax, it is enough to spend 1-2 minutes on the exercise.
Relaxing gymnastics for insomnia
Breathing exercises for sleep are effective on their own. However, its combination with relaxing gymnastics for insomnia makes breathing practices even more useful.
To perform the first exercise, you should take a lying position . Then, leaning on only one hand, turn your body on its side, while holding your hand above you. You should hold in this position for at least 30 seconds . After this, changing your supporting hand, take the opposite body position and stand there for at least 30 seconds. That is, the same amount of time as with support on the first hand. Note that this exercise is designed for more or less trained people. Therefore, include it in your training program at your discretion.
The second relaxation exercise, like the first, is static . Therefore, it is performed in a stationary position. To perform it, lie on your stomach, lift your leg up and hold it for 1 minute. Repeat the exercise in the same way with the other leg.
Both of these exercises will relax all the muscles in your body and allow you to fall asleep quickly.
Complications of sleep diseases
Sleep disorders can have serious consequences. Therefore, their diagnosis and treatment should be carried out by a specialized specialist.
Insomnia and snoring cause a lot of inconvenience. But not everyone perceives sleep disorders as a health threat. The list of symptoms only indirectly indicates how much impact sleep disturbance has on the body. In this case, the progressive disease leads to serious consequences, including:
- arterial hypertension;
- cardiac ischemia;
- heart failure;
- myocardial infarction;
- angina pectoris;
- stroke;
- obesity;
- hypoventilation (respiratory failure) in obesity;
- diabetes;
- impotence;
- reflux esophagitis;
- anxiety and depression.
To prevent the development of these diseases, it is important to be attentive to the signals that the body gives and respond to them in a timely manner. The first thing to do if you suspect a sleep disorder is to visit a somnologist. The specialist will analyze your symptoms, conduct the necessary research and, based on the information received, determine what is preventing you from sleeping normally. Remember: timely diagnosis and proper treatment of sleep diseases improves the quality of life and often saves from premature death.
How to relax before bed correctly
Edmund Jacobson once spoke about how to relax properly before going to bed . This American doctor in the mid-20th century developed a special relaxation technique aimed at reducing muscle tension.
Neuromuscular relaxation according to Jacobson involves alternately tensing the muscles of the whole body. As a rule, you should tense your muscles starting with your legs. That is, first the calf muscles, then the thigh muscles, then the buttocks, then the abs, etc., etc. Also, as an option, you can try to start with the muscles of the neck or arms, and finish with the muscles of the legs.
Each muscle must be tensed for 10 seconds, then relaxed for the same 10 seconds. Next, tense other muscles in sequence. For example, if you started with your legs, then tense your abdominal muscles, chest, shoulders, etc.
The effect of Jacobson's relaxation will be noticeable after 2-3 weeks of daily exercise . Doing exercises before bed every day will significantly improve your sleep and make it easier to fall asleep.
Exercise for insomnia
Breathing exercises for sleep go well with physical exercises for insomnia. Moderate exercise will relax the muscles of your body, and proper abdominal breathing will help calm your thoughts and set you up for sleep.
Among the exercises that are useful to perform before going to bed are the following:
- Exercise while sitting . Sit on the floor or sofa. Place your feet with your feet facing each other. Cross your arms in front of you. For complete immersion, close your eyes. Stay in this position for 2-3 minutes. At the same time, breathe correctly, “inflating” your stomach to the maximum as you inhale and drawing it in as you exhale;
- Lying exercise . Lie down on a hard surface and raise your legs a few centimeters up. Hold in this position for 10-20 seconds. Then lower your legs and rest. Repeat leg lifts a couple of times;
- Lying exercise No. 2 . While on the floor, do a reverse boat. To do this, you need to lean on the floor only with your shoulders and heels. Stay in this position for 15-20 seconds, then rest. Do 3-4 such approaches;
- Half-lifts of the body . From a lying position, you need to rise a little, as if bending the body on the abdominal muscles. Stay in this pose for 10-15 seconds. Return to the starting position. Then relax and repeat the exercise 2-3 times.