Mental and nervous diseases are quite common in people. The appearance of the first signs of these diseases causes confusion and stress for the patients themselves and their loved ones. In a state of fright, they do not immediately understand which doctor to contact. Our Leto clinic employs specialists who provide all types of psychoneurological assistance to people in need. Clients with Jacksonian epilepsy also come to us. This is the name of one of the variants of a group of diseases that occur with their own specific convulsive manifestations. If signs of illness or other problems appear, call us at: 8(969)060-93-93 . Our consultants will tell you what and how to do.
What is Jackson's epilepsy?
This pathology refers to a neurological disorder with its characteristic convulsions and sensory disturbances without loss of consciousness. Symptoms spread in a certain order. A variant of these epileptic disorders is not common, but has a characteristic clinical picture, without causing any particular difficulties for the doctor in diagnosis.
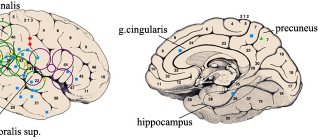
Jacksonian epilepsy is a manifestation of the focal form of the disease. The epileptiform focus is formed as a local zone in the area of the pre/postcentral gyrus of the brain. A detailed description of the symptoms was carried out by the French doctor Bravais and the English doctor Jackson, from whose name the name of the disease variant came. He was the first to identify the localization of a structural painful focus.
Symptoms of Jacksonian epilepsy
Convulsive paroxysms of the Jacksonian type are highly variable. Their common feature is local occurrence in a separate area of the body (usually in the hand or face) and subsequent spread, called the “Jacksonian march”. A characteristic feature is the one-sided nature and distribution of paroxysm in accordance with the projection of body parts onto the cortex of the anterior central gyrus. Jacksonian paroxysms can be sensorimotor, motor only, or sensory only.
“Motor Jackson” occurs during epileptogenic stimulation of the precentral gyrus cortex. It manifests itself as cramps, usually starting in the muscles of the thumb and gradually spreading to the entire upper limb, face, and then leg. When paroxysm begins from the facial muscles, it spreads to the arm (from the hand to the shoulder), then to the leg from the hip down. In rare cases, cramps begin in the 1st toe and spread up the entire leg, arm and face. Convulsions are clonic in nature, preceded by a short tonic phase. They may stop suddenly, but more often they pass in the reverse order of their onset. “Sensory Jackson” is caused by excitation of the postcentral gyrus cortex, has a distribution sequence similar to the motor one, but is associated with sensory disorders (paresthesia, loss of sensitivity).
In some cases, Jacksonian paroxysm is limited to the place of its occurrence and does not have a significant spread. Such an attack is called simple and occurs without loss of consciousness. During the “Jacksonian march,” loss of consciousness is often observed. In the case of generalization of paroxysm, the convulsions move to the other side, consciousness is lost. When status epilepticus develops, it can be localized only in the facial muscles, affect the muscles of one limb, or have the character of a “Jacksonian march” attack following one another.
As a rule, at the beginning, Jacksonian epilepsy occurs with simple paroxysms starting from the same place. Sometimes patients are able to stop the progression of seizures by holding the limb. Over time, epileptic seizures occur with an increasing spread of convulsions, and their relief by holding the limb is no longer possible. After a paroxysm, temporary paresis of the limb with which the epileptic attack began is often observed. An increase in the duration and severity of postparoxysmal paresis indicates a tumor process.
If the epileptic focus is located in the dominant hemisphere, motor aphasia is possible. Occasionally, paroxysms occur that occur in the form of transient paralysis of an arm or leg. Depending on the underlying disease in the clinical picture, other neurological symptoms are noted along with Jacksonian seizures.
Causes of the disease
During the survey and diagnosis, psychiatrists at our clinic identify various causal factors leading to the development of this disease.
Patients are diagnosed with:
Previous or currently existing infectious and inflammatory pathologies: arachnoiditis, encephalitis, meningitis.- Abscesses, tumor processes in brain tissue.
- Aneurysms of cerebral vessels.
- Parasitic lesions: cysticercosis, echinococcosis.
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Vascular anomalies.
- Hereditary predisposition.
In childhood, pathology is provoked by:
- Fetal hypoxia.
- Transfer of intrauterine infections.
- Birth injury.
Characteristic complaints and symptoms
Jacksonian epilepsy syndrome consists of a variety of manifestations. Paroxysmal seizures differ from the classic version. Doctors at our medical center always identify the typical pathological complex characteristic of this disease.
The most characteristic feature of an attack is the local appearance of convulsive twitching. Most often, trembling or unpleasant sensations (paresthesia, lack of sensitivity) are formed in the face, hand, and fingers. Next, the paroxysmal reaction goes to the shoulder area, then to the leg from the hip to the foot. This sign is called the “Jacksonian march” in medicine. Less commonly, paroxysm comes from the toes, then to the arm and face.
Another type occurs only in the focus of occurrence without spreading. With the classic version of Jacksonian epilepsy, the patient rarely loses consciousness. Sometimes complicated episodes are observed, including status epilepticus, which consists of alternating attacks one after another.
The following processes are distinguished by complexity:
Simple seizures. In this case, convulsions and paresthesias always begin from the same place. The patient can stop their spread by fixing the painful area with his hand.- Complicated paroxysms. Convulsive areas with altered sensitivity progressively spread to different muscles. It becomes impossible to stop their development.
- Complicated with consequences. After an attack, the patient develops paresis of the painful limb. Over time it goes away. This clinical variant alarms the doctor in terms of oncological processes.
Pathological paroxysms are accompanied by additional neurological symptoms characteristic of the main causative disease.
Symptoms of the disease
Seizures usually begin in the front part of the brain.
After this, they impulsively appear in the affected area of the body.
If a cramp affects a finger on the left hand, then with a high probability it can spread to the same finger on the right hand. Thus, the seizure does not spread to a large area (for example, the entire arm), but moves to a section located parallel to it.
Among Jacksonian seizures, the following forms can be distinguished:
- “March” - seizures come one after another with a small interval.
- The seizure affects the facial muscles.
- A seizure occurs in the muscles of a specific part of the body.
You can tell that a patient is having a seizure by tingling in the fingers of both limbs (much less often the entire limb cramps).
Some people may experience clouding of consciousness, leading to fainting.
Diagnostics
In our clinic, the diagnosis is established based on a comprehensive examination.
It includes:
- Questioning the patient to identify characteristic complaints characteristic of the disease.
- Determining the causative disease causing the attacks.
- Diagnosis of psychoneurological status.
- General examination and physical examination, including measurement of A/D, pulse, auscultation of the respiratory and cardiac organs, palpation of the abdomen.
When Jacksonian epilepsy is detected, a differential diagnosis must be carried out, excluding a number of pathologies that give similar symptoms.
The doctor checks the patient for the presence or absence of:
Myoclonic epileptiform seizures.- Hysterical neurosis.
- Paroxysms of unknown origin.
To eliminate mistakes, our doctors often use the consultation method, inviting an epileptologist and a neurologist.
Encephalogram data should be taken into account in the diagnostic process. Stimuli are used to identify indicators of epileptic activity in the form of focal cortical discharges. Clients are given light and sound signals, to which the body reacts with peak activity. In some situations, long-term video monitoring is required.
An informative picture is provided by computed tomography and MRI of the brain. With their help, tumors, cystic formations, signs of inflammation, and abscesses are identified.
Treatment of Jacksonian epilepsy
Therapy includes 2 components: antiepileptic (anticonvulsant) and treatment of the underlying disease. Without the effective implementation of the second component of treatment, relief of Jacksonian epilepsy is impossible. Anticonvulsant therapy is carried out in the form of monotherapy or complex treatment using phenobarbital, valproic acid, lamotrigine, primidone, benzobarbital. In parallel, dehydration agents (acetazolamide, furosemide, hydrochlorothiazide) and absorbable treatment (hyaluronidase, aloe) are prescribed.
In cases where Jacksonian epilepsy occurs against the background of a tumor, cyst, or arteriovenous malformation, consultation with a neurosurgeon is necessary to decide on surgical treatment. However, even after removal of the organic cause, persistent persistence of Jacksonian seizures is often observed. In such cases, with resistance to ongoing anticonvulsant therapy and a high frequency of epileptic seizures, the issue of surgical treatment of epilepsy is considered. Operations to dissect adhesions and remove scarred membranes have shown little effectiveness. After their implementation, only a temporary disappearance of paroxysms was noted. A more radical method of treatment is focal resection, in which the areas of the cortex responsible for epiactivity are removed. The consequence of the operation is paralysis of the limb, the motor zones of which were removed. Over time, muscle strength in paretic limbs increases, but paresis, expressed to one degree or another, remains for life. In addition, there is no guarantee that epilepsy attacks will not recur some time after the operation, since the intervention entails the formation of scar changes.
LiveJournal
What is needed to cure Jacksonian epilepsy
If you suspect the appearance of this pathology, you should undergo an examination by a specialist at our Leto mental health center. Hotline phone number: 8(969)060-93-93 . The call center is open 24 hours a day. Call us and the consultant on duty will give comprehensive answers to all your questions. The anonymity of the appeal allows you to talk about existing problems completely calmly. 24-hour consultation gives you the opportunity to make calls at any time convenient for you.
You can make an appointment with a doctor by telephone, and, if necessary, call a specialist to your home. If you need to transport a patient, we will provide conditions for a comfortable transfer.
In the inpatient department of the clinic, you can choose the most suitable ward for your stay.
We offer options:
- Standard (2-3-4 seats).
- Comfort for two people.
- VIP – for a stay of one person.
Attentive and qualified staff will monitor the patient around the clock.
Cost of services
| CONSULTATIONS OF SPECIALISTS | |
| Initial consultation with a psychiatrist (60 min.) | 6,000 rub. |
| Repeated consultation | 5,000 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychiatrist-narcologist (60 min.) | 5,000 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychologist | 3,500 rub. |
| Consultation with Gromova E.V. (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| PSYCHOTHERAPY | |
| Psychotherapy (session) | 7,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (5 sessions) | 30,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (10 sessions) | 60,000 rub. |
| Group psychotherapy (3-7 people) | 3,500 rub. |
| Psychotherapy session with E.V. Gromova (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| TREATMENT IN A HOSPITAL | |
| Ward for 4 persons | 10,000 rub./day |
| Ward for 3 persons | 13,000 rub./day |
| Ward 1 bed VIP | 23,000 rub./day |
| Individual post | 5,000 rub. |
| PETE | 15,000 rub./day |
This list does not contain all prices for services provided by our clinic. The full price list can be found on the “Prices” , or by calling: 8(969)060-93-93. Initial consultation is FREE!