When youth passes, people are left with a memory as a consolation, carefully preserving all the sorrows, joys, successes and achievements they have experienced. Alzheimer's disease and other types of dementia rob a person of more than memories - they literally rob him of everything that makes up life itself. To prevent the threat, we must try to do everything in our power.
Of course, forgetfulness with age is a natural thing. And not always, when memory weakens, you need to panic and suspect the worst. Indeed, according to statistics, for every person with Alzheimer's disease, there are 8 older people suffering from ordinary age-related decline in memory and intelligence.
The diagnosis is presumptive
It's not just Alzheimer's disease that can rob a person of memory and mental capabilities. “More than 30 other reasons can cause the development of dementia in old age. For example, vascular dementia is the cause of a third of such cases,” says Professor, Head of the Department of Geriatric Psychiatry, leading Russian specialist in the field of mental disorders of elderly and senile age, Doctor of Medical Sciences Svetlana Gavrilova. — Vascular dementia can occur both after major strokes and after repeated hypertensive crises and cerebrovascular accidents that were left without proper treatment. Weakened memory and decreased cognitive potential can also be caused by other causes: tumors, head injuries, intoxication, brain infections, metabolic disorders and even depression.”
In addition, as the expert said, doctors still do not have reliable non-invasive methods to accurately diagnose Alzheimer's disease. Therefore, during the patient’s lifetime, such a diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical symptoms and a whole range of studies, including by identifying biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease in the cerebrospinal fluid.
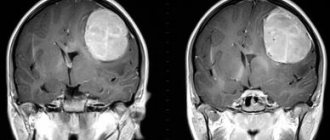
Among hardware studies, CT and MRI of the brain are used, and neuropsychological testing allows for a detailed examination of intact and impaired cognitive functions. As part of a neuropsychological examination, the patient must remember a number of words, numbers, geometric figures, read, count, repeat a complex phrase, draw a clock with a given time, copy a geometric figure. However, these studies do not have absolute diagnostic significance.
Be in line. Will late retirement help prevent dementia? Read more
Vascular dementia
Knowledge of the etiopathogenetic mechanisms of the formation of vascular dementia, risk factors, evidence-based medicine data has made it possible to formulate the basic principles of treatment and prevention of vascular dementia. The first step is to confirm the diagnosis of dementia. In this case, the identification of pre-dementia conditions, for which therapeutic possibilities are much wider, is of particular importance. Principles of treatment of vascular dementia: 1) etiopathogenetic; 2) drugs to improve cognitive functions; 3) symptomatic therapy; 4) preventive.
Treatment of vascular dementia is differentiated, which is determined by the heterogeneity of the pathological process. Due to the large number of etiopathogenetic mechanisms, there is no single and standardized method of treatment for this category of patients. Treatment of vascular dementia should include measures aimed at the underlying disease against which dementia develops and at the correction of existing risk factors. Considering that the main risk factor is hypertension, an important role is attached to its normalization, since adequate antihypertensive therapy is accompanied by a significant reduction in the risk of developing dementia of any etiology. Taking into account the fact that vascular dementia often develops in patients who have already suffered acute cerebrovascular accidents, the optimal blood pressure in these patients is within the range of 120/80 mm Hg. Taking into account evidence-based medicine, it is recommended to prescribe ACE inhibitors (perindopril, lisinopril, etc.), preferably in combination with diuretics.
Based on the characteristics of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, lisinopril is a priority in the combination of hypertension with diabetes mellitus (EUCLID), in persons with varying degrees of severity of acute hepatocellular failure and chronic diseases of the hepatobiliary system (the only representative of the group of ACE inhibitors, which is recommended for a single dose and at the same time represents finished dosage form that does not require additional biotransformation). Metabolic neutrality allows us to recommend lisinopril for the treatment of patients with manifestations of metabolic syndrome and obesity (hydrophilic substance). The pharmacological properties of lisinopril have been studied in sufficient detail (7 trials with “intermediate” endpoints (53,435 patients), and 5 trials with “hard” endpoints (53,030 patients), which is not inferior in scale to studies of representatives of the previous classes - captopril and enalapril, and also exceeds the breadth of trials of perindopril, fosinopril and moexipril). Based on this, we can welcome the expansion of the Ukrainian lisinopril market due to the emergence of highly effective and affordable drugs of European quality in a variety of dosages (Lopril 5, 10, 20 mg) and combinations (Lopril N 10, 20 mg).
Calcium antagonists and AT II receptor antagonists have an independent neuroprotective effect, including the prevention of dementia, in addition to lowering blood pressure.
In order to prevent the development of repeated cerebrovascular accidents and other cardiovascular complications (myocardial infarction, etc.), which contribute to the development and progression of vascular dementia, it is recommended to take antiplatelet drugs. The first-line drugs currently are: acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) - 50-325 mg 1 time per day, or clopidogrel - 75 mg 1 time per day, or a combination of ASA - 25 mg 2 times per day and a prolonged form of dipyridamole - 200 mg 2 times a day. The prescription of each of these drugs is individual and depends on tolerability and the presence of risk factors in each patient. In case of intolerance or ineffectiveness of ASA, it is recommended to take clopidogrel - 75 mg per day.
Since cerebral infarctions, which are caused by heart disease (primarily atrial fibrillation), are a common cause of vascular dementia, the use of oral anticoagulants (warfarin) under the control of the international normalization ratio (INR) is recommended.
Patients with critical stenosis of the carotid arteries of more than 70%, as well as atherosclerotic plaques, which are the source of embolism, are indicated for surgical treatment (carotid endarterectomy, angioplasty).
In patients with hypercholesterolemia, statins are recommended.
Since the basis of vascular dementia is cognitive impairment, to improve cognitive functions it is recommended to take different groups of drugs: - drugs based on Ginkgo Biloba (tanakan, memoplant, etc.); - anticholinesterase drugs (amiridine, rivastigmine, galantamine, gliatilin, etc.); — neurotrophic drugs (Cerebrolysin); - MAO inhibitors (selegiline); — nootropics (piracetam, pramiracetam); — neuropeptides (solcoseryl, actovegin, lipocerebrin); — membrane stabilizing (citicoline); - NMDA receptor antagonists (memantine); — antioxidants (vitamins C, E, carotenoids, flavonoids); - substances that affect the GABA system (aminalon, pantogam, noofen, etc.); - vasoactive drugs (nicergoline, vinpocetine, instenon, etc.); - combined (fezam, etc.).
It should be emphasized that drugs that improve cerebral blood flow and neuronal metabolism are more effective if they are prescribed in the early stages of cerebrovascular disease, when the severity of cognitive impairment has not yet reached the level of dementia.
Separate treatment may require the occurrence of depression, anxiety, hallucinations, or psychomotor agitation in patients. In the presence of depression in patients with dementia, preference is currently given to serotonin reuptake inhibitors, since, unlike tricyclic antidepressants, they have less anticholinergic side effects and do not depress cognitive functions.
The response to treatment should be carefully assessed in each patient, given the relatively frequent occurrence of paradoxical reactions and side effects of therapy. Treatment should be reviewed periodically, avoiding without proper justification long-term use of drugs that worsen cognitive function (benzodiazepines, anticonvulsants, antipsychotics, central anticholinergics, digitalis drugs).
Adequate therapy for concomitant somatic diseases that significantly affect the neuropsychic state of patients should be carried out jointly with other specialists. Psychological support for the patient is important.
Plague of the 21st century
More than a hundred years ago, the German psychiatrist Alois Alzheimer described a disease that people knew about before, although they did not consider it a pathology, believing that it was quite natural to not be friends with your head in old age. It turned out that dementia (dementia), which develops with Alzheimer's disease and other diseases, is not at all the norm. In addition, as it turned out, not only old people suffer from dementia.
The threat of memory loss and a decline in the mental potential of humanity could soon reach epidemic proportions. From 2010 to 2015 alone, statistics on dementia increased by 10 million cases. And scientists estimate that by the middle of this century there will be more than 130 million elderly people with dementia in the world. Moreover, if earlier this problem concerned mainly the population of high-income countries, today the frequency of the disease is growing like an avalanche in countries with middle and low incomes.
How to treat dementia in older people
It is better for the elderly to be treated in a hospital if:
- the disturbances developed quickly and sharply, over several days or weeks;
- confused consciousness - a person reacts poorly to the world around him, does not understand who he is, who the people around him are, where he is and what day it is;
- severe depression, anxiety, acute mental disorders (psychoses), which are characterized by hallucinations (perception of non-existent voices, sounds, visions), delusions (a pathological idea in which it is impossible to dissuade a person);
- serious condition due to other diseases of the body.
In other cases and after hospitalization (aftercare), therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis.
The approach to therapy depends on the stage of senile dementia. Treatment at an early stage is more effective. If the symptoms are severe (late stage), drug treatment is carried out very carefully.
Important
An older person's brain resources are limited. If you sharply “stimulate” the brain, an improvement will occur - but it will not last long, and then the disease will return with renewed vigor. And the brain no longer has enough strength to recover.
In senile dementia, symptoms and treatment depend on the cause of the disease.
For vascular dementia, the doctor prescribes drugs that improve blood circulation in the vessels of the brain, lower blood pressure and slow down atherosclerosis.
For Alzheimer's disease, a psychiatrist prescribes medications that protect brain tissue and restore impaired metabolism.
In case of organic pathology of the brain (stroke, cancer, traumatic brain injury), the psychiatrist prescribes treatment together with a therapist and neurologist. The doctor takes into account the interaction of drugs with each other (they can strengthen or weaken each other) and chooses the most gentle and safe medications.
Not simple forgetfulness
“As a rule, the course of the disease from the moment obvious symptoms appear is quite rapid. Although the latent period, during which asymptomatic death of brain neurons occurs, can last a long time, for 20 years, warns Doctor of Medical Sciences Svetlana Gavrilova . “But it is at this very early stage that treatment is more effective. “Alas, after the manifestation of symptoms, the average life expectancy of patients is approximately 8-10 years.”
Dementia begins quite harmlessly, with banal forgetfulness, which is almost always perceived by others calmly and even with humor. Well, whatever you want, old age is not a joy. Further - more: patients experience depression, irritability, aggression. Personality changes are very characteristic: a person was kind, generous and intelligent, but suddenly became rude, suspicious, stingy, angry and stubborn. However, all this is also sometimes attributed to senile grumbling and bad character.
Article on the topic
Dentist instead of neurologist. How can dental care protect against dementia?
No criticism
The first suspicions arise when the patient develops speech disorders (for example, slowing down) and difficulties finding words, as well as problems with orientation in unfamiliar areas. But, as a rule, people go to the doctor (or more often their relatives bring them) only when forgetfulness appears too obvious. In particular, there are lapses in memory (especially regarding recent events and names) and disorientation in time and space. For example, a person cannot remember what was discussed just five minutes ago; he tells or asks the same thing. Or he may be puzzled by the question of what date and year it is. Such a person is capable of getting lost in his own yard or even in his apartment. By the way, an important point: at the same time, patients lack self-criticism. They do not notice any oddities in themselves, believing that everything is fine with them. And suggestions from relatives to go to a neurologist, and even more so to a psychiatrist, are perceived with resentment.
But if the progression of the disease is not slowed down with treatment, people quickly cease to recognize even those closest to them, understand speech, and then even forget about who they are, losing all skills and the ability to self-care. They begin to suffer from hallucinations, delusional ideas (most often they begin to suspect others of stealing or causing damage), constant anxiety and motor agitation arise. Then - only “vegetative” existence and death.
Stay sane. Can Alzheimer's disease be prevented? More details
Insidious dementia
Average life expectancy is slowly but steadily increasing. This is directly related to improving the quality of medical care, which makes it possible to prevent death even in cases of severe brain injuries and diseases.
Every year in the world, according to statistics, almost 8 million new cases of the disease such as dementia are registered. According to the World Health Organization, as of April 2021, there are about 47.5 million people in the world with this nosology. WHO experts call it one of the main causes of disability among older people and express concern that by 2050 their number will reach 115 million people...
A number of people believe that memory loss is a clear sign of dementia. This is wrong. Memory loss occurs in many elderly people, and it does not make life very difficult for them. It’s okay that sometimes dates or names are forgotten. With age, changes in all physiological systems gradually develop in the body and the process of its adaptation to diminishing capabilities begins. An older person needs more time to remember past events and needs to make more effort to process a certain amount of information.
Dementia is an acquired dementia characterized by impairment of mental function, emotional control, loss of acquired skills and knowledge, and learning disability. The disease inevitably progresses and leads to complete disability of a person.
As a rule, mnestic disorders increase gradually, and these are mainly disturbances of attention, memory, and planning ability. The diagnosis of “Dementia” is established only if the disorders persist for six months or more.
The acquired nature of cognitive impairment is due to brain damage, which distinguishes dementia from congenital cognitive changes (oligophrenia).
Manifestations of dementia
There are seven signs of a cognitive defect (according to research by the American National Institute of Gerontology), in the presence of which you should not wait for events to develop, but you should consult a doctor. The main symptoms can be presented as follows:
- A person constantly asks the same thing.
- He often tells the same short story.
- Difficulty performing simple, familiar tasks, things that used to be commonplace.
- Impaired abstract thinking. The ability to understand documents during various transactions with money is lost.
- Loses things, unintentionally hides them, rearranges them, and forgets about it.
- Lack of initiative, loss of interest in the outside world, endeavors, and suggestions of other people.
- A person answers questions that he himself regularly asks others.
Why does dementia occur?
Symptoms of dementia appear as a consequence of various diseases, especially in older people. For example, with a severe respiratory infection, there may be temporary forgetfulness and restlessness. Taking a number of antibiotics or drinking too much alcohol may also be accompanied by behavioral changes. Many diseases contribute to the temporary manifestation of symptoms characteristic of dementia. Stressful situations can provoke the appearance of symptoms, for example, moving to a new apartment, hospitalization in a hospital, death of a loved one in older people, etc. But dementia mainly develops as a result of diseases of the brain.
Is it possible to prevent the development of dementia?
Today, much remains unknown about the mechanism of development of dementia, but several simultaneously operating “risk groups” of the debilitating process can be identified: heredity, old age, environmental factors, lifestyle, chronic diseases leading to circulatory disorders in the brain and hypoxia ( hypertension, cerebral atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus).
With all of them, with the exception of heredity, reasonable controlled physical activity, massages, finger exercises, hardening, contrasting water procedures, walking, intellectual activities (crosswords, puzzles, chess, learning languages, playing a musical instrument, reading, writing) are so necessary , drawing and painting), obesity prevention, smoking cessation and reasonable alcohol consumption.
It is advisable for patients to avoid prolonged stress, monitor weight, blood pressure, sleep, routine, balanced diet and sufficient fluid intake, and most importantly: maintain social contacts. Physical and social activity always have a positive effect on the patient’s condition. After all, every elderly person will benefit from walking, swimming, dancing, and Nordic walking, which is now widespread, is a new form of training, which is based on the natural nature of human movements.
The special technique of working with sticks makes it useful for patients with obesity, arthrosis, diabetes, osteoporosis, heart disease and, of course, anyone who wants to keep themselves in excellent shape. Social activities include traveling, visiting the theater, cultural events, playing cards, and board games. The results of the latest neurobiological studies have shown that changes in the brain begin 15-30 years before the first manifestations of dementia, so scientists recommend thinking about your lifestyle from the age of 40. Everything that is good for blood vessels is good for the brain, and this is a chance to reduce the risk of disease.
Should the patient be informed about his illness?
Already at the stage of establishing a diagnosis, the doctor expresses his opinion to close relatives. Often he is faced with the question: how to convey this news to the patient? Often the patient may react aggressively and refuse further examination. If a person categorically denies his obvious problems, it is difficult to talk to him about the result. On the other hand, knowing about the prospects for the development of the disease, the patient will be able to take measures to resolve his problems: these include financial issues, decisions about family members, whom he trusts to care for himself, and current family tasks, etc.
It is probably necessary to recognize the right of each person to decide for himself whether he wants to be examined or not. And yet, one of the important advantages of early diagnosis of Dementia is the opportunity for a sick relative to make certain decisions about his and your future. After all, there is a long and difficult journey ahead, on which psychological help may be required not only for the patient himself. One wise person on the path to diagnosis said: “As long as I can do something, I am not a patient with Dementia, but when the disease takes hold of me, then I will not be able to solve anything...”. That is why it is important to make a diagnosis in a timely manner and not hide it from the patient. And this is how the son of one patient describes the problem facing him in the novel by the Hungarian writer Peter Esterhazy “Heavenly Harmony”: “Ten years ago, when my father was full of strength, he asked his eldest son to tell him when signs of old age appeared. With a light heart, the son promised to do this. But even now, when his father, with the rudeness and rudeness inherent in the old prima donna, insulted him several times, he could not do it.” Indeed, it is very difficult for family members to tell the patient the truth about his illness. And many don't do this. Believe me, this is often not easy for doctors to do. In the same way, for a long time, doctors (at the request of relatives) hide the diagnosis of cancer from patients...
And yet times change. Knowing about the diagnosis of Dementia will not give strength, but there is no scientific evidence that it brings harm to such a person. Many people know that they have begun to have problems with their heads, even if they are not told about it.
Thus, the person or patient is not afraid of becoming crazy. Knowing the nature of the disease, you will not need to rack your brains about why it has become more difficult to live, and what generally happens to the individual. Finally, any secret always carries a mental load, and not everyone is given the ability to “play” this “role” well. This means that a patient who is informed about his illness can openly discuss many issues, and the doctor will be able to provide him with the necessary support and professional assistance.
The article was prepared by Artem Aleksandrovich Kachurin, psychiatrist, narcologist of the highest qualification category
Share
What to watch out for
As Svetlana Gavrilova said, in addition to hereditary predisposition (in 10-15% of patients), the development of dementia can be facilitated by:
- low mental and physical activity;
- depression and chronic stress;
- head injuries;
- thyroid diseases;
- high cholesterol;
- arterial hypertension;
- diabetes;
- smoking, alcohol abuse;
- obesity, unhealthy diet;
- insomnia (sleep apnea).
By improving your lifestyle and starting to control all of the listed diseases, you can reduce the risk of senile dementia. There is an assumption that Alzheimer's disease develops more often and is more severe in people with a low level of education, since educated people have stronger connections between neurons in the brain, and if some brain cells die, their functions are taken up by other cells. Therefore, intellectual work, curiosity and daily learning of everything new is the best prevention of senile dementia. It is useful to learn foreign languages, memorize poetry and prose, comprehend new things, solve puzzles and crosswords, and understand computer programs. It is also necessary to develop fine motor skills - this also contributes to brain development and strengthening neural connections. Therefore, knitting, modeling, drawing and even just rewriting text by hand will be very useful.
Article on the topic
Dementia or forgetfulness? How to distinguish memory problems from illness