Multiple sclerosis is a disease associated with damage to the nervous system. Diagnosis requires a comprehensive examination by a doctor, who is required to do a magnetic resonance imaging scan of the brain. Directly based on the severity of the disease, a person is assigned an appropriate disability group. Therefore, in any case, the person who submitted the application and documents for examination by a medical commission can count on being assigned disability for multiple sclerosis.
Classification of multiple sclerosis
The classification of the disease is determined by the degree of severity and the specific course of the disease:
- First degree. The manifestation in a person of symptoms of damage to the nervous system, but without any particular impairment of its main functions. In such a situation, performance is maintained.
- Second degree. The patient has a violation of not only the motor function of the nervous system, vision, but also coordination, on the basis of which his performance can be only partially limited.
- Third degree. The symptoms of the disease are clearly expressed and are persistent. It is difficult for a person with the third stage of multiple sclerosis to engage in work activities that require physical activity, as well as coordination and concentration.
- Fourth degree. Significant impairments in motor function and vision are acutely manifested, which precludes the ability to care for oneself. A patient with this degree of illness requires constant care and assistance from outsiders.
Among the causes of death are post-infarction cardiosclerosis, which complicates the functioning of the heart due to the existing scar formed in the place of dead muscle after a heart attack.
Initial signs of the development of multiple sclerosis
The risk group for multiple sclerosis is teenagers, young adults and middle-aged people. The disease leads to damage to the central nervous system, which does not allow one to fully perform one’s duties and leads to a deterioration in the patient’s quality of life. Initial signs of the development of the disease may appear in the form of visual impairment:
- The patient feels a foreign body in the eye.
- A veil appears before the eyes, the image becomes fuzzy and cloudy.
- The patient may lose visual color perception, not distinguish between colors or just one color.
Such visual impairment may occur in one or both eyes. Symptoms last for several days and then disappear. The patient may experience pain when moving the eyeballs, when pressing on the eye, and increased sensitivity to bright light. Other symptoms of multiple sclerosis include impaired calligraphy, inability to make coordinated movements of the legs and arms, general unsteadiness of the body, sensory disturbances, and urinary retention or frequent urination. The disease can manifest itself as depression, irritability, constant fatigue, and memory impairment.
Is disability granted?
To determine the correct diagnosis and establish a disability group, a person with multiple sclerosis needs to submit an application to a special commission of the VTEK.
After submitting approved documentation and undergoing a full medical examination by experts, a disability group is assigned
It is worth noting that a referral must be taken from the attending physician.
Registration of disability after a stroke
The expert commission can carry out inspection and certification in various places:
- in the hospital where the patient is being treated;
- directly to the VTEK premises;
- It is also possible to visit the patient’s home if circumstances so require.
Based on the results of the examination, the medical commission makes a conclusion and decides to assign the appropriate disability group, but also sets its duration.
This is due to the following:
- After treatment and rehabilitation procedures are prescribed, the condition may improve, so the group may be changed or removed completely.
- If there are no changes and the disease progresses, then an indefinite disability group is assigned, which does not require annual re-examination.
As for the direct question of whether multiple sclerosis gives disability and for which group, the expert commission focuses on the main indicators of health status during the observation process. This usually takes 3–4 months.
There is hope!
However, in the next year or two, patients with primary progressive multiple sclerosis may receive an effective cure for their disease. Today this drug, which has already passed clinical trials, is at the registration stage in Russia.
It is assumed that B lymphocytes play a critical role in the progression of the disease. As a rule, they are absent in the nervous system of healthy people, but are always present in patients with multiple sclerosis. Destroying these cells slows the progression of the disease. Selectively targeting CD20-positive B cells may be an effective therapeutic approach.
Important
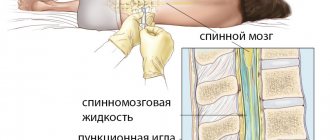
If you suspect multiple sclerosis, you should immediately contact a neurologist. In addition to examination and assessment of neurological status, you will need: – MRI of the brain and spinal cord; - blood analysis; – lumbar puncture (cerebrospinal fluid analysis).
Criteria by which a group is assigned
Taking into account the fact that the degree of the disease and the nature of its course may be different, patients are interested in the question of what disability group is assigned depending on the severity of disorders of the functioning of the nervous system:
- Group 3 – assigned to a person who has mild motor dysfunction, so they can carry out work activities;
- Group 2 – prescribed to people who have severe functional disorders that are responsible for movement;
- Group 1 – can be assigned to a disabled person if there are clearly pronounced impairments in motor and visual function.
After passing the VTEK examination, the appropriate disability group will be assigned.
Disability
Young patients with multiple sclerosis become incapacitated in 30% of cases within the first 2 years.
Obtaining disability is possible after examination by neurologists of the Medical Labor Expert Commission (VTEK). They have the right, based on the diagnosis, to assign a disability to the patient and record its category. The patient is examined (depending on the ability to move) in a hospital or at home. The duration of the award is usually 1 year.
The chief or attending physician of the hospital to which the patient is assigned will help you obtain a referral.
Disabled groups are assigned depending on:
- general condition of the patient;
- stages of visual impairment;
- deviations from the norms of motor function;
- self-service options;
- degree of nervous system dysfunction.
Among other things, some indicators can add points to the group identification scale: analysis of the general structure of the brain, possible swallowing disorders, speech problems.
Attention is also paid to the work of internal organs and the involuntary processes of bowel movements and urination.
In addition, with regular re-examination of the patient’s condition, if this condition worsens, a different degree of disability may be assigned. And if there is an improvement and, moreover, the patient becomes able to work, deprivation of the disabled group occurs.
There are 3 disability groups:
- (III) The third degree is characterized by social difficulties in interaction and progressive deterioration of body functions.
- (II) The second is awarded in case of extensive motor dysfunctions and limitation of life activities.
- (I) The first is given to patients with severe musculoskeletal disorders, paralysis, impaired vision, and inability to navigate and care for themselves.
Assigning a degree of disability without the right to re-examine is possible if doctors note the impossibility of overcoming social disability.
Due to loss of legal capacity and certified disability, a need arises to receive financial assistance.
What disability group do they give?
The VTEC Commission establishes a group according to the criteria and aspects of the diagnosis.
The following disability groups are assigned for multiple sclerosis:
1 – disorders and pathologies of visual function, as well as musculoskeletal function. Parts of the body are paralyzed, vision is lost or partial blindness is detected, muscles involuntarily contract. The patient is deprived of independence and is forced to be under constant care. The prognosis for the disease in this case is disappointing, recovery is impossible, which leads to the assignment of the first group on an indefinite basis.- 2 – the disease is characterized by nervous disorders, a malfunction of the immune system, inability to perform motor actions or their difficulties, work ability is limited or absent (contraindicated). Paralysis of the limbs (upper, lower), obvious dysfunction of movements, vision is impaired, and independent care is difficult.
- 3 – disorders after illness are moderate in nature and do not interfere with the citizen’s ability to work. The course of the disease is moderate, physical activity is not aggravating for movement, and vision does not cause discomfort.
Payment amounts for a given period of time
The pension benefit depends on the disability group received (as it depends on the degree of the citizen’s ability to work).
Scale
The disability scale for multiple sclerosis is calculated in points (from 0.0 to 9.0) using a special calculator.
The scales are represented by the following parameters:
- Visual functions.
- Condition of the spinal cord trunk.
- Functions of the pelvic organs.
- Pyramid system.
- Sense organs.
- Functions of the cerebellum.
- Cognitive abilities.
Kurtzke scale 10 points
1 point – nervous system disorders are mild.- 2 points – gait is upset, eye nystagmus is pronounced.
- 3 points – weakness of muscle tissue, paralysis, impaired coordination of movements.
- 4 points – there is the ability for self-service.
- 5 points – ability to work is maintained for several hours.
- 6 points – moves only with the help of other people for 100 m with supports.
- 7 points – movement in a wheelchair, independent transfer into it, partial self-care.
- 8 points – weakened upper limbs, bed rest.
- 9 points – needs help and care, speech may be absent.
- 10 points – paralysis, complete outside care.
Disability for multiple sclerosis: what group is given, how to get it
Multiple sclerosis is one of the common diseases of the central nervous system. According to statistics, it occurs in 5-70 patients out of 100 thousand people. In the European regions of Russia, the incidence is slightly higher than the average and is approximately 25-50 cases per 100 thousand.
Men and women aged 20 to 45 are at particular risk. In older people, multiple sclerosis (MS) is diagnosed much less frequently, and with similar symptoms, other pathologies are usually detected.
The disease is characterized by a chronic course with periodic exacerbations and, conversely, a decrease in symptoms. However, MS is constantly progressing and very often, even at relatively early stages, leads to a significant limitation of a person’s ability to work.
Multiple sclerosis as a basis for disability
Very often, MS leads to serious damage to certain areas of the brain and spinal cord. In humans this manifests itself:
- in speech impairment;
- deterioration in coordination of movements;
- numbness of the limbs up to complete loss of motor function;
- problems with mental state and other symptoms that do not allow him to continue working.
Therefore, in MS at certain stages, one or another disability group is assigned. However, in some cases, the disease may manifest itself in the form of symptoms only periodically, no more than once or twice a year. However, such symptoms can only slightly affect the ability to work.
Thus, the very fact of detection of MS does not necessarily mean the assignment of a disability group. In each individual case, this must be decided by a medical commission by conducting a medical and social examination (MSE). At the same time, in the decision-making process, doctors pay attention primarily to the coordination of the patient’s movements.
In this regard, there are the following criteria for selecting one of the groups:
- III gr. – the presence of mild or moderate impairment of motor function while maintaining ability to work;
- II gr. – the pathological state of the central nervous system has pronounced symptoms;
- I gr. – serious violations lead to severe loss of coordination of movements up to the complete loss of the patient’s motor ability.
Thus, disability requires serious diagnosis, and various forms of MS can become the basis for assigning any of the groups, from the third to the first.
Indications for medical and social examination
To obtain a group of limited work ability, you must pass the Medical Labor Expert Commission (VTEK). It is convened after the patient contacts his therapist or the head physician of the medical institution.
If specialists consider the existing grounds sufficient for the work of VTEC, then the patient’s personal file will be transferred to representatives of the commission to prescribe the tests and studies necessary for this procedure.
A meeting of the commission on the issue of assigning a disability group can take place:
- in the management of VTEK;
- at the home of a patient suffering from MS;
- in the hospital where the patient is being treated.
In this case, the following factors may be the basis for convening a medical and labor commission:
- Due to the symptoms of the disease, the patient cannot perform work in accordance with his job responsibilities or there is a forced need to significantly limit the workload.
- After a person sought medical help and was diagnosed, the prescribed course of treatment did not produce significant results. The patient's condition did not improve. Multiple sclerosis leads to serious pathologies that severely limit the life of the patient.
- The patient's condition is noticeably deteriorating due to the progressive disease, which has become permanently chronic.
- Due to the pathology, a person is temporarily disabled for more than 4 months.
It should be noted that the list of these grounds may be subject to correction depending on the patient’s condition and the attending physician’s conclusion about the need for a VTEC meeting or its absence.
List of studies and analyzes required for medical and social examination
Modern medicine offers several ways to detect MS, but the disease is still not detected in all cases and is considered difficult to diagnose. Not the least role in this is played by the fact that the clinical signs of the disease resemble many other pathologies of the central nervous system.
That is why the diagnosis of “multiple sclerosis” is made by doctors only after a comprehensive study of the patient’s condition:
- Foci of damage to nerve cells are identified during an MRI examination of the head and spinal cord.
- The development of MS can also show the state of the immune system, which is determined through a blood test from a finger and a vein.
- A lumbar puncture is also performed .
- Symptoms of MS can be diagnosed by an eye doctor or a doctor who specializes in diseases of the neck, ear, head, nose and throat.
- A patient with suspected MS is given an injection with the Margulis-Shubladze composition. If the test gives a positive reaction, then the suspected diagnosis can be confirmed. However, doctors never make a final decision without comparing the test results with other studies.
If, after conducting these studies and passing the necessary tests, it is confirmed that the condition of a person with MS gives him the right to be granted a disability group, the experts included in the commission make an affirmative decision. Its details will depend on more specific details.
Determination of disability group for multiple sclerosis
This procedure is carried out on the basis of regulatory documents regulating the work of VTEK. However, if a patient has MS, doctors often deviate from the general rules of disability, since the peculiarities of the symptomatic manifestations of this disease do not allow them to be followed.
When determining a patient’s disability group, members of the medical expert commission must take into account clinical features and take into account the social factor:
- An important clinical basis for disability in MS is the deterioration of the patient’s condition: more frequent attacks, symptoms that manifest themselves more intensely.
- The essence of the attacks is studied : how severe the symptoms are during exacerbation, how long this condition lasts and to what extent it improves during periods of remission.
- Experts take into account the psychological factor: how much the patient underestimates or overestimates his work capabilities.
- Assignment of a disability to a particular group may depend on the profession, qualifications of the patient and his lifestyle in general.
Based on these criteria, the following forms of disability are determined.
Disability group III
It is assigned if the following factors are present:
- the disease has developed into the second degree of severity;
- due to persistent deterioration of the condition and severe symptoms, the patient is unable to perform his work and must change his occupation;
- the person has a noticeable decrease in mobility.
Disability group II
This form is assigned after:
- transition of MS to the third degree of severity;
- development of the disease into the stem form;
- progressive pathological condition;
- loss of ability to work, with the exception of performing short and simple work;
- disturbances in motor activity and orientation in space.
Disability group I
The most severe degree is assigned if the patient cannot live without assistance. At this stage of the disease, partial or complete paralysis may occur.
Often patients go blind, and their digestive organs are disrupted. Mental deviations are also quite possible, up to the most severe pathologies associated with the destruction of a person’s personality.
It is known that disabled people of all groups, with a few exceptions, must annually confirm their status. In practice, persons who have group I due to the last stage of MS, after a five-year observation period, no longer undergo re-examination and the benefits they are entitled to are secured for life.
Contraindicated work and necessary working conditions
Patients with MS, even at the very initial stages of the pathology, can no longer perform certain types of work, otherwise this could significantly affect their health. In general, the more severe a person's disease, the greater these restrictions will be.
General contraindications include:
- mental or physical stress, night shifts and overtime work;
- strong anxiety and work under constant stress;
- professions related to the impact of vibration on humans;
- working with toxic substances;
- exposure to sunlight and overheating of the body.
In the future, as the disease progresses, those that require:
- constantly on your feet;
- lifting weights;
- strong concentration ;
- strain ;
- strict coordination of movements and maintaining a certain rhythm.
A patient with MS must create the following working conditions:
- The number of work duties associated with the need to travel on foot should be limited
- The employer needs to organize the workplace of a person with MS in such a way that it is easy for him to get to it by transport.
- psychological is extremely important so that a sick employee does not experience unnecessary stress.
- A mandatory condition for maintaining the ability to work with MS is to provide him with a break and exemption from overtime work.
- Persons diagnosed with the disease are predisposed to quiet sedentary work and mental work.
Protection of the labor rights of people with disabilities
Many people with early stages of MS voluntarily give up disability because they are afraid of losing their jobs or believe that they will not be able to get a new job with disabilities. As a result, the condition of patients quickly deteriorates and reaches the final stages of MS, at which the patient is no longer physically able to work.
That is why everyone who is faced with this problem should be aware of the legal protection measures for people with disabilities during employment:
- According to Russian legislation, each employer is obliged to allocate a certain quota of jobs for people with disabilities.
- Moreover, if an applicant with disabilities is hired beyond this quota, he cannot be refused only because of his health condition, if it does not interfere with the performance of duties and does not create a threat to other employees.
- Dismissal of a disabled person without reason or denial of employment can be appealed in court.
If all restrictions are observed under conditions of constant supportive therapy, a person with multiple sclerosis can maintain his or her work activity for a long time. And if his condition worsens, assignment to one of the disability groups will provide him with the social guarantees and benefits necessary for his life, as well as pension provision.
Source: https://nevralgia.ru/rasseyanniy-skleroz/vse-ob-invalidnosti/
Origin and development of the disease
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disease classified as autoimmune. As the disease progresses, it inevitably leads to disability, destroying human health in many ways. The main violations appear:
- loss of vision;
- hearing loss;
- paralysis of arms and/or legs;
- a general decrease in sensitivity to all stimuli.
MS can begin to appear in people of almost any age. The average starting age range is from 15 to 45 years; both children and old people can suffer from multiple sclerosis. In the initial stages, the disease is asymptomatic. Therefore, you need to monitor the manifestations of certain signs:
- blurred vision;
- problems with the vestibular system: dizziness, loss of balance and stability;
- problems with coordination of movements;
- slower reaction;
- general weakness;
- the presence of spasms and/or convulsions in the body.
All this may indicate the onset of MS, which cannot be stopped - the disease will progress and worsen. The presence of multiple sclerosis can be diagnosed based on the results of an MRI of the brain under the supervision of a neurologist. The presence of the disease can be assumed, but the diagnosis must be confirmed clinically. The disease can develop according to several scenarios, depending on the form of its course:
- relapsing or remitting. Remissions (can last a year or even several years) are interspersed with acute phases. “Gray matter” after damage is capable of both partial and complete restoration of the functions of the affected areas;
- primary progressive. A smooth but unstoppable trend of health deterioration, which, in the absence of acute phases, on average makes a person incapacitated twice as quickly;
- secondary progressive. In the early stages, it is very similar to the typical recurrent form, which subsequently develops into a continuously progressive one;
- progressive-remitting. It is the least common and combines the first two types. Parts of the brain that survive the attack do not regain their functions.
The disability group for multiple sclerosis is almost directly dependent on the stage at which the disease is located. There are four of them in total and are called ordinal numbers (from 1 to 4):
- The human central nervous system shows initial signs of a functional disorder, while continuing to operate generally stably;
- lesions of the central nervous system partially affect the organs of vision, reduce hearing, and impair coordination of movements;
- The central nervous system exhibits disruptions in its basic functions, the person loses attention and fine motor skills, and becomes tired above average;
- terminal stage of central nervous system depression. The patient is almost or completely unable to see, hear, or move. Can move around in a wheelchair and requires constant care.
FAQ
People who have encountered this disease themselves or observe its progression in a member of their family are wondering how to live on.
Can a person with MS study or work?
Due to the fact that MS is not characterized by a general manifestation, severity and frequency of occurrence, it is difficult to answer this question unambiguously. The ability to perform job duties or attend classes is affected by the degree of disability.
Therapeutic exercises for multiple sclerosis
If a person has group 3 disability, he can continue to lead the lifestyle to which he is accustomed.
During remission, the patient must assess the level of his capabilities in a specific industry:
- physical;
- social;
- cognitive abilities.
This will allow you to move towards the goal not only at this stage, but also in the future.
Should you talk about your illness to your family and friends?
The patient has every right to decide for himself whether to hide the discovered illness or tell his loved ones.
If there are no visible signs, then you don’t have to rush to inform your family.
But when you discover the secret, you will be able to take advantage of the benefits provided. For example, in educational institutions such patients are trained under special programs, can count on individual exams, etc.
How to live further after diagnosis?
If the disease is detected early, treatment will be more effective. It is necessary to take beta interferons, which will help slow down the process of disability and reduce the severity and frequency of exacerbations.
The patient should adapt to the disability (if it is not very pronounced) and continue to live his previous life.
There is no general treatment method. If a serious exacerbation is observed, the doctor will prescribe corticosteroids, methylprednisolone intravenously, with a further transition to prednisolone.
The severity and severity of exacerbation is reduced with certain drugs that were approved for use only recently:
Betaferon and betaseron.
The patient must undergo rehabilitation after an exacerbation.
In case of remissions, maintenance therapy is prescribed, as well as:
- physical exercise (stretching and coordination);
- speech therapy classes;
- physiotherapy.
Which specialists should I contact?
How to live without exacerbations or reduce them to a minimum? It is worth seeing specialists. Multiple sclerosis is the responsibility of a neurologist. Your family doctor will help you and your loved ones learn all the nuances about the course of the disease.
Many also turn to medical institutions for psychological support.
For specific problems that may arise due to the disease, contact:
Will volunteers help if I'm lonely?
Single people can count on support from social assistance workers in managing their household.
There are volunteer movements in the country that will support and help in solving problems.
Such organizations have special literature on multiple sclerosis, which is provided to patients free of charge. You can find the trust numbers and address of such a company on the RS International Portal.
Does MS in older people differ from the disease in young people and children?
MS can debut in a person of any age, but is most often diagnosed in people 25–35 years old, with females being at greater risk. In old age, as in young people, the disease rarely appears.
The course of multiple sclerosis in a two-year-old child is mild, and complications are minimal.
In young people and children (as opposed to older patients), the disease is accompanied by:
The remaining symptoms are general. According to research, if a child gets sick before the age of 16, the course of the disease will be more favorable. But there are cases when, after 20–30 years, such people experience significant disability.